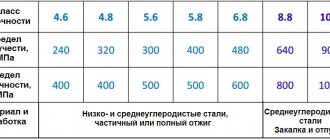
Steel pipe plays an important role in human life, as it is used every day in everyday life, construction and industry. The list of applications of steel can be endless, because it is present everywhere - in utility networks, interior parts, street handrails.
Steel pipes
Strength and reliability, long service life, affordable price - all these factors contributed to the widespread use of the material. There are different types of steel pipelines, which differ depending on the shape and size of the section, wall thickness, and the presence or absence of insulation.
Advantages and disadvantages of a steel pipeline
Steel pipes are produced at special metallurgical plants. The main characteristics of steel pipe products include:
- Resistance to mechanical loads;
- Long-term absence of corrosion;
- Possibility of operation under conditions of high operating pressure;
- Various wall thickness and diameter, wide range of products;
- Withstands temperatures up to 130˚C;
- High thermal conductivity coefficient;
- Small linear expansion, which allows the use of a pipeline for a heating system;
- Service life – 5-15 years.
The service life of steel products can be significantly increased by using a protective anti-corrosion coating.
Steel pipes
Such positive characteristics of steel pipe products allow them to be used for gas and oil pipelines, as well as water supply systems operating under conditions of high pressure of the transported liquid. However, in addition to its advantages, this pipeline has some disadvantages:
- Abrasive wear;
- Low frost resistance;
- Low resistance to corrosion and sedimentation, which shortens the life of the material;
- High roughness coefficient;
- Very heavy weight;
- Labor-intensive installation of water supply networks or gas pipelines, which requires the participation of special equipment;
- The need to use special branches to branch the network due to the complete lack of flexibility.
Damage to highways from freezing can be prevented through the use of high-quality insulation.
Profile pipe range: advantages, application
Seamless cold-formed pipes that comply with GOST 8734 are used in various types of industry, depending on the wall thickness. Thin-walled and especially thin-walled pipes with a galvanized layer are most often needed in various hydraulic systems (pistons and cylinders for motors and pumps), in the manufacture of precision refrigeration equipment, in medical production, cosmetics and food industries.
Seamless pipe with thick walls
Pipes with medium and high wall thickness and large diameter are used for the construction of pipelines, gas pipelines, in the energy, cryogenic industries, judicial proceedings and automotive industry (engine production.). The main advantage is the one-piece component, which does not have a welded seam, which means it has a large margin of strength and durability and other enhanced characteristics. Among the main advantages are:
- a wide range of finished products (in terms of wall thickness and diameter);
- maximum strength characteristics;
- durability and resistance to various types of climate change;
- aesthetics of the material and good performance properties.
The cost of seamless pipes depends on the grade of steel used for its production, wall thickness, diameter, manufacturing method and volume. In any form, it is more expensive than standard welded metal pipes, but it also has much greater potential. For some types of industry, the production of seamless pipes is carried out to order, since additional technical conditions and nuances are added to the GOST 8734 standards (especially for the production of materials for the chemical industry).
Profile pipes can be used in a wide variety of areas, which is why there are a large number of varieties. In this regard, a concept was introduced that helps to conveniently and clearly present the available types, which include profile pipes - assortment.
To explain it more simply, not using the example of profile pipes, the assortment is a concept that comes from the word “grade”, thus it means a list of the names of these products that are presented on the market.
Typically, the assortment is the main indicator of the availability of certain types of pipes at an enterprise or store. This is a table or list that lists the types of materials that comply with GOST standards. The range includes varieties as well as characteristics. The range includes a very wide variety of types of pipe products.
Classification is carried out according to different parameters, depending on the shape of the pipes:
- rectangular,
- flat oval,
- square,
- oval,
- with hollow ribs
- with a special profile.
The assortment is made separately for each variety, and is regulated in accordance with GOST.
Each listed type has many varieties according to parameters:
- mode of production,
- materials that were used in production,
- treatment,
- appointment.
Manufacturers use the range to show the options available on the market, as well as their development. The larger the range of products provided, the better it will be, despite the high costs and production capacity.
