01/17/2021 Author: VT-METALL
Issues discussed in the material:
- Types of welded joints of metal structures
- Requirements and types of quality of welded joints
- 6 methods for quality control of welded joints of metal structures
- Preparation of documentation for welded joints of metal structures
Welded joints in metal structures must meet strict quality standards to ensure that the final product is strong and reliable. Depending on the purpose and material of construction, various connections are used, each of which has its own requirements.
Equally important are methods of quality control of welds. Only after the necessary procedures and completion of documentation can the product be used. In our article we will tell you what types of welded joints there are and how to test them for strength and compliance with standards and requirements.
Types of welded joints of metal structures
There are several classifications of welded joints of metal structures:
- According to the type of junction of two workpieces.
- According to the type of weld.
- Depending on the welding technology.
- Taking into account the circumstances under which welding is carried out.
- Depending on the thickness of the workpieces.
- Taking into account the grade of steel from which the parts are made.
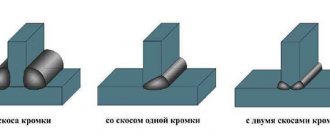
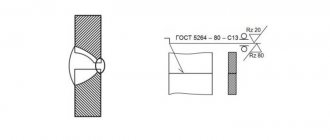
Depending on the type of placement of parts, there are four types of butt joints:
- Close, where two workpieces in the same plane are attached to each other.
- With overlapping, when the edges of the parts overlap one another.
- Angle connection. In this case, the two parts are at an angle to each other.
- Connection in the form of the letter T. Here one workpiece is adjacent to the other.
The most common welded joints in metal structures are close and corner welds. Let's look further at how they are obtained.
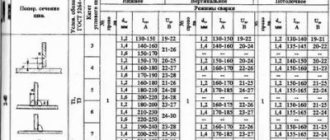
For butt joints, either lead strips are used, or the seam is welded throughout the entire thickness of the workpiece. When performing work outside the workshop, one-sided welding can be carried out, subsequently welding the root of the weld. Thus, the entire gap is filled along one of the edges.
The next technology - with lead gaskets - has many differences from the previous one. First of all, the gaskets are located on the side of the edges of the parts being welded. There should be a distance of up to 7 mm between the edges - for manual welding, and 16 mm for mechanized welding. The thickness of the lining is selected taking into account the prevention of burn-through during welding, and the current is set taking into account the welding mode.
In the joints of metal structures you can often find blanks of different thicknesses. In this case, using milling or gouging, the angle of inclination of the thicker edge is set, equal to a slope of 1:8 for tensile elements of a metal structure (such as pendants and consoles), and 1:5 for compressed elements (supports, racks).
Welded joints play the role of the main butt joints that support the entire metal structure. Based on this, already during the design they try to develop favorable conditions for welding joints. To do this you need:
- Make a butt or corner connection in welded assemblies.
- Weld in the down position.
- Use mechanized or automatic welding rather than manual welding.
Many types of welded assemblies have different requirements. For example, when making a beam assembly, the location of the welding seams relative to each other plays an important role. The distance between them must be no less than ten times the thickness of the thickest metal profile included in this assembly.
There is another point that does not affect the quality of welded joints of metal structures. There are two concepts: local strength and fragility. The first is welding areas with welded gussets, stiffeners, linings, etc. The second includes all existing cutouts on elements of metal structures, holes, lack of fusion in seams, gaps and cracks in joints.
When both sections are present in a structure, the structure itself cannot be considered strong. Because:
- In places with greater rigidity and strength of the connection, a greater concentration of forces occurs, affecting the entire structure as a whole.
- Where there is less rigidity, there are fewer acting forces.
Thus, if there is local weakness in a metal structure, even the most reliably welded joint can pose a danger. Therefore, local weaknesses must be avoided. Poor welding, even in the smallest areas, can render the entire structure unusable.
