H3121 Guillotine shears for sheet metal processing. Purpose and scope
Guillotine crank shears N3121 were produced in accordance with GOST 6282-64 from 1968 to 1983 and were replaced by a more advanced model NA3121
.
Mechanical guillotine shears N3121 with an inclined knife are designed for cutting sheet metal with a tensile strength (tensile strength) σ BP = 500 MPa (50 kg/mm 2 ). Transverse cutting of sheets up to 12.5 mm thick and up to 2000 mm wide is carried out in one knife stroke. Longitudinal cutting - with a sheet length of more than 2000 mm - is carried out by a series of repeated cuts while moving the sheet along the cutting line.
Main parameters of the N3121 machine:
- The largest dimensions of the metal to be cut are 12.5 x 2000 mm
- Ultimate strength (tensile strength) of metal σ BP, no more than - 500 MPa (50 kg/mm 2)
- Maximum cutting force - 500 kN (50 tf)
- Maximum clamping force - 29 kN (2.9 tf)
- Knife stroke frequency, no less than 40 min -1
- Knife stroke - mm
- The tilt angle of the moving knife is 2°10′
- Drive power - 18.5 kW
- Total vehicle weight - 7 tons
Design features of guillotine shears N 3121
The guillotine frame is welded, made of sheet steel. Two side posts are connected by a table and three ties. The table to which the lower knife is attached has an adjustment to set the required gap.
The N3121 shears are driven by an electric motor through a V-belt drive and a two-stage helical gearbox; the design of the closed helical gearbox ensures a significant reduction in the noise characteristics of the shears. The guillotine knife beam receives reciprocating motion from the crankshaft through the connecting rods. The knife beam is balanced by a spring balancer.
The force on the knife beam from the crankshaft is transmitted by two connecting rods. Scissor clutch with two rotary keys, band brake, intermittent action. The frequency of braking is achieved due to the eccentric location of the pulley relative to the axis of the crankshaft. This braking occurs when the knife beam is in the upper position, which prevents it from running under the influence of inertial forces.
The engagement clutch is rigid with two rotary keys and an electromagnet. The design of the main drive clutch ensures reliable operation of the sheet shears without air, which significantly reduces operating costs.
The material being cut is pressed against the scissors table by a pressure beam, the movement of which is coordinated with the movement of the knife beam.
Mechanical scissors H3121 are equipped with a back stop . For safe work on the scissors, a protective grid is provided.
H3121 guillotine shears can operate on single and automatic strokes. Push-button control from the control panel and from the foot pedal.
The design of the connection of the knife beam with the connecting rods provides for the possibility of increasing the open height of the knives by 20 mm, which is necessary for longitudinal cutting of the sheet.
pressed to the table by individual spring-loaded rods.
Cutting can be done either according to the markings or using a back stop.
Scissors can be used in warehouses and workshops of various enterprises where cutting sheet steel is required.
When cutting steel with a tensile strength greater or less than 50 kg/mm 2, to calculate the maximum cutting thickness, use the formula specified in the section “Adjusting the scissors.” In this case, the hardness of the sheet being cut should not exceed 35 Rockwell units on the “C” scale.
Scissors are manufactured with basic parameters in accordance with GOST 6282-64
Guillotine for cutting metal
The first installations were manually driven. In order to perform cutting, it was necessary to install not only the knife itself, you also need to have a counter plate (fixed knife).
General view of a modern manual guillotine for cutting metal: 1 – table; shear plate; 3 – knife; 4 – crank; 5 – knife feed lever
A manual metal guillotine allows you to cut relatively small workpieces; the cutting width rarely exceeds 1200...1500 mm. In this case, the thickness of the cut parts depends on the material used for manufacturing.
Typically, small industries use similar machines for steel with a thickness of up to 0.5...0.7 mm. You can cut off plastic or different types of films. Flooring factories cut vinyl tiles.
In printing houses, before binding books, brochures and other publications, blocks are formed using manually driven guillotines. Subsequently, they are sent to the press, where printed products are created.
The cutting process on a guillotine machine: 1 – table for feeding material; 2 – metal sheet; 3 – anti-cutting blade; 4 – knife
Gap adjustment
When working, try to reduce the distance between the edges of the blades. The smaller it is, the cleaner the cut. However, when working with metal, operators are forced to move the fixed blade to increase clearance. As the thickness of the metal being cut increases, the distance becomes necessary to increase.