Typically, profile pipes are classified into rectangular and square, which have different lengths and thicknesses. The manufacturing material is metal, which is gradually being replaced by plastic in recent years. Profile materials are used in various metal structures for various industries; they are an excellent alternative to bar construction. This is also facilitated by the rather low price and weight of the profile.
When installing structures, it is also necessary to choose the right profile metal product. It is necessary to correctly calculate the load-bearing capacity of the material, taking into account the possibility of using both rectangular and square profiles.
The mass and cross-section of a linear meter of each variety are also taken into account.
The most popular materials on the construction market are those pipes that have the following dimensions:
- 15 by 15,
- 20 by 20,
- 25 by 25,
- 30 to 30,
- 40 to 40,
- 60 to 60,
- 80 to 80,
- 100 to 100.
A profile pipe is a metal product with a cross-section that differs from a round one. The cross-section is usually rectangular or square and the most commonly used profiles are 25, 60, 100 mm, as well as 40 by 80, 40 by 100 and 50 by 50.
As structural elements, materials from a range of 100 mm in diameter are usually used and are a piece of metal that has four stiffening ribs and a low specific gravity. Products of 60 mm have good bending rigidity, and therefore can be used in construction and for the production of engineering systems.
- Low metal consumption, which allows you to save 25% of metal during the construction of the facility.
- Installation is very fast.
- Complies with sanitary and hygienic standards, and they are also easy to disinfect and sanitize.
- Complies with all fire safety standards.
- Even the most complex structures can be erected very quickly using this material.
Application
The products differ in their shape and cross-section, and therefore they can be used in different fields of activity.
The 60 by 30 pipe has a very low metal consumption; it can be used effectively if it is necessary to save metal. When constructing the frame of a structure, pipes of 15 by 15, 40 by 60, 60 by 100 mm are usually used. They are used as structural elements.
The 25 by 25 product has low weight, high strength, convenience and ease of installation.
The versatility and excellent performance characteristics of profile structures allow them to be used in various industries, for example:
- Profile pipe 25 by 250 is used in mechanical engineering.
- 60 by 30 pipe is used in the advertising industry in the production of frames, billboards and banners.
Read more: DIY instructions for welding and installing HDPE pipes
A lot of pipes are used in the construction of most warehouses and structures.
Rolled metal is usually produced up to 12 meters in length. Therefore, very often suppliers experience some difficulties when transporting this material.
For example, to transport a product 8-12 meters long, you need to use special cargo transport, which will cost a pretty penny.
The six-meter profile is the most common option. Delivery of such a structure must be done using a Gazelle, when one end is laid on a horizontal crossbar, and the other diagonally into the body. Using a Gazelle is much cheaper than transporting it by road.
You can always order the material to be cut, a six-meter profile will then turn out to be three meters, and in this case it will fit on the roof of any passenger car.
The deviation in the thickness of the profile wall must be regulated by the maximum deviation in the thickness of the original workpiece, which has a width of 1250 mm of normal rolling accuracy B according to GOST 199 03. The maximum deviation in thickness may not apply to bending areas.
All deviations in height and width must comply with certain parameters.
- If the profile height is up to 100 mm, then the error is /- 1.0.
- If the profile height is more than 100 millimeters, then the error is 0.8.
Profile pipes are currently an indispensable building material that is used in various frames and structures.
Thin-walled ones can be used for the manufacture of various partitions and devices that do not carry any specific load.
Profile pipe range: advantages, application Detailed information about the profile steel pipe range. Range of applications. Advantages of pipes. Features of transportation and delivery of material.
The profile pipe gained its popularity in the market of construction and repair equipment due to its numerous advantages. Among them the main ones are:
- a simple algorithm for carrying out installation work. The convenient square shape makes it easier to fix the part in place, and its light weight, compared to analogue reinforcement parts, helps save time and effort for installers;
- versatility. Such a pipe can be installed in buildings of any size and purpose. This could be anything from apartment buildings to supermarkets and commercial buildings;
- relatively low cost. As mentioned above, the range of profiled products is most often used as a replacement for reinforcing elements, which are more expensive and heavier;
- high strength. Metal itself is a very strong and dense material. The pipe, made of high-quality steel, is resistant to mechanical damage and weight loads;
- resistance to the adverse effects of extreme temperatures. Such pipes are not afraid of either heat or frost, since the metal has a very high melting point and a very low coefficient of linear expansion;
- convenient form. This greatly simplifies loading/unloading, transportation and installation of profile products.
