This flaw detection method has been known to mankind for a long time. We can say for sure that back in the Middle Ages, craftsmen used it to identify surface cracks on products invisible to the naked eye. It is also suitable for inspecting welds.
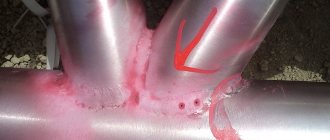
In order to perform color flaw detection, the prepared part is immersed in a special brightly colored solution - it is also called penetrant - kept in it for 5 - 10 minutes, and then washed in cold water. When the washing is completed, a thin layer of white paint or clay is applied to the controlled surface. When they dry, they absorb the solution remaining inside the cracks and are painted, repeating their shape. A clearly visible pattern appears at the site of the defect.
Advantages
This method of identifying weld defects has become widespread because it has a number of important advantages.
- No need for complex equipment. All the necessary materials are quite cheap and can be purchased at a regular hardware store.
- The examination does not take much time. This means that such technology can be used even in mass production.
- It doesn't matter what material the part is made of. This can be cast iron or steel, non-ferrous and non-magnetic alloys, various plastics and even ceramics.
- The technique is quite accurate because it allows you to detect cracks as small as one micron.
- The process of color flaw detection is simple, and even a person who does not have special skills can master it.
Color flaw detection
Capillary control methods.
LENTEST LLC has extensive experience in capillary control.
The most often ordered inspection is where the liquid penetrating into surface defects is colored bright red, and this is called color flaw detection. Less commonly ordered is testing where the liquid penetrating into surface defects glows in ultraviolet rays. The last option (luminescent control) is more sensitive, detects defects with a micron opening, but is more expensive and is used only on particularly critical products. Many regulatory documents and safety rules equate magnetic and capillary control, i.e. offer to carry out control of your choice. Our experience shows that on ferromagnetic materials the efficiency of magnetic control is significantly higher. In practice, due to the fact that capillary control is indifferent to “ferromagneticity” and does not require instrumentation, it has an unconditional leadership. More details about the capillary testing method It is necessary to take into account that penetrating testing requires surface preparation (Rz no worse than 20).
Pricing, as always, depends on a lot of things, for guidance (it may turn out to be cheaper if you specify the task - you need to call)
1 sq. meter of color flaw detection - 2500-3000 rubles 1 meter of seam - 600 rubles
We wish our Customers only suitable surfaces!
“Capillary (CD): color (CD) and luminescent (LD) inspection methods are designed to detect surface defects such as cracks, cavities, pores, fistulas, lack of fusion, etc. They are based on the penetration of surface defects wetted by a colored or luminescent liquid into open cavities registration of defects by a colored (usually red) pattern (trace) on a white background of a developer (kaolin) applied to the controlled surface, drawing a colored indicator liquid onto the surface of the developer layer (CD) or by the glow of a luminescent indicator liquid when the surface is irradiated with ultraviolet light (LD).
The LENTEST laboratory has modern flaw detection kits (cans, etc.) that allow capillary testing to be carried out at the level required by the standards for sensitivity class I.
Penetrant testing is highly sensitive to detecting small surface defects (opening 0.0001-0.001 mm, depth 0.02 mm). However, for example, in comparison with the magnetic particle method of testing surfaces, it requires a significantly higher cleanliness of cleaning the surfaces of the tested part in order to remove contaminants from the cavities of surface discontinuities.
Penetrant testing is based on the capillary penetration of indicator liquids (due to which it is also called color flaw detection) into defect cavities and is intended to identify defects that reach the surface of the test object. The capillary inspection method is suitable for identifying discontinuities with a transverse size of 0.1 - 500 microns, including through ones, on the surface of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, alloys, ceramics, glass, etc. Widely used to control the integrity of the weld.”
Flaws
Of course, there are also disadvantages that limit the use of this method of quality control of welds.
- Inability to detect hidden defects and cracks that do not appear on the surface. This is important in cases where the requirements for product strength are particularly high.
- Before starting the examination, the part must be thoroughly cleaned of dirt and degreased. It is at this stage that the most serious problems can arise. However, they will have to be solved, since otherwise the accuracy of the results obtained will be in doubt.
- Since bulky elements of welded structures, such as gas pipelines or building frames, cannot be placed in a container with penetrant, color flaw detection is used to a limited extent during construction.
- To guarantee the detection of defects, briefly placing the product in the solution is not enough. According to the recommendations, the time of such bathing should be about 30 minutes, and therefore the simple method is recommended to be used only for selective control.
All requirements for materials and methods for conducting color flaw detection are specified in GOST 18442-80, which classifies this method of checking welds as non-destructive capillary testing methods. If the work is carried out for personal purposes, then a free interpretation of this document is possible. In all other cases, you will have to comply, as they say. After all, deviation from the standards specified in GOST is punishable by law.
Security measures
Since quality control of welded joints using color flaw detection is carried out using flammable materials, personnel are provided with special clothing made of non-flammable fabric. There should be no source of open flame or sparks near the inspection site. In the premises for permanent work, signs with a smoking ban and fire safety rules are installed. Used cleaning material should be placed in a container made of non-flammable material.
