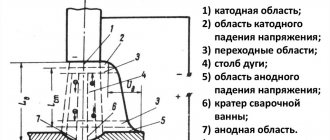
Regulations
State and industry standards, as well as methodological instructions, help to implement such a complex technological process, which is welding work. They contain sections that regulate safety measures when carrying out welding work.
This plays an immeasurably important role when connecting metal parts at hazardous production facilities. You should be guided by the requirements of the regulatory standard of the FNP, which is deciphered as “federal norms and rules.”
This regulatory document contains more detailed information about what safety rules exist and how they must be followed when welding. This document defines the requirements not only for workers who are directly involved in the welding process, but also for the managers of these works.
Safety rules for welding work stipulate that production facilities engaged in such work must have the required number of competent workers. Welders called upon to perform specific work must first be familiar with the technological map, which also contains a section that regulates labor safety during welding work. Drawing up a technological map is the responsibility of process engineers.
Only those workers who have completed the appropriate courses and received a certificate indicating the assignment of the title of welder indicating the rank may be allowed to carry out welding work. Regardless of what category they are assigned, they must be able to comply with safety requirements when performing welding work.
One of the main safety instructions when welding is the absence of medical contraindications for performers of this process. This is facilitated by regular examinations, including for prevention. Safety during welding operations is the responsibility of those in charge of these processes. They must have specific knowledge confirmed by the documents issued to them.
The task of welding managers is to prepare for this dangerous type of activity and competently select suitable performers. If an emergency situation arises, the work manager must take immediate action without delay. Safety precautions when working with welding require that only those workers who are over eighteen years old, who have completed training and received a certificate, can be allowed to perform this type of work.
Regardless of qualifications, before starting work, the welder must listen to an introductory briefing that will cover the features of this work. If the welder was allowed to work, but felt a sudden deterioration in health or an accident occurred, then the work manager must be immediately notified about this, who is obliged to urgently take all necessary measures.
If an unusual situation occurs, you should immediately turn off the equipment you are using. If there is a fire, use a fire extinguisher. Requirements for welding work include the presence of exhaust ventilation that is in good working order.
One of the fundamental regulatory documents to ensure safety during welding also includes GOST 13.3. 003-86. It outlines the safety requirements when carrying out welding work. These rules can also include the requirements set out in Chapter 22 of the regulatory document RD 153-34.0-03.301-00.
Possible dangers
A welder faces various dangers in his work. This is explained by the fact that the welding process can only be carried out when the metal is strongly heated, at which its melting temperature is reached.
Possible hazards facing a welder include:
- Electric shock if not grounded.
- High voltage.
- Evaporation of gases harmful to breathing.
- Getting entangled in a long cable.
- Injury due to a flying piece of slag.
- Impact of ultraviolet rays on the retina of the eyes.
- The occurrence of a fire.
- Increased noise, which negatively affects the auditory organ.
- Strong heating of objects that are placed near the burning place of the welding arc. Contact with them may cause burns to the skin surface.
- Welding spatter of metal landing on unprotected skin.
- Light irradiation.
- Explosion of a gas cylinder.
- Ultraviolet radiation.
- Poor ventilation.
- Falling down when working at height.
- Injury due to insufficiently good fixation of large mass elements being welded.
- Radiation damage due to some types of connection control.
- Damage to the respiratory system by harmful substances.
- Clothing catches fire when sparks hit it.
- Ignition of flammable materials in the immediate vicinity.
- Explosion of faulty equipment.
- Psychological overload due to excessive stress.
Following welding safety precautions will help reduce the likelihood of these events occurring.
Welding pipelines and other large round-shaped parts has an increased level of danger. To meet existing safety requirements, it is necessary to equip special areas that must be isolated.
If fixed pipes of large diameter are to be connected, then the use of special lifts is necessary. All metal parts and elements must be grounded. The welding area must have sufficient lighting.
Hazardous factors
Regardless of where welding equipment is operated - indoors or outdoors - there are always dangerous factors that affect both the welder and the people standing nearby. Protective equipment is needed not only by specialists, but also by assistants. It is worth considering, for example, that sparks from electrodes can scatter within a radius of up to five meters. You can catch the reflection of welding (the so-called “bunny”) from a distance of three meters.
There are many reasons that cause accidents and injuries:
- sparks easily burn through all types of fabric, except special ones, and can cause burns;
- the melt easily burns through modern shoes made from artificial materials;
- flammable materials may ignite in the area where sparks fly;
- hot fumes rise from the hot metal, which can injure the skin of the face or eyes;
- sparks can hit exposed skin and cause minor burns;
- Poor cable insulation may result in electric shock;
- if equipment or additional equipment explodes, fires may occur;
- poorly secured structural elements fall to the ground, injuring people;
- When performing welding work at height, the welder may fall.