In addition, this range is capable of providing non-standard engineering and design solutions.
The creation of structures from profile pipes is carried out using conventional welding, which allows work to be carried out even at home
Types of steel pipe products
There are different classifications of steel pipelines. In particular, depending on the thickness of the wall, the following types of products are distinguished:
- Thick-walled;
- Normal;
- Thin-walled.
Steel pipeline
Based on the cross-sectional shape, the following main types of pipelines are distinguished:
- Round;
- Square (GOST 8639 – 82);
- Oval;
- Rectangular;
- Hexagonal;
- Teardrop-shaped.
There are several classes of steel pipeline:
- First class or gas main, which is used for transporting liquids, gases, laying cables, as well as irrigation systems;
- The second class is used in high and low pressure lines for gas and oil pipelines;
- The third class of pipeline is designed to operate under high pressure and temperature conditions, mainly in the food and chemical industries.
Depending on the manufacturing method, a steel pipe can be:
- Seamless (cold-deformed, hot-deformed);
- Electric welding (straight seam, spiral seam, water and gas);
- Soldering.
Rectangular steel pipes
Based on the presence of anti-corrosion coating, products are distinguished:
- Galvanized;
- Non-galvanized.
What types of thick-walled pipes are there: types and materials
Pipeline with increased wall thickness is required in industries with extreme operating conditions, for example, on drilling rigs, where the product must withstand enormous internal and external pressure. The product is often used as a pipeline for the transmission of highly dangerous substances or liquids under very high pressure.
Large thickness pipes: dimensions
A thick-walled steel pipe is a rather vague concept; in any case, just indicating the wall thickness is not sufficient here. A product with a diameter of 1400 mm and a wall thickness of 4 mm clearly does not deserve such a title.
To make it more obvious, the description uses the ratio between the outer diameter of the pipeline and the wall size. Thick-walled pipes include products whose coefficient is in the range from 0.5 to 1. The photo shows a sample of the product.
The dimensions of thick-walled pipes are regulated by GOST 8732-78. The documentation indicates standard cross-sectional sizes and possible lengths and wall thicknesses.
- It ranges from 3.5 to 75 mm. Products with increased wall thickness are rolled metal with a value of at least 6 mm.
- A metal pipe of unmeasured length is produced - from 4 to 12.5 m with an error tolerance of 5 mm, as well as measured and multiple lengths - from 1.5 to 9 m. Here the error tolerance is 15 mm
GOST 8732-78 indicates the possible deviation not only in length, but also in weight and outer diameter. The tolerance depends on the overall dimensions of the products.
Manufacturing methods
Thick-walled pipe GOST 8732-78 is a seamless hot-rolled product. The absence of joints on the surface significantly increases the strength and ability to resist pressure, which, in fact, is the most valued quality of seamless rolled steel.
The pipeline is obtained using the following technology:
- a solid cylindrical workpiece - a rod - is heated to a plastic state, without reaching the melting point;
- on a piercing mill, a hollow billet is obtained from the cylinder;
- it is fed to rollers, where it is rolled out and stretched until the precisely specified cross-section and wall thickness are obtained;
- The thick-walled pipe is cooled and cut.
The parameters of the pipeline produced by the cold-rolled method are described by GOST 9941-81. This method gives steel products additional resistance to vertical loads and greater accuracy. With the same dimensions, the deviations here are minimal.
Cold deformation received its purpose due to the fact that a cooled workpiece is subjected to rolling. This is how they ensure extremely precise geometric parameters and resistance to loads.
But during cold deformation of the metal, residual stress arises, which can serve as a future core of deformation. Therefore, the finished product is annealed to relieve stress.
The raw material for thick-walled pipes is stainless steel, since it is least susceptible to corrosion, as well as black and other special grades of steel.
