General description of the part
The element serves to impart rotation to some parts of the system, while the core (usually a shaft) remains stationary. You can achieve high speeds and speeds, as well as increase resistance to pressure and friction, if you use the spare part correctly. Structurally, the mechanism is simple and consists of:
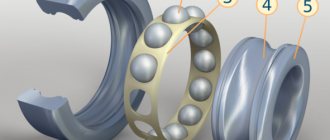
- outer and inner rings;
- bodies of rotation - balls or rollers;
- separators creating cells;
- seals to prevent dirt from entering.
In order for the mating surfaces to glide better, they need to be constantly lubricated. There are not only ones built on the principle of rolling, but also sliding. Instead of small metal elements, they contain a lubrication cavity or a solid liner, which improves movement and prevents the occurrence of high friction forces.
Either the bushing or the rim can remain stationary. In this case, it is necessary to achieve a high degree of alignment when fastening. But with the most efficient installation, there may be a gap; it is filled with lubricating substances. Sometimes one of the rings is completely missing, this has a very positive effect on mating, maximum contact is achieved, but can only be used in systems that are well protected from moisture and contamination.
The advantage and peculiarity of angular contact bearings, unlike thrust bearings, is that their design is designed for two types of loads simultaneously. Both for radial and axial to varying degrees. This allows the nodes to be used in various fields, significantly increasing their significance and relevance.
Purpose
Thrust bearings are designed to carry both radial loads, i.e. loads acting perpendicular to the axis of the shaft fixed in bearings, and mainly loads acting along the axis of the shaft in one or two directions.
The name of the bearings emphasizes that, first of all, they are designed to work with axial loads.
They also talk about radial (Radial bearings), angular contact and radial thrust bearings (Angular contact bearings).
Regardless of the name, any bearing absorbs both radial and axial loads.
The names only emphasize which of the loads - radial or axial (thrust) - is the main one. This article discusses thrust (thrust-radial) bearings.
Designs and versions
Selecting the type, design, etc. of a bearing for a specific mechanism is a difficult task. Methods and automated bearing calculation systems offered by bearing manufacturing companies can provide significant assistance in solving this problem.
GOST 3189-89 “Ball and roller bearings. The system of symbols" identifies the following types of thrust (thrust-radial), table UP-1.
Table UP-1. GOST 3189-89 “Ball and roller bearings. System of symbols."
Types of bearings.
| № | Bearing type | Designation according to GOST 3189-89 |
| 1 | Thrust or thrust-radial ball | 8 |
| 2 | Thrust or thrust-radial roller | 9 |
Single and double thrust ball bearings
Single thrust ball bearings, Figure UP-1, Figure UP-2, A), consist of rings, on the flat surfaces of which raceways are laid. Rolling bodies are balls.
Practically do not withstand radial loads.
The ring mounted on the shaft, the inner ring, is called the tight ring of a thrust bearing.
The outer ring is also called the free ring.
Double thrust ball bearings (Figure UP-2, B) contain a third, central ring, which is free. Two rows of balls are used.
To compensate for misalignment and installation errors, a spherical washer ring can be used, installed under the free ring.
Small thrust bearings typically use stamped steel cages, while larger ones typically use machined steel or brass cages.
Figure UP-1. Thrust single ball bearing.
Figure UP-2. Thrust single ball bearing, A) and thrust double ball bearing B), in cross-section.
Cylindrical roller thrust bearings
Such bearings (Figures UP-3 and UP-4) are capable of supporting higher axial loads than ball bearings of comparable overall dimensions. This is due to the fact that the contact spots of the rolling elements and rings have a linear shape, and, accordingly, a larger area than in thrust ball bearings.
They have high rigidity and are weakly sensitive to shock loads.
Practically do not withstand radial loads.
The standard design assumes the absence of radial loads and the presence of an axial load acting in one direction.
Single-row and double-row thrust bearings with cylindrical rollers are available.
Stamped steel cages are used, as well as steel or brass obtained by mechanical processing.
