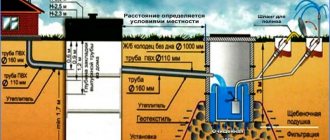
Industrial buildings require high strength and reliability with minimal construction costs, both time and money. Buildings with a steel supporting structure show the greatest efficiency. The quality of construction largely depends on how correctly the installation of metal structures is carried out. Of interest is the installation of columns, crane beams of trusses, half-timbering and flooring.
installation of metal structures during the construction of industrial (warehouse) premises
Installation of columns
Most metal columns are placed on a solid concrete foundation. When they are prepared for installation, marks are placed on them indicating the longitudinal axis and the top of the foundation. When installing, the columns are held in one of the following ways:
- Using anchor bolts that are embedded in the foundation. After the column is aligned along two perpendicular axes, the joints are filled with cement mortar.
- Directly with the foundation surface, which is erected to the level of the milled base at the column. In this case, no additional cement mortar is added.
- Using steel support sheets. Their top surface is planed. Pouring cement mortar is carried out if necessary.
To support columns with wide shoes and a height of up to 10 m, it is sufficient to use only anchor bolts. Columns with greater height and narrow shoes must also be supported by braces in the plane where the structural rigidity is minimal.
- The bracing is attached to the top of the column before it is lifted and placed.
- The other end of the braces is attached to anchors or foundation elements located nearby.
- After the braces are fully tensioned, the slings can be removed from the column.
- Complete removal of braces is permitted only after the column is secured with permanent elements. The stability of the column can be ensured by crane beams or ties, which are placed after the installation of the first two columns connected by a crane beam.
When installing columns placed on the foundation, they are secured with anchor bolts during the process. Any metal gaskets placed under the base must be welded. In turn, the columns on the upper tiers are also fastened with bolts or welding. This connection bears a high load, so its strength is carefully calculated during design.
fastening metal columns using anchor bolts
Installation of elements of metal structures using alignment is quite labor-intensive and time-consuming. Therefore, recently an installation method that does not require alignment has been increasingly used. This method allows both to improve the quality of the structure and to reduce the time required for the construction of the building.
Non-alignment installation requires preparation of the metal structure during the manufacturing process and directly on the construction site. To increase the accuracy of the design, the following technological techniques are used:
- Separate production of shoe and base plate;
- Milling the ends of two column branches;
- Planing of base plates;
- The presence of 4 welded strips on the base plate with cut holes for bolt placement;
- Presence of axial marks on column branches.
When installation is carried out without alignment, the columns are supported on steel plates. In this option, the foundation is initially concreted below the design value by 50-60 mm, and after installing the slab it is filled with cement mortar.
The base plate is placed using adjusting bolts on the support strips, which are concreted completely flush into the foundation, similar to embedded parts. The supporting surface of the slab is adjusted with nuts so that the difference between the actual elevation and the design position is no more than 1.5 mm.
When a column is being installed, the axial marks marked on the branches are combined with the marks on the base plates. This ensures sufficient placement accuracy, after which the column is secured with anchor bolts. In this case, there is no need to additionally align the column in height or axes. After the braces are installed, crane beams can be mounted on the columns. When the crane beams are aligned along the axial marks with the columns, they do not require additional alignment. After securing the beams, the braces are removed from the columns.
What does the cost of work depend on?
Construction of buildings using metal structures is inexpensive. The price for installation of metal structures is always calculated individually, since the tariff is formed taking into account many factors. Ordering is usually cheaper. But the following factors can affect the final cost:
- Building area. When installing metal elements, the size of the room is taken into account. Some companies offer discounts on wholesale orders if you plan to build a large hangar or pavilion.
- Complexity of design. Installing a garage is much cheaper than a shopping complex or pavilion for an industrial workshop. Therefore, some customers are advised to order simple but functional buildings to reduce costs. It can be a flat canopy instead of an arched one. From an aesthetic point of view, it loses, but will save the budget.
- Company pricing policy. Some companies position themselves as highly qualified professionals, so their rates are 30% higher. The quality of the work performed will not be better than in an ordinary average company. They usually include in the price the costs of advertising and promoting oneself on the market, and such costs usually have nothing to do with the quality of installation.
- Presence of forged elements. Some customers want a unique design and order metal structures with forged elements. Aesthetically, they look attractive, but you have to pay extra for exclusivity.
The complexity of the task also affects the final cost. Experts will calculate how far the object is from the city, what the terrain features are, whether there is infrastructure (convenient access, connection to the power grid, ability to accommodate workers). An important factor is also the qualifications of the personnel involved in the work.
Metal structures are used in various fields of human activity. They have a lot of advantages, they are characterized by mobility and ease of use in construction. Finished products are cheap and reliable; they make excellent industrial buildings, barns, and shopping complexes. Their production does not take much time, and they are convenient to use and transport. Installation does not take much time, which is the main advantage of using metal structures in construction.
