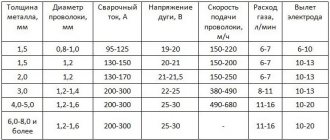
Material consumption standards for welding work, calculation rules
Welding in argon environments is in demand when working with stainless steel tubular products that are part of transportation systems for industrial liquids and gases. The high quality of the welded joint allows the method to be used when welding stainless pipes operated under fairly high pressure.
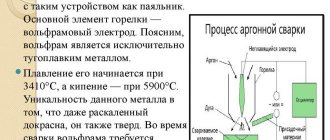
The main hand tool used when working with shielding gas is a special torch with an electrode fixed on it, through the nozzle of which an argon stream is supplied to the place where the stainless steel is welded.
A high-quality weld is prepared using a wire that is specially fed to the place where the arc is formed manually. In this case, all movements and manipulations with the burner are also performed only manually.
This technology, unlike other methods of processing stainless steel, eliminates any transverse displacement of the electrode and the filler wire brought to it.
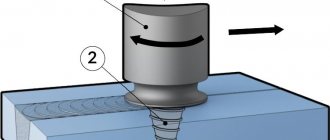
The only permissible direction of their movement is strictly along the axis of the connection being formed . The position of the torch during welding operations must correspond to the figure shown in the photo.
The requirements for the welder’s manipulations in the work area ensure that the weld pool is always located within the radius of gas protection. This is a necessary condition for obtaining a strong connection between stainless steel parts. You should also take care to protect yourself from the air layer on the back side of the seam, which is blown by an argon stream.
In this case, the total consumption of argon increases significantly, but the quality of the stainless steel connection in all areas of the seam increases. The general provisions on the consumption of argon for this type of welding, as well as the equipment used for this, will be discussed below.
How to weld stainless steel yourself with argon
Stainless steel contains a large number of alloying substances that actively react chemically with oxygen and nitrogen. When welding stainless steel with argon, the bath is protected.
No oxidation of components occurs. It remains to overcome the remaining characteristics of the metal, which create difficulties when connecting two high-alloy parts.
To do this, the weld area is prepared and non-consumable electrodes are used.
Welding stainless steel with argon
Technology
Argon welding of stainless steel is carried out using conventional technology in a shielding gas environment. The filler wire should only be moved along the seam. The electrode should not touch the metal; the bath is accelerated by an arc. Make sure that all consumables are sealed with argon gas.
The seam is stronger if argon arc welding is performed with additional injection of shielding gas. It's coming from the opposite direction. The pipe can be closed on one side and gas can be released on the other.
An oscillator or a graphite plate is used to ignite the arc. You cannot touch the part with the electrode; a burn will immediately form at the point of contact.
Gas supply continues for 4–8 seconds after completion of work.
Copper pads are used to join thin sheets. They are attached to the back of the seam to remove excess heat.
Advantages and disadvantages
To protect against oxidation and destruction, an inert gas is used, which is much more expensive than carbon dioxide. Argon consumption when welding stainless steel depends on the thickness of the metal being welded and the wire feed speed; it is 10–20 l/min.
Additional airflow from the reverse side of stainless steel parts requires another 6–7 l/min. The cost of work increases.
On the other hand, a durable, high-quality seam is obtained. It is done on critical parts, pipelines, and containers for aggressive liquids.
Thin stainless steel is welded end-to-end with a tungsten electrode. Copper backing plates can be used many times and can be given any shape during mass production. Costs for straightening and post-weld normalization are reduced.
Equipment and consumables
When processing stainless steel, you cannot ignite the arc in the standard way, striking the part. The equipment must provide non-contact ignition of the arc. An inverter and a semi-automatic machine operating in argon arc welding mode meet these requirements. The welding machine and the gas cylinder must operate synchronously, from one button on the holder.
Uniform distribution of gas is ensured by a mouthpiece with a mesh and a wide nozzle. They put it on the burner. As a result, the gas flows in a wide stream, covering the entire bath and seam. It has a low speed, it does not blow out molten metal and does not deform the seam.
