Rolling bearings: basic concepts
It is necessary to fix the spatial position of moving components. At the same time, it promotes rotational motion, receiving and transmitting loads from the part that is in motion to other structural elements (gears, gears, couplings, etc.).
To do this, the inner ring (cage) of the bearing is pressed onto the shaft journal and forced to rotate with it. The outer remains motionless, pressed into the body. The advantage of the presented part is minimal energy losses due to friction in it. This is its main advantage compared to a plain bearing.
Ball bearing device
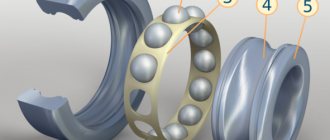
Ball bearings contain two rings, rolling elements of different shapes and a cage. Some types of bearings are manufactured without a cage, which is designed to separate the rolling elements from each other, determine equal distance and determine their movement. Outside the inner ring and inside the surface housing, tracks for moving the rollers in the form of grooves.
If it is necessary to reduce the dimensions, then the internal raceway is made on the shaft itself, on its neck or on the surface of the housing. In the case of a bearing without a cage, the ball bearing has an increased number of rollers and is characterized by increased durability. Such bearings cannot withstand too high engine frequencies, as the rotational resistance increases.
Mechanical working principle
The movement of the inner ring is repeated by the separator, rotating in the same direction. With a constant diameter of the separator, its rotation frequency directly depends on the diameter of the balls. An increase in this indicator leads to a decrease in speed and vice versa. From this it follows that the rollers in the bearing are selected precisely in size; their discrepancy leads to premature wear of the mechanism. When the roller bodies rotate around an axis, an additional centrifugal force arises, which is absorbed by the raceway.
In rolling bearings, virtually no friction occurs, with the exception of small friction losses between the cage and the rollers. Energy losses due to friction are reduced, and the service life of the device is increased and wear is reduced. When operating open ball bearings, there is a risk of various foreign bodies or contaminants getting into them. Closed devices with protective removable covers do not require maintenance and last longer.
Division of ball bearings by type of rolling elements
- roller;
- ball.
Depending on the device, bearings perceive different types of load:
- linear load;
- persistent efforts;
- persistent-radial work;
- radial load type.
- The number of rows of balls or rollers divides bearings into types:
- multi-row devices;
- double row bearings;
- single row mechanisms.
Some types of ball bearings can independently compensate for shaft misalignment during movement; they are called self-aligning. Other types require the intervention of a mechanic to adjust when an axis shift occurs during operation.
Characteristics of rings and bearing shells
Collapsible bushings are made of steel with bronze filling or TsAM 9–1.5L alloy.
Monolithic bushings are made from anti-friction cast iron of the AChK-2 and AChS-1 grades. When installing a bearing, it is necessary to position it so that the longitudinal groove for lubrication is on the opposite side of the operating pressure of the shaft axis. If the mechanism operates with extreme deviations, then additional bearing fastening is provided. The production of rings requires joint turning of the outer diameter of two shells - lower and upper, while leaving an allowance for finishing on the inner diameter. Parameters such as perpendicularity tolerance, radial runout of the hole in relation to the hole, ovality and taper are regulated by the data specified in the special GOST 24643–1981.
Rolling bearing device
The design of the rolling bearing is as follows. Most often, it is composed of a pair of rings (clips) - external and internal, rolling elements of different configurations (balls, rollers) and a separator. The service life depends on the latter, which ends after the destruction of its jumpers begins. It is needed to maintain a constant distance between the balls and the direction of movement, as well as to fix them in the rings. Radial bearings have annular grooves in the outer surface of the inner ring and the inner surface (for the outer race). For those who are stubborn, they are made at the ends of the clips. These are treadmills. In cross-section, they repeat the shape of the rolling body and direct their movement.
The main structural material for these parts is steel with a high chromium content or other properties. The latter are determined by the operating conditions of the bearing units. There are combined (hybrid) designs, when rollers, balls or separators are made of plastics (polyamide) or composite ceramics.