Release forms
Depending on production needs, products with different cross-sectional shapes are manufactured:
- round - used to transmit aggressive liquids under high pressure. Also indispensable for drilling and mechanical engineering;
- oval - are part of production cycles where rapid cooling of the liquid is required;
- profile - square and rectangular, serve as load-bearing supports in heavy building structures.
In most cases, for construction work, black steel products are used rather than stainless steel, since it is cheaper to prime and paint first.
Metal and non-metal products
GOST for thick-walled pipes allows for the production of not only pipelines of non-standard sizes, but also the use of other materials.
- Copper - intended for hot water supply systems, drinking water supply, since they do not affect its quality at all, as well as for air conditioning systems.
- Aluminum - can be round or profile. Due to their high inertness, aluminum products are used in the chemical and food industries, as well as in construction, in the construction of framed frames.
Application areas of steel pipes
The high coefficient of thermal conductivity and the ability to operate in high-pressure working environments have made it possible to widely use this pipeline for heating and plumbing systems. Steel products are also successfully used for:
- Laying gas pipelines;
- Cable laying;
- Transportation of non-aggressive liquids and bulk materials;
- Irrigation systems;
- Construction and mechanical engineering.
Steel products are extremely widespread: laying gas pipelines, oil pipelines, high-pressure water pipelines, heating and irrigation systems.
Galvanized steel pipes
Regulatory documentation for pipeline production
The production of steel pipes, their main characteristics and parameters are regulated by the state standard GOST. Standards for steel pipelines are specified in the following documents:
- GOST 10704 – 91 – Round straight-seam main line;
- GOST 8639 – 82 – Square products;
- GOST 8642 – 68 – Oval pipeline;
- GOST 8651 – 57 – Hexagonal steel products;
- GOST 8645 – 68 – Rectangular highways;
- GOST 10705 – 80, GOST 10706 – 76 – Long-seam steel pipe;
- GOST 10692 – 80 – Round metal pipe. Assortment;
- GOST 3262 – 75 – Steel pipes for water supply and gas pipelines;
- GOST 20295 – 85 – Welded products for oil and gas pipelines.
Distinctive qualities of galvanized products
Galvanized steel pipes resist corrosion better, have a high thermal conductivity coefficient and low linear expansion, so they are recommended for high-pressure and heating water supply systems.
Steel pipes for heating
The main distinctive properties that galvanized lines have include:
- Anti-corrosion coating helps to successfully resist rust (rust appears on galvanized products 10 times slower!);
- Galvanized products are easy to cut, shape and weld;
- The service life of a galvanized main increases to 25-50 years, which is 2-5 times higher than that of a conventional one;
- The outer diameter of a galvanized pipe does not differ from a regular metal one; the only changes are in the wall thickness due to the applied layer of zinc.
According to the cross-sectional shape, a galvanized pipe can be:
- Round;
- Oval;
- Square (GOST 8639);
- Rectangular;
- Hexagonal;
- Octagonal.
Steel pipeline in PPU insulation
A steel pipeline in polyurethane foam (PPU) insulation is used for gas pipelines and liquid transportation under conditions of high pressure working environment. Products in polyurethane foam insulation are manufactured in accordance with GOST 30732 - 2001 in the form of a pipe-in-pipe design. For thermal insulation, pipe products with a diameter of 25 to 1200 mm can be used, and poured polyurethane foam can be used as a thermal insulation layer.
Steel pipes in PPU insulation
The use of polyurethane foam insulation allows you to reduce the cost of laying a pipeline, because excavation work can be carried out without channels and wells. Thanks to the use of polyurethane foam, the walls of the products are reliably protected from freezing and heat loss.
You can also highlight the following advantages of polyurethane foam insulation:
- Products in polyurethane foam insulation are completely protected from external corrosion;
- Slight linear expansion;
- Service life is 2.5 times longer;
- Possibility of quick installation;
- Polyurethane foam gives durability and aesthetics to products.