If you do not do this, the edges of the blade will crumble. The metal undergoes deformation changes. It behaves like a plastic substance and is squeezed out between the edges.
Gap δ between cutting edges
The thinner the workpieces, the closer the blades should be placed relative to each other. Table 1 presents recommendations for clearances depending on the thickness of 08 sp steel.
Table 1: Gaps between cutting edges for a manual guillotine when cutting 08 sp steel
| Sheet thickness, mm | Gap between knife and shear plate, mm |
| 0,08…0,095 | 0,02 |
| 0,100…0,195 | 0,03 |
| 0,200…0,295 | 0,04 |
| 0,300…0,395 | 0,05 |
| 0,400…0,495 | 0,06 |
| 0,500…0,595 | 0,07 |
| 0,600…0,695 | 0,08 |
| 0,700…0,800 | 0,09 |
When working on installations with a hydraulic or crank drive, the speed of movement of the knife is higher. Therefore, it is necessary to slightly increase the gap (Table 2).
Table 2: Clearances between cutting edges for mechanical guillotines
| Sheet thickness, mm | Gap between knife and shear plate, mm |
| 0,080…0,095 | 0,04 |
| 0,100…0,195 | 0,06 |
| 0,200…0,295 | 0,08 |
| 0,300…0,395 | 0,10 |
| 0,400…0,495 | 0,12 |
| 0,500…0,595 | 0,14 |
| 0,600…0,695 | 0,16 |
| 0,700…0,800 | 0,18 |
At a high speed of metal displacement (mechanical knives), heating occurs. If you do not increase the gap, then after several consecutive cuts the edges can heat up to such an extent that the metal can weld to the knives.
Oblique cut
When creating the first machines for mass executions, poor-quality cutting sometimes occurred. The straight blade did not cut skin and bone tissue from the first blow. Louis XVI, who was present during the testing of the installation, suggested that the inventor improve the device by making a falling blade with an angle. Sliding entry allows you to optimize the cutting angle and redistribute the load in the device.
Design of guillotine shears H3121
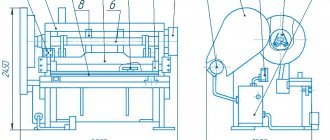
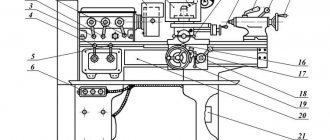
The shears consist of a frame, knife and pressure beams, drive, drive shafts, engagement clutch, back stop, balancer, brakes, guards, electrical and lubrication systems, and protective grille.
H3121 guillotine shear bed
The bed is the base unit on which all other scissor units are attached. The frame is a welded structure consisting of two racks connected to each other by channels.
The table rests on the racks, to which the lower knives are attached with screws.
To adjust the gap between the table knives and the knife beam, the table is moved with bolts screwed into the ends of the frame with the table fastening bolts relaxed. When regrinding, adjusting the knife height is done by grinding the spacers located under the knives.
The table has extensions with T-slots.
On the right edge of the table there is an extension fixed with pins, in the T-shaped groove of which the cross-cut stop is attached. To perform longitudinal cutting, this stop is removed.
Drive drive shafts of guillotine shears H3121
The shears are driven from an electric motor through a V-belt transmission to the flywheel, through gears and a clutch to the crankshaft (see Fig. 3).
The electric motor is attached to a sub-motor plate, hinged on the frame. Belt tension is adjusted using the eye bolt nuts.
Clutch for turning on guillotine shears H3121
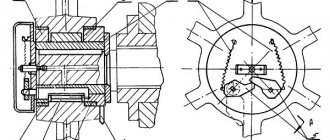
Clutch for turning on guillotine shears N3121
At the left end of the crankshaft, a keyed engagement clutch is installed in the gear hub.
Bushings 1, 2, 3 are stationary in the gear hub. The remaining parts are connected to the crankshaft. The rotating (working and locking) keys of the engagement clutch are activated by springs 6 and, turning, are captured by the semicircular grooves of the sleeve 2.
Bushings 8 and 9, having semicircular grooves, complement the sockets for the round ends of the key. The right end of the working key is equipped with an easily detachable shank 4, which, when the scissors are in operation, disables the keys connected to each other by levers 5. When the keys are turned on, their angle of rotation is limited by the groove of the drive sleeve 8.