For stainless steel products, it is important that the filler wire is selected of the same grade or as close as possible in terms of chromium, nickel, and manganese content.
The tungsten electrode is selected with a diameter smaller than the gap between the parts. Typically, electrodes with a diameter of 1–1.6 mm are used. The edge is sharpened and made sharp.
Preparation
When preparing, you should consider some features of stainless steel:
- low thermal conductivity;
- high melting point;
- a large number of alloying substances;
- large specific expansion.
It is recommended to heat thick-walled parts to 200–300 ⁰C. This will reduce the temperature difference between the weld and the base metal. This will reduce the risk of a coarse transition zone forming along the weld line.
Immediately before welding, the edges of the parts are prepared. They must be cleaned of dirt, dust, and grease. Then wipe with purified gasoline or acetone. The cleaning is completed with a soft abrasive wheel or sandpaper.
When placing parts under the tack, you should leave a large gap between them. When heated from the weld pool, the edges should not connect and press on each other, causing deformation.
Tacks should be made with the same electrode that will be applied to the root seam.
Rules and stages of welding work
Argon welding is used to join stainless steel pipes. When laying pipelines of increased responsibility and creating tanks, argon is supplied inside. It protects the reverse side of the seam from oxidation and burnout of chromium.
First, the ends are cut straight, etched and cleaned. Then the pipes are rigidly fixed in a special device. This allows you to cook without oven mitts.
The seam is applied in 2 passes from bottom to top with a slight transition at the junction points. After cooling, thick-walled parts are cleaned of slag, the quality of the seam is checked and a second layer is applied. This must be done immediately, before the joint temperature drops below 150⁰.
Manual
For manual welding with a non-consumable tungsten electrode, the filler wire is placed in advance in the seam or brought in front of the pool along the seam.
The gas is turned on 2–4 seconds before the arc forms. This ensures that the entire weld and hot metal are protected. After completion, argon blows over the seam for another 4 seconds.
What is argon welding
Hybrid technology, combining gas and electric welding methods, makes it possible to work with a wide variety of volumes and materials. It has proven itself excellent in welding cast iron, steel, copper and other metals. With its help, large steel pipes and miniature bronze hanger hooks can be welded well. Working with stainless steel is another example of the versatility of equipment and technology.
Without studying the theory of welding skills, it is impossible to become a good specialist. This is especially true for complex technologies, which include the argon method. In order to understand in detail the essence, advantages and features of the argon welding method, it is necessary to understand the physics of the processes that occur during operation. In order to connect two metal blanks together, it is necessary to melt some of their parts. And this can only be done by heating.
Raising the temperature involves the use of fire, which in turn requires oxygen. The latter enters into chemical oxidation reactions. And the faster the metal oxidizes, the more difficult it is to weld. Oxidation is one of the undesirable phenomena when welding metals.
Argon consumption when welding stainless steel
Stainless steel is used in many industries. It is found in factories as parts of production mechanisms, on the street as frames for bus stops and prefabricated summer structures.
Surgical and household instruments are made from stainless steel. This steel has even found its place in oil production and refining. Therefore, it requires craftsmen to be able to handle it correctly when welding.
Alloy stainless steel is processed in several ways in welding. Quite often, welding is carried out using argon and tungsten rods.
This type of work with stainless steel is financially affordable, because it does not require special equipment.
general information
The stainless steel type is not subject to corrosion. This metal is practically not afraid of rust even without special protective substances. This is the basis of the popularity of stainless steel.
With proper care, it can be used for decades, and therefore is in deserved demand. The elements of chromium, nickel and titanium included in this steel improve its physical and mechanical properties.
Which is also the reason for its application in different areas.
The advantages of stainless steel include the way it looks. Due to the bright, characteristic shine, things made from such steel are often not painted.
