Bearings play an important role in modern mechanics. Primitive analogues of this mechanism were known even before our era. Outwardly, such mechanisms vaguely resembled modern bearings, but structural similarities were present. This is evidenced by finds from various parts of the world. Modern bearings are actively used in various fields, significantly making human life easier. Why these mechanisms are needed, and what areas and applications of bearings you can find out in this article.
Types and types of bearings
The purpose of this mechanism is to ensure uniform rotational movement, while reducing the level of friction between surfaces. There are different types and types of bearings. Depending on the friction force, sliding and rolling bearings are distinguished. By the name, you can roughly understand what their difference is. Sliding bearings work thanks to sliding elements, and rolling bearings - rolling elements. The sliding elements in bearings can be shafts and strips, and the rolling elements can be cylinders, rollers or various balls.
Each type of bearing is classified into different types based on different characteristics. To have a rough idea of what we are talking about, here are some examples of types of rolling and sliding bearings. Rolling bearings are divided into roller and ball. Roller, in turn, are divided into cylindrical, needle, conical and many others. Sliding bearings can be divided into radial, thrust and radial thrust bearings.
Purpose and design of bearings
Bearing is a component of a mechanism or machine, which is part of a support that supports the shaft, providing rotation or linear movement with minimal resistance, receiving and transmitting the load from the shaft to the body parts of the mechanism or machine. A support with a thrust bearing is called a thrust bearing.
Bearings are characterized by the following main parameters:
- maximum dynamic and static loads;
- maximum rotation speed for radial bearings;
- landing dimensions;
- accuracy class;
- gap group.
The forces loading the bearing are divided into the following types:
- radial force acting in a direction perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the bearing;
- axial force acting in a direction parallel to the axis of rotation of the bearing.
According to their design, which determines the different principles of operation, all bearings can be divided into several types:
- rolling bearings;
- plain bearings;
- gas-static bearings;
- gas dynamic bearings;
- hydrostatic bearings;
- hydrodynamic bearings;
- magnetic bearings.
The main types of bearings used in mechanical engineering are rolling and sliding bearings.
Advantages of plain bearings: small radial dimensions; the ability to work under shock loads and use at high loads and high rotation speeds. Disadvantages: they cannot work without lubrication, do not allow shaft distortions, are difficult to install (require scraping).
Rolling bearings have the following advantages over plain bearings:
- significantly lower friction losses, and, consequently, a higher efficiency (up to 0.995) and less heating;
- 10...20 times less friction torque when starting machines;
- saving on scarce non-ferrous materials, which are most often used in the manufacture of plain bearings;
- smaller overall dimensions in the axial direction;
- ease of maintenance and replacement;
- less lubricant consumption;
- low cost due to mass production of standard bearings.
The disadvantages of rolling bearings include:
- limited possibility of use at very heavy loads and high speeds;
- unsuitable for work under significant shock and vibration loads due to high contact stresses and poor ability to damp vibrations;
- significant overall dimensions in the radial direction and weight;
- noise during operation due to errors in the shapes and sizes of parts;
- complexity of installation and installation of bearing units;
- increased sensitivity to inaccurate installation in the bearing assembly;
- high cost for small-scale production of uniquely sized bearings.
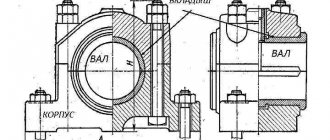
The design of rolling bearings consists of two rings, rolling bodies (balls or rollers) and a cage (some types of bearings may be without a cage), separating the rolling bodies from each other, holding them at an equal distance and directing their movement (Fig. 1). Along the outer surface of the inner ring and the inner surface of the outer ring (on the end surfaces of the rings of thrust roller bearings) there are grooves - raceways along which the rolling elements roll when the bearing operates.
Rice. 1. Radial ball bearing design : 1 – outer ring; 2 – ball (rolling body); 3 – separator; 4 – raceway; 5 – inner ring
In some components of mechanisms and machines, in order to reduce dimensions, as well as increase accuracy and rigidity, combined supports are used: in this case, the raceways are made directly on the shaft or on the surface of the housing part.
There are rolling bearings made without a cage. Such bearings have a large number of rolling elements and a large load capacity. However, the maximum rotation speeds of full complement bearings are significantly lower due to increased torques of resistance to rotation.
