Threaded connections, screw gears and worm gears of gear mechanisms are based on the contact of external and internal elements, the contacting parts of which have a surface formed by the spiral movement of a flat contour. Threaded parts are connected by rotation due to alternating protrusions and recesses according to the screw principle. The areas in contact in this way guarantee the reliability and functionality of the fastener, which is why threaded products are widely used in many industries.
Classification characteristics of threads
Threads are divided into two main groups. The first includes standardized products, the manufacture of which must comply with international and national standards, determined by multiple criteria. The second category includes non-standard parts with special characteristics, manufactured individually to perform specific tasks. Regardless of compliance with standards, all products have certain parameters on the basis of which classification is carried out. The thread is applied taking into account a number of characteristics:
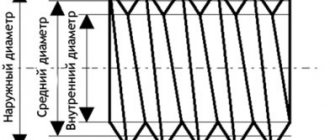
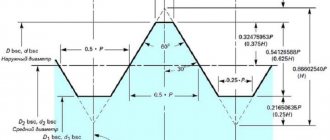
- The configuration of the contact surface
can be cylindrical or conical; - The profile shape
can be round, triangular, rectangular, trapezoidal; - The location of the thread
is possible on the outer and inner surface of the product; - The operational purpose
can be fastening, running, special; - The direction of the helix
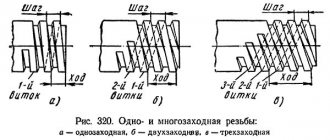
is divided into right and left; - The number of starts
classifies single-start and multi-start threads; - Units of measurement
define metric, inch, modular, pitch sizes.
The metric system is most widespread in Russian industry. When using it, the dimensions of the parts are measured in millimeters. In the production of large-diameter products, inches are used to measure thread parameters. The inch and metric systems are used for the manufacture of elements of threaded connections and screw gears. Modular and pitch threads are more specific. Pi-based calculation methods are used to determine worm parameters for gear-screw mechanisms.
Important point. To convert inches to metric format, you need to multiply the existing indicator by 2.54 to get the result in centimeters. For modular threads, when multiplying the module by pi, the value is converted to millimeters. Calculating pitch pitch is a little more complicated. The size in inches is determined by dividing pi by pitch and then calculated in centimeters if desired.
Modular thread
Modular threads are used for worms that engage worm wheels. The thread pitch of the worm Su is equal to the pitch of the teeth of the worm wheel. [1]
Modular threads are used for worms that engage worm wheels. [2]
Modular thread is designed for cutting worms. [3]
Modular threads are used in worm gears. [4]
Modular thread is used for worms. [5]
Modular threads are relatively often multi-pass and with large helix angles. Therefore, the cutters in question are usually manufactured with a cylindrical shaft, which allows for quick installation of the cutter as shown in FIG. [6]
Modular thread has a profile in the form of an isosceles trapezoid with an angle of 40, used on worms mated to worm wheels. [7]
Modular threads are used in worm gears. The diameter of the worm thread and the size of its profile are set depending on the conditions of joint operation of the worm and the worm wheel. The worm thread pitch is very modular, in rare cases it is pitch pitch. [8]
Modular threads are cut using worms working in tandem with worm wheels. The sides of the profile are most often straight, but can also be curved. [10]
When cutting modular threads, the kinematic chain differs from the previously discussed one only in the tuning of the guitar. [eleven]
To obtain large modular threads, a link for increasing the thread pitch and mmax of 48 lsh is used. [12]
To cut metric and modular threads, the M2 and M4 couplings are turned on, and the gear wheel 35 of the X shaft is turned off. [13]
To cut metric and modular threads, as well as to obtain mechanical feed, the feed box is rebuilt. Gear 35 on shaft X is disengaged from gear 37, clutches M3 and M4 are engaged, and clutch M3 remains disengaged. [14]
To cut metric and modular threads, as well as to obtain mechanical feed, the feed box is rebuilt. Gear 35 on shaft X is disengaged from gear 37, clutches L1 and M4 are engaged, and clutch M3 remains disengaged. In this case, rotation from shaft IX to shaft XIV is transmitted by coupling M2, shaft XI, Norton mechanism (in the opposite direction), coupling L14 and a multiplying mechanism. [15]
Modular thread. "Worm&.
From the author Dmitry Sabre. Added 5 months. back. Read more.
Modular thread cutting.
Modular thread cutting. From the author Elena Ivenski. Year 3 added. back. Read more.
Modular & pitchable.
From the author Vadim Lazutin. Added 2nd year. back. Read more.
A very important and necessary table.
For those who want to help About what this table is for. Which one does she play? From the author Tokibana-Nau. Added 2nd year. back. Read more.
Table of thread diameters, etc.
Outer and inner diameters for threads, number of threads, thread pitch, hexagon diameter. From the author Sergejs Belov. Added 2nd year. back. Read more.
Setting up a lathe for a bench.
Adjustment for metric threads. From the author Dmitry Kuprya. Added 2 months. back. Read more.
Modular thread cutting.
Modular thread cutting. Aideo presents the process of cutting modular threads. Not everyone saw her, but... From the author wim kielemoes. Added 2nd year. back. Read more.
Pitch 1.75 instead of 14 threads per 1 inch.
Sorry for the shaky camera. Short thread 14 threads per inch, can be replaced with a metric pitch of 1.75. Tap. From the author of Rural Diary. Added 1 year. back. Read more.
16k25 table in good quality.
For Mat and INSULTS BAN. Link to the table in JPEG format: Link to the file in which I made it. From the author Stanislav Khar. Added 2nd year. back. Read more.
Classification of threads. Educational prez.
XXX. From the author of The BEST Team. Year 3 added. back. Read more.
All types of carving and how to do it.
Different carvings. From the author Evgeniy Koval. Added 2nd year. back. Read more.
Modular thread on TV4.
From the author Andrey Zemtsov. Added 2nd year. back. Read more.
Dimensions of workpieces for threading with a cutter.
From the author Vadim Lazutin. Year 3 added. back. Read more.
Tape thread
From the author Turning Bres. Added 6 months. back. Read more.
16k20 – Table
For swearing and insults in the comments - BAN. Under this video I attach links to: 1. Spindle speed table. From the author Stanislav Khar. Year 3 added. back. Read more.
Pipe thread cutting 3/8&qu.
From the author Boris Kushnir. Added 2nd year. back. Read more.
TV-4 thread pitch 1.5 mm
How to cut threads with a pitch of 1.5 on a TV-4 machine with a standard set of gears for his guitar. RVO. From the author alexey wycb. Added 1 year. back. Read more.
Worm on the polar axis, arbitrary.
Manufacturing a worm shaft for a non-standard pitch. A homemade machine is used. Stage of construction of a home. From the author papa Slava. Added 5 months. back. Read more.
Thread cutting with a cutter on a lathe.
Cutting threads with a cutter on a lathe by moving the caliper in 2 planes. From the author Workr