Knife beam of guillotine shears H3121
The knife beam is an L-shaped welded structure reinforced with ribs. The back stop is attached to the knife beam.
The force from the crankshaft is transmitted to the knife by two connecting rods; in the upper position, the beam is held by balancing springs, pivotally connected to the beam, and during repairs, it is fixed in the upper position by two Ø25 pins inserted into the hole. knife beam guides.
Clamp and protective grid of guillotine shears H3121
While the scissors are working, the sheet being cut is pressed against the table by a pressure beam. When the knife beam moves downwards, the clamping beam, under the action of springs, lowers and presses the sheet, and first the sheet is pressed, and then the cutting begins. This is achieved by installing the beam at a height of 24 mm, and the knife - 26 mm from the table surface.
The lifting of the clamp is carried out by the stops of the knife beam, resting against the clamping plates.
The clamping force is adjusted using nuts that compress the spring of the clamping beam.
A protective grille is attached to the guides of the pressure beam, protecting the worker’s hands from falling under the pressure. When the scissors are working, the grille is lowered: the M8X40 screw on the left presses the microswitch rod, and the screw on the right limits the rotation of the grille to the clamp.
If necessary, the grille can be raised up, but turning on the scissors is impossible - the switching contacts are open. The grille is held in the lowered and raised position by a 2X16 spring.
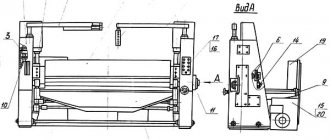
Rear scissor stop N3121
The back stop is installed on the back side of the knife beam and serves as a stop for the sheet during cross cutting. The back stop consists of two cylindrical cuts, moved manually by handwheels sitting on gear shafts meshed with racks. By moving the slats, the stop line is set at the required distance from the edge of the knife, which achieves measured cutting of the sheet using the back stop.
Scissor balancer H3121
The balancer is used to hold the knife beam in the upper position after each single stroke - when repairing scissors or changing knives. It consists of two sets of springs installed in cups welded to the upper channel of the frame. The rods are hingedly connected by axes to the knife beam. When the beam is lowered during cutting, the rods compress the springs. During the reverse stroke, the springs, unclamping, help lift the knife beam. Both sets of springs are rated at 1.0 ton with the beam in the top position.
Scissor brake H3121
An intermittent brake is mounted on the right end of the crankshaft. The frequency of braking is achieved due to the eccentric location of the pulley relative to the crankshaft axis.
Braking occurs when the knife beam is in the upper position, which prevents it from running under the influence of inertial forces.
Electromagnetic control of scissors N3121
When you press a button or pedal, an electromagnet is turned on, the armature of which turns the fork with a pin, releasing the shank that engages with it and is connected to the working key. After that, under the action of the key springs, the crankshaft turns and turns on. There is a cut. If the operator does not release the button or pedal in the “Single stroke” mode, an electrical lock is activated (see the electrical equipment section).
To repeat the working stroke, the button or pedal must be released, then pressed again. During automatic operation, the electromagnet armature is set to a stroke of 40 mm, and when operating on single strokes - to 20 mm.
Scissor guard H3121
The shear guard is made of 1.6 mm thick sheet steel and serves to protect the rotating parts of the shears. The guard consists of four casings that cover the motor pulley and the V-belt flywheel, six drive shafts and the scissor brake.
All casings are attached to the frame with M10 bolts.
Lubrication diagram for scissors H3121
Lubrication diagram for scissors N3121
- 1-2 Crankshaft supports - Central lubrication from pump
- 3-4 Crankpins - Centralized lubrication from the pump
- 5-6 Connecting rod pins - Central lubrication from the pump
- 7-8 Knife beam guides - Central lubrication from pump
- 9-10 Pressure guides - Manual lubrication with a syringe
- 11 Clutch - Manual lubrication with a syringe
- 12 Axle of the activation mechanism - Manual lubrication with a syringe
- 13-14 Drive and intermediate shafts - Centralized lubrication from the pump
The main rubbing surfaces are lubricated from a manual pumping station through feeders. Lubrication is carried out through all individual grease nipples installed on the scissors using a manual syringe. The drive gears are lubricated by applying grease to the gear teeth respectively.