Figure UP-3. Single row thrust roller bearing with cylindrical rollers.
Figure UP-4. Ring, rollers and cage of a single row thrust bearing with cylindrical rollers.
Tapered roller thrust bearings
Such bearings (Figure UP-5) are capable of supporting higher axial loads than ball bearings of comparable overall dimensions. This is due to the fact that the contact spots of the rolling elements and rings have a linear shape, and accordingly, a larger area than in thrust ball bearings.
Double tapered thrust roller bearings, drawing UP-6, are also produced.
Tapered roller bearings have high rigidity and are weakly sensitive to shock loads.
Bearings of this type support both axial and radial loads.
Stamped steel cages are used, as well as steel or brass obtained by mechanical processing.
Figure UP-5. Tapered roller thrust bearing.
Figure UP-6. Cross-sectional view of a double thrust bearing with tapered rollers.
Spherical roller thrust bearings
The free ring of this type of bearing has a “spherical” shaped raceway. Barrel-shaped rollers are used as rolling bodies, installed at an angle to the plane of the rings, figure UP-7.
Figure UP-7. Self-aligning spherical thrust bearing.
Bearings of this type are self-aligning. They have a high axial load capacity and at the same time can withstand medium radial loads.
Bearings of this type support both axial and radial loads.
Stamped steel cages are used, as well as steel or brass obtained by mechanical processing.
About bearing classification
The variety of types, designs, and sizes makes the systematization and classification of bearings a daunting task.
The main GOSTs related to bearings are:
1. GOST 520-2011. Rolling bearings. General technical specifications (ISO 492:2002, NEQ ISO 199:2005, NEQ).
This GOST also refers to the following standards for rolling bearings:
GOST 831, GOST 832, GOST 3478, GOST 4252, GOST 4657, GOST 5377, GOST 5721, GOST 6364, GOST 7242, GOST 7634, GOST 7872, GOST 8328, GOST 8338, GOST 8419, GOST 8545, GOST 888 2, GOST 8995 , GOST 9592, GOST 9942, GOST 18572, GOST 20531, GOST 23179, GOST 23526, GOST 24696, GOST 24850, GOST 27057, GOST 27365, GOST 28428.
2. GOST 3189-89. Ball and roller bearings. System of symbols.
This GOST also refers to the following standards for rolling bearings:
GOST 520-2002, GOST 832-78, GOST 3395-89, GOST 3478-79, GOST 4060-78, GOST 5377-79, GOST 5721-75, GOST 7872-89, GOST 24310-80, GOST 24696-81, GOST 24810-81, GOST 24850-81, GOST 28428-90.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) pays great attention to the standardization of bearings.
A number of leading bearing manufacturers offer their own classification systems, which are an extension of the ISO classification.
As an example, table UP-2 shows the correspondence of the names used in the Russian Federation and the companies SKF, Sweden, FAG, Germany, for single and double thrust ball bearings and double thrust radial bearings.
Table UP-2. Correspondence to the names of thrust bearings.
| RF, GOST 3189-89 | SKF, Sweden | FAG, Germany |
| 8100 | 51100 | 51100 |
| 8200 | 51200 | 51200 |
| 8300 | 51300 | 51300 |
| 8400 | 51400 | 51400 |
| 18200 | 53200+U200 | 53200+U200 |
| 18300 | 53300 + U300 | 53300 + U300 |
| 38200 | 52200 | 52200 |
| 38300 | 52300 | 52300 |
| 178800 | 234400 | 234400 |
| 178900 | 234700 | 234700 |
Kinds
Classification occurs according to various parameters - by size, the use of various bodies of rotation, by design features, the number of rows, as well as by manufacturers. The online store "Mobi Bearing" presents a wide range of products from domestic and foreign companies. If you don’t know exactly which model you need, our consultants will help you choose. The main thing is to know the size range and purpose of the knot. Let's look at what they are below.