Chemical and physical factors:
- operating welding equipment generates high levels of noise;
- infrared and ultraviolet radiation;
- when electric arc welding operates, blinding light is emitted;
- when working with metal alloys, lead, zinc, chromium, cadmium and other substances hazardous to the respiratory tract evaporate into the air;
- there is a high-temperature suspension with microinclusions above the bath;
- there is a high probability of thermal effects from a burner or electric arc.
Safety Basics
Welding safety rules:
- Concentration is required when carrying out the welding process. You cannot be distracted by extraneous matters.
- Do not keep flammable liquids, dry garbage, or oily rags nearby.
- Using a protective mask.
- Carrying or installing welded equipment to a new location is possible only when it is disconnected from the power supply.
- When working at height, it is necessary to use safety harnesses to avoid falling.
- Working outdoors is prohibited during precipitation.
- At sub-zero temperatures, it is necessary to have heating devices to prevent frostbite on your hands.
- When repairing vehicles, it is necessary to check the battery disconnection.
- During long breaks, disconnect electrical equipment from the network. Switched on devices must not be left unattended.
- Operating with faulty devices is unacceptable.
- The work place should be well lit.
- Reliable fixation of welded metal structures.
- Unauthorized persons and animals are not allowed at the welding site.
- Availability of necessary equipment. Avoid wet clothing and exposed skin.
Such safety rules for welding work must be observed by professional workers even when beginners carry out independent welding.
What hazards exist on the site?
There can be quite a few different hazards on a work site. When taking them into account, safety precautions are developed. The use of special equipment determines the following:
- There is a high risk of electric shock. If welding equipment is used incorrectly, current can spread through metal workpieces.
- Welding safety precautions are developed taking into account the likelihood of heat injury. At the time of welding, the workpiece is heated to high temperatures, the metal becomes liquid. If it comes into contact with an open area of skin, a burn may occur.
- If the elements being connected are not securely fastened, injury may occur. Fixation is also required in order to obtain a high quality seam.
- The resulting arc results in a bright flash. It can cause vision damage.
- When heating metals and various alloys, harmful gases can be released, which should not enter the respiratory tract.
Injury due to poor welding safety practices
In some cases, there may be other hazards on the site. An example is the case of using a cylinder with an explosive substance.
Premises requirements
Occupational safety rules when carrying out welding work include special requirements for the room where this process will take place. One of the main requirements relates to the presence of ventilation. If it is absent, then it is necessary to use respirators to protect the respiratory system.
Safety issues are especially important when performing gas welding, since in this case flammable gas cylinders are used. Safety precautions for gas welding and cutting require the presence of a special place in the room where flammable gas cylinders will be stored. Each such place must be isolated.
Great demands are placed on the illumination of the workplace. Sufficient access to light must be provided to the work area. The organization of the workplace is arranged in accordance with the recommendations of the NOT. If work is done at a workbench, then there should be a protective canopy on top. The welding room must be equipped with proper exhaust ventilation. There should be a rubber mat under the welder's feet.
Regardless of the size of the welding room and its location, the following requirements are imposed on it in order to ensure safety precautions when performing welding work:
- electrical wiring and water supply must be of high quality and be in good condition;
- changing rooms and bathrooms must be provided for workers;
- the walls of the room must be covered with a material the main requirement of which is that it is not prone to fire;
- the floor of the room must be made of concrete;
- the length of the cable should exclude the possibility of entanglement in it;
- good lighting, both natural and artificial, must be available;
- the room must be equipped with a reliable exhaust system;
- The welding room should not have high humidity;
- there must be a fire alarm;
- It is necessary to have a first aid kit with disinfecting and dressing materials;
- for quick evacuation in the event of an emergency, free passages must be organized;
- When carrying out gas welding, there must be free space so that the cylinders are located at a sufficient distance from the welding site.
Safety regulations for welding work must first of all provide that this type of activity has an increased risk of fire and fire.
An important point is what requirements apply to the storage room for welding materials. Electrodes, spools of wire, and flux are stored in warehouses. To keep them in proper shape and working condition, the storage room must be dry and protected from precipitation. It must have sufficient lighting, ventilation and heating. The temperature should not fall below fifteen degrees. Humidity should not exceed 40%.
When storing gas cylinders, drafts should be avoided. The walls of the room in which gas cylinders are supposed to be stored must be covered with fire-resistant material.