During operation, the scissors must be lubricated so that the lubricant comes from the side bearing locations. Any grease that comes out of the gaps must be wiped off. It is necessary to periodically check the condition of the oil nipples and oil passage holes in the parts and be sure to clean them. At least once every three months, the lubrication holes should be flushed with clean kerosene.
Parameters affecting the quality of guillotine cutting
Cutting a steel sheet on a guillotine occurs as a result of the relative displacement of two strong metal knives in a vertical plane. In this case, the upper knife can be installed parallel to the plane of the sheet being cut or at an angle to it. The second blade arrangement requires less force to do the job. The angle of inclination of the knife to the horizontal is called the cutting angle and is set depending on the thickness and strength of the material being processed.
The second parameter that ensures a high-quality cut is the gap between the knives . This is the horizontal distance between the vertical planes of movement of the cutting edges of the blades. The size of this gap is usually 6-9% of the thickness of the metal being cut and, in addition, depends on its strength, that is, the type of steel or non-ferrous alloy.
Adjustment of guillotine shears H3121
During operation of the scissors, the brake, engagement clutch, knife beam, clamp and gap between the knives may be subject to adjustment and adjustment. The operation of the brake must be periodically monitored by adjusting the tension of the springs and preventing contamination of the brake pulley.
The clearances of the knife beam guides and the clamp must be checked regularly in accordance with the feed accuracy.
Adjusting the pressure means that by pressing the spring, the sheet being cut is securely pressed against the table during cutting.
Devices for improving the quality of metal processing
The guillotine machine can be equipped with additional equipment to improve the quality of material processing and ensure the comfort of work for the specialists using it. The following devices are used:
- cutting line illumination,
- mechanical or hydraulic clamps for the metal being processed,
- stops with measuring scales for express assessment of workpiece dimensions.
The use of stops minimizes the risk of obtaining parts with bends and burrs. Illumination allows for precise positioning of the workpiece on the machine plane. The stops eliminate the need to take additional measurements of the overhang of the sheet being cut. A useful option can be the automation of the machine operation process: supplying material for cutting, removing workpieces.
Specialists using guillotines should remember safety precautions and use protective equipment: masks, goggles, gloves. High-quality metal cutting depends not only on the parameters of the machine used, but also on compliance with safety regulations by equipment operators.
Setting up and operating modes of scissors H3121
The scissors are adjusted to cut strips of a given length by moving the back stop. The distance of the back stop from the cutting edge of the lower knife is determined by the scale of rulers mounted on the back stop slats.
The electrical circuit provides for the possibility of operating the machine in the “Single stroke” and “Automatic stroke” modes. Cutting sheets of the maximum thickness and width specified in the technical characteristics of the scissors is not allowed on automatic strokes, since the power of the installed electric motor is designed to use 30% of the number of strokes of the knife beam.
Setting the gap between cutting edges
An absolutely even cut without burrs or bends on hydraulically driven guillotine shears can only be obtained with a correctly set gap between the knives. If the gap is too small, the metal will have an uneven edge, and if it is large, it will begin to bend during cutting.
Adjustment of the position of the cutting edges must be carried out even on high-quality equipment. It is done using control levers for the lower guide rollers of the scissors. The levers have several fixed positions, of which the uppermost one corresponds to the minimum clearance. When operating with numerical program control, regulation is carried out automatically using two horizontally located hydraulic cylinders.
Electrical circuit diagram of guillotine shears H3121
Electrical diagram of guillotine shears N3121
The circuit is designed to control a machine with a rigid coupling to clearly engage and disengage the moving slide with the tool. The clutch is activated by an electromagnet, which is activated by an intermediate relay.
Complete shutdown of the circuit is carried out by the input circuit breaker.
Electrical equipment of scissors N3121
The machine is controlled from the control panel. on which control buttons and mode switches are located
The alarm system is electric and light; the designation of modes and controls is symbolic.
- automatic (continuous running);
- single move.
- buttons;
- pedal only on single strokes.
The electrical circuit includes the following circuits:
- A. AC power circuit, voltage 380 V.
- b. AC control circuit, voltage 36 V.
- V. AC lighting circuit, voltage 5.5 V.
The following receive power from the power circuit:
- A. Main drive electric motor.
- b. Pulling electromagnet.
- V. The control, lighting and alarm circuits receive power from the secondary windings of the 2T transformer.