Single row angular contact ball bearings
The design of such ball bearings can be called classic. The balls are slightly offset in relation to the inner and outer rings, this allows them to absorb a high axial load on the part. They can be produced open or with closing seals. At the same time, there are separators everywhere. They can be stamped (a cheaper option) or more durable - made of brass. You can also divide all models into collapsible and solid. The first ones are good because they can be opened, cleaned and lubricated, and secondly, the lubricant is provided for the entire period of operation.
The peculiarities include the fact that they usually move in one direction, so if rotation in both directions is necessary, they are installed in pairs. They have low angular self-alignment, so they are not applicable in systems with high levels of vibration or frequent shocks or mechanical damage. Typically, the contact angle in the product reaches 40 degrees. This inclination provides good acceptance of axial loads and increased load capacity - all this in comparison with both support and conventional radial units.
Double row angular contact ball bearings
They are structurally similar to the previous type, but differ in two raceways with a separator between them and a correspondingly increased number of rotating bodies. The balls can be arranged symmetrically with respect to each other or in a checkerboard pattern. In general, the part resembles two double single-row ball bearings, but they take up much less space and are more compact than this tandem.
In terms of purpose, they are more universal, because due to the ability to work in two directions, the range of actions increases. They also have slight self-alignment (that is, a deviation of up to 4 degrees is permissible), and the contact angle is 25-35°, so the axial load on them is permissible less, but the load capacity is the same in both directions.
There is one more pleasant feature - strict alignment of the shafts is not necessary; operation will be optimal even with a small gap.
Radial roller, equipped with short cylindrical rollers
They can have any number of rows or paths. The main design difference is the presence of short cylinders instead of balls. This leads to a very large load capacity and the perception of significant external loads. But axial impacts are only permissible for short periods. This explains the lack of speed. The main application is in large machines, for example, for metalworking, when it is necessary to perform few rotations, but it is necessary to work with large and heavy adjacent spare parts.
Another significant advantage is the ability to self-install. It is typical for all roller bearings because the contact between the elements is much greater. The result is that there is virtually no edge stress and can be used even in conditions of frequent or intense vibrations.
They are products with increased strength and long service life.
Double-row spherical angular contact roller bearings: designation and differences
The main load is perpendicular to the shaft, and they can withstand a very large load capacity. The axle can also have a fairly large impact, but it should not be more than 25% of the permissible radial stress. Very unpretentious in terms of installation, alignment and other technical errors. They work in both directions due to two rows of bodies of rotation, which are spheres, not cylinders. Due to the rounding of the rollers at the edges, sufficient self-alignment is ensured, as well as the absence of edge stress.
The units find application in large objects that differ in size and misalignment of parts, and also do not require a high axial load. These could be water pumps, industrial fans, large gearboxes, saw frames, propeller shafts, rolling mills.
Markings and features of needle angular contact bearings
Needles are the same rollers, but with a smaller cross-section and a higher frequency of installation. Miniature width dimensions allow you to make small assemblies with high load capacity and the perception of high loads.
Differences and technical characteristics:
- Compared to ball bearings, they absorb more radial stress, although they may be the same size. This is explained by the contact of the elements, which exceeds the ball contact.
- Lack of sensitivity to mechanical shocks and vibrations.
- Possibility of manufacturing without separators - then the load can be increased, but the rotation speed will be reduced. Dividers are typically stamped or made from brass.
- There are options even without both rings - external and internal.
- Small dimensions.
- Low top speed.
They are usually marked with RN at the beginning, followed by numbers.
How to properly install and under what conditions to use angular contact bearings with twisted rollers
The coiling of bodies of rotation is carried out using a metal tape. If the product is two-row, then the direction of this process in different directions is important. This allows not only movement in two directions, but also promotes better distribution of lubricant. One of the advantages is that they are not sensitive to dirt and do not break from mechanical stress or shock.
But there are disadvantages regarding cylindrical rollers or ball bearings:
- axial load is not perceived at all;
- low load capacity;
- low rotation speed.
