Manual arc welding (also known as MMA, RD, RDS welding) with a carbon electrode was invented at the end of the 19th century by the Russian inventor Nikolai Bernardos. At the same time, the inventor patented his technology in many European countries. Later, he also invented resistance welding and gas-shielded arc welding.
Much time has passed since then, and the technology of manual arc welding has undergone many modifications. For example, among home craftsmen, it is not classic arc welding with a carbon electrode that has become widespread, but welding using consumable rods. Also, welding machines received many new functions, and metals with special properties began to be used in production.
Therefore, arc welding technology has become somewhat more complicated. In this article, we will tell you in detail what manual arc welding is, what are the advantages and disadvantages of this method of joining metals, and how RD welding of metal structures is performed.
general information
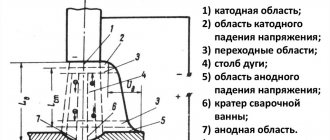
MMA manual arc welding (MMA is the common international name) is the process of forming a weld joint using an electric arc. The arc is ignited between the electrode and the metal surface, burns stably and forms an even seam. Electrodes for welding welding are made of metal wire and have a special coating that protects the welding zone from the negative effects of oxygen. The work uses electrodes up to 45 centimeters long.
In manual welding, the arc is ignited either by the tapping method (the welder taps the end of the electrode on the surface of the metal without using force) or by the striking method (similar to a matchbox). The arc melts the metal and the electrode melts at the same time as the workpiece. When the electrode melts, the metal is fused and a seam is formed. Minor metal spattering is acceptable.
Manual MMA arc welding using coated electrodes is one of the simplest types of welding. Hence there are many nuances in the work. With this welding method, working time is spent irrationally, a lot of effort is spent on forming a seam, and labor productivity decreases. Therefore, this technology is more in demand among home craftsmen than at a large factory.
But with the help of RDS you can surfacing shafts, welding many types of metals and relatively quickly repair metal products at home. Also, if you have experience and qualifications, you can make different types of seams, including labor-intensive ones, such as ceiling ones.
Main advantages and disadvantages of arc welding
The welding process occurs as follows: an electric arc is created, which must be placed between the product being welded and the electrode. The high temperature created by the arc is sufficient for the edge of the metal product and the electrode rod to begin to melt.
The metal of the product and the electrode goes into the liquid phase and mixes. This process is called a weld pool. Its dimensions are usually 8–15 mm in width, 10–30 mm in length and about 6 mm in depth. The electrode coating has such a chemical composition that, when melted, a gas region is formed above the weld pool, which does not allow the metal to interact with oxygen. After the action of the welding arc stops, the metal passes from the liquid phase to the solid phase, forming a strong seam between the parts being connected. The layer of slag that forms on top of the seam must be removed.
Advantages of arc welding:
- does not require complex training;
- high process productivity;
- low cost of consumables (welding electrodes);
- the simplicity of the process easily allows for its automation and mechanization;
- small surface heating area.
Disadvantages of electric arc welding:
- connection to the power grid;
- impossibility of working without current converters (rectifiers, inverters) and transformers;
- the presence of a preliminary stage of preparation of welded surfaces.
Advantages and disadvantages
It is not for nothing that manual arc welding with a consumable electrode is the most popular method of joining metals. With its help, you can perform simple repairs, form short strong seams, and carry out quick maintenance of some equipment. But that's not all the advantages.
Compared to other technologies, welding machines for RDS welding are inexpensive, they are compact and easy to use. Also, the work does not require additional protection of the welding zone with gas or flux, since the electrode copes with this task. Another plus is the ability to work in almost any conditions: on the street, in the workshop, in the wind, and under the scorching sun. And this is important if you need to make quick repairs in the field.
Do not forget that the RDS is suitable for welding a wide variety of metals: from carbon and alloy steels to cast iron, aluminum and copper. At the same time, the thickness of the parts can reach several centimeters and a powerful welding machine will cope with this task. It is also possible to weld in any spatial position, if necessary.
Now about the disadvantages. Metal workmanship requires frequent breaks in work. They are necessary to replace the melted electrode with a new one. And its consumption can be very high in the absence of experience or when welding thick metals. If the electrode has reached a length of 5 centimeters or less, it should be replaced immediately.
Manual welding using an electrode involves the formation of slag around the weld zone and seam. On the one hand, this is good, since the slag additionally protects the weld pool from oxygen. But after work, the slag must be removed from the metal surface. This process can be labor-intensive and time-consuming.
Because of these two disadvantages, manual arc welding is considered one of the slowest. It leads to time overruns and cannot be compared with competitors such as MIG welding. You must take this disadvantage into account.