The floor of the warehouse should not be slippery. To protect the cylinders from falling, they are installed in cages or nests. During storage, the caps of the cylinders must be protected, and there must be plugs on the valve fittings.
Measures aimed at preventing potentially dangerous situations
- Organizational. Training personnel in fire safety rules, familiarization with the necessary instructions on labor protection and fire safety techniques, conducting training evacuations in case of fire, successfully passing state fire supervision inspections, audits, fire prevention measures.
- Regime. Smoking ban in unauthorized places.
- Technical. Compliance with the rules for installing welding equipment, ventilation, grounding, etc.
- Operational. Compliance with the rules for using welding and other equipment.
During construction and installation work, there are the following types of equipment for fire protection.
- Fire trucks
- Fire extinguishing installations
- Fire alarm
- Fire extinguishers
- Fire equipment
- Manual equipment
- Rescue devices
Types of fire extinguishers
- Gas
- Foam
- Powder
Gas fire extinguishers are divided into carbon dioxide and carbon dioxide-bromoethyl. Carbon dioxide is used as a fire extinguishing agent. Foam fire extinguishers are used to extinguish fires that have just begun, solid objects, and flammable substances. Their use is unacceptable for extinguishing electrical networks, as well as when extinguishing alkali metals (the interaction of these metals with water from foam will only intensify the fire). Powder fire extinguishers are available with powder for general purposes to extinguish fires of categories A, B, C, E, as well as for categories B, C, E.
The fire safety instructions must contain the following information
- List of names of operations related to hot work.
- List of persons permitted to perform hot work.
- The procedure for obtaining access to hot work, responsibility for violating this procedure.
- Stages of hot work.
- List of prohibitions when carrying out gas welding work.
- List of actions that are not permitted in places during welding work.
- Actions of the work performer in case of fire.
Let's look at the basic fire safety rules using the example of construction work.
- Before starting welding of vessels that previously contained explosive, flammable substances, gases, they must be thoroughly cleaned, washed, and dried.
- Do not weld newly painted parts until they are completely dry.
- When welding, do not use gloves smeared with oil, gasoline or other flammable substances.
- Do not allow electrical wiring to come into contact with gas cylinders.
- The person responsible for safety must check that all rules are followed before, during and after welding work.
- Acetylene generators are installed at a distance of 10 meters from the place where welding is directly carried out.
- When using an acetylene generator, be sure to post signs with the warnings “NO SMOKING” and “NO TRESPASS ENTRY.”
- Calcium carbide must be modified after welding with an acetylene generator. Lime from the generator must be placed in a special container or in a special pit. There are open sludge pits and closed ones. In open ones, special railings must be installed, in closed ones there must be fireproof partitions, ventilation and hatches for removing silt.
- Gas-conducting hoses must be secured with special clamps or wire.
- Gas cylinders must be stored and transported only with special safety caps, and sudden shocks must not be allowed.
- To open the calcium carbide drum, special tools are used: a chisel with a hammer or a knife. Already open drums must be closed with a lid with a special requirement for the height of the side of the lid, it must be at least 50 mm.
- The container with calcium carbide should be stored vertically in well-ventilated areas. These should not be basements or low rooms.
Calcium carbide
- Electric welding work is carried out in rooms with good ventilation.
- Floors and walls in rooms where electric welding is carried out must be made of non-flammable materials.
- Welding equipment at the welding site must be provided with fuses.
- Conducting wires must be insulated and flexible. Do not use bare, uninsulated wires. The wire must be capable of carrying the required current.
- Electrical wiring of welding devices should be located at a distance of at least half a meter from oxygen pipelines, and at least one meter from gas wiring. This distance can be halved if the gas wire is located in a special protective metal pipe.
- The electric holder for manual welding should be lightweight. Its design must ensure prompt replacement of electrodes and prevent short circuits. The handle of the electric holder must be made of non-flammable material.
- Electrodes for welding must comply with the GOST standard and be factory-made.
- Remains of electrodes after welding must be thrown into a special metal bag.
- The welding machine must be grounded, the generator and transformer, if work is performed outdoors, must be located in places protected from moisture, as well as under canopies made of non-flammable materials.
- The welding device must be cleaned and repaired regularly.
- Do not allow the torch to be left while the arc is burning.
- When soldering, the work site must be cleared of flammable substances.
- Blowtorches should be checked monthly for serviceability and pressure tested once a year.
- You cannot use gasoline for a kerosene lamp, you cannot mix gasoline with kerosene; pour more kerosene into the lamp than three-quarters of the volume.