Plain bearings
Sliding bearings are fundamentally different from rolling bearings. But their task is the same - to ensure the direction of two moving parts or their support, while transmitting all the forces in the parts. The difference is that while in rolling bearings the rolling elements - balls and cylinders - work, then in sliding bearings this role is performed by moving parts (bars, shafts or journals). They slide along the surface of a fixed element (half ring or bushing). Thanks to this principle, the element slides between the antifriction layer of the bearing and the part for which it is used. Thanks to the embedded lubricant, as well as the coating, the contact area is actively lubricated. If the movement occurs radially, mobility is ensured due to the gap between the antifriction layer and the shaft.
There are many types of rolling bearings. These include radial bearings, thrust bearings, strips, half rings, and many other options and designs. They have a number of undeniable advantages - silent operation, the ability to withstand high loads, while rotating or oscillating relatively slowly. In addition, this type is recommended for work in harsh operating conditions where there is a temperature difference. Due to these unique properties, plain bearings are used in all areas of industry, especially for parts with limited space.
| Attention Bearing Buyers Dear customers, send your questions and requests for the purchase of bearings and components by email or call now: Delivery of bearings throughout the Russian Federation and abroad. Bearing catalog on the website |
Attention Bearing Buyers
Dear customers, send your questions and requests for the purchase of bearings and components by mail or call now: tel: +7 (495) 646 00 12 [email protected] Delivery of bearings in the Russian Federation and abroad. Bearing catalog on the website
themechanic.ru
Types of rolling bearings
The main feature by which bearings differ from each other is the shape of the rolling elements - balls or rollers (conical, cylindrical, needle, barrel-shaped and twisted). Depending on this, they are called roller or ball.
They are produced in 5 accuracy classes:
• 2 – ultra-high; • 4 – especially high; • 5 – high; • 6 – increased; • 0 – normal.
There are bearings without cages with a larger (than usual) number of rolling elements. Their load capacity is higher, and the permissible speed is significantly lower than that of standard ones. This type is used when it is necessary to reduce the diametrical size of the rotation unit. There are also so-called bulk ones (without rings), in which the balls can be easily replaced. Sometimes end protective covers are added to the design. They protect all internal elements and lubricant from contamination. This sealed bearing does not require maintenance during operation.
Where there is a bearing, there is a car
Two such global concepts as “bearing” and “car” are completely inseparable from each other, since in each unit and unit of the machine certain bearing forms and entities are used: rolling and sliding, radial, thrust and angular contact, ball or roller, heavy and light series... In general, it is clear that a self-propelled crew cannot do without such a useful part.
Rolling bearings, which will be discussed below, became widespread relatively recently, but they were invented a very long time ago - a gap in ideas and technologies; They say that the helicopter was invented by Leonardo da Vinci, but what's the point? It was not possible to manufacture such a working mechanism at that time.
With bearings, it’s a little more prosaic: in order for this part to fully fulfill its functions, it had to be made not only from a very hard, high-alloy metal, but it was also necessary to provide all mating parts with very high processing accuracy, because the higher the accuracy, the lower the rolling friction force and, accordingly, higher efficiency of the part. If the bearing is made somehow, it will not be much more effective than the classic friction pair of a village cart, flavored with tar, which was widely used in Russia until the middle of the last century. Precision machining was expensive, so such a part became really cheap only as technology developed and the term “mass production” appeared.
Nowadays, bearings are used everywhere; there is data on life tests of existing products and modifications made using the latest technologies. So, designers don’t have any questions about applicability; everything has become quite simple. There are undoubted production leaders on every continent: in Europe, in Asia, and in America - their names are well known. There is a certain top company that guarantees the quality of their products, and everyone knows them too. So, when buying a hub or generator bearing in a car store, you should pay attention to the brand - in our time of total globalism, the country of origin no longer plays any role. Moreover, in the case of a bearing, detecting a fake is quite simple - each well-known manufacturing company puts its markings on the outer ring of the race, all information is freely available, just go to the Internet, and since the race is made of very durable steel, in artisanal conditions It is unlikely that scammers will be able to perfectly repeat such a trick.
Over time, technologies improve, processing accuracy increases, the pressing issue of additionally increasing efficiency arises, and here lubricants and the possibility of supplying them to the required contact point come to the fore. For example, one of the manufacturers at one time brought to the market angular contact bearings with an external lubrication system, but the ease of use often did not provide for additional installation difficulties. But technologies change not only in mechanics, but also in chemistry; accordingly, new types of lubricants made it possible to eliminate the external reservoir, and a next-generation series with a modified internal lubrication system entered the market. Mechanics are also not asleep, using new materials and reducing weight, for example using non-standard rolling elements, removing approximately 15% of the “meat” from the balls, i.e. those segments that are not loaded. The result is an increase in the number of now not quite balls, an increase in DMN and load capacity. Naturally, as more and more advanced bearings appear, their dimensions and weight decrease, they immediately migrate to automotive equipment, but there are often a number of nuances here.