Metal pipes
1.1. Steel pipes
Steel pipes, despite the increasing use of other types of pipes, are often used in the water supply and wastewater industry. Pressure pipelines are installed from them to transport liquids (cold and hot water, waste water) and gases. These are durable products that can withstand significant loads. However, there are limitations in the use of steel pipes due to corrosion phenomena and the fouling of pipes with corrosive rust, even with protective coatings.
According to the production method, steel pipes can be divided into seamless (hot- and cold-deformed) (Fig. 1) and electric-welded (straight-seam, spiral-seam, water-gas, profile). Welded pipes are made from a flat steel sheet that is rolled depending on the cross-sectional shape and type of seam. If the seam is straight, then the steel strip is rolled into a tube using rollers and welded with a tungsten electrode in an inert gas (TIG welding) or with high frequency current (HF welding).
To obtain a spiral-welded pipe, a steel strip is wound in a spiral. Profile (not circular cross-section) and water and gas pipes are also produced using the welded method. Seamless pipes are produced from steel rods by drilling, casting, hot or cold forming.
Rice. 1. Seamless steel pipes
To protect pipes from corrosion, various types of coatings are used: zinc (cold and hot galvanizing), extruded polyethylene, polyethylene (in one or several layers), cement-sand mixture, epoxy-bitumen mixture, etc.
Advantages of steel pipes:
- strength, withstand pressure up to 30 atmospheres;
- good resistance to dynamic loads and bending forces;
- resistance to mechanical damage;
- non-flammability;
- heat resistance, withstand high liquid temperatures up to 130 ◦C;
- It is possible to completely recycle pipes at the end of their life cycle.
Disadvantages of steel pipes:
- high weight;
- tendency to corrosion or deposits on the internal surface depending on the composition of the transported liquid or corrosion of the external surface (“soil” corrosion);
- high thermal conductivity;
- significant internal roughness, which increases during operation;
- violation of the protective coating (for example, zinc) when connecting pipes by welding.
Several important parameters are used to characterize pipes:
- conditional diameter (DN) - a conditional value that represents the value of the actual internal diameter of the pipe, rounded to the nearest larger standard number. The conditional diameter is used to select connecting parts, for example, pipeline connections, fittings (fittings) and fittings. Measured in mm or inches;
- internal diameter - the actual value of the parameter obtained by direct measurement, in mm;
- outer diameter - the actual diameter of the pipe taking into account the wall thickness, in mm.
More details about fittings and other equipment on water supply and wastewater networks are described in Chapter 5.
Values of the nominal diameter of water pipes (mm) in accordance with GOST 28338–89 “Pipeline connections and fittings. Nominal diameters. Rows" are given below: 10–15–20–25–32–40–50–65–80–100–125–150–200–250–300–350–400–450–500–600–700–800–900 –1000–1200–1400–1600.
Steel pipes are marked in accordance with the standards of GOST 10692–2015 “Steel, cast iron pipes and connecting parts for them. Acceptance, labeling, packaging, transportation and storage”, introduced in the Russian Federation in 2021 to replace GOST 10692 - 80. According to the standards of this GOST, each product with a diameter above 159 mm must be marked with information about the product. For products with a smaller diameter, information is placed on a label attached to the product packaging.
Marking of steel pipes in accordance with GOST 10692–2015 is carried out at the factory after production and contains information about the size, grade of steel from which the pipe is made, as well as the manufacturer’s trademark. The size of the letters and numbers of the branding is directly proportional to the size of the product and can be applied using several methods. The most common are branding and waterproof paint. Several methods can be used.
Marking in accordance with this GOST can be applied on the outside of the pipe at different distances, but no more than 500 mm from the pipe cut and no closer than 20 mm, from the end of the pipe cut when the steel pipe wall thickness is 7 mm or more, as well as on the inside of the pipe when product diameter more than 350 mm. If necessary, the inscription can consist of several lines.
The marking of gas supply pipes contains information about the diameter of the pipe, the presence of insulation, the presence and type of thread, as well as other necessary information.
Let's look at an example of branding:
Ts-R-25×2.8 stands for:
- C - galvanized surface;
- P - thread; 25×2.8 - (inner diameter) × (wall thickness).