We recommend articles on metalworking
- Steel grades: classification and interpretation
- Aluminum grades and areas of their application
- Defects in metal products: causes and search methods
Proper welding is the most important factor in ensuring the reliability and safety of a metal structure.
Methods of fastening metal structures
The main methods of installing metal structures are welding, bolted and riveted connections.
Welding assembly of metal structures
Welding is one of the most common ways to firmly connect metal elements. As a result of the operation of the welding machine, a monolithic fastening is obtained, and a neat seam is formed at the joint. There are the following types of welding:
- butt
- parts are connected in one plane, which requires special precision and accuracy; - angular
- parts of the connected structures are at an angle; - overlap
- one element is partially overlapped with another; - tee
- the side of one part is welded to the plane of another part.
Metal structures obtained by welding are reliable - the seam is sealed and does not allow moisture to pass through. This type of connection allows you to create elements of complex shapes.
The disadvantage is the fact that the resulting monolithic structure cannot be disassembled. To carry out the work you need special welding equipment.
Assembly of metal structures with bolts
Mounting bolts of various diameters and sizes of normal or increased accuracy are used as connecting elements. Physically, this type of fastening is more difficult to implement than using welding. However, the bolted connection can be disassembled and reassembled, which explains the mobility of such structures.
The disadvantage of this method is the requirement that the elements being connected have no irregularities, otherwise it will not be possible to achieve an exact match and reliable fastening.
Riveted connection of metal structures
This method is easy to implement, convenient and allows you to get a reliable connection. The disadvantage is the high consumption of connecting materials - rivets, as well as painstaking work.
The connection method is justified when creating special structures where it is impossible to use welding, as well as in structures that are often subject to vibration during operation.
There are also options for connecting metal structures using gluing and soldering methods, but they are not widely used.
Requirements and types of quality of welded joints
When welding seams, the metal used must meet a number of requirements. Here are the main ones:
- the value of the relative elongation of the material is from 16% and above;
- impact strength of the metal is above 24 J/cm2, this value is measured at the average daily air temperature in the coldest five-day period;
- the ability of the metal of welded joints and seams of metal structures to have temporary tensile strength must be the same (or higher) as that of the main metal from which the welded products are made;
- when welding metal products at a factory, it is important that the hardness coefficient of the metal of the seam joint is up to 350 HV for metal structures of the 1st group and less than 400 HV for products of other groups described in SNiP II-23-81;
- when welding during installation and assembly of structures, the hardness coefficient of the weld metal should not be higher than 400 HV.
Following the necessary rules and monitoring the welds of metal structures will help maintain the integrity and safety of welded joints, avoid early loss of strength and emergency destruction of metal products.
According to the quality, seam joints are divided into three categories:
The first category includes seam joints that have the highest performance characteristics (strength, durability, tear resistance, etc.). These include the following types of seams:
- transverse butt joints subject to strong tensile stresses;
- lap, tee and fillet weld joints that operate under tensile stresses;
- seams in metal products classified according to SNiP II-23-81 to the 1st group (or to the 2nd group, if the air temperature where the metal structure is erected falls below -45 ° C).
The second category includes seams of average quality. These include:
- longitudinal joint elements subject to shear stress;
- connecting fillet welds in metal products of the 2nd and 3rd groups, which are subject to tensile stresses;
- seams in corners and joints connecting gussets with compressed elements of metal products.
The third category includes low quality seams, including:
- transverse seams in joints subject to compressive stresses;
- longitudinal connections at joints, as well as connecting seams at corners, which are used in compressed parts of structures;
- connections at joints and corners used in auxiliary parts of metal products.
Connecting metal structures: what types are there?
When people learned to smelt metal and make various metal products from it, the need arose to somehow hold them together.
Early attempts at this process encountered a variety of problems. These questions were related to the types of loads that fell on a given connection, the forms of mating connections, the operating conditions of the structures, and some others. Since almost all buildings, structures, ships, both sea and air, in one way or another, consist of metal structures, engineers have accumulated enormous experience in these matters, which was and is based on a powerful theoretical base.
