Welding - creating a permanent connection by establishing interatomic bonds between the objects being connected when heated. It’s simpler - when the atoms of the edges being welded, melting and mixing at the junction, form a weld. Weld metals and non-metallic materials: glass, plastic and others.
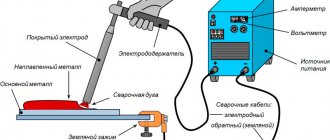
The arc welding process is the melting of material at the junction of parts. An electric current is supplied to the electrode, and upon contact, an electric arc arises between it and the metal being welded, in the zone of which the material melts, forming a weld pool.
Types of electric arc welding
According to the level of automation, electric arc welding is divided into four types:
- manual;
- mechanized - automation tools are used, but the participation of a welder is required;
- semi-automatic - the process is automated, but the parts are moved by the worker;
- automatic – the work is automated, the operator controls the progress of the process.
Classification and methods
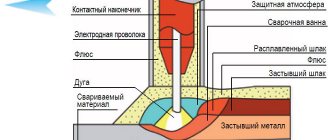
Electric arc welding is classified according to the method of protecting the weld pool:
- not protected - the process occurs with free access of air;
- in a vacuum – air is pumped out;
- the seam is made in a protective gas - inert or active;
- submerged arc process - liquid metal is protected from air by molten slag formed when the flux melts;
- combined methods of protection.
According to the type of current, it is divided into welding:
- variable - from a transformer;
- constant - from the network using a rectifier or generator;
- pulse-arc - electricity is supplied in pulses, this allows you to control the arc provided that the current is regulated.
Varieties
Types of processes are distinguished by arc type:
- direct action - occurs between the electrode and the part being welded;
- indirect action - the arc burns between the anode and the cathode, and the metal is not included in the electrical circuit;
- the arc burns between the consumable electrodes and the edges being connected, power supply with alternating three-phase current;
- compressed arc - the burning radius is limited by gas jets supplied to the welding site.
Electrodes can be consumable (steel, cast iron, aluminum, copper) or non-consumable. The former also perform the function of filler material.
For manual arcing - electrodes in the form of round rods of various diameters. The composition of the coating material is selected depending on the metal of the parts being welded and the characteristics of the technical process.
Electric welding at home
Electric welding is a process for effectively permanently joining metal parts. Today it is actively used to create mesh mesh, all types of frames, tanks. People with the appropriate skills can create canopies for roofs, openwork fences and other things needed in everyday life in their own backyard. This is why many people are concerned about learning to work with electric welding.
Recommendations:
- Clean welding surfaces thoroughly. It is important that they are free of rust and dirt.
- Insert the electrode into the special welding holder and form an electrical arc. To do this, it is necessary to cause current movement in the welding area.
- With an electric arc, it is necessary to make a gap between it and the connecting surface. It should be noted that the size of the gap should not vary from three to five millimeters. Otherwise, the arc will be periodically interrupted, which will lead to deterioration in the quality of the weld.
- The rod should be held at an angle of about 70 degrees. However, this value can be changed to improve the comfort of electric welding.
- Follow safety rules.
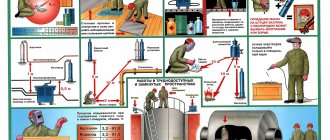
Electric welding requires compliance with the following safety rules:
- The wires that are connected to the power source and arc welding must be effectively insulated, and the body of the welding machine must be grounded. The use of a housing and additional electrical equipment is recommended.
- It is recommended to use special power switches in power supplies. During idling, they break the welding circuit and apply a voltage of 12 V to the holder.
- Welding work should be carried out wearing good, dry gloves and clothing. Please note that if you plan to work in a confined space, you should worry about preparing rubber mats or rubber galoshes.
- If several welding machines are used simultaneously, they must be positioned so that the distance between them is at least 0.35 m (the optimal passage width is about 0.8 m).
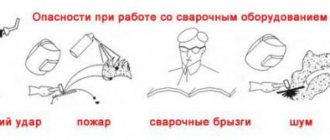
Great attention should be paid to these rules. After all, electric welding is a rather traumatic process . But any disaster can be avoided if you carefully study the issue and approach the matter responsibly.
