When laying an individual sewer pipeline, it is necessary to comply with certain requirements regulated by building regulations. One of the most important conditions that must be met when installing a pipeline for drainage is a sewer slope of 1 meter.
Not every owner of a private house can afford to order an expensive project and install sewer lines from the relevant organizations. In many situations, the pipeline is laid on its own. At the same time, knowledge of basic standards will allow you to competently carry out all work in accordance with the technological process and ensure efficient and uninterrupted operation of the sewer system for a long time.
Option for installing an external sewer system for a private house
Why is slope needed and what does it depend on?
Unlike a plumbing system, sewage drainage through pipes is carried out due to natural gravity without pressure, so a slope is necessary for transporting it to the collection point.
The standards regulate the minimum slope values, established experimentally, taking into account various factors, so violation of the parameters in the direction of decrease will lead to incorrect operation and frequent blockages in the sewer system.
The angle of inclination of the sewer pipe depends on the following factors:
- Pipeline diameter: as it increases, the slope becomes smaller.
- Pipe material: when laying pipelines with a rough shell, due to high hydraulic resistance, the slope is made higher. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes used in the installation of individual household sewerage systems are considered hydraulically smooth; a concrete pipeline has the highest roughness.
- Sewer system designs: in a main line that has a large number of bends and turns, the hydraulic resistance is higher than that of a straight line; therefore, when laying it, a greater degree of slope is required.
Roughness of various pipes
Pressure sewer
The calculated data on the slope of the gravity sewer according to SNiP must be strictly observed for the normal operation of the sewer system. The essence of the work of pressure sewerage is to collect wastewater into a storage tank, and then transport it through a pump.
You can find out the maximum distance for pumping pressure sewerage using the SNiP recommendations, which contain all the necessary formulas and coefficients.
Advantages of pressure sewerage:
- The depth of the pipes is less than that of other sewer systems. But the level of soil freezing must be taken into account.
- It is not necessary to observe a sewerage slope of one meter, unlike external sewerage.
- The purpose of the system is to self-clean the inner shell of the pipe.
However, with such positive characteristics, you still need to comply with the requirements dictated by regulatory documents.
What slope should sewer pipes have?
The slopes of pipes for gravity-flow external sewerage are regulated by SNiP 2.04.03-85; paragraph 2.41 specifies the following minimum values per 1 linear meter for all systems:
- 8 mm - when using pipes measuring 150 mm;
- 7 mm - for sewerage laid by pipes with a cross-section of 200 mm.
In SNiP 2.04.01-85 for internal water supply and sewerage of buildings in paragraph 18 (Calculation of sewer networks), it is recommended to use the following sewer pipe slope of 1 meter:
- 30 mm - when installing pipelines with a cross-section of 40 mm or 50 mm;
- 20 mm - if the sewer pipeline has a diameter of 85 mm or 110 mm.
- the maximum slope of the pipelines should not exceed 150 mm per linear meter.
For open storm drainage, the slopes and sizes of the trays are selected based on the condition of their self-cleaning by the high-speed flow of rainwater. Filling of storm gutters during drainage is allowed up to 0.8 of their height, the permissible width is at least 200 mm.
Based on the regulated values of slopes given in SNiP, for typical PVC pipes for domestic sewerage, similar standards are adopted for 1 linear meter:
- 30 mm - sewer pipe slope 50 mm for internal sewerage;
- 20 mm - when using a pipeline with a cross-section of 110 mm;
- 8 mm - when laying a main from a 160 mm pipeline, which is not used so often in individual sewers.
Slopes of sewer pipelines
Minimum slope of sewer pipes in sanitary facilities
Sewage pipes used for sinks and bathtubs, as well as for washing in the kitchen, have a diameter of 4 or 5 centimeters, their minimum slope according to the standards is 0.025, that is, 2.5 cm. For toilets, a drainage system is used, which is made with a cross-section of 10 cm, for it the minimum slope will be 1.2 cm.