Therefore, welding joints on steel products must be made not only reliable, but also preserving the appearance of the steel. However, this is only one of the aspects of working with steel.
Working with stainless steel is difficult. The same characteristics of the composition that protect the metal from rust make welding it a difficult task. This article is about the important points of welding work with stainless steel.
After all, this is a task for which special preparation is required.
Welding Features
The first thing about working with stainless steel is that the challenges come from the components included. Nickel and chromium are the two main elements that make welding difficult. Stainless steel also goes by the name "alloy steel".
It has increased thermal conductivity, and this is also important to remember when working with it. This indicator often becomes the reason why an inexperienced specialist encounters difficulty in melting metal during welding.
For welding work with stainless steel, 6000°C is required. This is quite a high figure. It is enough to melt stainless steel, but often the heating concentration is reduced to one point.
The surface overheats, which leads to deformation of the part. To process steel efficiently, the current is set 15-20 percent below the standard level.
Deformation of stainless steel during operation also occurs due to the increased coefficient of linear expansion. This leads to welding joints quickly becoming cracked.
To avoid such defects, a gap must be left between the edges for deformation. Thus, after steel expansion, shrinkage will have acceptable parameters.
Compliance with temperature conditions is the main indicator when welding stainless alloy steel. Violation of this process reduces the material's resistance to corrosion. To avoid overheating, parts are cooled immediately after work.
Metal preparation
When working with argon welding, the risk of defects threatens even at the preparatory stage. The preparatory stage is quite important here. That’s why you shouldn’t give it up.
After all, in essence, it consists of the same preparatory actions as during argon arc welding of other metals.
First, the edges are cut. Next, they are cleaned to a shine using a metal brush or a grinding machine. After this, the working area is degreased with a special liquid.
Gasoline or acetone-containing substances will do. This is done to improve arc stability, which speeds up the work process.
https://www..com/watch?v=3AqTU9vzijI
Don’t forget about the joint gap, which prevents defects. Before welding begins, not only the preparation of parts is carried out, but also the selection of components.
When argon welding stainless steel, a filler rod is used. An important nuance in the selection of a rod is the degree of alloying. It should be higher than this indicator for the part. Such elements should be taken from trusted companies.
The craftsmen are able to give advice on where and from whom it is better to get high-quality components for welding stainless steel with argon.
Argon welding technology
Argon arc welding of stainless steel is a task for a master with extensive experience. However, even a beginner can do it. But first, it’s worth conducting a couple of training tests on unusable parts that can be rejected.
Argon welding is most often used for thin-walled elements. After all, this welding process technique is quite neat. When processing thin-walled stainless steel using the argon arc method, the selection of equipment plays an important role.
A semi-automatic machine is suitable for working with stainless steel. This is a classic option. It is quite difficult to use, but sufficient experience ensures a reliable and aesthetic seam.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-EOLgT6zRf8u0026t=84s
Before work, the device is configured. The polarity is often straight. Also in the settings there are two types of current - alternating and direct. This parameter is set separately for each part.
When argon arc welding of stainless steel, a welding rod and a tungsten electrode are used. An important link is the gas burner in which the electrode is fixed. Argon is supplied through it.
The movement of the gas burner occurs manually. It is important to remember that it is carried out along the axis of the weld. Cross traffic is strictly prohibited.
When passing the torch across the joint, argon will not be able to protect the welding area from the destructive effects of oxygen. This will reduce the reliability and quality of the connection, and the part will be rejected.
The reverse side of the weld also requires protection. For this purpose, argon is also supplied to the other side of the part. This increases gas consumption, but increases the reliability of the seam.
When working with thin-walled stainless steel parts, the edge of the electrode is pre-melted. This is a precaution to avoid contamination of the seam surface of the part.
After all, the aesthetics of the connection is the main parameter when working with stainless steel. Graphite backings used during arc ignition also provide a more suitable weld appearance for this type of steel.
Oxidation activity of the metal or tungsten electrode is also a common cause of disruption of the welding process. The solution is to continue feeding argon into the weld pool after welding is completed.
