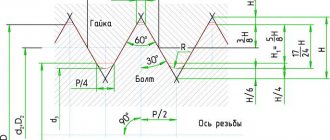
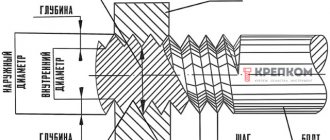
Trapezoidal threads are widely used to make various screws that are used for various production equipment. For example, for machines, lifting devices, presses. This thread has the form of an isosceles trapezoid, and the profile angle can have different values: 15, 24, 30, 40°. During the operation of a screw on which a trapezoidal thread is cut, frictional forces appear naturally caused. That is, due to the presence of lubricant, surface roughness, and profile angle.
Types of thread
Today there are the following types:
- Metric. It serves to secure several elements. The cutting conditions are established in the regulatory documentation. The profile is a triangle with equilateral angles. This indicator is 60°. Screws with metric threads are made in small and large pitches. The first type is used to secure thin-sheet elements to create increased tightness. This type of connection can be found in precision optical instruments.
- Conical. It is manufactured in the same way as the previous type, but twisting is done to a depth of 0.8 mm.
- Inch. To date, there is no regulatory document that would indicate thread sizes. Inch threads are used in the repair of various equipment. As a rule, these are old instruments and devices. Its main indicators are the outer diameter and pitch.
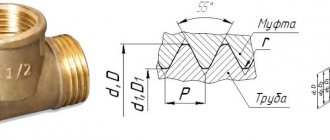
- Pipe cylindrical. This type is an isosceles triangle, the upper angle of which is 55°. This internal thread is used to connect pipelines, as well as parts made of thin sheet material. It is recommended when there are special requirements for the tightness of the connection.
- Pipe conical. The internal thread must comply with all regulatory requirements. The sizes are completely standardized. It is used to connect various types of pipelines.
- Persistent. This type is an unequal trapezoid, where one side is inclined by 3° and the other by 30°. The first side is the working side. The shape of the profile, as well as the diameter of the steps, are determined by regulatory documents. In accordance with them, threads are made with a diameter from 10 to 600 mm, with a maximum pitch value of 24 mm. They are used where increased holding forces are required.
- Round. The thread profile consists of various arcs connected by straight lines. The profile angle is 30°. This type of thread is used for those connections that are exposed to aggressive environments.
- Rectangular. It is not supported by any regulatory documents. Its main advantage is high efficiency. Compared to the trapezoidal type, it is less durable, and also causes many incomprehensible moments during its production. The main place of application is jacks and various types of screws.
- Trapezoidal. It has the shape of an isosceles trapezoid with a profile angle of 30°. Trapezoidal threads, the dimensions of which are fixed in the documentation, are used to connect various elements of production equipment.
Kinds
There are the following types of trapezoidal threads:
- Left: Created by a contour with a flat surface that rotates counterclockwise, away from the observer. It is one of the oldest methods of connecting components in mechanisms and is used in the mechanical engineering sector to secure workpieces to the shaft of a lathe. This design prevents the possibility of the part unscrewing during the processing procedure. Left-hand threads are used to secure nipples for radiators of heating systems, wheels of trucks or SUVs, chucks with drills, blades from room fans, a gearbox for stopping the torque of a car engine, bicycle parts and components of circular saws. It has also found use as a protection mechanism against dangerous activities. With its help, the working tools processing the workpiece are monitored. The propane cylinder reducer is equipped with a left-hand thread. This type of cutting is actively used by machine manufacturers to prevent counterfeiting of its main components. It is marked with the Latin symbol “L”.
- Right: formed by a flat contour that performs a clockwise rotational movement. It moves along an axis relative to the observer. This type of cutting is most often used to secure workpieces using screws, nuts, studs and bolts. On an industrial scale it is used for screwing in screws and self-tapping screws. To determine the right-hand thread, a method is used to position the fastening tools with the chamfer facing up on the palm. It is important to consider that the turns of the spiral are directed towards the observer. Reducers of cylinders filled with oxygen are equipped with right-hand threads, designed to reduce the risk of emergency situations during processing. This type of cutting can be easily counterfeited, so it has not found application in the branding of automotive parts. This type of cutting is designated using the Latin letter “R”.
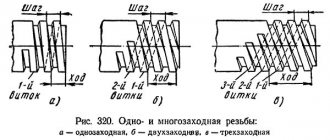
- Single-pass: formed by the movement of 1 profile. To determine it, you need to look at the end of the screw or nut. If only 1 end of the turn is visible, then the thread is single-start. For this type of cutting, the step is equal to the stroke - the distance between adjacent threads. The machine is configured for single-start threads depending on the pitch values. The disadvantage of this type of cutting is the low strength of the processed parts, due to the small length of the internal diameter. This factor does not allow her to transmit great forces. Single-start threads are marked with the Latin symbol “H”.