Control and protection equipment (transformer, magnetic starters, circuit breaker) are located in the electrical cabinet.
The operation of the scissors is controlled from the control panel.
Description of the operation of the electrical circuit
The electrical circuit provides the ability to operate the scissors in the following modes: “Single stroke”; "Automatic moves."
The selection of the operating mode is carried out by readjusting the scissors (by adjusting the electromagnet thrust) and setting the operating mode switches PR and PU to the desired position, located in the lockable control panel. When resetting the PR and PU switches, the electric motor must be turned off with the 2KU button.
Single move mode
In this mode, operation with a button and a pedal is possible. The PR switch is set to the “Single stroke” position. The thrust of the electromagnet is mechanically adjusted.
a) Button Control
The PU switch is set to the “Button” position. When you press the “Drive Start” button (2KU) along the circuit 1-9-7-15-19-23-3-2, the magnetic starter 1K is turned on, which turns on the main drive electric motor (1D).
Through the normally closed contacts of the 4KU button and the 2K magnetic starter, the 1RP relay receives power via circuit 19-17-115-21-2, becomes self-powered, and with its normally open contacts (circuit 25-31) prepares the 2K magnetic starter, which turns on the electromagnet, for switching on. When you press the 4KU button, the 2K starter is turned on, and therefore the electromagnet E. The 2K starter, turning on, breaks the circuit 21-115 with its normally closed contact,
1 PR turns off and turns off with its no. O. contact circuit 25-31. This turns off the electromagnet E., i.e., electrical blocking from doubling of strokes.
b) Pedal control
The PU mode switch is set to the “Pedal control” position. When you press the “Drive Start” button (2KU), it turns on the electric motor of the main drive 1D.
When you press the pedal, the 2K magnetic starter and electromagnet E are turned on.
Electrical blocking against doubling of strokes is carried out in the same way as when operating buttons.
Automatic mode
The electromagnet thrust for automatic strokes is mechanically adjusted. The PR operating mode switch is set to the “Automatic” position, and the PU switch is set to the “Buttons” position.
When you press 4KU, the 2K magnetic starter is triggered and turns off the electromagnet. Starter 2K with its own no. O. contacts 25-105 become self-powered, automatic movements occur until the 3KU button is pressed.
Locking and alarm
Locking, which ensures complete voltage relief from all equipment when opening the electrical cabinet door, is achieved by turning off the 1A circuit breaker.
The interlock, which ensures that the control circuit is turned off, is achieved by the 1VK limit switch located in the electrical cabinet, which turns off the control circuit when the door is opened.
The blocking, which excludes the possibility of obtaining moves when the protective grille is raised, is carried out by the 2VK end.
The blocking, which prevents the clutch from engaging when operating on “Single and automatic strokes” without turning on the main drive, is achieved by contact 1K (circuit 15-19).
The electrical circuit provides an alarm indicating the presence of voltage in the control circuit. When voltage is applied, a white 1LS lamp on the control panel lights up.
When the main drive motor is turned on, green lamp 2 lights up on the control panel (engine is on).
Protection
Protection of the electrical equipment of the scissors from short circuit currents is carried out by a 1A circuit breaker and fuses 2P, 3P, 4P.
Thermal protection of the main drive motor is carried out by a thermal relay RT, built into 1K magnetic starters.
Zero protection of the electrical circuit is provided by magnetic starters 1K, 2K.
Safety precautions
The electrical equipment of the shears must be reliably grounded in accordance with the current “Rules for Electrical Installations” by connecting the shear frame and electrical cabinet to the workshop grounded circuit.
Before starting work, inspect the scissors and check the grounding.
In order to increase the safety of operating personnel, the electrical circuit provides for locking:
- electrical cabinet doors;
- control panel doors.
During long breaks in scissor work or after the end of the shift, the input circuit breaker is turned off.
The first switching on of the circuit breaker should be carried out briefly, followed by inspection and verification of the correctness of the light signals.
The control panel has a red mushroom-shaped “General Stop” button (1KU) to completely disable the circuit.
It is strictly forbidden to work with scissors if the locks are faulty.
The installation of PU and PR switches is carried out by an adjuster.
Access to the electrical cabinet is permitted only to electrical personnel assigned to the machine.