Before the process starts
Before starting the welding process, it is necessary to carry out preparatory operations. Safety requirements for welding work require checking the equipment used. Safety precautions when working with welding equipment involve an external inspection and verification of its performance. Working with faulty devices is strictly prohibited.
It is necessary to check the presence of reliable grounding to eliminate the possibility of electric shock, as well as to exclude a short circuit. The integrity of the cable insulation should be checked. Excess debris and oily rags must be removed at a distance of five meters from the work site.
It is necessary to exclude moisture from the floor in the room and ensure that the clothes and shoes used are dry. You need to make sure you have a fire extinguisher. Securely fix the metal structures to be welded.
Prepare a container of water to cool the instruments. Try on the tightness of the mask on your head. Make sure there is free access to the welding site. If it is carried out on the street, then this place should be fenced off with identification signs.
If the work is carried out at height, then you need to make sure that the devices on which the welder will climb and carry the equipment are stable. In industrial production, before starting work, you must listen to instructions on ensuring the safety of a specific job.
Such actions will greatly ensure safety during welding work and prevent the possibility of unpleasant problems.
To gain access to the site, an employee must?
When hiring, all future employees are subject to certain requirements. Safety precautions when welding must be observed. Among the features of employee access to the site, we note the following points:
- Knowledge of safety precautions related to the supply of electricity must be checked.
- Only persons over 18 years of age may be allowed to perform welding work and enter the work area. At the same time, they must undergo training and obtain the appropriate permit.
- Proficiency testing may be carried out from time to time.
If a future employee does not have the appropriate education and skills, then he should not be allowed to work. The welder must also prevent strangers from entering the work area, as they may also be harmed.
electrical safety
Safety precautions when welding include strict adherence to work rules. Electrical safety during welding is an integral part of this type of activity. It must be remembered that injury can result from electric shock if its value exceeds 0.05 Ampere. Voltages greater than 110 volts are dangerous to life. Safety precautions during manual arc welding are of particular importance.
When performing the welding process, you must follow the welding rules:
- To illuminate the workplace, use a current of 12 Volts. You can use a small transformer for this.
- All equipment must be reliably grounded or connected to zero. This check must be carried out before switching on.
- The maximum open circuit voltage of the welding machine is 90 Volts.
- Wires must have reliable insulation. The presence of burns, cracks and other mechanical damage in it is unacceptable.
- If the insulation is damaged or the cable breaks, contact is allowed only by connecting the two ends with couplings.
- The length of the connecting wire should not exceed ten meters. Cable twisting is not allowed.
- Power supply must be provided through the distribution board. It must be equipped with fuses.
- When moving welded equipment, the wire should not come into contact with water or oil.
- During long breaks, electrical equipment should be disconnected from the electrical network.
- If the welding machine is exposed to rain, work can begin only after it has completely dried.
Electrical safety when performing welding work is the key to the success of this process. Due to the open nature of the process, safety precautions during electric arc welding are of particular importance.
Clothing and special protective equipment
The welding arc is a source of radiation with different wavelengths. Both ultraviolet and infrared waves are present here. The brightness of these waves is quite high. In addition to these risk factors, it is worth considering that the arc burns intermittently, which causes contrast in the lighting.
Light radiation during welding can blind, ultraviolet radiation can cause corneal burns, and infrared radiation can cause clouding and cataracts. To avoid the negative effects of radiation, the welder must observe the work through a special protective glass. It protects the retina from light and UV rays, which can cause burns. Such glass should completely retain ultraviolet radiation and become a barrier to IR rays.
The rest of the body must also be protected: a mask, mittens and overalls are used for this. The most popular protective welding helmet is the “Chameleon”. It can be adapted to any type of welding and provides optimal visibility and reliable protection. Some models of masks are equipped with a special turbo unit, which pumps air under the mask, which ensures long-term continuous work of the welder.
According to safety requirements, it is necessary to protect not only the welder himself, but also the people who work in his vicinity.
The following requirements also apply to welder clothing:
- It must be in perfect protective condition and dry.
- Work must be carried out in special gloves.
- When exposed to drops of metal, the overalls should not smolder or burn out..
- Work is prohibited without protective headgear.
- It is advisable to use respirators for additional protection against gases released.
Thus, when working with manual arc welding, the welder must use personal protective equipment: gloves, mask, etc.
Gas welding
An increased danger comes from working simultaneously with electrical appliances and gas under pressure. Safety precautions for gas welding require strict adherence to existing rules, since the need to use flammable gas cylinders introduces additional danger.
