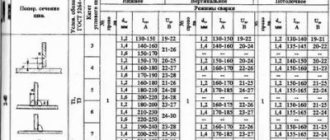
Types of welding
GOST 15878 of 1979 was issued to replace a similar document dated 1970 - it described the main types of contact welding techniques, as well as other methods, some of which we will consider in more detail.
Spot
This welding method of small-sized contact is used in many areas of human activity: from construction to the production of aircraft and rockets. For example, when creating the durable skin of modern airliners made of aluminum and its alloys, millions of spot welded objects are located on the hull, which form a strong connection.
The principle of operation of spot welding machines is extremely simple - the metal at the joint is instantly heated to the melting temperature with simultaneous strong compression on both sides, resulting in a durable and aesthetic seam that can withstand any loads and vibrations. This method allows you to reduce to a minimum the time of joining metals into one whole . This technique is used to firmly connect sheet material and metal rods by butt welding.
Embossed
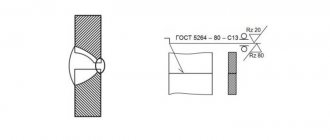
Resistance welding GOST 15878-79 is a type of spot technique when it is necessary to connect structures with complex edge relief.
In practice, many varieties of this type of welding are used, and the most common is the overlap of sheets, which is carried out using reliefs of different configurations. For example, spherical surfaces with complex convexities that, when combined, form a circular shape. During the application of the relief technique, plastic deformation of the welded material occurs , which is typical for conditions conducive to the formation of a reliable connection after final hardening.
Suture
Used to create straight and continuous seams - the machine creates a series of points, onto which similar points are subsequently superimposed . As a result of such an intense attack, a strong connection is created that fully complies with GOST requirements. Three types of techniques are used:
- Continuous option. An even seam is created by the constant mechanical action of the rollers on the surfaces being joined and the continuous supply of electrical potential. Such devices work very efficiently, but are prone to overheating, and the rollers quickly fail due to high loads - the contact surfaces are erased. Pre-processing of the parts to be joined is required.
- With the step method, the roller mechanism is in constant contact with the welding surface and puts pressure on the part, which moves intermittently, which avoids the negative effects of overheating and subsequent deformation.
- The broken line is characterized by the use of pulsating pulses. The workpiece is in constant motion between two pressure rollers, and the points constantly overlap each other to form a sealed seam.
The third option is used more often and is more popular than the previous two.
Condenser
GOST for capacitor welding can be easily found in the list of relevant documents, and a similar technology was developed at the beginning of the last century and has not undergone significant changes during its use, having proven itself to be a reliable and simple method of joining metals. The welding unit has a simple design, there is a small load on the electrical network, and the productivity is quite high.
The essence of the process is similar to resistance welding, only here the current is supplied pulsed and powerful , for which powerful capacitors with a large capacity are used.
Schematic representation of capacitor welding.