Due to the fact that the electrodes cannot be fully used in the work, and it is customary to often replace them with new ones, there is an overconsumption of components. It turns out that no more than 70% of the electrode is used in the work, the rest is considered cinder. This fact increases the cost of work.
Despite its relative versatility, RDS cannot weld tin or zinc. And in general all metals with a low melting point. This is due to the fact that the heat input coefficient is too high when welding with an electric arc. Also, manual arc welding with a consumable electrode is not suitable for joining parts made of titanium, tantalum and any other metals with active chemical properties. The electrode will not be able to adequately protect the seam from oxidation.
Well, there is one last minus that needs to be mentioned. In manual arc welding, the current passes along the entire length of the electrode, and if the current value is too high, the rod may overheat and the protective coating will be destroyed. Because of this, you simply cannot set high current values in order to somehow speed up the operation. This is another reason why work speeds when manually welding metal structures may be slower than when using other welding methods.
Preparation of the metal surface for welding and requirements for the assembly of metal parts before welding
Preparation of parts for welding consists of straightening, marking, cutting, preparing edges for welding, cold or hot bending.
Metal straightening is performed on machines. Sheet and strip metal are straightened on various sheet-straightening rollers. Angular steel is straightened on roller machines. I-beams and channels are straightened on cam-type straightening presses.
Marking is an operation that determines the configuration of a future part. The use of marking and marking machines with a pneumatic punch ensures a marking speed of up to ±1 mm and allows the use of software control. The use of gas-cutting machines with a large-scale photocopying control system or program control allows you to do without marking.
Mechanical cutting is used for straight cutting of sheets, and sometimes for curved cutting of sheets when using roller shears with circular knives for this purpose. Carbon steels are cut by oxygen and plasma arc cutting. In terms of mechanization, these methods can be manual or mechanized. For cutting alloy steels and non-ferrous metals, oxygen-flux or flame-arc cutting can be used.
The form of preparation of metal edges for welding depends on the thickness of the sheets. Before welding, the base metal and filler material must be thoroughly cleaned of rust, oil, scale, moisture and various types of non-metallic contaminants. The presence of these contaminants leads to the formation of pores, cracks, and slag inclusions in welds, which leads to a decrease in the strength and density of the welded joint.
Requirements for the assembly of metal parts before welding. The assembly and welding devices used must ensure accessibility to the installation sites of parts, handles of fixing and clamping devices, as well as tack and welding areas. These devices must also be sufficiently strong and rigid, ensure precise fastening of the parts in the desired position and prevent them from deforming during the welding process. In addition, assembly and welding fixtures must ensure optimal assembly and welding order:
— the smallest number of turns when applying tacks and welds;
— free access to check the dimensions of products and their easy removal after production;
— safety of assembly and welding works.
Any assembly operation should not impede the next operation. Parts received for assembly must be carefully checked. All geometric dimensions of the part and the prepared shape of the edges for welding are subject to verification.
As a rule, the assembly of welded structures is carried out either according to markings or with the help of templates, stops, clamps, clamping mechanisms, stands or special jig devices that facilitate assembly operations. The assembly accuracy is controlled with templates, probes (Figure 36), as well as measuring instruments.
Figure 36 — Inspection of assembly for welding
The preparation and assembly of products for welding is carried out in compliance with the following basic mandatory rules:
— the blunting of the edges and the gaps between them must be uniform along the entire length;
- the edges of the elements to be welded and the adjacent areas 25 - 30 mm wide from the end of the edge must be dried, cleaned of burrs after cutting, oil, rust and other contaminants;
— in order to avoid deformations, tack welding should be performed with high-quality electrodes at intervals of no more than 500 mm with a length of one tack welding of 50 - 80 mm;
- to ensure normal and high-quality formation of the seam, it is necessary to grab the lead strips at the beginning and at the end of the product.
Welding Features
Understanding the principle of manual arc welding with a consumable electrode, you can begin the welding process itself. First, let's figure out in what cases such welding is advisable. RD for metal is advisable if the thickness of the part starts from 2 millimeters and does not exceed 50 millimeters. It is also advisable to weld alloy, carbon and stainless steels. RDS is perfect for small-scale production or for welding piece products. If the metals are thicker and there are a lot of parts, then we recommend replacing MMA welding with MAG.
If the parts are too thin, they will melt too quickly. This leads to the formation of defects; the seam simply does not have time to form. Even if you set the current to the minimum value. Use other technologies for welding thin metal, do not take risks.
We wrote above that welding of parts up to 50 millimeters thick is possible. But we still recommend connecting metals with a maximum thickness of 20 millimeters. Welding thick parts is not economically viable when using manual arc welding technology. All these rules do not apply to the situation where you need to weld a short seam to make a small repair. If the welding area is too small, you will not use expensive equipment, gas, fluxes, etc. In such situations, manual MMA arc welding is quite appropriate when welding parts up to 200 millimeters thick.