1.2. Pressure pipes made of high-strength cast iron with spheroidal graphite (ductile iron)
The main disadvantage of steel pipes and gray cast iron pipes for external water supply is problems with corrosion, overgrowth of the internal surface and poor strength characteristics of gray cast iron pipes.
In recent years, a new type of cast iron pipes has found application in plumbing practice (Fig. 2) - pipes made of high-strength nodular cast iron (ductile iron).
High-strength cast iron with nodular graphite, which undoubtedly has a rare combination of physical and mechanical characteristics, is obtained by modifying graphite particles in cast iron. In 1943, American researcher Keith Millis obtained spherical graphite in cast iron, instead of the previously existing plate-shaped one, by adding magnesium to the alloy.
Rice. 2. VChShG pipes (range of cast iron pressure pipes)
Ductile iron pipes have the following properties:
- durability (predicted service life from 80 to 100 years or more);
- impact resistance;
- high plasticity;
- environmental friendliness (after the end of its service life or in case of failure, complete disposal of the pipe is possible);
- cold resistance (predicted to –60 °C);
- low accident rate (compared to pipes made of other materials);
- high speed of installation, ease of installation of pipes during laying;
- resistance to changes in hydraulic pressure (withstands possible peak values of up to 550 N/mm2);
- high resistance to external loads (it is possible to lay a ductile iron pipe in the ground to a depth of up to 8...10 meters without preparing a “bed” or “cushion”);
- anti-corrosion properties (ductile iron pipes are not susceptible to overgrowing and corrosion of the internal surface, perfectly maintaining the high quality of tap drinking water).
Ductile iron pipes are used:
- in hot and cold water supply;
- sewerage and drainage;
- heat supply;
- cathodic protection of pipelines;
- pipelines for oil-containing liquids.
In our country, pipes made of high-strength cast iron are produced by only one enterprise - Lipetsk Pipe. The company's share in the supply of material for housing and communal services pipelines is about 25% in Russia.
The official website provides the following information:
- nominal diameter of products varies from 80 to 1000 mm;
- standard pipe length is 6 m;
- All products of the Lipetsk plant are manufactured exclusively for socket joints with a rubber seal. In this case, the manufacturer uses three types of locks, differing in the operating pressure range and application conditions (Table 1);
- The locks make it possible to install pipes not only on the same longitudinal axis, but also with a deviation from the straight line of 1.5 - 5° angular degrees without the use of fittings and without violating the tightness.
Figure 3 shows the connection of ductile iron pipes with a Tyton o-ring. This type of pipe connection at the joint under a double-layer ring seal is used for cold water supply and sewerage pipes.
Table 1. Types of ductile iron pipe connections
| Compound | Working pressure, MPa | Diameter, mm |
| Tyton | 3,0–6,4 | 80–1000 |
| Tyton-SIT | up to 1.6 | 80–400 |
| R.J. | 2,5–8,8 | 80–500 |
| R.J.S. | 1,6–3,2 | 600–1000 |
Despite the corrosion resistance, the products are additionally equipped with protective coatings. Let's look at protective coatings in a little more detail.
The outer protective coating consists of two layers:
- metal zinc;
- bitumen varnish.
Rice. 3. Pipe connection with Tyton1 O-ring
The protective coating is interesting because it is capable of self-healing. How does this happen? The fact is that zinc forms a galvanic couple with iron and alloys based on it, including ductile iron. If the zinc layer is damaged, the exposed cast iron acts as a cathode, and the galvanized surface of the pipeline acts as an anode. The migration of zinc ions gradually restores the protective layer. In addition, when laying pipes in the ground, an extremely durable and practically insoluble layer of zinc oxides, salts and hydrates is formed on the surface of the pipeline.
All products are ductile iron pipes with a cement-sand coating (CSC). What is CPP? This is a coating that protects the walls from the aggressive effects of the transported environment.
The manufacturer emphasizes that the CPP provides passive and active protection. Passive protection refers to primitive mechanical protection against abrasive wear and direct contact with an aggressive environment. Active - consists of the gradual saturation of the pores of the protective layer with cement hydration products, primarily calcium hydroxide, which provokes the transformation of iron in the surface layer into oxide (Fe2O3), which is retained by the cement-sand coating from destruction, which can prevent further corrosion of the walls.
