Visual and measuring control of welded joints is used for all metal structures and metal products during and after production. This study is performed to evaluate the quality of welds and check for compliance with standards. That is, VIC is also flaw detection of welded joints.
In principle, inspection of welded joints can be divided into two types: destructive and non-destructive. Non-destructive testing methods do not affect the quality of the seam, whereas during destructive testing, samples are taken from building structures. NDT methods often include visual assessment. Moreover, it is considered a mandatory procedure and is carried out both independently and in conjunction with other studies.
Checking the quality of a welded joint begins with visual inspection. Simple measuring instruments or special equipment may be used. A visual inspection reveals large defects, while measuring instruments reveal small ones that are difficult to notice with the naked eye.
What is visual measurement inspection of welds?
Visual inspection of welds involves checking the junction of workpieces both before and after welding. The procedure is necessary to confirm the accuracy and proper quality of the assigned task. Violations of the technological process and standard requirements may ultimately lead to the destruction of the structure before the warranty period. There is a special GOST that regulates the procedure and method of monitoring and reporting documentation.
Measuring work using a template and an optical tool is a non-destructive VIR testing method. Thanks to it, it is possible to obtain reliable information about the condition of the welded joint while maintaining its integrity. If suspicions arise, additional examinations are prescribed to allow for a more complete and accurate analysis. These include spectroscopy and ultrasound diagnostics.
The examinations are carried out by specialist controllers who have previously completed a training course, passed tests and received certificates of the appropriate type. There are different methods of control: visual, tactile, using optical instruments, using measuring equipment. The diagnostic results, comments and recommendations for their elimination are recorded in the inspection report.
Definition
Visual quality control is a procedure for examining the joint both before and after making a seam. The purpose of the inspection is to ensure that all stages of the work are carried out in accordance with the rules. Failure to comply with standards can result in structural failure, injury and death. Technological violations due to ignoring standards are prosecuted by law. In this regard, GOST has been developed, which regulates the procedure and method of conducting an inspection, as well as maintaining relevant documentation.
Measuring seams and joints using optical tools and templates is a non-destructive test that allows you to maintain the integrity of the structure and its joints, but gives a certain understanding of their condition. If hidden defects are suspected, an examination by other methods (ultrasound, spectroscopy) is prescribed.
visual measuring control of welded joints
A specialist inspector is invited to carry out the examination, who must undergo appropriate training and have a certificate. Control is carried out visually, using an optical instrument, measuring devices and tactile sensations (relates to determining the roughness of a seam). The assessment and all comments are recorded in the inspection report and stored.
What does the method reveal?
Visual inspection of welded joints allows you to identify the following defects:
- incorrect geometry of the seam leg;
- burning;
- incorrect proportions between the width and height of the overlap;
- rare scaliness;
- too large melt flows;
- craters in the weld pool;
- undercuts due to high current;
- uncooked areas;
- discolored metal caused by overheating or an incorrectly selected additive.
The use of optical magnifying devices expands the possibilities of visual inspection of welds. You can identify:
- transverse and longitudinal cracks;
- manifestations of corrosion;
- disturbances in the metal structure, in particular delamination;
- unwanted solid inclusions in the alloy;
- open pores through which gas escaped;
- nadirs, sinks, nicks;
- defective protective coating made of polymer or paint;
- seam displacement.
Initial control at the preparatory stages makes it possible to determine how well the edges are prepared. The same method is used to control the overlay of markings or a professional welder’s mark.
Basic requirements for welds
After manufacturing structures by welding joints of elements, an assessment of the finished product is required. After the inspection of welded joints, a report is issued, which is filled out on the basis of inspection and changes in the main elements of the weld. The width and height of the roller must be within the specified limits, and the seam must be uniform, without depressions or protruding parts. The seam should have a uniform structure without scales. In addition, there should be no cracks, burns, unwelded areas or other defects.
Advantages and disadvantages
According to the provisions of GOST 23479-79, measurement control is the primary method of inspection. After its completion, the responsible persons make a decision on the advisability of carrying out diagnostics using other methods. Positive aspects of measurement control:
- minimal time spent on checking;
- ease of implementation;
- allows you to obtain the majority of information about the external state of the welded joint;
- no complex expensive equipment is required;
- the result is easy to check.
