Welding metal parts has been known to mankind for a long time. However, with the development of metallurgy, the emergence of new alloys and compounds, technology began to improve in order to meet all the requirements of emerging realities. Any novice welder needs to learn more information about TIG welding: what it is, how to use the equipment, what strengths and weaknesses it has.
TIG welding
What is TIG welding?
Before moving on to a description of the equipment and an analysis of the advantages and disadvantages, it is necessary to understand the principles of technology and the features of TIG welding. TIG welding is a method of joining metals that uses a tungsten electrode with a shielding gas. The rod is considered “non-melting”. The welder must sharpen it before use to ensure a stable arc and a straight weld.
The tungsten electrode is fixed in the torch in the center of the nozzle. At the edges of the burner there are holes through which protective gas is supplied. Argon is used for this. It protects the welding site from the formation of an oxide film. Additionally, filler wire must be used. It is desirable that it be made of the material that needs to be welded.
FLAWS
We also consider it our duty to tell you about the disadvantages of TIG technology.
- Windy weather can ruin your welding plans by blowing gas out of the weld area (you can install shields for protection, but this will waste more gas).
- Meticulous preparation of metal surfaces before welding is necessary. Parts must be clean and free from oil, dirt and grease. Without this mandatory step, the quality of the weld will significantly decrease.
- The torch mechanism does not make it easy to weld parts in hard-to-reach areas. You can make the rod extend longer or make the electrode smaller, but overheating or other problems may occur.
- If you are not experienced in TIG welding, striking an arc outside of the welded area can create marks that must then be cleaned up.
History of appearance
Welding has been known to mankind for decades. The idea that it was possible to join metal parts under intense heat first appeared at the beginning of the 20th century. Charles L. Coffin, an American engineer, thought about creating such equipment. However, the first samples of equipment did not allow the device to be used in industrial conditions or to weld metal alloys.
A non-consumable tungsten electrode and a shielding gas (inert helium) were first tested in the 1940s. Using this technology, it was possible to combine aluminum, magnesium, and nickel. The method became popular in aircraft and rocket engineering, and then gained popularity among other areas of industry.
Application area of TIG welding
TIG welding is a universal method in its properties, because it can be used to reliably join different types of metals. In some cases, it is even possible to weld dissimilar alloys together. Its scope of application is limited only by the fact that you will have to constantly carry a heavy gas cylinder with you.
Therefore, such welding is more stationary than mobile, but in some cases it is still popular with on-site work.
It is mainly used for welding non-ferrous metals, because it allows you to work in an environment with an inert gas without access to oxygen, which is a powerful oxidizing agent.
When argon enters the melting area, the air is squeezed out by it, which creates optimal conditions for melting without scale. It also perfectly welds various metal parts from other types of alloys, creating bimetallic joints, so it is universal and can be used to work in any situation.
It is especially worth mentioning the possibility of welding thin-walled parts, pipes, thin profiles, which cannot be said about the electric arc welding mode. By fusing metal over the parts, a thick seam is formed due to the deep penetration of the melt between the parts.
Advantages and disadvantages
Any technological process has strengths and weaknesses. Advantages of argon TIG welding:
- Thanks to the use of protective gas, the seam is uniform, without pores, cracks, or voids. Argon protects the heated surface from the oxide film formed when hot metal interacts with oxygen.
- Internal stresses generated during welding without shielding gas are reduced.
- Metal does not splash.
- After welding, the products do not require additional processing.
- TIG welding can be used to join most known metals and alloys.
- It is enough to try to operate the equipment 2-3 times to master the skill of creating high-quality, beautiful seams.
Disadvantages of TIG welding:
- When using equipment outdoors, the connection point must be protected from the wind. Air flows disrupt the direction of movement of the protective gas, deteriorating the quality of the seam.
- It is necessary to carefully prepare the work surface.
- You cannot select an acute angle of inclination of the torch relative to the workpiece. This complicates the workflow.
- At the place where the electric arc ignites, a mark remains that will need to be cleaned off.
Considering the shortcomings of TIG equipment, you can prepare for possible difficulties during welding operation.