Structural elements
A manual guillotine for cutting metal has the following components:
- Bed;
- Desktop;
- Knife;
- Vertical guides;
- Toothed racks (drive);
- Gearbox;
- Lever arm;
- Ruler.
Desktop Features
The working surface is a metal plate no less than 1 cm thick. It is not recommended to use wood for this, even if it is a very thick panel, as it will spring back and become deformed. It is important for the equipment to remain in one unchanged position.
2 guides are installed on the plate (round or profile pipe). The upper beam with the knife will move along them. It is advisable to choose thick-walled material. In this case, the guides must be placed in such a way that they are exactly parallel to each other and in a perpendicular plane to the table.
The knife will subsequently be attached to the horizontal beam. The beam must be allowed to move freely along the guides. In this case, there should not be excess resistance, but there should also be no backlash. This can be achieved by welding bushings along the edges of the beam, which will be inserted into the guides with a small gap. The inner surfaces of the bushings should be lubricated.
Drive mechanism
The vertical movement of the beam can be ensured using gear racks by welding them at its ends. By placing the slats on both sides, you can achieve uniform movement. The forces on the rack will be transmitted from the gears connected to the lever mechanism. By considering different leverage ratios and gear diameters, it is possible to achieve the required force applied by the knife. In this case, the impact on the drive will be minimal.
In order to ensure uniform rotation of the gears, they must be connected by a common shaft, which can be placed under the working plane. An analogue of the design can be a pedal drive. To prevent spontaneous lowering of the beam, it is recommended to install an upper position lock or a return spring.
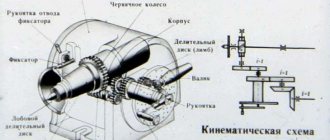
Drawing of guillotine shears knife N3121-11-402
Drawing of guillotine shears knife N3121-11-402
Knife for guillotine shears 25 x 60 x 625
- Knives must be made of steel grades 5ХВ2С, 6ХВ2С and 6ХС according to GOST 5950-73
- The hardness of the knives is HRC 54. 58
- Surface flatness tolerance B - no more than 0.1 mm over a length of 100 mm
- Tolerance field of dimensions s a B of a set of knives - according to h11
- The permissible difference in the sizes of the set knives at the junction is no more than 0.03 mm
- H14; h14; ±IT14/2
- The following markings must be applied to the knife: trademark of the manufacturer, designation of the knife, quality control department mark, code (number) of the kit (for composite knives).
- The remaining technical requirements for the set of knives N3121-11-402 in accordance with GOST 25306-82 Flat knives for sheet shears. Main and connecting dimensions. Technical requirements
Replacing and adjusting the position of cutting knives on a guillotine-type machine
The basic set of guillotine shears usually includes blades designed for processing soft, low-carbon steels and non-ferrous metals.
However, if cutting high-alloy materials is required, then it is necessary to use a cutting tool of a completely different quality, since ordinary knives will very quickly lose their sharpness and may even break. Therefore, for the manufacture of products and blanks from stainless steel, special, especially durable blades are purchased, and the knives are replaced on the machine. This operation is not so complicated, but it has certain specifics and requires some skill.
General characteristics
Modern guillotine shears have various technical characteristics that must be taken into account by specialists from industrial enterprises, as well as owners of private workshops engaged in the manufacture of rolled metal products and structures. Among them, the most important parameters are:
- number of operations performed;
- size of the processed sheet;
- assortment of rolled products that a specific machine can process;
- maximum permissible thickness of cut metal;
- performance;
- type of knives;
- power;
- type of drive.
Types of machines
Depending on the type of machine drive, the following types of scissors are distinguished:
- manual;
- pneumatic;
- hydraulic;
- electromechanical.
Principle of operation
Metal cutting using guillotine shears is carried out by applying a large pressure force and a sharp edge of the blade to the metal workpiece, acting on the principle of conventional scissors. During the working process, the two blades of the cutting device are brought together. After the sheet or rolled metal is fixed, they move its adjacent layers and then make a cut using a sharp blade.
The process of cutting a metal workpiece using a guillotine machine consists of two operations - cutting and breaking.
When using a high-quality machine for cutting metal, the amount of metal scrap generated is very small and does not exceed 10%.
At the same time, the cut acquires a smooth edge without requiring additional processing. When cutting a workpiece with a dull cutting device or an incorrectly set gap, the ratio of cut to scrap changes. As a result, this leads to the appearance of a sharp protrusion on the lower edge, called a burr - a sign of poor cutting quality.