It is worth following the evolution of wheel bearings - a very important element, without which the car simply will not move, and this will be an excellent example of design trends in the modern automotive industry and their inextricable connection with marketing. The car hub is loaded with radial and axial loads; accordingly, no one is surprised by the use of roller or ball angular contact bearings in this unit. But since the axial load during movement can change from “+” to “-” and back, two of them are needed for each hub. The scheme has not changed to this day, but the execution has changed significantly. Previously, when installing a unit or replacing it, a mechanic had to follow a number of simple rules: choose the correct size of the adjusting ring installed between the inner races and observe the tightening torque. Incorrect assembly could reduce the service life many times over, and then the chassis, like the car as a whole, is a high-risk product. A loose or jammed wheel is unlikely to please the driver, so over time, instead of a pair of independent bearings, a simple rolling unit called HUB-1 appeared. If earlier, for example, on an old Mazda 323, when replacing the rear brake pads, the technician had to unscrew the central nut at the same time, which resulted in access to the bearing assembly, which seemed to subtly hint: “Are you changing the pads? Then rinse and put new grease in the bearings,” then later, after the appearance of HUB-1, the unit became maintenance-free. Two angular contact bearings with set gaps and lubricant were already installed in the cage, closed on the sides with plastic or rubber seals. Convenient when replacing? Undoubtedly. No repair kit, adjusting rings, or additional seals are needed. The old HUB was taken out, the new one was installed, that's all, the assembly line was also simplified. Naturally, if there is a problem with plumbing skills, then you can ruin everything - for example, hammer HUB-1 into the hub, which will repeatedly reduce the service life and can damage the seals. Still, an appropriate mandrel and a hand press are required.
And here the next modification of the bearing unit, called HUB-2, comes onto the scene, which significantly simplifies the assembly or replacement process, further reducing the dimensions of the structure as a whole. The HUB-2 now features a brake disc mounting flange on the outer or inner race, depending on whether the axle is driven or driven. But HUB-2, as it turned out, is also imperfect - it still needs to be pressed into the steering knuckle, which requires, albeit minimal, qualifications from the maintenance personnel, and, quite logically, a next-generation development called HUB-3 appears.
Now, apart from a wrench, you don’t need anything at all: using the latest technologies. So the designers have no questions about applicability, everything has become completely different. Actually, this trend is observed not only in the automotive industry, so that, despite mass production and a reduction in cost in light of this, the final part may end up being more expensive - this is such a paradox. It’s just that no one will sell it to you separately anymore, since now it is supplied only as part of a unit, and a non-separable one.
Bearing classification
Depending on the number of rows of rolling elements, bearings can be single-, double- or four-row. Self-aligning ball bearings are also available. Their inner race has a slight spherical offset. Thanks to this, it is possible to eliminate angular (up to 3°) misalignments of the axes of the mating shafts. This value does not exceed tenths of a degree if self-centering is not provided for by the design.
There are the following types of forces experienced by supports:
• axial, directed along the axis of rotation. • radial, acting perpendicular to the axis.
Depending on the direction of the force that must be compensated first, there are the following types of bearings - thrust, radial and their thrust-radial and angular contact varieties. Finally, depending on the outer diameter of the bearing (with one inner diameter), they come in 5 series - heavy, medium, light, extra-light and ultra-light. And according to the width of the clip - normal, narrow, wide and extra wide.
Support diagrams by their types and description
In industry and everyday life, a huge variety of units are used that reduce friction during rotation and longitudinal glossing.
Next, we will provide drawings of the device and show what parts the rolling and sliding bearings and its components consist of.
Ball radial
These devices are the most common type, consisting of an outer and inner ring with a technological recess. Metal or ceramic balls secured by a separator are inserted into the space between them.
