Regulatory requirements and calculations when creating welded metal structures
According to ENiR 22 1, welding work must fully comply with the requirements and regulations of SNiP III-18-75. The standards are taken into account when carrying out repair work, as well as when constructing new facilities from welded metal structures. In addition to instructions on welding techniques, the document also contains prices for the work performed.
Creation of metal structures using the manual arc method
In order for metal products to comply with ENiR, welding work must be performed in compliance with certain stages:
- turning on the equipment and setting all parameters, including the main operating mode;
- preparation for welding of all elements and parts, thorough cleaning of the metal at the joints from traces of oil and other contaminants;
- the process of welding elements into integral structures;
- removing crusts from slags generated during the work process from welding seams;
- monitoring connections for strength, presence or absence of defects.
Depending on the shape of the edges and thickness, different electrodes are used. Often the diameter of the electrodes used is indicated in the product flow sheet or drawings made before welding. As for brands, according to ENR recommendations, welding will be of higher quality and more reliable when using electrodes marked OZS-4, 21, 18, 17N; VSF-5U and 65U; UONI-13/85; ANO-11 and 14; ANP-2; NIAT-ZM.
This list is not a strict limitation; the welder can work with other brands, while multiplying prices and standards by the coefficients indicated in the document.
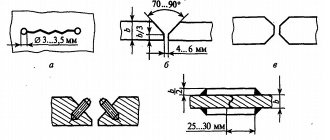
The picture below shows the most common types of butt joints, which are created in different positions:
- a) in the bottom;
- b) in horizontal;
- c) in the vertical - lap seams;
- d) T-joints and overlap joints - in the ceiling;
- e) at the bottom - overlap seams;
- e) in the ceiling;
- g) corner joints in the ceiling;
- h) angular in the lower position.
Below is a table according to which you need to calculate tariffs for welding work.
Mechanized and automatic submerged arc welding
In accordance with ENiR, welding of metal structures performed directly in a workshop or on a plant premises using automatic or mechanized submerged arc welding should only occur in the lower position. The work order is as follows:
- turning on a semi-automatic device;
- thorough preparation of metal surfaces: cleaning edges, removing corrosive deposits and dirt;
- filling the flux with a powdery composition;
- installation of wire into the mouthpiece and into the wire feeding mechanism, using specialized reels for this; selection of optimal welding mode;
- work on welding elements;
- pulling out previously installed wires from all mechanisms;
- removal of slag formations;
- control and measurement of seams for compliance with parameters.
Following the requirements of ENiR 1 22 1, welding work is carried out using filler wire, the diameter of which for automatic equipment does not exceed 5 mm, for a mechanized process - 2 mm.
Tariffs for ENiR for welding work on metal structures can be calculated using the tables below.
Welding with flux cored wire
Work using flux-cored wire is performed using a mechanized technique in the same order as the two types of welding described above. Only in this version, a reel with wire wound on it is installed on the turntable of the semiautomatic device, after which the wire is installed in the electrical holder. The mouthpiece is replaced as necessary. The diameter of the wire material should not exceed 3 mm.
According to the ENiR rules, welding work on metal structures should be carried out in a lower spatial location. When welding products in a confined space or in outdoor conditions, deviations from the established norms are allowed.
Tariffs are calculated according to the table below.
Mechanized welding in a carbon dioxide environment
After turning on the device, the current strength is adjusted and the desired welding mode is selected. All parts to be welded are thoroughly cleaned of traces of dirt, dirt and rust, and the edges are cleaned. A spool of wire and a gas cylinder are installed, the hoses are purged, and after that you can start welding.
After removing the wire and removing the slag, the dimensions of the seam are measured and a visual inspection is carried out.
The table for calculating tariffs is given below.
Gas cutting
In accordance with ENiR 22 issue 1, welding work using manual gas cutting is carried out in the following order:
- gas cylinders are checked and installed;
- cutters are adjustable;
- test cutting is performed and if everything is normal, the steel is cut;
- The gas supply is shut off and the hoses are disconnected.
Mechanized gas cutting is carried out in the same sequence, only in this case it is necessary to adjust the operating mode. Below is a table used to calculate gas cutting tariffs.
Standards for welding work
The purpose of the standard values is to regulate the quality of the work performed, the speed of completion, the time it takes to complete certain works, production standards, the energy consumption that will be required to perform the welding work, the required number of components, and the time required to perform the welding.