Closed rolling bearings (with protective covers) require virtually no maintenance (lubricant replacement), open ones are sensitive to the ingress of foreign bodies, which can lead to rapid destruction of the bearing and failure of mechanical equipment.
Application of rolling bearings
As already mentioned, the main structural elements of rolling bearings are rollers and balls. The design of such bearings allows them to support various shafts, axes of mechanisms and parts that are in motion.
The areas and applications of bearings are extremely important. For example, such mechanisms are indispensable in the manufacture of various vehicles and mechanisms. Let's look at some areas and applications of rolling bearings.
- Equipment production. Rolling bearings are used in equipment for various types of industry, for example, in the food industry. Such mechanisms allow increasing productivity and more rational allocation of resources.
- Steel industry and non-ferrous metallurgy. Bearings are used at various stages of production. They have high mechanical resistance and therefore are not afraid of shock loads.
- Automotive, aviation. For example, ball bearings have shown themselves to be excellent in cases where the loads are constant and medium loads. Roller bearings are used if the loads are significantly higher.
- Production of household appliances. Needle bearings are often used because they are good for use with small objects.
Everything about bearings in one article: history of invention, varieties, their advantages and disadvantages
It is very difficult to imagine modern life without bearings, and even more so - production. The bearing is absolutely indispensable in the vast majority of rotating parts of a wide variety of components and mechanisms. They are widely used both in miniature household appliances and in giant mechanisms of industrial production equipment.
Not a single enterprise, not a single production association, not a single industrial complex can refuse to use bearings, which have a limited service life. This is because there is no real alternative to bearings today.
In this regard, the efficiency and uninterrupted operation, and therefore the economic efficiency of each enterprise, production association or industrial complex, directly depends on the timely replacement of worn-out bearings, the supply and installation of new ones, as well as the repair of failed bearings.
History of the invention and evolution of the bearing
Everything new is well forgotten old. This immortal and no less brilliant statement can be safely applied to almost all modern technologies. It also applies to the bearing, despite the fact that from the time of its invention to the present day, the bearing has gone through a long evolutionary path before it took on the form familiar to all of us. True, in this case it would be more correct to say: “everything new is an evolved old thing.”
Let's look back and remember how things were.
So, in 3500 BC. Representatives of the well-known Egyptian civilization already made full use of primitive, but quite effective support bearings, although without the use of balls.
Around 700 BC. The Celtic civilization knew and quite successfully and widely used cylindrical rolling bearings.
In 330 BC. Greek military engineer Diad managed to create a siege engine using primitive bearings. It was a heavy ram that moved easily along roller guides. Thus, the basic operating principle of rolling bearings was applied in practice, i.e. sliding friction was replaced by rolling friction, which allowed the machine to perform its tasks using not so much force.
In 1490 A.D. The great genius of that time, Leonardo da Vinci, shared with the world the first drawings of a rolling bearing. This caused a real sensation in certain circles, but found no practical application.
In 1794, Philip Waugham patented the first analogue of the modern rolling bearing. Unfortunately, his sample was never put into practice, since there were no suitable technical capabilities for the full implementation of the idea - manual polishing of the balls did not provide the required accuracy.
In 1839, the American scientist Isaac Babbitt became the inventor of the alloy, which made it possible to produce balls for full-fledged rolling bearings. The alloy consisted of lead, copper, antimony and tin.
This was followed by a boom in technically sound ball bearing designs, many of which were patented. And in 1853, Phillip Moritz Fischer designed the first pedal bicycle, the mechanisms of which used real bearings.
The last significant event for the start of the widespread distribution and use of bearings was the creation by Friedrich Fischer in 1883 of a machine, thanks to which it was possible to grind hardened steel balls. At the same time, the grinding accuracy was at a level unattainable until that moment. The creation of this machine made possible the founding of the famous Schweinfurt bearing factory, thanks to which rolling bearings began to be used everywhere.
Since then, bearing technology has been continuously improved. Eventually, the bearing acquired its familiar form, and today no production can be imagined without its use.
The most popular and in demand today are rolling and sliding bearings, and now we will talk about them in more detail.
Rolling bearings, their types, advantages and disadvantages
The operating principle of such a bearing is based on the use of rolling friction force. A rolling bearing is a structure consisting of two metal rings with grooves, between which balls or rollers/needles are placed, fixed inside a cage installed between the rings. Some types of such bearings do not use a cage.