- Multi-thread: formed by many screw-threaded projections. The most common representative of this subgroup is a double-start thread, which has 2 turns and symmetrical starts. In this case, the magnitude of the move is equal to the product of the number of entries per step. Multi-start threads are used in tension structures. It performs operations to increase the strength of the connection, change the gear ratio (when processing motor gearboxes) and create a significant displacement of the fastening mechanisms in the screw rods, provided that the number of revolutions produced is low. In the international system, this species is designated by the Latin letter “S'.
The dimensions and technical characteristics of all types of trapezoidal threads are indicated in the form of standards in GOST 24739-81 and GOST 25347-82. These documents provide profile standards and maximum tolerances required for processing finished workpieces.
Download GOST 24739-81
Download GOST 25347-82
Manufacturing conditions
Compared to other types, trapezoidal threads are much easier to manufacture.
That is why it is more often used in various fields. The most popular is the trapezoidal thread screw, which has a profile angle of 30°. The production technology is very similar to that used for cutting rectangular threads. But there are still significant differences regarding the accuracy and cleanliness of manufacturing. Cutting a trapezoidal thread is no different from the same procedure with a rectangular thread. At the moment, there are several such methods.
Isosceles and rectangular trapezoids
The version of the trapezoid that we examined is the most common types of geometric figure. But there are also special cases:
An isosceles trapezoid is one whose lateral (non-parallel) sides are equal. It is also called isosceles or equilateral.
She looks like this:
This example graphically shows that sides AD and BC are equal to each other. Small dashes indicate this.
A rectangular trapezoid is one in which one of the sides and the base form a right angle.
She looks like this:
In this example, angles DAB and ADC are right angles, that is, equal to 90 degrees. And accordingly, the trapezoid is called rectangular.
It is important to note here that only one side should go at a right angle to the base. If there are both, then the trapezoid will automatically turn into a square .
Making a screw with one cutter
Single-start trapezoidal threads are manufactured as follows:
- the workpiece is prepared and channels for sharpening are created;
- The cutter is sharpened according to a special prepared template;
- The sharpened element is installed and secured. It should be positioned so that the centers coincide and are parallel to the cutting axis;
- the equipment is turned on and the workpiece is fed for thread cutting;
- the finished part is checked in accordance with the finished template.
Manufacturing methods
It is important to know how to cut a trapezoidal thread in order to avoid malfunctions during its operation. Trapezoidal threads are easily produced on an industrial scale. Its manufacturing technique is similar to the production of rectangular carvings. The following cutting methods exist:
- From the use of 1 cutter. Before carrying out this procedure, it is important to prepare the workpiece for cutting: measure its length and width using a ruler or caliper. The product is placed on the lathe table. You need to make a groove in the workpiece into which the cutting tool will fit. When applying the cutter, it is worth checking the correctness of its location, placing it parallel to the thread axis. After completing the preparatory work, you can turn on the machine. During processing, the cutting edge of the tool makes a translational movement, forming a thread on the profile of the part. It is important to compare the processed part with the template after completing the work process. Their profiles must match. Due to the inaccuracy of the cutting tool, minor errors may occur.
- Use of 3 incisors. Before carrying out the procedure, preparatory work is also carried out: setting up a lathe, calculating the dimensional parameters of the product and setting up 3 cutters. Cutting tools are applied to the grooves of the workpiece and checked for secure fastening. According to the diameter and helix angle of the product, the tapping cutters can be installed parallel to the sides of the helical groove and opposite to the thread axis. 3 cutters perform translational movements, forming the final profile. Verification of processing accuracy is carried out by comparing the resulting part with a template.
When creating screw structures, a different cutting method is used. An incomplete groove is made using a cutter. After this, you need to select a smaller cutting tool and increase the length of the groove to the internal diameter. The procedure is completed with a profile cutter. The processing result is checked using nominal and limit calibers.
During cutting, it is important to follow basic safety rules when working with cutting devices and lathes:
- Work with tools must be carried out by a specialist with appropriate instructions.
- Person The worker is required to have a special uniform, consisting of a work coat, safety glasses with clear lenses, a hat, boots and gloves. Overalls must be repaired and clean. Before working with tools, it is important to ensure that the suit is fully buttoned and fits snugly to the body.
- No foreign objects should be placed in the workplace.
- Before sharpening, it is important to check the condition of the lathe. It must contain mechanisms for removing production waste, tubes and hoses for cooling, and shields for reflecting the emulsion. The lathe should be checked at idle speed, assessing the performance of its main components.
- There should be no chips or foreign objects on the lathe chuck.
- During processing, it is important to check the strength of the cutting tools and the location of the workpiece.
- You cannot secure a workpiece weighing more than 16 kg and take measurements while it is rotating.
- It is necessary to promptly remove industrial waste using special chip removal devices.
- To cut parts made of ductile metals, special cutting tools with sharpening are used.
- While processing workpieces, it is forbidden to lean on the machine, lubricate parts, support the product with your hands, or get rid of chips using a stream of air.
- When turning, it is necessary to use steady rests if processing is carried out at high speed.
- It is important to monitor the drainage of coolant from the lathe.
- Do not leave the machine while it is in use.
In the event of fires at work, it is necessary to turn off the machine equipment, move to a safe distance and notify the competent authorities. Compliance with safety precautions will reduce the risk of emergency situations.