Manual arc welding
The parameters of manual electric arc welding are specified in the interstate standard GOST 5264-80 , which replaces GOST 5264-69 . It takes into account:
- connection type;
- shape of prepared edges;
- nature of the weld;
- cross-section of the seam and edges;
- thickness of welded parts.
GOST regulates maximum deviations in combinations of the above characteristics. The requirements of GOST 5264-80 do not apply to welded joints of steel pipelines; for them - GOST 16037-80.
Operating principle
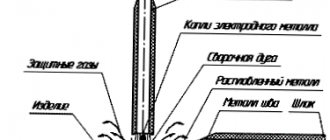
The source of heating of the joint is the welding arc - concentrated radiant energy in the gap between the electrode and the workpiece. Power comes from a transformer for alternating current or a converter for direct current. From the source, power is supplied by wires to the electrode clamped in the holder and to the product. Upon contact, an arc occurs between them. The seam is formed by melting the electrode and the edge being joined.
Creating an Arc
The arc arises from heating the end of the electrode, which is the cathode in the electrical circuit. It comes into contact with the product, the circuit closes. When current passes through a contact with high resistance, a large amount of thermal energy is released. When the electrode is lifted to a distance of 1-2 millimeters, an arc is ignited and thermionic emission begins. Ignition and combustion are possible in the presence of three components:
- An electrical power source whose open circuit voltage is higher than the arc voltage.
- Ionization in the arc column.
- Reactance in the welding circuit - this increases combustion stability.
Welding arc diagram
Welding arc areas
The welding arc includes three main zones:
- Cathode – located between the arc column and the cathode surface.
- The arc column is between the cathode and anode zones.
- Anodic - consists of an anode spot and a near-electrode part. The current in it is formed by the flow of electrons from the column.
Under the influence of high voltage near the cathode, free electrons escape from its spot and fly to the anode. Due to the bombardment of electrons, the cathode is intensively heated.
Power supplies
A transformer is a power source for an electric arc . The voltage of the current supplied from the network is changed by adjusting the distance between the primary and secondary windings: proximity reduces the inductive reactance and increases the current. Removal reduces it. The winding connected to the network is primary, to the holder and the welded product is secondary.
Approximate cost of transformers. Yandex Market
Electrodes used
When welding with direct and alternating current, different electrodes are used; the first ones are marked with the letter abbreviation UONI, the second - MR. Both are coated with a special coating for welding steels:
- carbon and low-carbon structural;
- alloyed structural;
- alloyed heat-resistant;
- highly alloyed with special properties;
- for surfacing surface layers with special properties.
The thickness of the coating is directly dependent on the ratio of the diameter of the electrode to the diameter of the steel core:
- with a thin coating, ratio less than 1.20;
- with average, D/d between 1.20 and 1.45;
- with thick, D/d between 1.45 and 1.80;
- with particularly thick ones, D/d more than 1.80.
The composition of the coating is marked as follows:
- sour – A;
- cellulose – C;
- rutile - P;
- main – B;
- others - P.
Mixed coverage is marked by a combination of symbols corresponding to it.
Another marking is based on the position of the electrode in relation to the surface of the part:
- for all – 1;
- for all except vertical – 2;
- for lower, horizontal to vertical welding plane and vertical from bottom to top – 3;
- for the bottom and bottom in a boat (welded surfaces at right angles) - 4.
Approximate cost of electrodes. Yandex Market
Selecting other welding parameters
Wire feed speed is directly related to welding current. When the feed speed changes, the welding current also changes accordingly. The voltage must match the welding current and wire feed speed. Only in this case is it possible to ensure welding stability. But when problems arise, it is often very difficult to assess which parameter was selected incorrectly and in what direction it needs to be changed in order to achieve good results.
There are a number of signs by which the discrepancy between parameters can be assessed. For example, the arc voltage is too low if:
- the arc makes too much noise,
- the metal is spattering too much,
- the seam turns out to be very narrow, and the head is high.