These products can be open or closed (a washer is placed between the cages to prevent dirt from getting inside and lubricant from leaking out). The industry produces all standard sizes in different designs with one or two protective washers, with membranes to prevent dirt from entering. In such products, factories make a groove in advance for fixation using a ring. If rolling elements with a very long service life are required, then models are created with reinforced housings of greater width and thickness.
The separator can be manufactured:
- made of bronze (this material has a low coefficient of friction, but is expensive);
- made of metal (more common option);
- made of plastic (dramatically reduces noise, but requires constant active lubrication, used in vehicle gearboxes).
Parts with two rolling rows are produced.
This mechanism can withstand twice the load and is able to maintain the orientation of the axis. In some cases, one such node can replace a group of two single-row ones.
Ball thrust
They are designed to limit the movement of the shaft along the axis of rotation. Typically they consist of upper and lower washers with technological grooves and a separator with balls.
These devices come in single-row and double-row, with both sequential and radial arrangement of rolling elements. To simplify installation work, products are produced with an additional platform that provides uniform support force.
Thrust radial
In cases where it is necessary not only to achieve easy rotation, but also to limit the movement of the rod along the axis, such settings are used.
They are:
- Single row. They provide rotation and longitudinal support in one direction.
- Double row. They allow you to fix the shaft in the desired position and maintain the alignment position relative to the holder. For example, they are widely used in the wheel hubs of modern passenger cars.
- Collapsible. They have the possibility of additional lubrication. For proper functioning, rigid fixation of the lower rings is necessary.
- Non-separable. They are supplied from the factory and require no maintenance.
Roller rolling
| External ring | Internal clip | Elements | Separators | ||
| plastic | steel | brass | |||
| id=”docs-internal-guid-a42e8407-7fff-78bd-8287-f10a0643de24″> | |||||
This type is used for nodes with heavy loads. The following types exist:
- With one nearby. They are divided into: with a groove in the outer ring; internal; in two at once. This determines whether the rod will have an axial displacement.
- With two rows, it is required in cases of large forces transmitted through the shaft. This design allows the axis to be fixed in the desired position.
Structure and design of the support bearing
The part is necessary to limit the longitudinal movement of the rotation axis. It is an analogue of a persistent ball device.
Tapered roller group
If it is necessary to compensate for radial and axial loads, units with cone-shaped rolling elements are used. The most common type is single-row.
| Outer ring | Inner race | Links | Separators | |
| polymeric | steel | |||
This spare part is dismountable and has an adjustment function after long-term use. In most cases they are placed in pairs. All passenger cars in the past and most trucks now have such a device in the wheel hub. It is also widespread in agricultural machinery, where great forces are applied in the middle, but the speed is not high. This unit is gradually being phased out, as it requires constant maintenance.
Double row
Instead of using two parts, you can use one. At the same time, the possibility of adjustment is retained and the axial displacement control function is not lost. In helical gears, this design ensures constant alignment of the gears.
Such a block is indispensable in heavy industrial and mining equipment, and in railway transport.
Roller support
With increased force directed along the middle, the installation of bearings of a slightly different structure is required. They come with conical, spherical and cylindrical rolling links.
| Bottom washer | Upper washer | Rollers | Steel separator |
In mechanisms where self-centering of the supporting element is necessary, parts with spherical rollers are used. They withstand heavy loads, high rotational speeds, and are not critical to the alignment of the rod and the landing site. They are used in devices with high axial pressure, such as: wind generators, extruders, rotary devices in heavy industry, metallurgical equipment.
Self-aligning bearings (floating)
In production, it is necessary to achieve stable, long-term rotation of shafts that are impossible or impractical to accurately center. For example, drives on agricultural machinery, on an irrigation system. In this case, sliding units are used that automatically select the plane of rotation.
A common feature of these blocks is the processing of one of the surfaces in the form of a ball.
As can be seen from the diagram, the product has the ability to rotate freely if the landing and support coordinates do not match. This type often uses an additional component - a wedge-shaped lock for fixation on the shaft.
This illustration shows well the main advantage of this type. It works stably with axial displacement and with mismatched planes.
Self-aligning mechanisms are divided into two main classes:
- Ball:
- single row;
- double row;
- with a degree of freedom in the outer ring;
- in the inner.
This device is easy to install, but does not withstand very high overloads.
- Roller:
- With one row of rolling elements. The simplest and most common option.