Installation of crane beams
These beams are installed after installing a pair of columns. During lifting, the beam is held in place by two guy wires. To receive it at height, installers are located on scaffolds, platforms and assembly ladders. The workers’ task is to keep the beam from touching the previously installed structural elements and give it the desired position. To control the descent of the beam, there are risks on the console. To eliminate vertical deviation, steel pads are used, placed under the beam. Anchor bolts are used to temporarily secure the beam.
installation of crane beams
If crane beams are installed on columns with milled soles, the foundation of which is concreted to the design value, or columns on planed metal slabs, then it is enough to check the position of the beams along the main axis.
Stages of manufacturing metal structures
The technology for manufacturing metal structures from rolled metal at a plant includes several stages:
- Design. The future product is designed by qualified employees, taking into account the scope of use, type of mechanical loads, specifics of connecting parts and other features. At the first stage, the choice of metal for the production of the structure also occurs.
- Creation of a blank. At this stage, the weight of the future structure is calculated and its quality is checked. If necessary, mechanical or heat treatment of the workpiece is used: chopping, cutting and other methods.
- Part processing. The workpiece can be shaped by drilling, joining, grinding, seam processing, etc.
- Assembly of metal structures. It occurs by welding or manually.
- Treating metal structures with anti-rust agents.
- Labeling, packaging and quality control of the finished product.
- Delivery of metal structures to the site and their installation.
Truss installation
Before installation, the truss must be prepared - assembled, equipped with ladders and braces. Its rotation across the span is carried out using braces. For temporary fastening, braces are also used, as well as spacers, guys and jigs. The truss is verified by axial risks, which are located at the ends.
To lift the trusses, the crossbeams of one or two cranes are used, it depends on the weight and size of the structure being lifted. Their slinging is carried out exclusively in the nodes of the upper chord, otherwise significant bending forces may arise in the rods. Typically, slinging is performed at 4 points using traverses equipped with semi-automatic grips with remote control. If during installation the structural elements experience significant loads, they are reinforced with steel pipes or wooden plates.
The first truss, lifted by a crane, is turned by guys into the required position so that 0.5-0.7 m remains to the top of the columns. The truss is lowered onto the mounting tables located on the columns. Temporary fastening is carried out with bolts, after which its position is verified and the structure is finally attached. To protect against swinging, the truss is held in place by 4 flexible stays during lifting.
Subsequent work on the installation of metal structures of this type is carried out similarly. The second installed truss is connected to the first using purlins, spacers and ties. A rigid spatial structure is formed there. Trusses of adjacent rows are bolted together to increase rigidity.
Rust control technology in the manufacture of metal structures
The fight against corrosion is the most important stage in the production and operation of a metal product. There are several ways:
- Avoiding contact of the object with water. This method is suitable when there are no restrictions on the functionality of the structure.
- Adding special chemical elements. They take on the effects of corrosion first. Such chemical elements ensure the strength of the metal structure.
- Treatment of the product with water-repellent agents. These include varnishes, paints and more. The hydrophilic layer prevents direct contact of metal with liquid and protects the product from rust.
- Bimetal. In this case, the manufacturing process uses an alloy of two metals, one of which is more resistant to rust. This method is used at the procurement stage.
The use of rust control measures increases the service life of metal structures.
Flooring installation
Industrial buildings with a steel or reinforced concrete frame are often clad with profiled steel decking. This helps reduce the mass of the structure. Profiled panels equipped with insulation show high efficiency. They allow you to significantly save heat, which is quite important in the climatic conditions of our country.
For flooring, stainless steel sheets are used, which are additionally coated with an anti-corrosion compound. Sheets with a length of 3-12 m, a width of 0.86-0.85 m and a thickness of 0.8-1 mm are used. The length of the sheets is usually a multiple of 3 m and is selected during design depending on the location of the truss runs. The standard height of longitudinal corrugations is 60-80 mm.
Before installation, the sheets are connected into cards, since installing the sheets separately is very labor-intensive, given that all work must be carried out at height. Assembly is carried out on horizontal stands, which have corners according to the size of the cards. The sheets are joined using rivets or spot welding. If rivets are used, the holes in the laid out sheets are drilled by hand. The distance between the holes is specified in the project and is usually 50-60 mm. Rivets are placed into the resulting holes, after processing which a single card of the required size is obtained.
Slinging is carried out according to the diagram, depending on the size of the card. The flooring is laid on purlins or floor blocks. The purlins are placed on the nodes of the trusses, and, if the trusses are created from rectangular profiles of a closed structure, then directly on the upper chords of the trusses. Placing cards from profiled sheets is done using marks that mark the place of placement.
For fastening to purlins, equipment for installing metal structures is required, which allows you to quickly connect them to sheets using dowels or electric rivets. The most common fastening is with a nut driver, which is tightened with 6 mm diameter screws with plastic or steel washers under the head.
Main types of metal structures
Metal structures are strictly classified in accordance with certain criteria, since their scope is diverse.
According to the manufacturing technology of metal structures and the method of their assembly, they are distinguished:
- screw - assembly using hardware;
- riveted - assembly using rivets;
- forged - produced by riveting;
- welded - production by welding;
- stamped - production by stamping of rolled metal;
- combined - manufactured in various ways (for example, welded-cast).