On the contrary, too high arc voltage can be recognized by other parameters:
- the noise produced by the arc is muffled or almost inaudible,
- the arc is too long,
- the seam is too wide and low,
- when using filler material, large droplets are formed,
- a large undercut appears.
To obtain good results, a number of tables and guides have been developed to help with the work. Help for welders is provided by welding machines with a built-in function for determining the required voltage for a given speed and welding current. But even with this function, sometimes additional voltage adjustment is required. This is due to differences in the characteristics of the filler material from different manufacturers.
In some cases, it is not possible to accurately adjust the arc voltage in relation to the wire feed speed. Fine adjustment is made by changing the wire feed speed, not by changing the voltage.
Manual arc welding technology
Before the main process, preparatory work is carried out, without which the weld will not be of high quality: straightening, cleaning, marking, cutting and assembly. Ignition of the arc between the electrode and the product is performed in two steps: touching the surface, short circuit, and separation at a distance equal to the diameter of the electrode. They light it in two ways: end-to-end and by striking. In the first case, the metal is heated at the point where the short circuit occurs, in the second - in several places.
After ignition, the electrode and base metals begin to melt, and a melt pool is formed at the weld site. The welder’s task is to maintain the arc length constant , the quality of the connection depends on this. The optimal arc length is from 0.5 to 1.1 times the diameter.
The angle of inclination to the surface provides a sufficient depth of melting of the welded parts. It also depends on the thickness and composition of the metal, the diameter of the electrode, the thickness and type of coating, and the location of the weld in space.
Preparation of edges for welding
Edge cleanliness and configuration are a very important part of the welding process. As for the configuration of the edges, they can be flat, V-shaped and X-shaped. The first ones are most often used for joining thin workpieces, the second and third ones for thick ones.
Edges can be trimmed using hand tools or machines. This is, so to speak, a cold option. Thermal - using burners manually or automatically. Cold edge preparation is the cutting of profile chamfers. For large workpieces, milling machines are used; chamfers for small parts are made with various hand tools. It should be noted that cold-made edges are of higher quality. At the same time, the assembly accuracy of the welded structure is several times higher. Chamfers after heat treatment sometimes need to be modified to the desired shape and size.
As for cleanliness, it must be noted that any metals that come into contact with air begin to oxidize. An oxide film is formed on the surface of the welded surfaces, which is heat-resistant. So you need to get rid of it. Therefore, before starting welding work, the edges and adjacent areas are cleaned with an iron brush manually or using a grinder. If the ends of the welded edges have stains of oil or grease, then rule number one is that all this must also be degreased using any solvent.
In industrial conditions, cleaning can be done with sand or shot blasting machines. And dry cleaning involves immersing parts in a bath of chemicals, where the workpiece must lie for a certain time. There is also a jet cleaning method, when chemical solutions are applied to the chamfers with a jet under pressure.
Typically, chemical cleaning of metal workpieces is carried out when preparation of workpieces made of non-ferrous metals is needed, and mechanical cleaning for ferrous steel parts.
What affects the quality and size of the weld
These two indicators depend on the choice of welding mode:
- diameter and angle of inclination of the electrode;
- speed;
- arc voltage;
- welding current.
The diameter of the electrode is selected based on the thickness of the metal and the types of joints and seams. The quality of the seam is significantly affected by the length of the arc. In practice, its optimal value was determined to be 2-8 mm.
The welding current is set depending on the diameter of the electrode.
Section “Control of welding work and welded joints”.
The section should contain types of control (input, operational), scope and methods of control (visual and measuring, ultrasonic, radiographic, etc.), quality assessment standards, types of tests. The section should define the procedure (methodology) for control and standards for assessing the quality of welded joints. The types and scope of control, quality assessment standards should be determined in accordance with the design documentation. If necessary, it is necessary to determine the scope, types and methods of mechanical testing of tolerance samples, types and procedure for testing the welded structure.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of manual arc welding include:
- simplicity of the process, compactness and mobility of equipment;
- ability to work in different spatial positions;
- welding in hard-to-reach places.
Disadvantages:
- dependence on the qualifications of a specialist;
- low efficiency compared to automated processes;
- harmful effects on the welder’s body.
View this post on Instagram
How to get a job as a welder