- With two rows. This part is operated under high pressure.
- With a spherical surface on the outer ring.
- On the inner ring.
- With the ability to move the rollers in two planes. It allows you to achieve a strong deflection of the shaft from the support.
This class is used in structures where it is impossible or impractical to achieve a high degree of alignment of nodes. Also in cases where the landing points cannot be stationary. One of the disadvantages of such a connection is the difficulty of retaining the lubricant inside the part.
Needle-shaped
The rolling element in the form of an elongated oblong cylinder allows you to dramatically reduce the gap between the outer and inner diameters. The size of the sliding device becomes noticeably smaller. This quality has found application in structures where it is impossible to install classic ball or roller bearings due to their too large dimensions. They are used in transmissions for cars and trucks. The cardan shaft crosspieces are made on this basis.
| Outer ring | Clip | Needle links | Separators | |
| plastic | steel | |||
Instead of an outer or inner race, this design often uses a seat with high quality processing. This allows you to save a few millimeters of required space. There are models of a needle device without a separator, designed for low angular velocities or swing motion (universal drive).
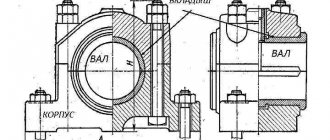
Sliding bearing - what it consists of, its structure
We encounter this mechanism at every step. In any device that has mobility, you can find the following part: door hinges, baby stroller wheel bushings, sliding pads in household appliances, in a car starter.
The structure consists of a body, a sliding layer and rotating elements. Engineers try to achieve minimal resistance between surfaces, so they use materials with a low coefficient of friction (bronze alloys, cast iron, polymers, ceramics). The next step to facilitate glossing is the introduction of an additional layer that creates a gap between the planes. For this, different types of lubricants are used, such as: specialized oil, lithol, graphite, water for ceramics, inert gases, emulsions with lithium soap and calcium sulfate.
Sliding devices are divided into two main types: radial and thrust. For example, the connection between the connecting rod and the crankshaft uses bearings to provide rotational motion. Between the block and the crank there are spacers that limit axial displacement.
Radial ones are:
- One and many are superficial. This depends on the number of bushings sliding relative to each other.
- With the possibility of adjustment. During production, due to the displacement of the liner, the resulting gap is reduced.
- Hydrostatic with forced lubrication. This requires a constant supply of lubricant under high pressure.
- Hydrodynamic, where the glossing element is drawn between planes due to its own rotation.
- Built-in. When one or both holders are a structural part of the mechanism, making it impossible to replace an individual part.
- Collapsible. In this case, there is no need to repair the entire device; it is enough to replace only the spare part.
Let's take a closer look at the version with liquid lubricant.
When making revolutions, liquid is drawn into the space between the rubbing surfaces, this creates a gap and sharply reduces resistance. If it is not possible to maintain a constant fluid level, then it is advisable to use a system with artificial injection of lubricant under pressure.
Modern products use not only oil, but also standard substances. For example, water is used in ceramic bearings of household circulation pumps.
Rotation device based on a gas layer
At high speeds and low loads, it is necessary to use other technical solutions. High-tech gadgets use a sliding product where gas serves as a lubricant. Similar to hydraulic systems, two technologies can be used:
- artificial injection of pressure in the space between the rubbing surfaces;
- creating a sliding film due to high speeds.
One of the disadvantages of such a system is the low force on the axle. Moreover, the virtually complete absence of friction in standard operating modes makes it indispensable in solving many engineering problems. This type has poor resistance characteristics in start and stop mode.
Magnetic
The newest type of friction-reducing device is a mechanism based on the physical principle of repulsion of magnets with different polarities. With the development of science, it became possible to suspend the axle between the solenoids so that it does not have contact with the mandrel.
The main advantage is the complete absence of obstacles to rotation. In this case, practically no heat is generated. This means the problem of removing excess heat is solved. With the help of strong magnetic fields it is possible to achieve high workloads.
An important disadvantage of such complexes: the complexity of the design; the mandatory presence of an additional source of energy, which requires more as the force of impact increases.