Common production method
It is in production that cutting trapezoidal threads takes place in this way:
- working equipment is checked and adjusted;
- thanks to the slotted cutter, small indentations are made on the screw;
- using a narrow slotted element, the screw is cut to a certain diameter;
- with the help of a profile slotted element, the final production of trapezoidal threads is carried out;
- the finished part is checked in accordance with ready-made templates.
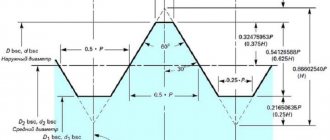
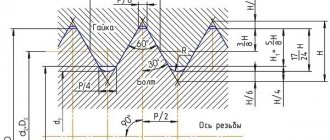
Trapezoidal thread: dimensions
As mentioned earlier, this type of thread has the shape of a trapezoid, in which the angle between the sides can have different values. All main dimensions are set in accordance with GOST.
For a single-start type, trapezoidal threads (dimensions - GOST 9481-81) have dimensions and pitches of various diameters - from 10 to 640 mm. In addition, it can be multi-pass, as well as twisted to the left or right side. These indicators are standardized by GOST 24738-81.
Main profile of external and internal trapezoidal threads
The following table shows the characteristics of the main profile of external and internal trapezoidal threads:
| Distance between adjacent profile points (step) | Distance between top and bottom |
| 1.05 – 1.07 | 2.08 – 3.01 |
| 2.03 – 2.05 | 3.07 – 5.05 |
| 3.03– 3.05 | 5.06 – 7.02 |
| 4.03– 4.05 | 7.05 – 8.08 |
| 5.03– 5.05 | 9.03 – 10.04 |
| 6.03– 6.05 | 11.02 – 12.09 |
| 7.03– 7.05 | 13.06 – 14.05 |
| 8.03 – 8.05 | 14.09 – 15.02 |
| 9.03– 9.05 | 16.07 – 18.03 |
| 10.03– 10.05 | 18.06 – 21.08 |
| 12.03– 12.05 | 22.03 – 26.01 |
| 14.03– 14.05 | 26.02 – 28.04 |
| 16.03 – 16.05 | 29.09 – 31.05 |
| 18.03– 18.05 | 33.06 – 35.09 |
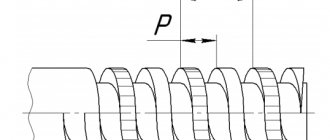
Features of multi-start thread
To provide the screw with strength characteristics and increase its stroke, multi-start trapezoidal threads are used. In this case, all parameters, such as the height of the thread, its diameter, are absolutely the same, with a single-start appearance. The only difference is the number of moves per step. For example, three-start threads have a stroke three times their pitch. All this can be seen in the pictures.
Let us give an example so that this type becomes clear to every person. Everyone uses regular lids for canning vegetables and fruits. To open them you need to make a minimum of effort. When using large diameter cylinders, it is much more difficult to get into the grooves of a single-thread thread. That is why multi-pass ones are used.
This type of carving can be determined visually, just look at the drawing.
You can see exactly how many turns go from the beginning of the screw. Multi-pass threads are manufactured using complex technologies and, accordingly, are more expensive.
DESIGNATIONS OF THREAD PARAMETERS
1. DESIGNATIONS OF THREAD PARAMETERS
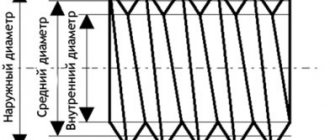
1.1. The designations adopted in this standard are given below: - outer diameter of the external thread (screw); - average diameter of external thread; — internal diameter of the external thread; — internal diameter of the internal thread (nut); — average diameter of the internal thread; — outer diameter of the internal thread; — thread progress; — thread pitch; — number of visits; — make-up lengths of the “normal” group; — make-up lengths of the “long” group; , , , , — tolerances of diameters , , , , ; — upper deviation of external thread diameters; — upper deviation of internal thread diameters; — lower deviation of external thread diameters; — lower deviation of internal thread diameters.
Other advantages
Trapezoidal joints have many positive qualities. That is why they are used in various manufacturing industries. The most common field is mechanical engineering. So, their advantages include the following:
- the ability to assemble and disassemble various devices an unlimited number of times;
- convenient disassembly and assembly process;
- reliability of the threaded connection;
- easy manufacturing process;
- independent regulation of compression force;
- production of parts in various designs.
Disadvantages of connections
There are not many negative aspects to this type of connection. One of them is the occurrence of high stress in the depressions. In addition, they cannot be used in devices and mechanisms that have high vibration, since the screws can unscrew on their own, which is not a good sign.
Therefore, it is necessary to monitor this, and if such a situation arises, correct the position of the screws.
Quality such as cost can be attributed to both positive and negative aspects.
Single-stroke threads cost significantly less than multi-stroke threads. Here everyone chooses according to personal preferences. Many design organizations use multi-pass threads, as they are reliable and durable.
So, we found out what this type of connection is, such as a trapezoidal thread, its dimensions, advantages and disadvantages.