Safety precautions for gas welding pay great attention to the rules of working with cylinders and the procedure for storing them:
- Gas cylinders can only be transported when they are in an upright position. During transportation, the valves are closed with protective caps.
- Before work, you should check the degree of filling of the gas cylinder. This will help avoid a sharp decrease in gas pressure.
- If popping noises occur as a result of a reverse impact, you should immediately turn off the gas.
- To ensure safety, hoses should be suspended during operation.
- The condition of the burner must be carefully checked. There should be no oil residues in it. The gearbox and injector are also inspected.
- During operation, you must constantly ensure that the gas pressure remains constant.
- The distance between the working area and the gas cylinder is at least five meters.
Safety precautions for argon arc welding, which is a progressive method, also require strict adherence to these rules. An important question is at what distance the welding cables should be located from the cylinders.
In this case, the following criteria should be adhered to:
- cylinders should be placed no closer than five meters from the location of the heating devices;
- the distance from the welding site to the gas cylinder is at least ten meters;
- Electrical cables and wires should be located at a distance of half a meter from the oxygen line and at a distance of one meter from the acetylene line.
The gas cylinder must be checked for leaks before starting work.
Causes of fires
Negligence is the main cause of industrial fires
There are two hazards to consider: equipment and human factors. A person who picks up a welding machine must understand that it is necessary to follow certain fire safety rules. Reasons for human character:
- cluttering of the 5-meter working area with flammable materials and liquids;
- carrying out work in an unprepared space;
- inept handling of the tool;
- the use of blowtorches to heat metal;
- negligent inspection of equipment before work.
Possible technical reasons:
- unstable voltage;
- faulty equipment;
- wide zone of hot metal splashing;
- unreliable electrical wiring;
- lack of fuses in the power supply system;
- corrosion damage to the welding holder;
- violation of the rules for transporting gas cylinders, heating them in the sun;
- water seal malfunction;
- oiling of the oxygen cylinder fitting;
- increased working gas pressure.
Fire safety
Safety precautions during welding work include fire safety. A phenomenon such as fire can occur both during industrial production and during individual work. To prevent a fire, all measures must be taken. This includes not only the procedure for carrying out welding work, but also preparatory operations.
In this sense, manual arc welding is particularly dangerous. Sparks in this type of welding process scatter over a considerable distance, reaching up to five meters. A fire may occur in the place where they fly. When performing welding work, TB strongly recommends that before starting the welding process, conduct a thorough inspection and clean up nearby flammable materials, oily rags and dry debris located at a specified distance.
If welding is carried out in a carbon dioxide environment, then splashing of the metal in a hot liquid state becomes possible. When using the gas option, the burner will become a source of increased danger. During electric welding, hot pieces of metal can fly a considerable distance and create a fire hazard there. If they come into contact with flammable substances, a so-called “silent fire” may occur. Over time it will begin to gain strength.
Potential causes of fire include faulty electrical wiring. If the safety precautions for welding with gas cylinders are violated, then there is a danger of their explosion, and, as a result, a fire. It can also be caused by flying sparks.
The presence of a human factor cannot be rejected, for example, if the smoking ban in the workplace is violated. Violations include improper transportation of gas cylinders. Their delivery to the work site must be carried out using a special trolley. If carried by hand, they may fall, causing an explosion. Cylinders should be located away from heating, and when working outdoors, in the shade. Exposure to sunlight on gas containers is unacceptable.
The necessary measures to ensure the safety of welding work in terms of the possibility of a fire can be divided into:
- Organizational . These include briefing and familiarization with the technological map for a specific welding process.
- Technical . Consists of preparing equipment and consumables.
- Operational . Consists in the correct choice of operating modes.
Important fire-fighting measures include preparatory operations. They consist of properly equipping the workplace and clearing it of unwanted elements.
When working indoors, make sure that the exhaust ventilation is working properly. A fire extinguisher is required at the welder's workplace. The welding area must be fenced. The height of the partition must be such that sparks and splashes cannot fly through it. When working outdoors, the welding area should be fenced off and warning signs placed on the fence.
If a fire occurs, for example, in the event of an electrical fire, the area should not be filled with water, but rather a fire extinguisher should be used. There are different types of them. Universal fire extinguishers include powder ones marked “D”. In addition to fire extinguishers, it is advisable to have a box of sand, a shovel and a mound at the welding site.
To quickly evacuate people in the event of a fire, it is necessary to clear passages. If all fire safety regulations have not been met, then it is prohibited to begin the welding process. Fire safety includes requirements for personal protection of the work operator.