It is required to control the quality of the weld at all stages: at the stage of preparatory work, during welding of workpieces and after its completion. This approach is necessary for a comprehensive objective assessment of the result. However, even in such situations, the method cannot be called perfect, since it has disadvantages:
- conclusions about the quality of work are made only on the basis of the visible part of the seam. While it is not possible to identify hidden defects;
- conclusions depend on the expert’s skill level and his approach to completing the task;
- Suitable only for detecting large defects that are easily visible to the human eye.
Flaws
- Visual inspection of welded joints helps to detect only external defects, while internal ones may remain hidden;
- The results are recorded exclusively manually, and then only with the use of measuring instruments.
Regulations
There are a number of regulatory documents according to which visual quality control of welds is carried out. This is not only GOST 23479-79, which specifies the requirements for optical non-destructive testing methods. This could also be RD 34.10.130-96 and instructions for measuring and visual inspection, RB 089-14 - safety guidelines during inspection of welded joints, and so on.
Test Tools
When visual and measuring inspection of welded joints is carried out, additional tools can be used to help record the exact position and size of detected defects, as well as determine the weld parameters. After all, the unevenness of its surface, as well as too high or low a height, can also be considered defects. Among the tools used are:
- A probe is a scaleless measuring instrument that has a number of plates of a certain size, by which it is possible to determine the compliance of the workpiece with the specified parameters;
- A caliper is a tool with three types of measurements that can help measure external and internal dimensions, including diameter, as well as the depth of pores and cracks;
- A magnifying glass is an optical instrument that has a certain magnification value and helps to magnify external defects for better detection;
- Metal rulers are one of the simplest and most commonly used measuring tools used in the field;
- Goniometer - allows you to determine the angle of the connection and the relative location of the parts to be welded.
Tools for visual inspection of welds
The essence of an external inspection
The physical foundations of the visual optical testing method provide the determination of primary information about what qualities a compound may have. If the products are reliably welded and have no defects, then they have approximately the same qualities as the base metal. The more defects, the lower the reliability of the connection. Due to its simplicity and the absence of any cost for consumables, the method allows you to determine obvious defects that can be corrected even before using other methods.
There are different types of welds and joints, but visual inspection is applied to almost all of them. In the professional field, it is not used as the main one, due to the inability to determine the internal state of the seam, but it is still always used so as not to subject obviously defective products to expensive inspection methods. After the professional inspection has been completed, a visual inspection report of the welds is drawn up.
Requirements for welds
The report of visual inspection of welds, a sample of which is given to the specialist conducting this inspection, must contain all the important data about the specific object being examined. This is very important when one or more samples from a series can be controlled. It must meet the basic requirements for this type of connection. The height of the roller and width must be within the specified limits; it must be uniform, without various depressions and protruding parts. The structure of the seam should look uniform, and depending on the type, the presence or absence of scales is determined. There should be no pores, cavities, cracks, chips, uncooked areas, and so on.
Step by step order
- First of all, the seam is prepared for inspection. The slag is cleared from it, metal splashes are erased, and the surface is cleaned.
- Next comes a naked eye inspection, which helps to quickly check the quality of the connection. In this case, only the most obvious defects can be detected.
- Next, an inspection is carried out using additional tools that can provide accurate data about the resulting connection.
- If the parameters meet the requirements, then the product is allowed to work; if not, then the detected defects are recorded and included in the report.
Method capabilities
Naturally, this is not an ideal method and first of all you need to understand what determines the choice of a visual control method. It should be noted right away that these are exclusively superficial flaws. Among them:
- Pores;
- Cracks and microcracks;
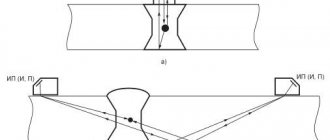
Weld gap measurement diagram
- Sinks;
- Chips;
- Insufficient level of cooking.
Scheme for measuring displacements when welding seams
When is visual inspection performed?
You can visually control the quality of welding work at any stage. Already at the preliminary stage, it is possible to determine the readiness of parts for welding. The compliance of the markings and the integrity of the workpieces are checked. Then you can control the assembly of parts for welding, the quality of cleaning the surface from oil, paint, rust and other contaminants. It is worth focusing on cutting the edges. It must be performed in accordance with the type of connection to be made; taking into account the thickness of the metal and the strength of the welding current.
Upon completion of welding work, the seam is checked for defects that can be determined visually. You should look for holes, cracks, lack of penetration, pores, undercuts and other visible defects. In cases where it is necessary to apply several overlays to a joint, the application of each layer is controlled. Upon completion of the inspection of critical structures, an inspection report is drawn up, where its results are recorded.
