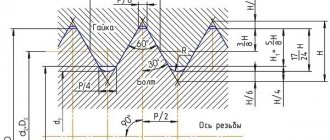
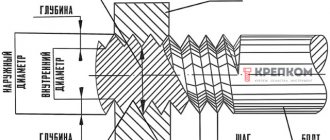
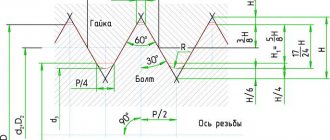
The term “thread” is used to define helical grooves having a constant cross-section and pitch, applied to the side surfaces of a cylindrical or conical shape. It is used for organizing threaded connections and screw (gear-screw) gears. Used in machines, engineering structures, etc.
It is characterized by such indicators as the unit of measurement of diameter, location, profile of the generatrix of the surface on which it is applied, purpose, direction, number of passes. It is these parameters that are decisive when choosing one type of thread or another.
Pipe thread
Pipe threads are a group of standards intended for connecting and sealing various types of structural elements using pipe threads. The quality of work when cutting grooves has a great influence on the reliability of the connection and the structure obtained in this way. Particular attention should be paid to the correlation of the thread with the axis of the pipe to which it is applied.
When cutting threads manually using a die, the alignment is far from ideal, which can affect the reliability and quality of the connection. As for the use of tools such as a lathe or electric threading machine, the use of threading heads with an accurate threading knife , here the indicators of the applied thread are comparable to theoretical values.
Our catalog contains thread-cutting machines, thread-cutting dies, heads, knives that ensure the performance of work with high precision. All equipment fully complies with international standards in this area.
Tapered pipe thread, R (BSPT)
Used for organizing pipe conical connections, as well as for connecting internal cylindrical and external conical threads (GOST 6357-81). Based on BSW, it is compatible with BSP.
The sealing function in connections using BSPT is performed by the thread itself (due to its compression at the connection point when the fitting is screwed in). Therefore, the use of BSPT must always be accompanied by the use of a sealant.
This type of thread is characterized by the following parameters:
- GOST 6211-81
—Basic standards of interchangeability. Conical pipe thread. - ISO R7
- DIN 2999
- BS 21
- JIS B 0203
designation based on the profile shape – inch thread with a taper (profile in the form of an isosceles triangle with an apex angle of 55 degrees, cone angle φ=3°34′48″).
When designating, a letter index of the thread type is used (R for external and Rc for internal) and a digital indicator of the nominal diameter (for example, R11/4 - conical pipe thread with a nominal diameter of 11/4). The index LH is used to designate left-hand threads.
Thread parameters
Inch thread with taper 1:16 (cone angle φ=3°34′48″). The profile angle at the apex is 55°.
Symbol: letter R for external threads and Rc for internal threads (GOST 6211-81 - Basic norms of interchangeability. Conical pipe threads), numerical value of the nominal thread diameter in inches (inch), letters LH for left-hand threads. For example, a thread with a nominal diameter of 1.1/4 is designated as R 1.1/4.