Beautiful weld seams
TIG
This abbreviation translates from English as “tungsten and inert gas,” the most common being argon. We have already understood that the use of tungsten infusible electrodes is typical for hand-held equipment. Advantages:
- a very beautiful seam is immediately formed that does not require stripping;
- preventing porosity;
- filler wire - from the same composition as the workpiece;
- no oxidation;
- small heating zone, so you don’t have to worry about deformation;
- an easy method, even beginners can use it;
- few harmful substances are released during operation.
Application
Since TIG technology allows you to connect many metals and alloys based on them, it is used in various areas of industry:
- Automotive industry, manufacturing of parts for industrial equipment.
- Space industry.
- Construction of ships and airplanes.
- Manufacturing of medical instruments.
- Construction, creation of power tools.
TIG technology is often used at home. Using machines with tungsten electrodes, car body parts are welded and radiators are repaired.
Peculiarities
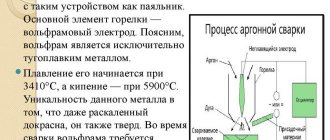
If you translate the name of the mode into Russian, which gives the abbreviation TIG, you get “tungsten with inert gas.” Let us examine in more detail the purpose of each element in the welding process. Metal penetration is carried out under the influence of an electric arc, which is created between two electrodes under high voltage. The role of one electrode is played by the part being welded, and the other is played by a special tungsten rod, which is controlled by the welder.
The tungsten electrode melts at a temperature of 4000°C degrees. This indicator is significantly higher than that of other metals and alloys, so this electrode can be used to weld almost any type of steel. To obtain an accurate and neat seam, the electrode should be periodically sharpened. The tungsten rod is fixed in the torch collet, and the unused part is placed in a special cap that prevents short-circuiting.
The welding machine torch is designed in such a way that an electrode is placed in the middle of the nozzle, and gas is supplied in a circle. Since argon acts as a shielding gas, this welding method is called argon arc welding. The idea of inert gas protection is to displace oxygen. If it penetrates into the weld pool, hydrogen will begin to be released as a result of chemical reactions, which will lead to the appearance of many cracks during metal crystallization. For each alloy, its own welding mode is determined, characterized by a certain amount of gas and voltage value on the electrodes.
With sufficiently precise processing of the edges of the parts being welded, their penetration and subsequent crystallization occur. If there is a gap between the surfaces that cannot be eliminated, then a special filler substance is used, which is fed into the welding zone in the form of a wire.
The TIG welding type has become widespread. Due to the fact that the arc temperature is quite high, it is possible to work with carbon steel, as well as non-ferrous metals and their alloys. TIG welding is used when processing cast iron, copper and aluminum products, but it shows its main advantage when welding stainless steel. Stainless steel can also be welded using MMA inverters, however, argon arc welding produces a neat and precise seam, which should not be subsequently cleaned of slag.
The wire for the additive must be made of the same material as the elements being welded. TIG welding allows you to weld aluminum. If there is no protective gas, the molten aluminum quickly oxidizes. In an argon environment, the characteristic oxide film does not form, and the edges melt evenly.
TIG welding is most often used in the following jobs and industries:
- mechanical engineering;
- work with food steel, production of tableware;
- production of containers for storing chemically aggressive substances;
- car repair.
Like any other type of welding, argon arc welding has a number of requirements and has certain features. Every welder should know about them, since otherwise it will be impossible to guarantee a high-quality result.
- The parts to be welded, in particular the edge surfaces, must be cleaned of foreign elements and degreased.
- The tungsten electrode is connected to the negative terminal of the inverter.
- Welding aluminum requires equipment that operates in AC mode (alternating current).
- It is necessary to correctly calculate the welding current based on the operating conditions. In particular, the choice of its value is influenced by the diameter of the electrode. Excessively high current will cause the electrode to melt, which is undesirable.
- In the absence of proper experience, it is recommended to form a small arc.
- Before welding, it is necessary to prepare the torch. The tungsten electrode should protrude 3-5 mm from the collet.
- It is necessary to pay attention to the uniform distribution of gas across the cross-section of the burner nozzle.
Modes
TIG equipment operates using unipolar or alternating current. Each of the individual TIG welding modes is used for different materials.