Color flaw detection cannot detect internal defects. Therefore, when testing structures with high strength requirements, it is supplemented with magnetic, radiation or ultrasonic testing. After obtaining a complete picture of the state of the connection, a method for eliminating the detected flaws is chosen.
Application area
The method of color flaw detection of welds has proven itself well in situations where, for some reason, it is impossible to use more modern inspection technologies. The scope of its application is wide.
- Shipbuilding. When installing hull cladding or partitions between compartments, it is important to ensure the tightness of the welds. After all, no one wants a ship launched from the slipway to immediately develop a leak.
- Laying pipelines for various purposes. It doesn’t matter what is pumped through the pipes - ordinary water or toxic chemicals, neutral or flammable gases. Under pressure, they will quickly find their way out. A water leak in a residential building will lead to flooding of apartments, and you will have to pay for their repairs. A domestic gas leak may well cause an explosion that will kill people.
- Production of various containers. Transport tanks or stationary tanks - they all must be sealed. After all, even ordinary water costs money. What will happen if an expensive chemical reagent leaks out through a crack invisible to the eye?
- Construction of houses. The frames of reinforced concrete structures are subject to high loads. In order for a building several dozen floors high to stand for its intended period, the quality of welding must be impeccable.
Wherever the use of complex inspection methods requiring special equipment is difficult, color flaw detection comes to the rescue. However, despite its simplicity, this technology still requires caution.
Without deviating from GOST
First of all, the part will have to be cleaned of dirt. For this purpose, the current standard allows the following processing methods:
- Mechanical cleaning. During its implementation, various technological techniques can be used. The material is treated with a stream of abrasive material such as sand or shot, or simply by hand. Even a regular wire brush will do. You will have to make an effort and work hard, because if even minor contamination remains, all the work will go down the drain.
When mechanical cleaning has been completed, you should begin degreasing the part. In this sense, GOST provides the opportunity to choose from several options. Cleaning can be done:
- Steam, treating the part with vapors of organic solvents.
- Solvents, the simplest of which is water. To obtain better results, detergents are sometimes added to the water. But, if the material of the part allows, you can use solvents with higher chemical activity.
- Chemical reagents that react when introduced into a solution.
- Electrochemically, simultaneously affecting the part with both a chemical solution and electric current.
- Ultrasound, which enhances the cleaning effect of the solvents and chemicals used.
- Thermally. It is recommended in cases where the material of the product can withstand significant heat without damaging its structure.
The listed methods can be varied depending on the available technological capabilities. The main thing is to get a good result. Only after this should the part be treated with penetrant.
Then you can use one of several options for color flaw detection. When choosing them, everything depends on the specific capabilities and conditions for processing parts.
Requirements for the place of control
The flaw detection operation can only be carried out in a specially prepared room. It is important to take into account the requirements for the communication equipment of the place, air characteristics, technical support, etc. The room must be ventilated and not have sources of open flame or intense heating. Lighting should be general and local; lamps close to the operation site should be protected from thermal effects.
You should initially take care of creating an optimal microclimate - only in favorable conditions can color flaw detection be carried out efficiently. GOST 18442-80, in particular, indicates that the air should be dry and warm - if necessary, to achieve these characteristics, you can use an infrared heater, which will ensure drying of the developer at a level of 5 ° C. Technical equipment will depend on the methods of applying chemical components. In particular, paint sprayers, aerosol cans, brushes, etc. can be used to apply the same penetrant.
Various recipes
The chemical composition of the solution used to control the quality of welds varies. As one of the possible options, use a product made according to a simple recipe, which contains the following ingredients:
- Kerosene – 65%.
- Transformer oil – 30%.
- Turpentine – 5%.
By adding a small amount of organic dye, for example aniline, to the resulting mixture, mix everything thoroughly, after which you can begin to work.
Since it is not always possible to ensure precise control of time, and during prolonged treatment with water the coloring solution is washed out of the cracks, its excess can be removed in another way. For example, by carefully wiping the part with a cotton swab or a clean cloth. After this, they begin to apply the developing coating. Regular whitewash or water-based paint are quite suitable for this. When they dry, they will absorb the remaining solution with the dye, forming brightly colored nodes in the defect areas.
The coloring solution, made according to a slightly different recipe, has proven quite good.
- Kerosene – 80%.
- Transformer oil – 15%.
- Turpentine – 5%.
For each liter of the resulting composition, add 15–20 grams of fat orange or Sudan 3 as a dye. The part treated with this mixture is kept for 30–60 minutes, after which it is thoroughly washed with water, completely removing all traces of the dye solution from the surface. If you then apply whitewash to the surface of the product, the layer of which should be as thin as possible, then when it dries, stripes and spots will be clearly visible in places of defects.
Both compositions comply with GOST requirements and are recommended for use for non-destructive quality control of welds.
Applying developer
As with indicator layers and cleaning compounds, the developer is applied in a variety of ways, from brushes to sprays. The main thing at this stage is to maintain the uniformity and solidity of the formed coating. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully check spraying tools, nozzles and other elements of devices that affect the quality of delivery of the product to the target location. All this will further affect the inspection by color flaw detection, as well as the quality of subsequent inspection operations. After applying the developer, drying occurs. It doesn’t have to be done, waiting for polymerization under natural conditions, but to speed up the process, the use of low-power spot heaters is allowed.