The burr makes the product unsafe, increasing the risk of injuring your hands, especially if a stainless steel workpiece was chosen for cutting. To prevent this, it is necessary to follow safety regulations when using guillotine-type scissors. Under no circumstances should you start cutting metal without gloves made of thick fabric or leather stripes. When a burr appears, the worker must immediately stop cutting metal and correct the mistake made - change the settings or sharpen the knives.
Mechanically driven guillotines
Hydraulic driven units
A distinctive feature of such machines is the ability to cut fairly thick metal workpieces. Equipment manufacturers note in their operating instructions that for structural steels the maximum thickness can be up to 40 mm.
Similar devices on the edge of the blades develop a force of 200...400 tons. In this case, it is important to use thick knives that can transmit forces in the cutting zone.
Installation with hydraulic drive. The pumping station is located outside the machine
To operate a hydraulically driven guillotine, you must have a special pumping station. From it, oil is supplied through reinforced hoses to the actuators. Liquid pressure can reach up to 135...150 bar. Hydraulic cylinders transmit force to the actuator through a system of levers.
The main advantage of such guillotines is their quiet operation. The knives move without impact.
On the control panel, the operator specifies a number of parameters, the built-in computer will make the calculations itself:
- what gap is required between the knives;
- where to set the emphasis;
- at what speed should oil be supplied to the hydraulic system?
If it is indicated that several parts of the same type will be cut, then this parameter is also indicated. Then the material will be supplied automatically.
The operator and assistant can only:
- place the sheet of metal on the work table;
- align it with the guides;
- align with stops;
- indicate the number of the program by which you want to cut metal;
- set the number of required parts.
At the end of the cycle, on the back side of the machine there will be chopped blanks or parts that need to be taken to the semi-finished product site. Other employees of the company use them in the following production processes.
The price for such machines is high, amounting to several tens or even hundreds of thousands of euros. Guillotines of this type are made to order. In the future, the equipment manufacturer maintains it throughout the entire life cycle of the process unit, provides it with programs and offers original spare parts. If necessary, even a fairly old machine can be modernized. After modernization, it is ready to serve on equal terms with new units for quite a long time.
Video: cutting metal with a guillotine.
Video: CNC hydraulic guillotine.
Electromechanical guillotine shears
The most common type of machine is the electromechanical guillotine shear. A shaft with a flywheel constantly rotates in them. Through the crank mechanism, torque is transmitted to the active knife.
To make a cut you need:
- place a sheet of metal on the table;
- set the focus to the specified size;
- fix the workpiece on the table and press it against the stop;
- press the control pedal.
The metal will be cut according to the markings. By moving the sheet again to the stop, you can repeat the operation.
These machines are quite lightweight. They equip small workshops and fairly large enterprises. They are characterized by high performance. You can cut up to 60 parts in a minute.
The disadvantage is the noise during operation. Here the metal is cut with a strong blow. You often have to send knives for sharpening. Edges tend to chip when subjected to impact loads.
Read also: Do-it-yourself lug lugs for a car
It is necessary to frequently check the condition of the edges of finished products. If the formation of bent edges and burrs is observed, then the knives are removed and sent to a sharpening machine.
Video: operating principle of electromechanical guillotine shears.
Pneumatic guillotines
If there is a developed system of pneumatic pipelines, the enterprise uses equipment powered by compressed air. Pneumatic guillotines use air compressed by compressors to carry out basic production activities. They are equipped with pneumatic cylinders.
Installations of this type require a receiver. The volume of air used in the cycle can reach several liters, so a supply of working fluid is needed.
The operation of such devices is somewhat louder than when using hydraulics. But there are also advantages. On such machines it is easier to install computer control. Therefore, a number of European countries producing technological equipment are focusing on creating just such guillotines. It is easier to configure here; programs for managing production operations are written relatively simply.
Training operators for such machines is also easy. After just 2-3 days of work, workers master the basic techniques of working on a guillotine. All that remains is to issue them a production task, indicate the placement of workpieces and areas for unloading semi-finished products.
Video: guillotine shears.
Additional options in the workplace
To facilitate the work of operators on guillotine machines, pneumatic lifts with vacuum grippers are installed to help them.
- To lift a sheet from the bag, you need to move the gripper to the top sheet.