Table 3
Designation of thread size, steps and nominal values of the outer, middle and inner diameters of conical pipe threads (R), mm
| Thread size designation | Step P | Thread length | Thread diameter in the main plane | |||
| Working | From the end of the pipe to the main plane | Outer d=D | Average d2=D2 | Internal d1=D1 | ||
| 1/16″ | 0,907 | 6,5 | 4,0 | 7,723 | 7,142 | 6,561 |
| 1/8″ | 6,5 | 4,0 | 9,728 | 9,147 | 8,566 | |
| 1/4″ | 1,337 | 9,7 | 6,0 | 13,157 | 12,301 | 11,445 |
| 3/8″ | 10,1 | 6,4 | 16,662 | 15,806 | 14,950 | |
| 1/2″ | 1,814 | 13,2 | 8,2 | 20,955 | 19,793 | 18,631 |
| 3/4″ | 14,5 | 19,5 | 26,441 | 25,279 | 24,117 | |
| 1″ | 2,309 | 16,8 | 10,4 | 33,249 | 31,770 | 30,291 |
| 1.1/4″ | 19,1 | 12,7 | 41,910 | 40,431 | 38,952 | |
| 1.1/2″ | 19,1 | 12,7 | 47,803 | 46,324 | 44,845 | |
| 2″ | 23,4 | 15,9 | 59,614 | 58,135 | 56,565 | |
| 2.1/2″ | 26,7 | 17,5 | 75,184 | 73,705 | 72,226 | |
| 3″ | 29,8 | 20,6 | 87,884 | 86,405 | 84,926 | |
| 3.1/2″ | 31,4 | 22,2 | 100,330 | 98,851 | 97,372 | |
| 4″ | 35,8 | 25,4 | 113,030 | 111,551 | 110,072 | |
| 5″ | 40,1 | 28,6 | 138,430 | 136,951 | 135,472 | |
| 6″ | 40,1 | 28,6 | 163,830 | 162,351 | 160,872 | |
Pipe cylindrical thread. GOST 6357 - 81
Parameter Unit: Inch
Direction: Left
Accuracy class: Class A (increased), Class B (normal)
Why in inches?
The inch size came to us from our Western colleagues, since the requirements of the GOST are formulated on the basis of BSW (British Standard Whitworth or Whitworth thread). Joseph Whitworth (1803 - 1887), a design engineer and inventor, demonstrated the screw profile of the same name for detachable connections back in 1841 and positioned it as a universal, reliable and convenient standard.
This type of thread is used both in the pipes themselves and in the elements of pipe connections: locknuts, couplings, elbows, tees ( see picture above
). In the profile section we see an isosceles triangle with an angle of 55 degrees and roundings at the tops and bottoms of the contour, which are made for high tightness of the connection.
Threading of threaded connections is carried out on sizes up to 6”. All larger pipes are fixed by welding to ensure a reliable connection and prevent rupture.
Symbol in the international standard
International: G
Japan: PF
UK: BSPP
The letter G and the bore diameter (internal Ø) of the pipe are indicated in inches. The outer diameter of the thread itself is not included in the designation.
Example:
G 1/2 - external cylindrical pipe thread, internal pipe Ø 1/2". The outer diameter of the pipe will be 20.995 mm, the number of steps over a length of 25.4 mm will be 14.
The accuracy class (A, B) and the direction of turns (LH) can also be indicated.
For example:
G 1 ½ - B - cylindrical pipe thread, internal Ø 1 ½ inches, accuracy class B.
G1 ½ LH- B - cylindrical pipe thread, internal Ø 1 ½ inches, accuracy class B, left.
The make-up length is indicated by the latter in mm: G 1 ½ -B-40 .
For internal pipe cylindrical threads, only the Ø of the pipe for which the hole is intended will be indicated.
Parallel Pipe Thread Size Chart
| Thread size | Thread pitch, mm | Threads per inch | Thread diameters | |||
| Row 1 | Row 2 | d=D | d2=D2 | d1=D1 | ||
| 1/16″ | 0,907 | 28 | 7,723 | 7,142 | 6,561 | |
| 1/8″ | 9,728 | 9,147 | 8,566 | |||
| 1/4″ | 1,337 | 19 | 13,157 | 12,301 | 11,445 | |
| 3/8″ | 16,662 | 15,806 | 14,950 | |||
| 1/2″ | 1,814 | 14 | 20,955 | 19,793 | 18,631 | |
| 5/8″ | 22,911 | 20,749 | 20,587 | |||
| 3/4″ | 26,441 | 25,279 | 24,117 | |||
| 7/8″ | 30,201 | 29.0З9 | 27,877 | |||
| 1″ | 2,309 | 11 | 33,249 | 31,770 | 30,291 | |