Manual arc welding technology starts with the basics about spatial position. We wrote that manual arc welding with a consumable electrode is possible in any position. This is true, but with reservations. The fact is that not all electrodes allow you to make complex ceiling or vertical seams. They melt too quickly and the flowing metal does not allow the formation of a seam. Please pay attention to this before performing important work.
For this reason, the best result is achievable in a lower or horizontal spatial position. Such work can be performed by a welder even with low qualifications; you can use electrodes of larger diameter and set a higher amperage on the welding machine to speed up the work process. So if you can replace the ceiling seams with lower ones, do not refuse this decision.
If you are using the manual arc welding method with coated rods and still need to make a ceiling weld, then select small diameter electrodes and set the welding current to the minimum value on the machine. Do not work slowly or quickly, try to find the “golden mean” in the speed of the arc. Lead the arc confidently and do not deviate to the sides.
Now let's talk about the type and polarity of the current. MMA welding can be performed continuously or alternatingly; the choice of mode depends on the electrodes. Be sure to read the packaging of your rods before use; some electrodes may only be designed to operate on one type of current.
One thing is certain - with direct current the arc burns more stable than with alternating current. This is noticeable even when using universal rods that can work with any kind of current. In short, if you are a beginner welder, then purchase universal components and experiment with the settings.
As for the polarity, its choice depends on what speed of melting of the electrode you need. If you select reverse polarity and set the current to constant, the electrode will melt more slowly and evenly. This is the most acceptable option. There are electrodes that work well with any polarity.
Manual welding of iron or nickel has its own difficulties. In operation, metal can be susceptible to a problem called magnetic blowing. Magnetic blowing is when the arc begins to involuntarily deviate from the weld pool due to the magnetic properties of the metal. To avoid these problems, install alternating current on your welder, this may help.
How does electric arc welding work?
The operating principle of such a device is to supply current from the inverter unit to a certain type of electrode. Closing the circuit at the moment of contact of the electrode with the surface being treated creates conditions for the occurrence of an electric arc.
After this, the arc melts the electrode and a weld pool of certain parameters is formed. At this point, a mixture of molten metal and electrode fills the crack or joint between the two workpieces.
Depending on the characteristics of the work, welding machines are of the following types:
- automatic - all processes for supplying electrodes and adjusting the power of equipment are carried out directly by the equipment without the need to carry out such activities manually;
- manual - the simplest units in design for work, with which the welder independently adjusts and controls the welding stages;
- semi-automatic – devices with a combined welding control system.
Selection of electrodes
Electrodes are as important as adherence to welding technology. The quality of the future seam largely depends on their correct choice. You need to select rods in accordance with the metal you are going to weld. Many characteristics of an electrode can be recognized by its markings. We talked about how to read the markings in this article.
When working with manual arc welding, pay attention to the properties of the electrodes you choose. Properties depend on the type of coating. Electrodes for RDS most often have a rutile or basic coating. We will not say which one is better. Let's just list their positive and negative sides.
Rutile-coated electrodes are often used by beginners because they are easier to ignite and maintain an arc. They are presented in a wide range, there are both budget and expensive brands. We do not recommend buying overly expensive electrodes for home welding, as they simply will not reach their full potential.
One of the disadvantages of rutile coating is the increased hydrogen content in the welded joint, which somewhat deteriorates the quality of the seam. But the metal practically does not spatter during welding, which is very important. For beginners, we recommend electrodes of the MP-3 brand, as they are one of the most affordable and widespread.
Basic coated electrodes are the choice of experienced professional welders. It is quite difficult to work with such rods, since the arc ignites reluctantly and must be very short during the welding process. All this requires experience. But if you are a beginner, do not be afraid to use such electrodes in your practice. This way you can learn faster. Basic coated electrodes provide excellent seam quality. If you need to weld relatively thin metal, then choose electrodes with a basic coating.
Electrodes are also selected based on economic factors. With such a slow welding method as RDS, it is important to know the deposition rate of the rod in order to determine how much time and electrodes will be needed to form the weld. There are special high-performance rods that make work faster. But, as a rule, they can only weld horizontal seams.
We wrote above that the electrode should be used at 70% percent, leaving approximately 5 centimeters of the rod. Some beginners deliberately overuse electrodes, using only half of them. Many people explain this by saying that they are simply worried about the length of the electrode and prefer to leave the rod with a reserve. We do not recommend doing this in our practice. You will have to interrupt welding even more often and change the electrodes with new ones.