- A command is given to pump air out of the suction cups.
- The lift lifts the sheet to the desired height.
- The operator places it on the work table.
- The vacuum is turned off.
Machine-building and metalworking enterprises produce a wide range of metal products and structures, the manufacturing technology of which requires cutting profile and sheet metal. Sometimes even owners of home workshops, as well as workers at a construction site, have to perform this mandatory operation. To quickly and efficiently cut metal, you need to have the right equipment on hand. One of the most popular are guillotine shears, which today are available in several versions.
It is often necessary to cut metal using a guillotine when the owner of a home workshop or a worker at an industrial enterprise is faced with the task of producing large rectilinear parts - triangles, rectangles and strips with sides ranging from several centimeters to several meters. To obtain the required workpiece, it is necessary to process rolled metal with a thickness of 2 to 60 mm, a width of up to 2 meters and an almost unlimited length.
Manual metal cutting machines
Mechanical guillotine machines , which cut metal driven by a lever or pedal, can most often be found in industrial enterprises, as well as in private workshops. They remain in demand, even though they have limitations on the thickness of the workpieces processed and their types.
When equipping such guillotines for metal, the functions of the cutting element are performed by two knives. During the entire metal cutting process, the lower knife remains motionless. The main part of the work is performed by the upper knife, moving vertically downwards along the guides or rotating around its axis. In such machines, there is a rotation point at one end of the knife beam, and a handle at the other.
The cutting device, which can cut sheets more than 1 mm thick, drives the gearbox. Starting the mechanism in these machines can be provided by two types of drive:
- foot-operated, where the motor is turned on by a pedal;
- manual, in which the launch is carried out by a special lever.
Some models can use both types of drive simultaneously. To perform high-quality cutting of a metal workpiece, the guillotine machine must be installed on a flat surface on which the stability of the equipment will be ensured.
Guillotine machines for cutting metal are one of the most popular types of industrial equipment, which is used not only in the metalworking industry, but also in home workshops. Since manufacturers produce these machines in a wide variety of configurations, for each case of metal cutting, you can choose the most suitable model, taking into account the tasks at hand.
Equipment for cutting metal of the guillotine type is very popular, primarily due to the high productivity and accuracy of cutting metal workpieces. They can be used to cut not only metal, but also other materials, including aluminum, copper, brass and others. It is also important that these machines are very easy to use, so even the owner of a private workshop can quickly acquire the skills to work with such a machine and take advantage of all its advantages.
In some cases, if metalworking qualifications allow, it is even possible to make such a machine with your own hands. However, it is more advisable to purchase a ready-made machine that you can start using without prior preparation.
Hydraulic guillotine shears
Industrial equipment designed for cutting metal, which uses a hydraulic drive system , has a large power reserve and is characterized by high productivity. It is used mainly in serial or piece production of blanks with straight edges from rolled metal with a thickness of 2 to 20 mm and a cutting length of 1 to 3 m.
Industrial enterprises in their production activities use hydraulic machines that allow cutting sheets up to 6 m wide and more than 20 mm thick. This equipment has significant weight and dimensions, and is most often produced in single copies.
When using hydraulic guillotine-type machines, the cutting device creates a pressure exceeding 400 mPa along the entire length of the sheet being cut. The main working element is knives that can move in a straight line thanks to vertical guides or along an arcuate path. The latter option is capable of cutting workpieces made of thicker metal or an alloy of increased strength, even with less force exerted by the hydraulic drive. Moreover, this does not in any way affect the cutting accuracy.
to control the gaps between the knives , and their location can be adjusted either manually, semi-automatically or automatically. A fairly popular type of hydraulic machines is CNC equipment. Its main advantages are minimal setup time and ease of changing the manufacturing mode of any of a dozen possible types of products, for which you only need to press one button. Due to the fact that all information is stored in the machine’s memory, this task is simplified as much as possible.
Read also: Metal detector frame operating principle
Hydraulic guillotine-type shears differ from similar devices in their quiet operation - while cutting metal, the knives move smoothly, without exerting strong impact-type impacts that accompany metal cutting when using electromechanical and pneumatic machines.
Photo sensors installed in the work area, protective screens and feed mechanism stroke limiters help resolve the issue of safe To timely return the beam to its initial upper position, springs or storage shock absorbers are used.