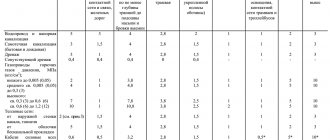
| Device | Slope | Distance between drain and siphon, cm | Pipe diameter, mm |
| Bath | 1:30 | 100-130 | 40 |
| Shower | 1:48 | 150-170 | 40 |
| Toilet | 1:20 | up to 600 | 100 |
| Sink | 1:12 | 0-80 | 40 |
| Bidet | 1:20 | 70-100 | 30-40 |
| Washing | 1:36 | 130-150 | 30-40 |
| Combined drain (sink, bath, shower) | 1:48 | 170-230 | 50 |
How to calculate the slope angle
In apartments and private houses, two types of pipes are used for laying sewer systems - 50 mm and 110 mm; an internal small-diameter pipeline leads from the installed plumbing - sinks, bathtubs, showers, kitchen sinks to a central riser or outlet pipe with a cross-section of 110 mm. The toilet is connected directly to a large pipe (110 mm) through corrugation or plastic adapter couplings of a similar size.
Even a junior school student can cope with the task of calculating the total angle of inclination of a sewer line; to do this, its total length in meters is multiplied by the standard slope indicator adopted for one linear meter.
For example, if the bathtub is located 3 meters from the central riser, then the height difference between the ends of the pipes entering the siphon and the riser should be 30 mm x 3 = 150 mm. It can be seen that the difference is quite large, so they tend to locate bathtubs, showers and toilets as close to the riser as possible. Siphons of sinks and sinks are located at a greater height from the floor level, so they can be carried over long distances from the riser.
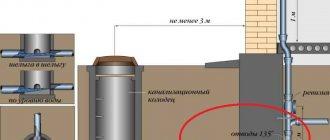
When laying external sewerage, a pipeline with a diameter of 110 mm is used; usually the wastewater is discharged into a storage tank or septic tank for further purification. In this case, slopes play a decisive role in determining the distance from the house to the treatment plant, which is discussed in the examples below.
In a standard septic tank, the neck is located approximately 600 mm above the tank into which the sewer pipe enters. This means that if the pipe extends from the house along the very surface of the earth, and the 110 mm sewer pipe should have a slope of 20 mm per linear meter, then the septic tank will have to be placed at a distance of (600 mm / 20 mm = 30) 30 m from the house. The maximum distance can always be made smaller by increasing the pipeline slope by a certain amount, but for various reasons it is undesirable to do a rapid gravity flow.
To protect the sewer pipe from freezing, it will have to be insulated and lowered underground at the base of the building by at least 200 mm, in this case the septic tank will have to be brought closer to the house by 10 m. With a greater depth of the external sewer pipe with a higher chance of protection from freezing, to for example, at 400 mm, the distance from the house to the septic tank will be only 10 m.
Sewage slope of 1 m: SNiP and general rules
With regard to pipelines through which liquid (especially liquid with solid inclusions) flows into a centralized sewer or septic tank, certain rules apply:
- reducing the diameter of the pipe requires increasing its slope and at the same time a lower percentage of filling;
- if the diameter of the pipe is calculated incorrectly, then the correctly selected slope will not save it from clogging and insufficiently rapid waste drainage;
- An increase in the angle of inclination of the pipes above normal leads to the fact that the water does not have time to wash away organic deposits from the walls; it is also possible that the pipe mouth is completely blocked and the water seals are broken.
Thus, the maximum and minimum slope of sewer pipes for gravity flow (gravity system, drainage without creating excess pressure) is determined from tables compiled on the basis of long-term observations and experiments.
When making calculations, it is necessary to take into account that, depending on the source of reference information, the slope angle can be given in degrees (deviation of the center line of the pipe from the horizontal), millimeters per meter of length of the pipeline section, or in the form of a fraction. In the latter case, the fraction is the ratio of the height difference in the pipe section to its length.