CPP has additional beneficial properties, namely:
- despite the relative roughness, it reduces the hydraulic resistance of pipes, preventing the formation of deposits;
- is self-healing under conditions of transportation of the aquatic environment. When cracks occur and the coating is moistened, the same hydration of cement with the formation of calcium hydroxide and carbonate contributes to their gradual filling.
Corrugated pipe: characteristics and use
Corrugated steel pipe is universal in its application; it can be used for gas pipelines, cold and hot water supply, high-pressure water supply systems, air conditioning systems, as well as for laying cables.
Corrugated steel pipes
The corrugated line has smooth inner walls and a ribbed outer surface. It is this design that provides a lot of advantages that a corrugated pipe has:
- Resistance to external and internal mechanical influences;
The corrugated pipe can withstand water hammer up to 65 atmospheres.
- Flexibility and ductility, absence of microcracks;
- The corrugated line has internal walls that are resistant to silting;
- Frost resistance;
- Environmental friendliness;
- Resistance to the formation of fungi and mold;
- High heat dissipation;
- Possibility of installation under a concrete screed (this feature is especially in demand if a gas system, heated floors are being installed, or electrical wiring is being laid);
- Easy installation;
- No need for line maintenance.
Corrugated steel pipes
A corrugated pipe can bend in any direction without the use of special tools and negative consequences in the form of destruction of the integrity of the structure. The corrugated line is connected without welding; the elements are joined using brass fittings.
Corrugated stainless steel products come in the following types:
- Annealed;
- Unannealed;
- Sheathed in polyethylene.
Types of water pipes and basic requirements
Water is supplied for various purposes:
- drinking, cooking;
- for watering;
- fire extinguishing;
- hot water supply;
- ensuring the production and technological cycle.
For external or internal water supply networks, the following pipes are used:
- straight-seam steel according to GOST 10704;
- copper for water and gas GOST 52318;
- pressure ones made of polyethylene according to GOST 18599;
- pressure ones made of thermoplastics according to GOST 52134;
- multilayer of metal and polymers in accordance with GOST 53630;
- asbestos-cement according to GOST 539-73;
- cast iron according to GOST 21053.
The standards regulate the internal and external diameter of the pipe, wall thickness, weight per linear meter, strength, composition and properties of materials. The structures must be resistant to constant pressure and withstand the operating temperature of the environment. Damage, deformation, cracks or cavities are not allowed on the internal and external surfaces.
The external water supply is laid underground, the internal network is located in the building along or in the thickness of the walls, under the baseboards or under the floor.
Scheme of internal water supply in a two-story house
The highest requirements for the quality of pipes for supplying drinking water to a home. Hazardous substances can penetrate the liquid and harm human health. Thus, an excess of copper leads to liver cirrhosis, and an increased concentration of iron leads to the deposition of toxic compounds in human organs.
Main characteristics - external (Dn), conventional or nominal (DN or DN) diameters, wall thickness. Products with a diameter of 5-102 mm are classified as small-sized, 103-427 - medium, over - large-sized.
Pipe parameters
*
Water supply networks are designed for a certain pressure indicator:
- up to 12 atmospheres - low pressure;
- 12-25 - average;
- over 25 - high.
In apartments or private houses, pipes must withstand a pressure of at least 2 atm. The pressure in the internal fire water supply system is higher - up to 10 atm.
To transfer cold water, pipes with a temperature resistance limit of up to +46° are used. Transportation of higher temperature media is carried out by “hot” pipelines.
The question of which pipes are best to use for plumbing can be answered by considering all the options and weighing the advantages or disadvantages of each.
Stainless steel corrugated pipe
| Author | Share | Rate |
| Victor Samolin |
Interesting on the topic:
The concept of specific gravity and methods of calculation
The value of the specific gravity of steel pipes and calculation methods
Classification of ventilation pipes
Comments on this article
remenergo-pro Is it better to use regular steel or galvanized pipes for a home heating system?
Which ones will be more reliable and last longer? 03/11/2016 at 10:39