The duration of this action is only 15-20 seconds. However, this will improve the quality of the seams and protect them from cracks. And the level of argon consumption is quite small.
During welding, the ideal gas consumption level is 12 liters. It is worth making sure that it is not more than 15 liters. in a minute. However, these indicators are characteristic of highly qualified craftsmen who have extensive experience in this area.
For beginners, overspending is normal. With experience, the process will proceed faster, and this indicator will return to normal.
Conclusion
The TIG welding process for stainless steel is complex, but doable.
It is enough to correctly understand the nuances of welding technique, choose a reliable machine and monitor the level of gas consumption.
When welding, it is important to follow safety precautions and use protective equipment.
Technology and modes of welding stainless steel in argon
Welding stainless steel with argon is a popular technology that allows you to obtain a joint of this alloy of the highest quality, compared to other working methods.
Difficulties
Alloying additives that are part of stainless steel increase its quality characteristics, imparting corrosion-resistant properties, but they negatively affect the welding process.
Compared to other types of steel, the thermal conductivity of stainless steel is 2 times lower.
This means that when the surface is exposed to temperature, the heat will be concentrated at the point of contact, and not evenly distributed over the plane, removing excess energy.
For this reason, novice welders are unable to qualitatively weld the alloy without overheating and burn-through. Technical manuals recommend setting lower amperage characteristics of welding equipment when welding this alloy.
An important factor to consider at the planning stage is the high linear expansion rate. Excessive temperature exposure easily deforms the heat-affected zone, so it is necessary to leave a gap sufficient to prevent the formation of cracks.
High electrical resistance also negatively affects welding quality. Consumables heat up very quickly. After some time, they begin to melt not in the weld pool, but at the end of the arc.
There are also temperature restrictions for the welding process. At a temperature of 500 Cº, compounds begin to form in the intercrystalline space, deteriorating the quality of the weld - chromium and iron carbide. To prevent this process, the part must be cooled immediately after completion of work.
Preparatory work
Argon welding of stainless steel should begin with high-quality surface preparation . The procedure for preparing the alloy in question does not differ from other types of metal and includes the following steps:
- The surface is cleaned of foreign elements. In this case, the edges must be cleaned to a metallic shine. Welding stainless steel GOST 14771-76 does not indicate exactly how the preparatory work will be carried out. It follows from this that it is possible to use both hand tools and mechanized methods.
- The next stage includes degreasing the surface with any suitable liquid.
- The preparation is completed by installing a gap that compensates for deformation processes.
Modes
The operating mode of the welding machine must be selected carefully, taking into account all the initial data. The result largely depends on this. So:
- Direction and polarity of current. The determining criterion is the metal with which you have to work. Most steel workpieces, including stainless steel, require forward direct current. Regarding non-ferrous metals, magnesium and aluminum, everything is exactly the opposite. It is best to choose alternating current with reverse polarity.
- The consumption of inert gas is determined by two factors - operating conditions and argon supply rate. Welding metal in an open area with strong winds entails increased consumption of inert gas. Therefore, you should always have at least two sides protected from the wind.
At first glance it may seem irrational, but oxygen is present in the argon mixture. Its share is small and does not exceed 5% of the total volume. It would seem that this would negatively affect the quality of the seam. But no. In small doses, oxygen performs a positive function: it burns small harmful impurities. They react with the gas and burn.
Technology and modes of welding stainless steel in argon
Welding stainless steel with argon is a popular technology that allows you to obtain a joint of this alloy of the highest quality, compared to other working methods.
Argon arc welding with non-consumable electrodes
The technology of using a non-consumable electrode in an argon environment is used for welding stainless pipes. A distinctive feature of this method is high-quality and neat seams with an attractive appearance . Argon arc welding is also used for critical work with tanks and other vessels that are operated under pressure.