| 1⅛» | 37,891 | 36,418 | 34,939 | |||
| 1¼» | 41,910 | 40,431 | 38,952 | |||
| 1⅜» | 44,323 | 42,844 | 41,365 | |||
| 1½» | 47,803 | 46,324 | 44,845 | |||
| 1¾» | 53,746 | 52,267 | 50,788 | |||
| 2″ | 59,614 | 58,135 | 56,656 | |||
| 2¼» | 65,710 | 64,231 | 62,762 | |||
| 2½» | 75,184 | 73,705 | 72,226 | |||
| 2¾» | 81,534 | 80,055 | 78,576 | |||
| 3″ | 87,884 | 86,405 | 84,926 | |||
| 3¼» | 93,980 | 92,501 | 91,022 | |||
| 3½» | 100,330 | 98,851 | 97,372 | |||
| 3¾» | 106,680 | 105,201 | 103,722 | |||
| 4″ | 113,030 | 111,551 | 110,072 | |||
| 4½» | 125,730 | 124,251 | 122,772 | |||
| 5″ | 138,430 | 136,951 | 135,472 | |||
| 5½» | 151,130 | 148,651 | 148,172 | |||
| 6″ | 163,830 | 162,351 | 160,872 | |||
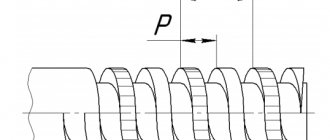
How to determine the pitch of an inch thread
I’ll give you a picture from the English-language Internet that clearly demonstrates the technique. Pipe threads are characterized not by the size between the tops of the profile, but by the number of turns per 1 inch along the thread axis. A regular tape measure or ruler can help. Apply it, measure one inch (25.4 mm) and visually count the number of steps.
In the picture with an example ( see above
) threads - from English these are literally “threads of thread”. In this case there are 18 of them. by one inch.
It’s even easier if you have a thread gauge for inch threads lying around in your tool box. It is very convenient to take measurements, but it must be remembered that inch threads may differ in the apex angle of 55° and 60°.
| Thread pitch P, mm | Threads per inch |
| 0.907 | 28 |
| 1,337 | 19 |
| 1,814 | 14 |
| 2,309 | 11 |
NPSM (National pipe thread) thread
Complies with American standard NSI/ASME B1.20.1.
This type of thread is characterized by the following parameters:
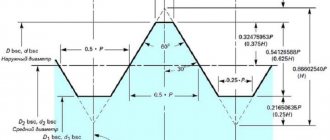
- designation according to the profile shape - inch cylindrical pipe thread (profile in the form of an isosceles triangle with an apex angle of 60 degrees);
- theoretical profile height (H) - 0.866025Р;
- Thread size range: 1/16" to 24" (in accordance with NSI/ASME B36.10M, BS 1600, BS EN 10255 and ISO 65).
Table 4
Designation of thread size NP, steps and nominal values of outer, middle and inner thread diameters, mm
| Thread size designation | Threads per inch | Thread length | Thread diameter in the main plane | |||
| Working | From the end of the pipe to the main plane | Outer d=D | Average d2=D2 | Internal d1=D1 | ||
| 1/16″ | 27 | 6,5 | 4,064 | 7,895 | 7,142 | 6,389 |
| 1/8″ | 7,0 | 4,572 | 10,272 | 9,519 | 8,766 | |
| 1/8″ | 18 | 9,5 | 5,080 | 13,572 | 12,443 | 11,314 |
| 3/8″ | 10,5 | 6,096 | 17,055 | 15,926 | 14,797 | |
| 1/2″ | 14 | 13,5 | 8,128 | 21,223 | 19,772 | 18,321 |
| 3/4″ | 14,0 | 8,611 | 26,568 | 25,117 | 23,666 | |
| 1″ | 11½ | 17,5 | 10,160 | 33,228 | 31,461 | 29,694 |
| 1.1/4″ | 18,0 | 10,668 | 41,985 | 40,218 | 38,451 | |
| 1.1/2″ | 18,5 | 10,668 | 48,054 | 46,287 | 44,520 | |
| 2″ | 19,0 | 11,074 | 60,092 | 58,325 | 56,558 | |
| 2.1/2″ | 8 | 72,699 | ||||
| 3″ | 88,608 | |||||
| 3.1/2″ | 101,316 | |||||
| 4″ | 113,973 | |||||
| 5″ | 141,300 | |||||
| 6″ | 168,275 | |||||
| 8″ | 219,075 | |||||
| 10″ | 273,050 | |||||
| 12″ | 323,850 | |||||
NPT thread (National pipe thread)
NPT is an American standard used for inch pipe threads. It is used, as a rule, in connections for which it is important to ensure increased tightness of pipes under conditions of exposure to high pressures (gas or liquid). The NPT thread meets the requirements established by the domestic standard GOST 6111-52 (classified as an inch conical pipe thread with a profile angle of 60 degrees).