Occupational Safety and Health
INSTRUCTIONS
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS FOR MANUAL
ELECTRIC ARC WELDING (FOR WORKERS)
1.1. Persons who have reached of 18 , who have undergone a preliminary medical examination, appropriate training, instruction and testing of safety knowledge with registration in a special journal, who have an electrical safety qualification group of at least II degree and an appropriate certificate are allowed to perform electric welding work.
1.2. a category of at least III are allowed to carry out steeplejack welding work at a height of more than 5 m from the surface of the ground or ceiling using a safety belt .
Women are not allowed to do this work, as well as work in confined spaces (wells, tunnels, inside pipelines, boilers, closed containers).
1.3. Welders who work in confined spaces or weld non-ferrous metals must undergo a medical examination with a chest x-ray, blood and urine tests once a year.
1.4. Welding at temporary workplaces can only be carried out with the written permission of the persons responsible for fire safety at this construction. And in confined and hard-to-reach spaces, near gas pipelines, in existing fire and gas hazardous workshops, workers who have undergone additional training, passed an exam and received a written permit may be allowed to cook.
1.5. You can only perform the work that has been assigned by your immediate superior (foreman, foreman) and provided that you know the safe methods for performing it. It is prohibited to carry out orders if they contradict the rules of occupational safety and health.
2.1. Before starting work, you must be briefed by your supervisor on the rules for the safe performance of specific work, study the working documentation, obtain protective equipment and, if necessary, a work permit, indicating where to attach the carabiner of the safety belt. Make sure that your workplace is equipped in accordance with the requirements of the work project and safety regulations.
2.2. The workplace should be fenced; If it is on the roadway or in aisles, install warning signs. Welding can be carried out no less than 10 m from gas cylinders, flammable and explosive acetylene generators.
2.3. Before performing work at a height of more than 1.3 m from the ground level of the floor or tier, you must make sure that the workplace is equipped with working scaffolding, a cradle or scaffolding with railings at least 1.1 m high and a side board 150 mm high; wooden handrails must be cut off, and metal ones must not have burrs, sharp edges, or uncleaned welds. Side boards must be installed on the deck, and railing elements must be attached to the posts from the inside.
2.4. To perform a small amount of work at a height of up to 3 m, you can use a special (assembly) ladder no more than 5 m long.
2.5. Work clothes and safety shoes must be put in order. The suit, mittens with leggings made of canvas canvas with combined impregnation must be intact, dry, and oil-free; boots with side fasteners, glued soles. Trousers - without cuffs, at the bottom - wear only untucked. Close the jacket pockets with flaps and tie the ends of the sleeves with ribbons. Cover your head with a regular headdress or, if necessary, a helmet with shoulder pads. When working on metal surfaces, use a rubber mat, knee and elbow pads lined with felt, and rubber galoshes.
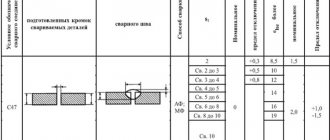
2.6. The protective shield (or mask) must be free of cracks and crevices. Protective glass should be selected depending on the intended welding mode:
at a current of 60 - 15 A - S-5;
150 - 275 A - S-6;
275 - 350 A - S-7.
It is prohibited to use filters made by painting.
2.7. Remember that mittens, special clothing, safety shoes, a shield or mask and other protective equipment that have become unusable ahead of time must be promptly repaired or replaced intact and in good working order.
2.8. For work, you should use a lightweight and convenient standard electrode holder with an insulated handle, which ensures reliable clamping and quick change of electrodes without touching live parts, ensuring a strong connection with the welding wire.
2.9. Make sure there are fire extinguishing means near the workplace.
2.10. It is necessary to organize the workplace in such a way that there is at least 10 m for the wires between the power supply network and the mobile power source.
2.11. Make sure that the current source is technically sound, and there should be corresponding entries in its registration log. There should be no obvious damage to the device, the terminals should be covered with terminal boxes, etc.
2.12. The housing of the current source (including the unit for welding in field conditions, the terminal of the secondary winding of the transformer must be reliably grounded or grounded / solidly grounded in networks /. The grounding wire is copper with a cross-section of at least 6 mm2 (iron 12 mm2). If there is no standard grounding circuit, as grounding, you can use a steel pipe with a diameter of 37-50 mm or a strip with a thickness of more than 4 mm and a cross-section of 48-50 mm2, 1-2 m long, burying it in the ground and connecting a grounding wire to it. It is prohibited to use a grounding loop, railway .paths, process equipment, pipelines and other non-weldable structures as a return wire.