Work can be performed on both direct and alternating current of straight polarity. The heat source is a torch with a tungsten electrode through which shielding gas is supplied. The seam is formed by melting the filler material, which are rods fed into the melt zone.
Welding in TIG mode has some features:
- When tungsten particles enter the melt zone, the quality of the weld deteriorates. To ignite the arc, a special carbon plate is used, after which it is transferred to the working plane.
- Upon completion of the work, it is necessary to continue supplying the protective gas until the electrode and the hot seam have completely cooled - this will avoid oxidation of the working area and the burner electrode.
During operation, it is necessary to maintain a certain angle of inclination of the torch and rod relative to the surface, as well as relative to each other. These are basic skills taught in welding training courses.
Using a semi-automatic machine
Novice craftsmen often ask the question: “How to weld stainless steel with a semi-automatic machine?” This method is characterized by high productivity due to the continuous supply of electrode wire . The visual qualities of the seam are not as attractive as with argon arc welding, but the reliability of the connection is not inferior to the previous method.
Semi-automatic argon welding is considered a universal technology, since it allows you to work with workpieces of various thicknesses. With its help, you can perform any work - from welding railings in a country house to connecting a complex structure according to the provided drawings.
There are special requirements for consumables. A prerequisite is the presence of nickel in the wire composition. Otherwise, it is considered non-compliant with current standards.
The main modes of work execution are:
- Short arc . In arc welding, the exposure temperature depends on the length of the discharge. The short distance between the burner and the surface is ideal for thin-walled products.
- Pulse . In this case, the wire is fed into the melt zone at short intervals, which reduces the likelihood of spattering, minimizes the temperature effect on the part and reduces wire consumption.
- Jet . Used for welding parts up to a centimeter thick.
Thin material connection
Welding thin stainless steel with argon should be done with great care. Experienced specialists recommend using special metal linings with high thermal conductivity . This serves several purposes:
- the lining will act as a heat remover, reducing the risk of carbide formation;
- molten metal will not flow out from the back of the seam;
- The working plane is fixed.
If all rules are followed, the quality of the connection will be higher than using an inverter.
In some cases it will be advisable to use a spot welding machine. In this case, it is also necessary to correctly configure the operating parameters: with increased amperage characteristics, stainless steel rusts after resistance welding due to the formation of carbides.
Pipes
A high-quality stainless steel welding machine is capable of connecting pipes made of the appropriate alloy that are used in home water supply systems. Having certain skills, you can easily cope with this task yourself.
A feature of the technology is the need to protect the inner surface of the pipe . To do this, you need to plug the hole on one side using available materials:
- Rags;
- Foam rubber;
- RTI;
- Paper.
Then a tube is installed in the plug, which will serve as a conductor of the protective gas. It is important that it is hermetically sealed to avoid leaks.
The operating gas pressure is set depending on the work conditions. There is only one requirement - the gas should not squeeze the melt onto the surface. In this case, the quality of the seam is guaranteed.
Pulse Mode
Modern equipment is equipped with a function to perform work in pulse mode. Its main purpose is to connect elements of different thicknesses.
As mentioned above, this technology helps save consumables. In addition, the finishing time of the surface is reduced due to the low amount of molten metal splashes.
Thus, it is possible to reduce the intermediate stage of mechanical grinding of the product, moving on to processing with acids and gels in order to remove the oxide layer and give the seam the necessary resistance.
With foreign metal
Inexperienced welders often have difficulties because they do not know how to weld stainless steel with ferrous metal.
Argon arc welding has proven itself best, since argon reliably protects the melt zone from contact with the environment.
To avoid hot cracks, it is necessary to use rods based on chromium and nickel.
Pros and cons of this method
The advantages of using argon include:
- The gas reliably protects the molten metal, excluding its contact with atmospheric air, which improves the quality of the connection.
- Low thermal conductivity helps weld complex parts without affecting their design.
- The high temperature of the welding arc has a positive effect on the speed of the process.