TIG welding mode
D.C
Equipment operating on direct current has certain advantages. These include:
- The efficiency of the work process increases.
- You can weld parts to great depth. The seam is narrow, but deep.
- The speed of the welding process increases.
The minus is fed to the tungsten electrode, the plus goes to the workpiece. Equipment operating on direct current is suitable for joining alloy steels and stainless steel.
Alternating current
Equipment during operation of which there is an automatic change of minus and plus. As the reverse polarity increases, the surface is more effectively cleaned of the oxide film.
What is needed for argon welding
The method of welding metal using inert gas implies great possibilities in terms of choosing equipment and materials. This can sometimes be confusing for new welders. But in fact, their fears of doing the wrong thing are completely unfounded. Most of the equipment and accessories on the consumer market are universal and suitable for a wide range of jobs.
Installations designed for argon-arc welding are divided into three groups:
- Specialized . Designed specifically for performing the same type of work. Most often in demand in industry, when you need to quickly and accurately process workpieces of the same type.
- Special . Another type of equipment in demand at industrial enterprises, which is designed to work with workpieces of the same size.
- Universal . It has become the most widespread and in demand among a wide variety of categories of users - from professionals to novice welders.
In addition to the device, additional equipment is also needed:
- tungsten torch and consumables;
- contactor – used to connect power to the burner;
- cylinder with a reducer for inert gas;
- relay - responsible for connecting the oscillator or contactor;
- rectifier – converts voltage to DC 24V;
- timer - used to control the period of time for blowing the working area with argon;
- ammeter – measures current strength;
- power supply valve;
- battery to stabilize the AC circuit;
- filter – controls high voltage pulses.
To operate, you will need two transformers: the main and auxiliary. The oscillator is connected in parallel with the power source. It is required to supply a high-frequency pulse, with the help of which an arc is ignited between the metal and the non-consumable tungsten rod. In a household network, the voltage is 220 V and the frequency is 50 Hz. After the oscillator, these figures are 6,000 volts and 500,000 Hz.
To work with workpieces of large thickness or to increase the productivity of welding equipment, additional equipment is required:
- a special burner into which several electrodes are inserted at the same time. As a result, a good quality seam is obtained at a higher torch speed;
- device for preheating filler wire.
Pulsating current supply makes it possible to make micro-pauses in work, which contribute to the crystallization of the melt and improve the quality of the seam.
Equipment
The welding process can be carried out with shielding gas and a non-consumable tungsten electrode using a conventional inverter with a torch that can supply gas. However, there are two types of specialized tools:
- TIG inverter. It is complemented by a block that can generate direct or alternating current. Thanks to this, the functionality of the device increases. Makes it possible to work with steels, aluminum, alloys.
- Welding rectifiers. The device converts alternating current into direct current. It is a professional device.
Equipment and consumables must be selected depending on what metal or alloy will be processed.
Inverter TIG welding
Algorithm for assembling a welding machine
After purchasing the installation, consumables, and connecting elements, you need to assemble the individual parts and mechanisms together. Assembly steps:
- Connect the oscillator to the inverter.
- Secure the wire responsible for ground to the terminal marked with a plus sign.
- The wire that is connected to the burner must be connected to the terminal with a minus sign.
- Attach the burner to the sleeve through which the gas flow will be conducted.
- Prepare an argon cylinder. Screw on the gearbox.
- Secure the gas supply hose to the reducer.
- Connect the inverter to a common network - 220 V. The oscillator must be powered from a power supply that produces 6 V.
To avoid mistakes when connecting elements, you can watch diagrams and training videos. After assembly, you need to configure the device. The quality of the work performed will depend on this.
Advice from experienced welders
- One of the first recommendations is to carefully study all the information regarding the heating mode, the characteristics of the alloy, the capabilities of the welding machine and the nuances of the block of parts. It would not be amiss to familiarize yourself with examples of technological (operational) maps drawn up in production for specific welding operations. In this case, parameters such as gas flow, welding current mode, electrode feed speed (for automatic machines), thickness and material of the parts being welded are necessarily standardized.
- It is necessary to turn on the supply of argon to the zone 20 seconds before the ignition starts, and turn it off no earlier than 10 seconds after it is turned off.