This type of thread is characterized by the following parameters:
- designation according to profile shape:
- inch pipe cone (angle φ=3°34′48″, taper 1:16) - American standard;
- pipe inch tapered thread with a profile angle of 60 degrees - domestic standard;
- theoretical profile height (H) – 0.866025Р.
Also, in accordance with ANSI/ASME B1.20.1, cylindrical threads (NPS) also belong to this type. Within this standard there is also NPTF. Its peculiarity is the formation of a seal due to the compression of the thread at the connection point.
Inch pipe thread (American standard) (NPT) with a taper of 1:16 (cone angle φ=3°34′48″) or cylindrical (NPS) thread according to ANSI/ASME B1.20.1. The profile angle at the apex is 60°, the theoretical profile height is Н=0.866025Р. NPT thread corresponds to GOST 6111-52 - Conical inch thread with a profile angle of 60 degrees. There is also an NPTF thread - compaction occurs due to thread compression.
Correspondence table for various types and standards of threads
TABLE OF CORRESPONDENCE
| Thread type, designation | Application area | Regulatory and technical documents | Thread sketch | |
| Russian | Foreign | |||
| Metric M12; M20x2; M20x2 LH | general mechanical engineering | GOST 24705-2004 | ISO 724; DIN 13 (Germany); BS 3643 (England); ANSI/ASME B1.13M (USA); NF E 03-050 (France); JIS B 0205, JIS B 0207 (Japan) | |
| Trapezoidal Tr 40×7; Tr 40×7 LH | Lead screws in general mechanical engineering | GOST 24737-81 | ISO 2904; DIN103 (Germany); BS 5346 (England); NF E 03-618 (France); JIS B 0216 (Japan) | |
| Pipe cylindrical 55° G 1 ½ | used in cylindrical threaded connections | GOST 6357-81 | ISO 228/1; DIN ISO 228, DIN 259 (Germany) BS 2779 (England); ANSI/ASME B1.20.1, ANSI B 20.3 (USA) NF E 03-005 (France); JIS B 0202 (Japan) | |
| Pipe Taper Thread (55°) or British Pipe Taper Thread BSPT Rc 1 ½; Rp 1 ½; R 1 ½ | in gas water supply and sewer fittings. For greater tightness, use conn. internal cylindrical with external conical thread | GOST 6211-81 | ISO 7/1 DIN 2999, DIN 3858 (Germany) BS 21 (England); ANSI/ASME B1.20.1, ANSI B 20.3 (USA) NF E 03-004 (France); JIS B 0203 (Japan) | |
| Unified thread (ISO thread) ¼-20UNC-2A; 0.250-20UNC-2A; 10-32UNF-2B; 0.190-32UNF-2B | general mechanical engineering application, common in the USA | — | ISO 725; BS 1580 (England); ANSI/ACME B 1.1 (USA) | |
| Metric thread with MJ profile MJ 6×1 | in the aviation and space industry | — | ISO 5855; DIN ISO 5855 (Germany); BS 6293 (England) | |
| Unified (inch) external thread with standardized root radius UNR, UNRC, UNRF and UNREF | — | — | ANSI B 1.1 (USA) | — |
| Unified (inch) thread with increased root radius UNJ, UNJC, UNJF and UNJEF | used in the aviation and space industries | — | ISO 3161; BS 4084 (England); ANSI B 1.1 (USA) | |
| Unified (inch) thread with special diameters, pitches and make-up lengths UNS | — | — | ANSI B 1.1 (USA) | — |
| Whitworth Straight Thread ¼-20 BSW or BSF, BSP | in gas, water and sewer fittings. | industry standards, for example, OST NKTP 1260 | DIN 49301, DIN 477, DIN 4668 (Germany); BS 84:1956 (England) | |
| Trapezoidal thread 1 ¾-4 ACME-2G | Lead screws in general mechanical engineering | — | BS 1104 (England); ANSI B 1.5 (USA); JS B 0222 (Japan) | |