You can visually monitor the condition of the weld even on a working structure. This is practiced in cases where the guaranteed service life of the welded joint is coming to an end. An examination is also ordered in any case when there is a suspicion of deterioration in the quality of the connection. This is necessary to prevent equipment breakdowns and unnecessary downtime.
GOST 5264 80
GOST 5264-80 for manual arc welding is a document that establishes the parameters of welded joints (steel, iron-nickel alloys). There is a way to check the quality of welded joints by measuring geometric quantities to determine compliance with GOST. The disadvantage of this method is that it only measures the height and width of the object being studied. Although the strength is influenced by both the angle of transition from the fused metal to the base metal and the radius, the quality of the weld surface and its aberration from the geometric center of the axis.
Visual measuring control RD 03-606-03
RD 03-606-03 is an instruction that defines the process of VIC welds and surfacing. It is necessary for organizations that carry out visual or measurement control during repair, manufacturing, construction, safety assessment in an industrial environment, installation, reconstruction, etc.
The inspection is carried out in strict accordance with the requirements of specially developed standards.
Visual inspection RD 03-606-03:
- Checking at each stage (input control, production, etc.);
- a clear definition of the professional qualifications of everyone who conducts VIC;
- determination of equipment and its quality for non-destructive testing;
- checking the literacy of the VIC (searching for a suitable place, preparing for the test itself, etc.);
- description of methods and equipment for monitoring and measuring certain quantities;
- summing up the overall result of the study and recording it in the documentation;
- safety precautions.
Advantages and disadvantages of visual measurement control
VIC advantages:
- Simple and clear method.
- Testable and repeatable.
- Allows you to obtain up to 50% of all information about the quality of the structure under control.
- No expensive equipment required.
- Not labor intensive.
Disadvantages of VIC:
- The results are influenced by the human factor.
- Suitable for finding only relatively large and obvious faults.
- Subjectivity of some results.
- A guarantee of the inspector's professionalism is required.
- Only the visible part of the object is analyzed.
A visual method of monitoring seams is necessary at all stages of diagnosis.
Instruments for visual inspection of welded joints
To check the weld by visual method, special equipment provided by GOST 23479-79 is used. The set of tools is divided into two groups: workshop - works in the temperature range of 5-20 degrees; field - can be used outdoors in a wide range of temperatures - from -55 to +55 degrees Celsius. The set is represented by the following list:
- templates for checking the geometry of the weld;
- measuring magnifiers;
- squares for checking right angles;
- protractors with vernier;
- micrometers, calibers and bore gauges;
- probes for measuring gap width;
- tape measures, rulers, calipers;
- pipeline wall thickness meters.
Proper examination is only possible with sufficient lighting. Natural light or artificial lighting inside buildings is sometimes not enough. Therefore, the controller should always have flashlights or other light-emitting devices with him. Sometimes you have to use special equipment - borescopes and microscopes. They are necessary in order to determine as accurately as possible the severity of the identified defect. In cases where the weld is located at a height inaccessible to the expert, the use of binoculars of various power levels is allowed.
But it happens that you need to provide visual inspection of welds that the inspector simply cannot access. This applies to structures located underground, in narrow tunnels, in aggressive environments or high radiation. Then specialists are brought in to manage remote platforms with video surveillance or other special transmission equipment. With its help, the inspector examines the condition of the weld as far as remotely controlled equipment allows. Such diagnostic methods are used extremely rarely.
Tools used
GOST 23479-79 also indicates the use of specific equipment and tools for qualitative visual research. It is divided into workshop devices that can operate at temperatures from +5 to +20, and field devices that operate from -55 to +55 degrees. These tools include:
- measuring magnifiers;
- welding templates for checking weld geometry parameters;
- squares for checking 90 degrees;
- bore gauges;
- protractors with vernier;
- probes for monitoring gap maintenance;
- micrometers;
- thickness gauges for determining pipeline walls;
- calibers;
- calipers;
- rulers and tape measures.
Good lighting is necessary for proper inspection and control, so the inspector should always have a flashlight and additional lighting equipment. In some cases, microscopes and borescopes are used. This allows you to more accurately determine the nature of the defect and its severity. If the product is located at a high altitude, and it is not possible to deliver a specialist there, then binoculars of various powers are used.