Installation of such units occurs in low-speed machines without the need for high speed, but with operation in conditions of possible contamination. For example, in agricultural machines.
GOST for angular contact ball bearings
Here we will no longer divide them into single-row and double-row, but we will present the general features of the design. The regulatory document that governs their production and use is GOST 831-75. But the standards are so international that there are foreign repetitions of Russian products of any standard size. The documentation provided contains a detailed nomenclature of all sizes, as well as several drawings. Let's list them here:
It is virtually impossible to fully implement the size range within one article, but we will give an example of a table below to make it clear how to handle it.
Tapered angular contact roller bearing
Cone-shaped rollers provide an advantage in terms of absorbing both axial and radial loads. The first ones depend on the area of contact of bodies of rotation with raceways. The higher it is, the greater the load capacity.
Their permissible speed and rotation frequency are small even compared to cylindrical roller bearings; it is more comparable to spherical ones.
They can be single-row, double-row, four-row, as well as with a removable design and one-piece, without an outer or inner ring.
What does a thrust ball bearing consist of?
The radial load is small, as is the contact area of the balls with the track. But there is good axial load capacity and increased rotation speed. To avoid high friction forces, separators are often made not by metal stamping, but from glass-filled polyamide.
Thrust roller
Similar to the previous one, but in a roller bearing there is a higher permissible stress perpendicular to the shaft. Therefore, they are used on larger products. In this case, the rotation speed decreases proportionally. The peculiarity of how to install angular contact roller bearings is that they do not require high accuracy and alignment. They will work with deviations of up to 2.5 degrees.
Articulated
This is a unit that does not operate on the rolling principle, but on sliding technology. These are two rings - the outer and the inner, which have spherical surfaces. Thanks to them, the products are self-centering. The load is distributed very evenly, because If there are no bodies of rotation, then there is virtually no edge load either, so we can talk about very high axial and radial stresses.
Depending on the manufacturing materials and coatings, they can change their characteristics - be more or less durable, require additional maintenance (lubrication) or not.
Thrust ball bearings - description and dimensions
Single-row thrust ball bearings are suitable for supporting unilateral axial loads, and, accordingly, can unilaterally fix the position of the shaft; They do not take radial load.
Single row:
- 8000 - the main design. The most common products. For example, thrust bearing 8206. According to the international numbering, which is used when marking imported bearings, it is designated as 51000 (bearing 51205 is an analogue of our 8205).
- 18000 - with free self-aligning and backing rings. The presence of the latter makes it possible to compensate for technological errors in processing the supporting surface of the housing. For example, bearing 18210 (or 53204U according to the international nomenclature).
- 28000, 188000, 958000 - special design (very rare).
- 88000, 868000 - cageless (also practically not used).
- 688000 - with casing (closed), for example, release bearings 688811 and 688911.
- 876000, 948000 - without rings.
- 218000 - with a conical mounting hole.
- 308000 - without one ring.
- 98000, 9588000 - closed type, for example, thrust bearing 9588214.
Double:
- 38000 - with three rings.
- 48000 - with backing rings.
- 58000, 908000 - with three rings.
- 538000 - cageless.
Single-way thrust ball bearings contain a tight ring with a raceway installed on the shaft, a set of balls with a cage, and a loose ring with a raceway installed in the housing. The free ring may have a flat or spherical bearing surface. Bearings with a spherical washer can compensate for initial misalignment if used in conjunction with a washer ring that has a corresponding spherical surface. The spherical backing ring must be installed separately. Bearings of this type are detachable, their installation is simple, since the elements can be mounted individually.
Double thrust ball bearings can support axial loads on both sides and can therefore be used to secure the shaft on both sides. They must not be subject to radial load. Double-way thrust ball bearings contain one taut ring with a raceway on each ring surface, two sets of balls with cages, and two loose rings with a raceway. Bearings of this type are detachable. The loose rings and ball and cage sets are the same as those of the corresponding single bearings. Thrust ball bearings allow significantly lower rotation speeds than other types of ball bearings because the raceways can only support limited centrifugal loads that occur when the balls move.