The disadvantages are the high cost of welding equipment, which does not always allow its use when doing household work. In addition, working with argon has its own characteristics that require specific skills.
Argon burners
The torch applies voltage to the tungsten rod and serves to form an inert gas shield around the work area. It is important to pay maximum attention when choosing it, as well as selecting consumables. As mentioned above, argon arc technology is based on the use of tungsten electrodes, which do not melt, and inert gases. From this follow the main criteria by which you need to select a burner:
- maximum permissible power and current;
- Is there a tungsten rod holder included?
- it is desirable that the nozzle be made of ceramic;
- burner cooling option when working with thick and thin workpieces;
- versatility of burner use. This means the possibility of its communication with welding machines of various types;
- power supply cable length.
The operation of the burner can be described step by step as follows:
- Everything starts working at once: the cooling system circulates, inert gas is supplied to the burner, and the welding machine itself starts.
- Immediately after the formation of the protective layer, the gas arc is initialized. The workpieces are heated to the melting temperature. At this moment, you need to feed the filler wire into the working bath.
- Next, the filler wire, together with the tungsten rod, moves in the direction of the joint of the workpieces.
Non-consumable electrodes
Manual argon arc welding is usually equipped with non-consumable tungsten electrodes. They are best suited for welding stainless steel and non-ferrous metals with high chemical activity - aluminum, titanium, magnesium.
The electrode is mounted in the current supply collet of the torch with a ceramic nozzle, which directs flows of inert gas to the working area. The system is water-cooled. The diameter of the electrode directly depends on the current strength, which is selected depending on the thickness of the workpiece. Due to the fact that when welding metals in this way there is no splash, the burners are equipped with a mesh filter, which serves to uniformly distribute the flow of inert gas.
The mechanized burner has a slightly different design. In addition to the elements already listed, it is additionally equipped with a flywheel for raising and lowering the tungsten electrode. The current-carrying collet is attached using a threaded connection for changing rods of different diameters.
Consumable electrodes
Semi-automatic and automatic argon arc welding is most often equipped with a torch with a consumable electrode. During operation of the machine, the arc is maintained between the surface to be welded and the filler wire. Depending on the performance of the installation, the cooling system can be air or liquid. The nozzle design and operating principle are completely identical to analogues equipped with non-consumable rods.
Welding stainless steel with argon: technology, how to weld correctly, important nuances
12Nov
articles
In this article we will talk about technologies and training in argon welding techniques for thin stainless steel. This steel is a convenient, popular material for many metal structures. Its main advantage is the slow corrosion process, which quickly ends the life of the product.
Features of welding stainless steel with argon
You can find an approach and adapt to any alloy if you know special techniques. The basics of welding work remain the same, you also need to prepare the material and equipment, create an electric arc, and make an even seam. But due to impurities in the metal - chromium and nickel - there are difficulties.
Rules to remember:
- reduce the usual current by at least 20%;
- leave a larger gap between the two elements being welded;
- do not use alloyed electrodes; if there are no others, then only short ones will do;
- do not allow heating above 500 degrees;
- Cool parts quickly.
What are the difficulties?
Alloying additives provide the following nuances:
- Low thermal conductivity. For this reason, the workpiece does not warm up completely, and high temperature accumulates at the joint. Burns or excessive deposits may occur.
- Due to linear expansion, final shrinkage is possible, which will lead to deformations and cracks.
- The high electrical resistance of steel when connected to alloyed electrodes leads to overheating.
- Possibility of loss of anti-corrosion properties due to elevated temperatures and the formation of new chemical elements on the surface that are prone to rust.
Equipment and consumables for argon welding of stainless steel
The welder's kit will consist of:
- liquefied gas cylinder;
- burners;
- inverter;
- oscillator;
- wires, hoses.
This is a basic kit that will last a long time. Only the filler wire will have to be changed (filled), it is more convenient than electrodes, and the inert gas itself. The additive must be of the same composition as the workpiece. Additionally, a gas lens can be installed on the burner. It reduces consumption. And instead of a wire consumable, you can use an electrode method - made of tungsten.