2.13. Reliably insulate the welding and return (“welding ground”) wires and ensure they are firmly connected to the terminals of the power source. Remember that the wires should not be intertwined with gas hoses and cables (the distance between them must be at least 1 m).
2.14. It is not allowed to connect or disconnect welding equipment to the network yourself, or to repair it. This work must be performed by electrical personnel.
2.15. Before working on used vessels, it is necessary to clarify what they were filled with. If it was a flammable liquid, you must require that the vessel be cleaned, washed with water and steamed, or washed with a caustic soda solution and then purged. Then, in all cases, the vessel must be filled with water to the maximum possible level, and all upper hatches and valves must be open.
2.16. Before putting into operation a unit driven by an internal combustion engine, check the serviceability and tension of the fan and regulator belts (the deflection between the generator and fan pulleys should be no more than 12-15 mm2, and between the fan and regulator pulleys - 10-12 mm2). It is strictly forbidden to work with the unit if the connection of the speed controller rod with the levers and the throttle valve is unreliable, the governor bracket is cracked or broken, the fastening of the fan hub to the water pump shaft is loose, as well as without a protective casing on the generator shield on the collector side.
Fuel can only be poured into the tank when the engine is not running. You need to check for fuel leaks from the tank and gas line.
2.17. In places where the formation and accumulation of harmful gases is possible, ventilation must be installed or a respirator, gas mask, or hose gas mask (with air supply to the breathing zone) must be used.
2.18. It is strictly forbidden to start welding vessels under pressure.
2.19. Require that the metal be cleaned of paint, oil, dirt, and rust before welding.
2.20. Workplaces must be equipped, in addition to general lighting, with local lighting: stationary 36 V lighting and portable 12 V lighting.
3.1. Do not weld in open areas during rain, snow and thunderstorms.
3.2. Welding outdoors is permitted at temperatures below minus 30°C. Require heating options near work areas. It is not allowed to work at height when the wind force is 6, and when installing blind panels - 5, as well as when there is ice.
3.3. When welding in confined and hard-to-reach spaces, you must wear a safety belt with a safety rope, the other end of which is located at one of the workers at the control post with a qualification group of at least II. Control station workers must be trained to assist the welder in the event of an accident or malfunction. Workers at the control post must constantly monitor the work of the welder. The simultaneous work of electric and gas welders (gas cutters) in these conditions is prohibited. The welding installation must have an idle speed limiter that reduces the voltage on the holder to 12 V when the arc breaks. Work in such conditions should be carried out only with a permit and all the necessary protective equipment (dielectric galoshes, gloves, mat).
3.4. If you have to weld galvanized metal, it is necessary that the suction or blowing away of the smoke by the wind occurs to the side. It is recommended that before welding (15-20 minutes before) apply FP-Ts flux paste diluted in liquid glass in a ratio of 1:1 to the welded edges. Respirators (ShB-1 “Lepestok” and others) also protect against the effects of zinc oxide.
3.5. When working with another welder in the same cabin, it must be blocked off with shields. When working at different heights along the same vertical, it is necessary to install partitions that protect workers located below from metal splashes and from accidental falling of cinders and other objects.
Do not move welding machines that are energized.
4.1. When dealing with slag and metal splashes, only wear safety glasses with clear lenses.
4.2. Turn off the power source, disconnect from the source and remove the welding wire. Clean up the workplace and carefully check that there are no sources of fire.
4.3. Notify the foreman (foreman) about the completion of work, any malfunctions detected, and hand over the workplace to a replacement.
Equipment
The rules for carrying out welding work pay great attention to how the welder is protected. Safety measures when welding require full equipment, which will completely protect his skin and eyes from possible injuries. This applies to consumables.
The main requirement for safe equipment is that short-term exposure to a welding arc should not cause significant damage to it. The safety of a welder can only be ensured if he is wearing clothing, shoes and a mask. They must completely protect his skin from hot splashes, and his vision from the blinding light of the arc. Protective equipment must be of high quality.
The suit that a welding producer must wear is called a robe. This suit is made of fire-resistant material, as a result of which, even if hot splashes come into contact with it, it will not burn or ignite. When carrying out welding work at home, purchasing such a suit will be too expensive. Instead, you can simply use fairly thick clothing. The main condition is that it must cover all areas of the skin.
For this purpose, you should use canvas mittens for your hands. Even if it is not so convenient to work in them, you should understand that the welder’s hands are at the epicenter of danger. Feet should be protected from sparks by durable shoes with thick soles. It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that clothes and shoes fit the specific welder. They must match his height, build and foot size.