The cage of a thrust bearing can be of two designs - completely closed, solid, with a separate ball in each hole, and stamped from tin, the so-called “open” one, in which there are no separate seats for balls. The first option costs manufacturers much more, so thrust bearings with such a cage are rare. At the same time, the use of a product with an “open” cage at high rotation speeds is highly not recommended, since the jumpers may simply not withstand the load and all the balls will gather in one “pile”, which, in addition to the failure of the bearing itself, can lead to the breakdown of an expensive equipment. In such cases, it is recommended to buy high-quality, expensive imported bearings - with a cast cage (each ball in a separate “socket”), possibly with an increased degree of accuracy (/P4 to the right of the number).
They are used in low-speed gearboxes, in spindles and rotating centers of metal-cutting machines, in jacks, valves, rotating devices, etc. Thrust-radial ball bearings are installed as rotary supports.
| Name | d, mm | D, mm | h, mm | Weight, kg |
| BALL THRUST BEARINGS 1681XX SERIES | ||||
| 168160 [——] | 300 | 380 | 62 | 15.5 |
| 1687/XXX SERIES BALL THRUST BEARINGS | ||||
| 1687/770 X [——] | 770 | 1000 | 150 | 292 |
| 183XX SERIES BALL THRUST BEARINGS | ||||
| 18324 (53324 + U324) | 120 | 210 | 80 | 11.9 |
| BALL THRUST BEARINGS SERIES 31688/XXX | ||||
| 31688/630L[——] | 630 | 780 | 112 | 112 |
| 81XX SERIES BALL THRUST BEARINGS | ||||
| 8100 [51100] | 10 | 24 | 9 | 0.02 |
| 8101 [51101] | 12 | 26 | 9 | 0.023 |
| 8102 [51102] | 15 | 28 | 9 | 0.024 |
| 8103 [51103] | 17 | 30 | 9 | 0.026 |
| 8104 [51104] | 20 | 35 | 10 | 0.039 |
| 8105 [51105] | 25 | 42 | 11 | 0.059 |
| 8106 [51106] | 30 | 47 | 11 | 0.068 |
| 8107 [51107] | 35 | 52 | 12 | 0.084 |
| 8108 [51108] | 40 | 60 | 13 | 0.124 |
| 8109 [51109] | 45 | 65 | 14 | 0.148 |
| 8110 [51110] | 50 | 70 | 14 | 0.162 |
| 8111 [51111] | 55 | 78 | 16 | 0.234 |
| 8112 [51112] | 60 | 85 | 17 | 0.291 |
| 8113 [51113] | 65 | 90 | 18 | 0.331 |
| 8114 [51114] | 70 | 95 | 18 | 0.361 |
| 8115 [51115] | 75 | 100 | 19 | 0.402 |
| 8116 [51116] | 80 | 105 | 19 | 0.425 |
| 8117 [51117] | 85 | 110 | 19 | 0.475 |
| 8118 [51118] | 90 | 120 | 22 | 0.661 |
| 8120 [51120] | 100 | 135 | 25 | 0.993 |
| 8122 [51122] | 110 | 145 | 25 | 1.06 |
| 8124 [51124] | 120 | 155 | 25 | 1.124 |
| 8126 [51126] | 130 | 170 | 30 | 1.73 |
| 8128 [51128] | 140 | 180 | 31 | 2.14 |
| 8148L [51148] | 240 | 300 | 45 | 7.61 |
| 8152 [51152] | 260 | 320 | 45 | 8.24 |
| 8156 [51156] | 280 | 350 | 53 | 12.3 |
| 8172L [51172] | 360 | 440 | 65 | 21.5 |
| 82XX SERIES BALL THRUST BEARINGS | ||||
| 8201 [51201] | 12 | 28 | 11 | 0.034 |
| 8202 [51202] | 15 | 32 | 12 | 0.046 |
| 8203 [51203] | 17 | 35 | 12 | 0.05 |