It happens that the need for visual inspection arises on structures where it is impossible to deliver an inspector and with which there is no direct visual contact. This can be underground in specialized tunnels, or in an environment with high temperatures and dangerous background radiation. Then, to search and analyze defects, remote platforms with video surveillance and television installations are used, through which the inspector can monitor the area being inspected. In addition to robotic systems, lighting equipment is installed. But these automated means are used extremely rarely with the visual method of monitoring welded joints.
Preparing to perform an inspection
Regardless of the type and characteristics of the object being examined, its surfaces must be properly cleaned. Any foreign coatings that are not part of the natural structure of the seam must be removed. This applies to scale, paint, dirt, traces of rust and slag remaining after welding. Objects whose surfaces have tarnished colors are not always allowed for inspection. If the surface being tested belongs to parts of operating equipment, then the unit must be stopped for the duration of the research.
As a rule, this applies to technological equipment that has been repaired by welding. We are talking about ventilation systems, cooling systems, compressor units, etc. Particular attention during preparation is given to the visual inspection tool kit and consumables that will be used during the work. Instruments must be properly adjusted, calibrated, and tested for functionality and accuracy.
Control tool used
At a basic level, simple visual inspection tools are used, including magnifying glasses, calipers, rulers and squares. Specialized devices for professional testing include eddy current and ultrasonic thickness gauges, which give an idea of the dimensional parameters of defects.
Templates are also widely used for visual inspection, which can be used to determine deviations of seam characteristics from standard values even without specific measurements. This comparison usually determines the shapes of gaps, edges and assembled parts for subsequent connection. Profilometers are used specifically to determine the degree of waviness and surface roughness.
Pros and cons of the method
Visual quality control of welds has many advantages:
- The most economical method, requiring virtually no costs.
- There is no need for special reagents or other consumables.
- Makes it possible to identify the bulk of defective seams.
- Assessment of the surface condition is usually carried out quite quickly.
- The person performing visual non-destructive testing may not have special knowledge and skills.
This is an excellent preliminary method, which is usually followed by others using special means. However, it has negative sides, including:
- The visual inspection system makes it possible to identify only flaws on the surface of the product. Internal ones go unnoticed.
- Defects can only be recorded manually, even if visual inspection devices are used.
- Slight chance of small surface defects.
- The detection of deficiencies is highly dependent on subjective circumstances. Among them are visual acuity, overwork, and insufficient work skills of the employee performing the inspection.
Despite the listed disadvantages, the low labor intensity and good information content of the method make its implementation a mandatory procedure, followed by other checks. Any control of a product begins with a simple inspection.
The procedure for carrying out incoming inspection
The first stage of external control within the production process, which aims to check blanks and parts before assembly operations. At this stage, cracks, sunsets, nicks, delaminations and cavities of welds are identified, which are incompatible with the requirements of further technological operations. According to the instructions for visual inspection at the entrance inspection stage, the length of sections that can be checked without auxiliary equipment can be no more than 100 mm.
Otherwise, measuring instruments are used that make it possible to record the geometric parameters of defects in an on-line mode. By the way, in addition to the welds themselves, at this stage the condition of the edges of parts that will still be assembled by welding can be assessed.
Stages of control
Visual inspection is divided into several stages, each of which is aimed at identifying a specific defect. The first thing any specialist should do is inspect the seams “by eye”. In this way, the most obvious defects that weaken the connection are detected. The uncooked area and the sink are easily identified. Ignoring the “lock” or leaving a crater from the weld pool will not go unnoticed. Rough scales, sagging and too narrowed seams indicate a violation of the technological process. When examining a commissioned element, you can easily notice corrosion damage.
After carrying out the above actions, the second step of the procedure begins - studying the seams using an optical device. With their help, the area is detailed and the parameters of defects are clarified. Applicable: magnifying glass, borescope and microscope. For example, a visual inspection may help identify a risk, but the depth is unknown. The use of a microscope will reveal the degree of defects and the need to use a different method of examination.
The third stage of the procedure.
The third and final stage of the inspection is measuring the characteristics of the weld when using tools. There is a change in the length of the seam and a comparison with the necessary standards applicable to this area with its load. Afterwards, the surfacing leg is removed. The caliper determines the height and width of the spot. All of the above parameters are compared with the wall thickness of the main workpiece. The square is used to determine the correct side installation and offset when using the product.
Interesting: Description and types of welded joints
Upon completion of the event, an inspection report is drawn up, which contains a list of defects found, a description of the condition and personal recommendations of the inspector on the use of other methods for determining the defect.