In addition, the control of welded joints and methods for its implementation are regulated. The requirements of the SNiP document are subject to the release of drawings and documentation, in particular, technical specifications. Particular attention is paid to ensuring safety when carrying out welding work.
SNiP consists of four parts independent from each other, which contain standards for welding work.
Rules regarding time
The standard time for welding is calculated based on the concept of the standard time for welding 1 m of a seam. A qualified welder must have the ability to independently calculate the time during which he can perform specific operational actions. The performance and productivity of the work performed will depend on the correct calculation.
When making calculations, the welder must take into account the time standards for welding work specified in SNiP. They consist of the time spent specifically on the welding process, as well as the time spent on preparatory work and various production operations.
There are three types of production operations included in the concept of norm:
- Main.
- Auxiliary.
- Additional.
The concept of the main production operation includes the provision of consumables for welding, the necessary processing of the main metals being welded and carrying out preparatory operations. Basic production welding is the welding process performed.
The auxiliary operation includes: delivery to the welding site of the parts to be welded and the selected equipment, further control of the resulting joint and its movement according to the technological process, for example, to the assembly workshop.
Additional time is taken into account for servicing the process, setting the necessary parameters on the equipment, drying the electrodes, checking the functionality of the devices used, replacing the electrodes, and applying flux. This concept may include the time it will take to deposit, if necessary.
The calculation must include time for caring for your workplace, changing into a protective suit, rest and lunch break.
When calculating, the qualifications of the performer are taken into account, which affects the speed of the welding process, and a special coefficient is applied. There are several methods for calculation, the most common of which is calculation using work units. Each unit is equated to one product being welded.
Production rate
The standardization of welding work regarding their production determines the work performed in a specified time. The unit of measurement is the number of products or the value of the weld seam in meters that have undergone the welding process in one hour or per shift. The production rate can be a component of the time rate or calculated separately.
Electricity consumption rate
SNIP for welding requires keeping records of the costs of electricity required to carry out the work. They depend on the equipment used and its power, indicated in the passport. In addition, sufficient lighting of the work area is necessary. The unit of measurement is kilowatt-hours.
Standard for components
When welding, not only time and electricity are consumed, but also components and tools. SNiP for welding work also provides for these circumstances. Components without which welding cannot be carried out include electrodes, flux, and gas.
Costs of this type include wear and tear on equipment and individual specific elements - roller guides, contact jaws and similar products. Equipment wear and tear depends on numerous factors. For example, on the material used to manufacture components, as well as on the operating mode selected and installed on the equipment.
Timing
For the convenience of carrying out calculations, SNiP for welding contains auxiliary material for faster and more convenient calculations. These include various tables. An example is the following table for standardization of welding work:
The table given as an example applies to conditions where welding is carried out on only one side and there is no bevel of the edges. In this case, the position of the seam in space and the category assigned to this type of work play a role. The thickness of the parts to be welded is of great importance, which takes into account the time standards for welding metal structures.
Welding time can be calculated using the following formula:
- t0 is the required time;
- L —seam length;
- F is the cross-sectional area of the seam;
- I is the current value;
- Kn is a coefficient characterizing surfacing.
In the indicated formula, the value 7.85 is the density of the metal. In each specific case, you should substitute your own value. To calculate the time spent on welding work in one work shift, the result of the calculation should be multiplied by the number of hours using the formula.
If gas welding is carried out, it is convenient to use the following formula:
- S —thickness of the metal to be welded;
- K is a coefficient depending on the metal. It will be different for different species.
The formula used to calculate welding time with oxygen is:
- L is the length of the welds;
- V is the welding speed.
Unified time standards for welding work are specified in the normative document SNiP. The unit of measurement can be the welding time of 1 meter of seam. Also in the calculations, a unit of measurement is used, such as the welding rate in meters per day.
Organization of the workplace for successful compliance with standards
In order for all design standards for welding work to be met, it is necessary to properly organize the place where the welder will work.
It is arranged in accordance with the recommendations of the scientific labor organization NOT. Sitting at a metal workbench should be comfortable. There should be a protective visor on top. The room must be equipped with exhaust ventilation. There must be sockets for connecting welding equipment. Safety equipment is required.
READ ALSO: How to Use a Polypropylene Pipe Cutter Video
Pipeline welding
The standards for welding pipeline joints are described in detail in the second issue of EniR. Here the requirements for manual arc welding, automatic in carbon dioxide and submerged arc welding, gas cutting and welding of joints, heat treatment of welded joints are clearly defined.