| 8204 [51204] | 20 | 40 | 14 | 0.079 |
| 8205 [51205] | 25 | 47 | 15 | 0.111 |
| 8206 [51206] | 30 | 52 | 16 | 0.14 |
| 8207 [51207] | 35 | 62 | 18 | 0.223 |
| 8208 [51208] | 40 | 68 | 19 | 0.271 |
| 8209 [51209] | 45 | 73 | 20 | 0.32 |
| 8210 [51210] | 50 | 78 | 22 | 0.385 |
| 8211 [51211] | 55 | 90 | 25 | 0.591 |
| 8212 [51212] | 60 | 95 | 26 | 0.675 |
| 8213 [51213] | 65 | 100 | 27 | 0.747 |
| 8214 [51214] | 70 | 105 | 27 | 0.788 |
| 8215 [51215] | 75 | 110 | 27 | 0.843 |
| 8216 [51216] | 80 | 115 | 28 | 0.936 |
| 8217 [51217] | 85 | 125 | 31 | 1.24 |
| 8218 [51218] | 90 | 135 | 35 | 1.7 |
| 8220 [51220] | 100 | 150 | 38 | 2.23 |
| 8222 [51222] | 110 | 160 | 38 | 2.52 |
| 8224 [51224] | 120 | 170 | 39 | 2.77 |
| 8226 [51226] | 130 | 190 | 45 | 4.22 |
| 8230L [51230] | 150 | 215 | 50 | 6.54 |
| 8236 [51236] | 180 | 250 | 56 | 8.37 |
| 8240 [51240] | 200 | 280 | 63 | 12.7 |
| 8240L [51240] | 200 | 280 | 63 | 12.7 |
| 8244 [51244] | 220 | 300 | 63 | 13.9 |
| 8256L [51256] | 280 | 380 | 80 | 28.2 |
| 8260G [51260] | 300 | 420 | 95 | 43.3 |
| 8268L [51268] | 340 | 460 | 96 | 49 |
| 8272G [51272] | 360 | 500 | 110 | 70.2 |
| 8272L [51272] | 360 | 500 | 110 | 70.2 |
| 8292G [51292] | 460 | 620 | 130 | 118 |
| 83XX SERIES THRUST BALL BEARINGS | ||||
| 8305 [51305] | 25 | 52 | 18 | 0.173 |
| 8306 [51306] | 30 | 60 | 21 | 0.268 |
| 8307 [51307] | 35 | 68 | 24 | 0.386 |
| 8309 [51309] | 45 | 85 | 28 | 0.682 |
| 8310 [51310] | 50 | 95 | 31 | 0.952 |
| 8311 [51311] | 55 | 105 | 35 | 1.34 |
| 8312 [51312] | 60 | 110 | 35 | 1.4 |
| 8313 [51313] | 65 | 115 | 36 | 1.57 |
| 8314 [51314] | 70 | 125 | 40 | 2.09 |
| 8315 [51315] | 75 | 135 | 44 | 2.66 |
| 8316 [51316] | 80 | 140 | 44 | 2.75 |
| 8318 [51318] | 90 | 155 | 50 | 3.79 |
| 8320 [51320] | 100 | 170 | 55 | 5.63 |
| 8320L [51320] | 100 | 170 | 55 | 5.63 |
| 8326L [51326] | 130 | 225 | 75 | 13.9 |
| 8330L [51330] | 150 | 250 | 80 | 17.1 |
| 8336NL [51336] | 180 | 300 | 95 | 28.5 |
| 8368NL [51368] | 340 | 540 | 160 | 147.8 |
| BALL THRUST BEARINGS SERIES 91681/5XX | ||||
| 91681/500G [——] | 500 | 600 | 60 | 30 |
| BALL THRUST BEARINGS SERIES 91682/XXX | ||||
| 91682/670 [——] | 670 | 900 | 140 | 220 |
| 983XX SERIES BALL THRUST BEARINGS | ||||
| 98316 [51316] | 80 | 145 | 45 | 2.9 |
| THRUST BALL BEARINGS SERIES 78682/XXX | ||||
| 78682/710 [—-] | 710 | 950 | 109 | 184 |
Purpose and installation diagram of angular contact bearings
They find their application in products for which both types of loads are important. At the same time, they further look at the required speed, load capacity, operating conditions, the presence of vibrations and shocks, the need for self-installation, directionality in one or two directions and other characteristics in order to select a model from the classification list that we have given today.