Each student of a technical university begins his educational activity by studying special disciplines, the knowledge of which helps him navigate the issues of calculation and creation of metal structures and methods of connecting them. This includes metal science, parts of machines and mechanisms, theoretical mechanics - and the king of all construction subjects - strength of materials (strength of materials).
Preparation of documentation for welded joints of metal structures
Based on the test results, a report of defects in welded joints is drawn up. Each flaw is recorded and given a brief description. The results are entered into the welding log. Such documentation is maintained by the team at all sites. A special journal is a primary document maintained in accordance with SNiP for each structural unit.
Upon completion of the work, the log along with the rest of the documentation is transferred to the customer.
In addition to the special magazine, during welding work they make a diagram of the joints with a full description of the technology. They are supplemented with certificates for the materials used (electrodes, flux or filler wire). Certificates of research of welded seams (quality control of seams on the outside of the product), the time of instrument diagnostics, its results, and inspectors’ conclusions are written individually for each individual welder.
These documents are needed to be presented to the court in the event of an accident. Working with critical structures is burdened with serious requirements. The object will not be accepted in finished form unless a seam inspection certificate is provided.
If a defect is detected, the connection is overcooked, even if it is not the welder who is to blame, but the poor-quality material. Only after passing the inspection are the remaining actions taken to accept the metal structure of the object.
Requirements for welding metal structures
The welding process in technological terms must provide the completed connections with the required geometric parameters, dimensions and high quality. The structure should be strong and durable, and the risk of deformation should be zero.
Welding of metal structures.
That is why the technology for welding metal structures must be implemented taking into account certain requirements, which will largely determine the quality of the created welds:
- If simple connections are created without using a jig, as well as when creating complex seams, before turning on this tool, it is important to leave a gap between the parts being fastened. Then, when the elements are displaced, the seam will not be damaged. But the gap dimensions must correspond to the permissible standard, otherwise the system will not be strong and durable.
- When welding critical metal structures, welders check strict compliance of the installed part with its location, according to the map. When the workpiece arrives on the slipway, it is worth preparing each of them for the final stage.
- All parts must strictly correspond in type and size to the parts of the future structure specified in the project. This will preserve the functionality of the product.
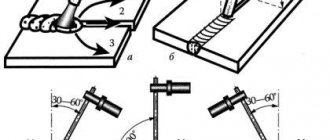
- When performing manual arc welding, it is important to apply the root layers of the seam with electrodes with a diameter not exceeding 3-4 mm.
- When strengthening, metal structures will need to be positioned so that stitches can be placed predominantly in the lower position. This is necessary to provide the welder with safe working conditions.
- It is important to take strict control of the corners of the metal structure, for which you should use special tools and a jig. All angles between planes must be right, if provided for by the design. Otherwise, parts will become distorted, which will lead to a violation of the integrity of the mechanism and loss of its functionality.
- The finished structure must have minimal shrinkage stresses and deformations, for which welding work must be carried out in a stable mode with deviations from the specified values of current and arc voltage of no more than ±5%.
It is important to take into account the described recommendations already at the stage of assembling parts into an integral structure, and not just before performing welding work. Especially if the automatic mode is selected, in which it will not be possible to correct the mistakes made.
In general, it is this type of welding work that is considered the most acceptable, since when welding processes are automated, the influence of the human factor on the quality of the seams is reduced to zero.
It is also important to weld the process sample under conditions that completely coincide with the conditions for welding structures at the production site.
If you have to work with a welding machine at low air temperatures, it is worth welding the butt samples before starting operations at the negative temperature conditions provided for by the technological process. This will allow them to be further tested mechanically.
If it is necessary to carry out welding work on particularly critical metal structures made from new steel grades or using new welding consumables, the craftsman will need to make control samples in the same spatial position and with the same materials and equipment as when welding the assembled structures.
This will allow the welder to assess the situation from all sides before starting work and avoid mistakes during its implementation.