Calculation of pipe fullness
SNiP 2.04.01-85 (clause 18.2) provides the following formula for hydraulic calculation of sewerage:
V × √H/D ≥ K , where
V is the speed of wastewater movement in m/s;
H/D - filling, where H is the level of the water layer in the pipe, D is the diameter of the pipeline;
K – coefficient equal to 0.5 for polymer pipes and 0.6 for communications made of other materials.
The SNiP 2.04.01-85 standards indicate that in practice the speed of liquid flow should not be less than 0.7 m/s with a minimum filling of pipes of 0.3. As can be seen from the formula, the pipeline will be maximally filled when the H/D ratio is equal to one, that is, the optimal filling value should be in the range from 0.3 to 1.
In practical use, they try to maintain the fill rate in the range of 0.5 - 0.6, that is, if the sewer pipes have a diameter of 110 mm, then when filled with drainage to a height of 60 mm, the fill rate will be 60 mm / 110 mm = 0.545 mm. This indicator corresponds to the optimal value when using hydraulically smooth PVC sewer pipes.
Examples of installation of individual sewerage
Errors during sewer installation
Although installing a sewer system does not seem to be a very difficult task, many users make the following mistakes when installing it:
- They violate the sewer slope for a private home, forgetting to check it, and an underestimated value leads to frequent blockages and freezing of water in the pipeline in winter. Too much slope causes liquid fractions to drain quickly, while solid waste remains in the pipes - this also increases the likelihood of blockages.
- They do not install a vent riser to remove gases (methane), as a result, foreign odors appear and the fire hazard in the house increases.
- Unjustifiably, wastewater is divided into gray water from the kitchen, bathroom, household appliances and sewage from the bathroom. As a result, some pipes remain clean all the time, while the other part is subject to too much contamination, which leads to incorrect operation of the sewer system.
- When calculating the permissible diameter of the pipeline, along with the total volume of wastewater, as a rule, one-time drainage from the simultaneous use of a bathtub, sink, toilet, shower, and household appliances is not taken into account.
- The use of bends with right angles during installation leads to a significant increase in hydraulic losses, slows down the flow of wastewater, and increases the likelihood of blockages.
- Insufficient deepening of the pipeline on the street or lack of insulation with an electric cable, a shell made of thermal insulation materials, leads to freezing of the underground line in winter and disruption of the entire system.
- The absence of a check valve on the way to the septic tank during blockages or emergency situations can cause reverse pressure flow of wastewater into residential premises.
- Installing plumbing equipment without siphons in the absence of water seals causes unpleasant odors to appear in the house.
- The use of PVC pipes in risers often leads to increased noise and, accordingly, a decrease in living comfort. To combat noise, special types of silent pipes are used or PVC pipelines are covered with noise-insulating materials.
Option for laying internal sewerage
When installing individual sewer systems, one of the most important conditions is the accurate maintenance of standard slopes - this ensures correct and long-term trouble-free operation of the entire system. Knowing the correct angle of inclination of sewer pipes, it is easy to independently design the location of indoor plumbing fixtures and external treatment facilities in the form of septic tanks.
Rules for installing internal pipelines
The construction of a sewer network in the private sector consists of 4 stages:
- installation of the internal system;
- installation of treatment facilities;
- assembly of external sewerage;
- installation of a vent riser, which will prevent the entry of unpleasant odors into the room.
They begin work with the central riser, from which they begin to install the wiring and direct connection of plumbing fixtures.
During the process, the following rules should be followed:
- All plumbing fixtures must be placed in close proximity to the riser. This will prevent blockages from occurring.
- Whenever possible, sharp turns should be avoided when installing the pipeline. Try not to use 900 connections. If such a need arises, it is better to use two 450 turns or three 300 turns.
Despite the fact that the work is quite labor-intensive, requiring a lot of time and effort, however, according to its design principle, it is considered uncomplicated. If you have the appropriate tools and follow all the rules, you can install a sewer system in your house with your own hands.