Tariffing of work is carried out according to ENiR “pipeline welding” based on the table below.
Manual arc welding
ENiR 22 2 “welding of pipelines” using the manual arc method provides for the use of specific brands of electrodes, a list of which can be found in the text of the document itself. When using electrodes of other modifications, the coefficients indicated in the table should be taken into account.
Gas welding
Work begins with preparing the cylinders, attaching a burner to them and purging the hoses. The edges must be cleaned of dirt and dust. Light the burner, adjust the flame and start welding. Depending on the size of the pipeline in diameter according to ENiR 22 2 for welding work, prices and time standards for one joint are indicated in the tables.
Automatic submerged arc welding
The standards require the use of electrode wire with a diameter of 2 mm. Pipes of 11-12 meters in length assembled into links are subject to welding. Tariffs and time standards can be viewed in the tables directly in the ENiR document, which are given separately for each type of welding installation.
Automatic carbon dioxide welding of steel pipelines
According to the standards stipulated by ENiR 22, welding work is carried out to connect pipe assemblies and pipe links made of carbon and alloy steels in a rotary position of the joint. It is recommended to use machines of the TGS-7, TGS-6 and TGS-5 types.
The work process is carried out according to the following scheme:
- the links assembled on special electric tacks are placed on roller supports and firmly fixed in the rotating device;
- the welding head is placed on the joint with simultaneous mode regulation;
- the rotator starts;
- welding is performed;
- then the head is removed from one joint and moved to another;
- the rotation mechanism is turned off;
- seams are branded;
- the links are removed from the supports.
During the welding process, the transition distance is up to 25 meters.
Optimal speed
Quantitative calculation of the rate of time spent determines the welding speed, which should ensure a high-quality seam. To a predominant extent, it depends on two values: the thickness of the product and the weld seam. You need to work so that the liquid melt does not overfill the working bath, does not form sagging, and smoothly passes to the main part of the parts.
Exceeding or decreasing the speed leads to a sharp deterioration in the quality of work, changing the welding time. At optimal speed, the seam is deep enough, but not very wide.
This guarantees compliance with quality standards. For manual arc welding, the best results are usually obtained by welding work carried out at a speed of 30-40 m/hour.
Standard values may vary depending on the specifics of the material. With semi-automatic welding, speeds are often higher. This is understandable and explainable by the specifics of the equipment used.
How to calculate time standards
To establish, with an accuracy of up to a minute, the time standards for welding pipeline joints, the first thing you need to do is measure the length of the butt joints of each individual element. Since there are many seams, each is calculated separately using the formula:
- Tosn = I/Vsv , where Tosn is the time spent on creating one connection;
- I - length;
- V is the speed of the welding process. In most cases, a constant rate of 6 m/h is used. But here it should be taken into account that welding of metals of different compositions occurs differently.
The calculation with a constant value is given as an example. If there are 4 seams with a length (in cm) of 40, 35, 20 and 10, then the time standard will not be difficult to find out. By dividing we get, respectively (in minutes) 6.6; 5.83 min; 3.33 min; 1.66 min.
The total time is determined cumulatively and in a particular case is 17.42 minutes. This is the time spent on the welding process itself, but you also need to calculate the inspection of the weld using the formula: Tism = 0.35 multiplied by 17.42 (total time) and we get 6.097 minutes.
In addition, additional time will be required to prepare connections. You can find out by multiplying the length of all seams by 0.6. According to our example, the length is 1.05 m and it will take 0.63 minutes to clean one meter of joints. Approximately 5% of a certain Tosn is provided to the welder for preparatory work, and this is 0.87 minutes. Also, with a long working period, short-term rest breaks (10% of the total time) should be taken into account.
It turns out that to create four joints 1.05 meters long, the time required is 26 minutes, taking into account rest, welding, preparation of equipment and elements used to create metal structures.
Importance for calculating material quality
A welder, in accordance with his qualifications, has to work with a variety of materials. This significantly affects the standard welding time.
It is customary to distinguish several main groups, differing in the content of chemical components and purpose. For example, group M01 includes structural steel alloys with a carbon and low-alloy composition. The yield strength of these materials does not exceed 360 MP.
As the value of the number in the marking increases, the characteristics of the alloys improve. Thus, class M07 includes reinforcing steels intended for the manufacture of reinforced concrete structures. When calculating time standards for welding work, the quality of materials is of fundamental importance.