| Trapezoidal thread with reduced profile height 0.500-20 STUB ACME | Lead screws in general mechanical engineering | — | ANSI B 1.8 (USA) | |
| Thrust thread (metric Buttress) S 48×8 | general mechanical engineering | GOST 10177-82 | DIN 513 (Germany) | |
| Armored pipe thread Pg 21 | used in electrical engineering | — | DIN 40430 | |
| Thrust inch (American Buttress) 2.5-8 BUTT | casing pipes in mining | — | ANSI B 1.9 (USA) | |
| Buttress thread (API Battress) | casing pipes used in the oil and gas industry | — | API spec. 5B (USA) | |
| 60° Inch Pipe Thread K3/8″ 3/8-18 NPT | fittings and connections for machines and machines | GOST 6111-52 | ANSI/ASME B 1.20.1 (USA) | |
| 60° Inch Pipe Thread 1/8-27 NPTF | sealed thread of fuel lines | — | ANSI B 1.20.3 (USA) | — |
| Round thread RD | food industry and fire extinguishing systems | — | DIN 405 (Germany) | |
| Locking thread according to API Z-117 4 ½ Reg | rotating drilling tool (rods, bits, etc.) | GOST 28487-90 | API Specification 7 (USA) | |
| Locking thread API RD 8 TPI | tubing, casing and drill pipes | — | API Specification 5B (USA) | |
Notes:
1. UNC, UNF, UNEF
– threads with appropriate pitch for different diameters:
UNC
– coarse pitch;
UNF
– small step;
UNEF
is a particularly small step;
UN
– threads with one pitch value for different diameters. 2. Threads with a taper of 1:16 are similar in profile to OTTM and OTTG threads (GOST 632-80). Threads are not interchangeable. However, under certain conditions for choosing a tool, it is possible to process external threads in accordance with GOST 632-80. 3. API RD 8 TPI thread (pitch 3.175) is interchangeable with tubing threads according to GOST 631-75, GOST 632-80 and GOST 633-80.
Related documents:
GOST 3469-91 - Microscopes. Lens thread. Dimensions GOST 4608-81 - Metric thread. Interference fits GOST 5359-77 - Ocular threads for optical instruments. Profile and dimensions GOST 6042-83 - Edison round thread. Profiles, dimensions and maximum dimensions GOST 6111-52 - Conical inch thread with a profile angle of 60 degrees GOST 6211-81 - Conical pipe thread GOST 6357-81 - Cylindrical pipe thread GOST 8762-75 - Round thread with a diameter of 40 mm for gas masks and calibers for her. Main dimensions GOST 9000-81 - Metric thread for diameters less than 1 mm. Tolerances GOST 9484-81 - Trapezoidal thread. Profiles GOST 9562-81 - Single-start trapezoidal thread. Tolerances GOST 9909-81 - Tapered thread of valves and cylinders for gases GOST 10177-82 - Persistent thread. Profile and main dimensions GOST 11708-82 - Thread. Terms and definitions GOST 11709-81 - Metric thread for parts made of plastic GOST 13535-87 - Reinforced thrust thread 45 degrees GOST 13536-68 - Round thread for sanitary fittings. Profile, main dimensions, tolerances GOST 16093-2004 - Metric thread. Tolerances. Clearance fits GOST 16967-81 - Metric threads for instrument making. Diameters and pitches GOST 24737-81 - Single-start trapezoidal thread. Main dimensions GOST 24739-81 - Multi-start trapezoidal thread GOST 25096-82 - Persistent thread. Tolerances GOST 25229-82 - Metric conical thread GOST 28487-90 - Conical locking thread for drill string elements. Profile. Dimensions. Tolerances