Non-rotating sliding mechanisms
In the standard sense, this is the part between the housing and the shaft. It is required to achieve minimum resistance during longitudinal movement. Devices that provide this function are called the same. They are divided into sliding and rolling. For example, in modern furniture, drawers are equipped with strips, the elements of which are made of balls. Printers, scanners, and computer hard drives use a device that allows smooth and unhindered movement along guides with a high degree of processing.
There is a need to reuse the threaded connection. To avoid abrasion, longitudinal-radial mechanisms are produced. They are an analogue of a screw drive using balls to reduce friction and energy costs.
In our article, we gave some examples and diagrams, told what a ball, roller, needle and plain bearing consists of. You can see the variety of these products on the website, which sells a wide range of products from the best domestic and foreign brands.
Application of rolling bearings
The use of rolling bearings is determined by industries that produce equipment with rotating parts. These include primarily all types of mechanical engineering - metallurgical, food, mining, transport (cars, ships, aircraft), road construction and energy (engines, turbines, compressors, fans and air conditioners). They are used in the manufacture of household appliances (washing machines, dishwashers, sewing machines, freezers and refrigerators) and microelectronics (personal computers, laptops, DVD players, etc.).
The world demand for these products is constantly increasing. The world's leading manufacturers of rolling bearings are SKF (Sweden), American Roller Bearing and Boston Gear LLC (USA), FAG (Germany), NTN (Japan), as well as Vologda, Kursk (Russian Federation) and many other bearing plants.
Devices and features of thrust bearings
A single-row thrust ball bearing designed for one-sided axial load consists of a tight ring mounted on the shaft and a loose ring mounted in the housing. Between them there are spherical bodies that provide rolling, as well as separators. A single bearing of this type is made dismountable, which greatly simplifies its installation on the shaft and in the mechanism housing. The free ring of these thrust parts can have not only a flat, but a spherical bearing surface. Such ball bearings can compensate for slight misalignment of the shaft relative to the surface of the housing on which the rotation unit rests.
Previously, to assemble a rotation unit with multidirectional axial loads, two thrust bearings were used, which were mounted according to a special scheme. Such a tandem worked as a single support and provided sufficient efficiency and reliability. But this system had a number of important disadvantages, among which the most significant were the rise in cost of the unit, the increase in its dimensions and the complexity of installation and maintenance. Today, double-row thrust ball bearings, compact and inexpensive, are more often used for double-sided thrust loads. These supports have one central tight ring and two loose rings, each with its own set of balls and separators. Just like single-row models, they can only be used for persistent loads. The design of these products is also collapsible to simplify installation. A radial ball bearing with two rows of rolling elements does not belong to supports used in units with high rotation speeds. This limitation is due to the fact that under severe centrifugal loads, the balls of such supports can leave the tracks, which will cause the destruction of the support. In those rotation units where, in addition to axial forces, there is a radially directed load, angular contact ball bearings are used. They are persistent, they are distinguished by the distribution of loads inside the part - the combined thrust-radial force acts on the balls at an angle and is transmitted to tracks with massive sides. The contact angle of the rolling elements with the track is one of the most important characteristics of such a support, since the magnitude of the axial or radial force with which the part can work depends on it. As a rule, particularly stringent requirements are placed on the materials and accuracy of radial thrust products. This is due to the fact that they operate at higher speeds, and their design is an order of magnitude more complex than that of conventional thrust bearings. When the question arises about how much load a particular type of thrust ball bearing can handle, it is important to remember that there is no compromise and models designed to handle axial forces will quickly fail where a radial load is applied to them. The material of the rings and cages of thrust parts is less durable than thrust-radial ones - this provides some savings, at the expense of reliability. High-carbon chromium steels are used for the manufacture of rings and rolling elements. If it is necessary for the ring to have a special margin of strength, it, like the ball, is made from special grades of steel, from which non-metallic inclusions are removed using various methods. This ensures high homogeneity of the metal and the absence of negative internal stresses. The cages of thrust and thrust radial bearings are usually cast and massive. They are made from the following materials: • Brass; • Polyamide; • Textolite. The most durable, but also the most expensive models are produced with cast brass separators. Polyamide is an excellent material for supports that are relatively small in size. This polymer is very resistant to abrasion, but has a significant drawback - it is afraid of heating above +120°C. In terms of its performance properties, textolite occupies an intermediate position between brass and polyamide, and a thrust ball bearing with a cage made of this material performs well where loads and temperatures are moderate.