Preparation of material
First check the metal. Not everything that has a bright metallic sheen is called stainless steel. You can check it with any magnet. It will not be magnetized to steel with anti-corrosion properties. Then:
- wash off all visible dirt;
- dry;
- carefully walk over the surface with a metal brush (a grinding machine is also suitable), smooth out defects;
- degrease the outer layer with acetone or gasoline.
Pay special attention to the joints.
How to Prepare Small Stainless Steel Parts for TIG Welding
The algorithm remains the same, sometimes it is even easier to completely place the element in a container with a degreasing liquid. The peculiarity is the difficulty of fastening. If possible, secure the small workpiece so that it does not move while welding. After this, select the correct additive with an alloy equal to or slightly less than that of steel. The following models are actively used:
| Welding wire: brand description | Classification | Typical chem. composition of the deposited metal | Mechanical properties |
| OK Autrod 347 Si (OK Autrod 16.11)* Corrosion-resistant chromium-nickel welding machine for stainless steels type 08X18H10, 12X18H9T, 08X18H10T, (304, 308, 347) and the like in shielding gases (Ar). Alloyed with niobium and silicon provides high resistance to intercrystalline corrosion and high quality welds. Widely used in mechanical engineering for the petrochemical and food industries, in the energy sector, etc. Current = (+). | ER 347 Si / AWSA5.9G 19 9 Nb Si / EN12072 Wire analog: 06X21H7BT06X19Н9Т01X18Н1001Х19Н9 |
We do argon welding at home
Although argon arc welding technology is complex and is characterized by many technical nuances, many home craftsmen manage to complete the work using improvised means. To do this, you must have inverter welding, although in some cases it can be replaced with a retrospective transformer installation. Naturally, it is necessary to have a cylinder with inert gas, a mask and a reducer.
In addition, to implement the idea of a homemade argon apparatus you will need the following tools:
- electric drill, grinder and conventional welding machine;
- wrenches, screwdriver, hacksaw, pliers;
- tester, ammeter, micrometer, voltmeter.
The current source can be made from a welding transformer and a rectifier, which in this case will need to be combined with an oscillator. The primary winding must be made of copper wire up to 0.8 mm thick. For the secondary winding, copper of a much larger diameter will be required - no thinner than 3.5 mm.
The gas burner will be next in importance. It is advisable to use brass for the body, and the nozzle itself can be machined from copper. Heat-resistant rubber is suitable for sealing the joint between these two components. Moreover, it is not difficult to make a gasket from flexible material.
Argon will be supplied to the burner through a copper tube, which is inserted into a hole in the housing, and the joining seam is sealed. The same line will become an excellent conductor of current, which is necessary for igniting and maintaining the arc. The tungsten electrode must have a sharp end that is ground at an angle of approximately 45 degrees. The approximate length of the rod will be 25-30 cm.
It is important to understand that making equipment for argon arc welding at home is quite a difficult task. And not always “the game will be worth the candle.” If the equipment is rarely used, the cost of its production may never be recouped. Very often it is much more practical to use the services of a specialist with his own equipment or to purchase a ready-made device in the budget price segment.
Argon welding of stainless steel: subtleties of technology and basic rules for carrying out work
November 22, 2021 Argon welding of stainless steel: subtleties of technology and basic rules for carrying out work
Issues discussed in the material:
- What are the features and advantages of argon welding of stainless steel?
- How to prepare materials for argon welding
- How is argon welding carried out using a non-consumable tungsten electrode?
- What is argon welding of stainless steel semi-automatically?
- What is important to consider when argon welding stainless steel
Stainless steel is a rather difficult material for welding. However, the use of welding with argon cooling allows you to obtain an even and high-quality seam connecting stainless steel parts.
It is necessary to begin learning this process by becoming familiar with the various characteristics of this difficult alloy to join.
Our article will introduce you not only to what argon welding of stainless steel is, but also to the features and technology of the work.