Rolling bearings are classified depending on:
- The types of bodies used to achieve rolling are ball and roller/needle.
- Type of load - radial, angular contact, thrust, linear, and ball screw gears.
- Number of rows of balls or rollers/needles – single-row, double-row, multi-row.
- Possibilities to compensate for the lack of alignment of the shaft and bushing are self-aligning and non-self-aligning.
Rolling bearings have the following advantages:
- High efficiency achieved due to minimal friction losses
- The friction moment is several times, or even tens of times, lower than in plain bearings
- There is no need to use expensive non-ferrous metals, without which the effective functioning of sliding bearings is impossible, which has a positive effect on the cost of production of rolling bearings
- The ability to create bearings of almost any size in the axial direction, which expands the range of their application
- Excellent performance characteristics and low maintenance, relative ease of replacement
- Minimum lubricant consumption
- Low cost, which is a consequence of mass production and the materials used
- High degree of interchangeability, which has a positive effect on the simplicity and speed of repair of various machines and equipment
But they also have disadvantages:
- Relatively limited range of applications - ultra-high speeds and heavy loads, including shock and vibration, are not subject to such bearings
- Significant mass and dimensions in the radial direction
- Impossibility of creating silent bearings, which is caused by form errors
- The relative complexity of installing bearing units
- The need for very precise installation: inaccuracy can damage the unit
- When producing small batches of bearings of non-standard sizes, their cost increases significantly
Sliding bearings, their types, advantages and disadvantages
A sliding bearing consists of a housing with a hole in which a lubricating device is located, as well as a bushing made of antifriction material (usually an alloy of non-ferrous metals). The shaft rotates due to the gap provided between it and the sleeve hole. This clearance is carefully calculated to ensure efficient bearing performance.
Sliding friction in such bearings is divided into:
- Liquid. Thanks to the layer of liquid lubricant, there is no direct constant contact between the surfaces of the shaft and the bearing. Direct contact may either be completely absent or intermittent in some areas.
- Borderline. The lubricant is a thin film, and the contact between the bearing and the shaft is either complete or affects areas of considerable length.
- Dry. Lubrication is not used, and contact of the bearing with the shaft occurs along the entire length, or over areas of considerable length.
- Gas. Due to the presence of a gas layer between the shaft and the bearing, their direct contact is impossible.
Lubricant in such bearings is liquid, plastic, solid or gaseous.
Sliding bearings are classified depending on:
- Hole shapes – single- and multi-surface; with or without surface displacement; with or without center offset.
- The directions of the perceived load are radial, axial, radial-thrust.
- Designs – one-piece, detachable and built-in.
- The number of oil valves used is with one or more.
- Adjustability – adjustable and without such an option.
Sliding bearings have the following advantages:
- Significant range of applications due to the ability to function normally at ultra-high rotation speeds and under heavy loads, including vibration and shock
- Economical when using a shaft of significant diameter
- Suitable for use as split bearing (e.g. crankshaft)
- The ability to adjust the gap, which allows you to set the shaft axis with maximum accuracy
They also have a number of disadvantages:
- Not the highest efficiency due to noticeable friction losses
- Inability to work without constant lubrication
- Uneven wear of the journal and the bearing itself
- High cost, because non-ferrous metals are often used in production
- Significant labor intensity of production
Well, we hope this article was interesting and useful to you - it brought more clarity to your ideas about bearings, which will make your work more efficient.
has been a reliable partner for the supply of bearings for 18 years. If you decide to work with professionals, then contact us!
You can get advice and purchase these items by calling multi-channel tel. or send a request by Email, or by contacting your personal manager!
Application of plain bearings
Sliding bearings are different from rolling bearings, but their applications are similar. Such bearings are actively used for the manufacture of various equipment, railway equipment, the automotive industry, and the aviation industry. Radial plain bearings are especially popular.
Spheres and areas of application of sliding bearings also include agricultural machinery and construction equipment. Such bearings are actively used in cases where there is a possibility of high shock loads and unfavorable environmental conditions.
Of course, at the present stage of development of any industry it is impossible to do without the use of bearings. This area is actively developing in many countries of the world, including Ukraine.