Safety precautions during welding work regulate the mandatory presence of a protective mask as the main and integral attribute of the equipment. Making it yourself is very problematic, but there is a wide range of this protective accessory on sale. The function of the mask is to protect the welder's face and eyes from all possible damage.
Regardless of the method by which the welding process is performed, it remains dangerous and can cause significant damage to the worker. In particular, the welder's vision is at risk. Having a mask will prevent sparks from the arc from hitting the welder’s face, neck and, most importantly, eyes. The mask provides protection from both ultraviolet radiation and infrared radiation. The mask also provides protection against unauthorized contact of hot metal particles and harmful fumes on a worker’s skin and eyes.
The mask should be considered an integral part of the welder's equipment. This does not depend on whether he already has extensive experience or is new to this matter. It is important not only to choose the appropriate type of mask, but also to decide on its size. You should select a mask for a specific person’s head. It should sit tightly on your head, not fall off, but not squeeze either.
The welding helmet has a viewing window that is transparent. Through it, the welder has the opportunity to observe how the welding process is progressing. The viewing window is covered with thin plastic or tinted glass. The most basic types of masks include welding glasses.
Outwardly, they are similar to ordinary glasses, distinguished by the presence of special glasses, the coating of which is mineral glass or polycarbonate. A variation is closed welding glasses. In them, fixation on the welder’s head is carried out using an elastic band. Most models of these glasses have anti-fog protection. The advantage of welding glasses is their low cost, but the disadvantages include the fact that part of the welder’s face and neck remains unprotected.
A more expensive, but incomparably better option are protective masks. The advantages of using welding masks include their complete protection of the wearer’s face, eyes and neck. Of the available options, it is recommended to give preference not to those masks that need to be held in the hand, but to those that are attached to the head.
It should be taken into account that during the welding process, regular inspection of the intermediate results of the work performed is required, as well as the need to replace the electrode. You have to take off the mask or lift it, which causes some inconvenience. Protective masks called “Chameleon” do not have this drawback.
The Chameleon's automatic window tinting adjustment solves the problem of having to remove the mask from your head at the right moments. This option makes the welding process more convenient. The Chameleon mask has a crystal-based light filter in the viewing window. It has the property of transmitting only visible rays, and blocking ultraviolet and infrared rays.
The “chameleon” sits tightly on the welder’s head, but there is no unnecessary tension. This happens thanks to the existing voltage regulator. The mask thoroughly covers the neck. The available ventilation helps to protect the glasses of the mask from fogging.
The auto-dimming control performs the main important function. It is thanks to the presence of this regulator that the welder does not have to remove the mask from his head every time, since the mask device itself has the ability to monitor the light level. This is possible due to the presence of polarizing filters in it.
When the welding process begins and a bright arc flashes, the viewing glass of the mask becomes as dark as possible. After exposure to bright light stops, the glass becomes transparent and through them you can look at the results of the work done or replace the burnt electrode with a new one. The filter also reacts sensitively to small changes in the brightness of the arc.
The advantages of the Chameleon mask include light weight and the possibility of a wide view. Working with masks of this type ensures the greatest possible safety.
Means of protection
According to safety regulations, the welder must wear special clothing when performing electric welding. The company provides him with protective clothing. It is purchased in specialized stores and must meet a number of requirements.
Welder clothing is made from non-flammable, natural materials. Synthetic fabrics cannot be used. The most common suits are made of canvas, split leather or suede. When cooking in harsh winter conditions, you can wear cloth clothing.
To protect hands, the welder is equipped with protective gloves or mittens. The most reliable protection is provided by work gloves made of split leather or suede. The tarpaulin quickly burns out, and such gloves often do not withstand even one shift.
Shoes are made from various materials. The most common are tarpaulin boots and boots. The sole can be rubber or other more modern materials.
When choosing shoes for welding work, experienced welders give preference to soles without shoe nails. Otherwise, even with minimal humidity, the welder will experience discomfort, especially a specialist with a reduced level of body resistance.
Protection of the face and organs of vision is carried out using a welding mask or shield. Many craftsmen try to make them themselves. But even a small gap in the structure can cause great harm to the eyes and skin.
Therefore, it is better to purchase a simple industrial mask for very little money than to walk around the apartment like a mole all night and put novocaine or albucid in your eyes.
The labor protection inspectorate and safety regulations place increased demands on the welding helmet.
According to the standards of GOST 9497-60, the light filter must provide not only the retention of harmful light radiation, but also the possibility of normal control over the weld pool and the position of the electrode. The viewing window must be of normal size and provide visibility for the welder.