Classification of argon welding by type
The division is carried out based on the level of mechanization of the process. There are three types of argon welding:
- Manual . Both the filler wire and the torch itself are moved by the welder. For such work, exclusively non-consumable tungsten electrodes are used.
- Semi-automatic . In this case, the torch is controlled by the welder, and the wire feed is controlled by the mechanism.
- Automatic . The torch and wire move mechanically, and the operation of the machine is controlled by the operator. Nowadays, it is not uncommon to find installations that operate even without human intervention. Robotic systems are used, for example, in pipe welding.
Necessary equipment
To weld aluminum, you need a source (apparatus) that produces alternating current. The technology will not work on direct current.
The device must have the following functions:
- non-contact ignition;
- crater filling;
- current balance adjustment.
These settings (discussed below) are sufficient for high-quality argon welding of aluminum.
Argon gas must be pure; purchase cylinders without atmospheric air. If the reducer on an argon cylinder is made in Russia, then it is recommended to set the flow rate to 12-15 l/min. And if it’s a Czech brand, then 8 liters is enough.
Filler rod. There are several types of material, two are widely in demand:
- for welding pure aluminum (No. 5356);
- rods with silicon for compounds with impurities (No. 4043).
Table with numbers of rods and their areas of application:
Tungsten electrodes can be used - universal (AC/DC), different colors or only for alternating current (AC) welding, painted green.
The minimum electrode diameter for argon arc welding of aluminum is 2.4 mm. Before work, it is sharpened, making it not sharp, but with a slight dullness. Don’t try too hard; during welding it will take its correct shape, like a droplet. The droplet should be the same size as the diameter of the electrode, shiny in color with a smooth sphere.
If the color is dull, it means there is not enough gas coming in or it is of poor quality. If the electrode melts, it means it was chosen incorrectly. It is necessary to install a larger diameter electrode.
When welding aluminum, it is recommended to use a gas lens (collet holder). A mesh is inserted inside the structure, passing through which the gas creates better protection for the tungsten electrode and the weld pool.
There are special nozzles with different diameters for the lens. The larger the nozzle diameter, the better the protection.
The electrode should protrude from the nozzle by 3-5 mm. With a larger shot, tungsten heats up more and is destroyed faster.
Video: about equipment.
How to set up the device
Let's look at the step-by-step instructions for beginners using the Ironman 200 AC/DC welding inverter as an example.
1) The leftmost function is the AC balance setting (CLEAN WD.), which has 2 polarities - minus and plus.
Our connection technology uses 50/50 polarity; the polarity changes depending on the type of task. For example, when welding pure aluminum, the balance is adjusted in the negative range. This way the metal, bath, and electrode will heat up less, and the seams will turn out thin and beautiful. Due to the low heating of the electrode, it can be sharpened more sharply.
For dirty aluminum, it is better to set the positive range, so the heating of the metal will be stronger, and the cleaning of the bath will be better.
Be careful: a positive half-wave has a detrimental effect on the tungsten electrode.
Based on the diameter of the electrode, the correct balance of alternating current is adjusted.
2) The next function (CURRENT) is the welding current setting. To weld aluminum, for example, 2 mm thick, it is enough to set the force to 60-65 A.
3) Third toggle switch (DOWN SLOPE) - crater filling setting (slow arc decay). Setting the arc decay time depends on the thickness of the metal. For 2 mm it is enough to set it to 3 seconds.
4) The final function (POST TIME), gas purge, is necessary to cool the bath, electrode and torch at the end of welding.
Video: on setting up a TIG machine.
Material preparation and process technology
The technique of welding aluminum differs from other types of metal joints. Aluminum is a thermally conductive material with a low melting point.
Please note: at the beginning of the work, the workpieces must be warmed up well (as if there is not enough current), and during the welding process the aluminum quickly overheats (excess current) - take these nuances into account.
How to clean workpieces? You can use a steel brush.