Use - in general technical industries everywhere, in mechanical engineering, tank building, aircraft manufacturing, the chemical industry and numerous other areas.
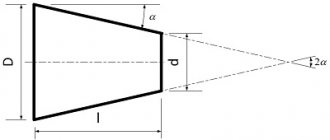
Let's show the distribution diagram of radial and axial load:
Size tables
All standard sizes can be found in numerous GOSTs. The documents provide an extensive list, but we will show what it looks like and how to use it, using the example of single-row angular contact ball bearings - their difference from radial bearings is that they can simultaneously perceive axial stress.
| Marking | Inner diameter | External diameter |
| 7200V | 10 mm | 30 mm |
| 7201B | 12 mm | 32 mm |
| 7301B | 12 mm | 37 mm |
| 7202V | 15 mm | 35 mm |
| 7302B | 15 mm | 42 mm |
| 7203B | 17 mm | 40 mm |
| 7303B | 17 mm | 47 mm |
| 7204B | 20 mm | 47 mm |
| 7205V | 25 mm | 52 mm |
| 7206B | 30 mm | 62 mm |
| 7207B | 35 mm | 72 mm |
| 7208V | 40 mm | 80 mm |
| 7209B | 45 mm | 85 mm |
| 7210V | 50 mm | 90 mm |
| 7211B | 55 mm | 100 mm |
| 7212B | 60 mm | 110 mm |
| 7213B | 65 mm | 120 mm |
| 7214B | 70 mm | 125 mm |
| 7215V | 75 mm | 130 mm |
| 7216B | 80 mm | 170 mm |
In the same way, you can look at other tables; we will present several markings to understand how to distinguish one product from another by letters or numbers. In the table we have given only the list with “B” at the end, but there are also “A” and “C” of the same sizes. The difference lies in the load capacity and the materials used. You can also find the following designation - 72 BE or 72 B - this is the same, but in a foreign style, however, all standard sizes comply with GOST. Plus, suffixes - “A”, “AC”, “B”, “CA” and others can be added to the marking; they indicate the contact angle and other design features. You can find out more about each model by calling a consultant at the Mobi Bearing online store. There are good prices and quality service here.
Bearing: general concept
In a broad sense, a bearing is a support for a rotating axle/rotating shaft. This support takes on the radial/axial load intended for the axle or shaft and then transfers it to the area of the frame, housing or some other part of the mechanism.
At the same time, the bearing performs an important function - it reliably holds the shaft in the given space, while allowing it to freely, depending on the design, swing/rotate/move linearly.
All these shaft movements occur, thanks to bearings, with minimal energy consumption. The quality of work and productivity of a particular mechanism, device, machine, and so on depend on the correctly constructed order of this chain.
Today there are the following types of bearings:
- Ball radial-single row;
- Ball radial-double-row;
- Radial roller, equipped with short cylindrical rollers;
- Roller double-row spherical;
- Needle-shaped;
- Radial roller (rollers are twisted);
- Angular contact balls;
- Roller-conical;
- Thrust ball;
- Thrust roller;
- Articulated.
All of them are presented in our bearing catalog in the section “angular contact bearings”
Next, we will look at the angular contact ball bearing in detail.
Installation
Recommendations for installation:
- check the assembly for visual defects, rotate it;
- measure the radial clearance;
- the shaft needs to be looked at for the straightness of its axes;
- the alignment should not exceed that allowed in the technical accompanying documentation;
- The mating surfaces must be clean, dry, and, if necessary, treated with lubricant.