According to the method of use, metal structures are divided into:
- stationary (solid) – created using a stationary structure for a long service life and cannot be dismantled;
- transformable - allow you to create metal structures of different sizes and configurations from the same set of elements;
- prefabricated - assembled and disassembled directly on site, they can be reused as necessary.
According to their purpose, metal structures are divided into:
- load-bearing (frameworks of products that provide rigidity and configuration of the structure);
- fencing (parts that perform a protective function: sandwich panels, fences, etc.).
Technologies for the production of metal structures are classified according to the material from which the products are made. For these purposes, metal alloys of aluminum, titanium, cast iron, steel, etc. are used.
Connecting metal structures by welding
Most of the installation connections are made by welding, a smaller part by bolts, and rivets are used even less often. This affects the cost of installing metal structures - welded joints are the cheapest. Connecting with rivets is the most labor-intensive, however, in some cases it is necessary to use only it. An example would be the building of a forging and press shop, in which bolts or welding cannot be used to create a load-bearing metal structure—the constant vibration created by the forging equipment will inevitably destroy these connections.
Welding is used when a rigid connection of structures is required, with a tight fit of the element and a water- and gas-tight seam. This is the only way to connect sheet structures in the casings of blast furnaces and thermal furnaces, tanks, dust collectors and gas holders. Among supporting structures, welded joints are used for the joints of columns with crane beams and trusses. Elements of steel structures can be welded with reinforced concrete elements. In such cases, the profiles are welded to the embedded parts.
To obtain a high-quality seam, the parts to be welded are pressed tightly against each other. Basically, rough mounting bolts are used for this. In some cases, additional metal joining plates are used to create a connection.
Columns whose height exceeds 18 m are divided into shipping elements for transportation, the dimensions of which depend on the means used for transportation. For installation, parts of the columns are assembled into a single whole. Column joints during the construction of one-story industrial buildings are usually made in the part above the crane, above the crane beams. The milled ends of the main and crane parts of the columns are joined and welded along the contour of the joint. To increase the rigidity of the connection, butt sheet overlays are used.
To install crane beams, they are supported on the corresponding column slabs and connected first with bolts and then welded. Additional fastening of the beam is carried out to the crane part of the column using brake structures. They are also initially bolted and welded with an extended seam. The connection of trusses with columns is carried out in a similar way.
When installing buildings made of metal structures, the quality of the welds performed is of great importance. They are checked by external inspection, which can determine deviations from geometric dimensions, cuts, lack of penetration or large pores. The surface of the weld should be smooth or have small flakes, and the deposited material should be of the same density. The permissible sizes of deviations and defects are specified in regulatory documents.
How is the quality control of metal structures produced?
Quality control of metal structures allows us to determine the suitability of products to perform their intended functions. This process takes place in accordance with regulatory and technical documentation. It involves several stages:
1. Input.
The materials that will be used for the manufacture of metal structures are being assessed. Accompanying documents, appearance of raw materials, quality of metal and consumables, rust control products, etc. are checked.
The results of the examination are recorded in a special journal for recording.
2. Operating.
This stage includes the selection of parts for subsequent testing for compliance with documents and standards. The characteristics of the structure and its parts, the quality of the elements and their assembly are assessed.
The results of the inspection are recorded in the operational quality control card.
3. Periodic.
At this stage, the load-bearing characteristics of the product, the reliability of the results of the two previous controls, the ability of parts to be assembled, and the accuracy of technological operations are checked.
4. Acceptance.
A visual check is carried out for defects, strength of parts, markings, integrity of packaging, strength of connections.
The results of the inspections are entered into the certificate of conformity and recorded in the report.
Connecting metal structures with bolts
Bolted connections can be made with bolts of varying accuracy depending on the purpose of the connection and the loads it can bear. Fasteners of normal and high accuracy are mainly used. For connections that are subject to shear loads, normal and rough precision bolts must not be used.
Holes for bolts are drilled or pressed so that the diameter of the hole exceeds the outer diameter of the bolt by 2-3 mm. This simplifies assembly, but makes them less resistant to deformation. For this reason, bolts classified as coarse and normal in accuracy class are used only when one element directly rests on another. Examples include connections on support tables, strips and flanges.
Connections that use high-precision bolts are an alternative to rivet connections in hard-to-reach areas. For such connections, the diameter of the holes is larger than the diameter of the bolt by up to 0.3 mm. If this requirement is met, the bolts sit in the holes very tightly and withstand shear loads well.
High strength bolts are the most effective fasteners. They combine high load-bearing capacity with significant resistance to deformation. Such bolts can be used instead of rivets in almost all connections. The nuts for such bolts are tightened using ratchet wrenches, which allows you to control the tightening force.
Soldering:
This is one of the oldest methods of joining metal elements. It is also used to create permanent structures. Soldering requires the presence of solder - a special composition that forms an alloy together with the parts being soldered.
Soldering can be capillary, diffusion, reactive flux, or contact reactive. There is also soldering and welding. Capillary soldering is the most common connection method. It involves filling the gap between the parts being soldered with molten solder. In this case, the base metal is melted in the solder, resulting in the formation of an alloy. After it cools, a seam is obtained. In second place in popularity is soldering and welding. This technology is similar to fusion welding, but using solder.