- To prevent the electrode and filler wire from oxidizing, they must always be in the gas protection zone.
- The filler wire is fed into the melting zone at an angle to both the electrode and the weld. This will allow you to get a better and narrower welding strip.
- The burner should be moved along the seam carefully, without sudden transverse movements - this makes the seam uneven and excessively wide.
- The smaller the arc, the deeper and smoother the seam will be, but reducing the arc requires the electrode and filler wire to be as close as possible to the weld pool.
- It is impossible to complete the work by abruptly turning off the arc. It is necessary to weld the crater with a gradual decrease in current strength (regulated by the rheostat of the device).
- When working with voluminous or complexly shaped parts, it is necessary to provide in advance for the possibility of a gradual transition of the welder from one area to another and, accordingly, the required length of the hose and, in some cases, the use of a mobile platform for the welding machine and a cylinder with a reducer. In other cases, it is more convenient to use a rotary/movable table with the welding block rigidly fixed to it.
Welding technique
The DIY welding process requires preliminary setup of the machine. To do this, the welder needs to perform a number of actions:
- When using non-consumable tungsten electrodes, they must be prepared in advance. The working rod must be sharpened using a needle file.
- After sharpening the electrode, it must be installed on the burner. A collet clamp is used for this.
- Open the valve on the argon cylinder. Using the reducer, set the operating gas flow rate. The optimal rate is 13 l/min.
- Fix the mass on the workpiece or metal work table.
- Turn on the oscillator. Bring the burner to the metal surface.
- After pressing the power button, a spark will appear. Open the gas supply to the burner.
The distance between the end of the electrode and the working surface must be at least 3 mm. You can guide the pointed part in different ways. If you increase the distance between the tungsten tip and the metal, the seam will become wide and the welding depth will decrease. When connecting thin workpieces, you need to move the torch from right to left. To make a root seam, you need to guide the electrode evenly. Corner joints are connected at an angle of 45 degrees.
TIG welding is used to join metals and metal-based alloys. The shielding gas used during the work prevents an oxide film from appearing. It is important to set up the equipment correctly, sharpen the non-consumable electrode before work, and keep the arc at the same distance from the workpiece.
Working principle of argon arc welding
In international designation, the argon arc method has the abbreviation TIG. It is actively used in production and workshops. It is used to connect cracked car parts (crankcase pans, engine cooling blocks), assemble containers for the food and chemical industries, make stainless heated towel rails, manifolds, liquid filters, etc. In a garage, such a device can successfully perform body repairs or produce small parts. products.
The operating principle of argon welding is to join metals with an electric arc in an inert gas environment. The process requires a current source that lowers the voltage and increases the amperage. The current is supplied to a torch equipped with a tungsten electrode. It is non-consumable, so it is easier for the welder to control the length of the arc, which should be 2-5 mm. The ground cable is connected to the product.
Touching the tip of a tungsten needle to the part initiates an electric arc. For thin seams, transverse vibrations are not required - the electrode is moved evenly, from right to left along the seam line, the joint surface is smooth as a mirror. If there is a gap between the parts or it is necessary to expand the boundaries of the seam, then when moving the torch, the welder makes slight oscillations on the sides, stretching the weld pool. This promotes the formation of small scales.
Tig welding process.
The arc temperature ranges from 2000 to 5000 degrees, depending on the current strength. This allows the edges of the metal to be melted and joined with a thin seam. To strengthen the structure, filler wire is used, fed with the welder’s second hand into the weld pool. Thus, you can increase the height of the bead, give the seam a scaly appearance, and even perform metal surfacing for subsequent mechanical processing (turning on a lathe, grinding).
To protect the weld pool from the external environment, the inert gas argon is used. It is supplied from the cylinder to the burner and displaces normal air. This eliminates the formation of pores in the seam structure. The connection is tight and durable. At the same time, the shielding gas cools the tungsten electrode and ceramic nozzle so that they do not overheat. At the final stage, when the arc is extinguished, argon helps to solidify the seam.
Scheme of the argon arc welding process.
Pros and cons of the TIG method
The TIG method has clear advantages over other welding methods, but working with an argon welding machine also has several disadvantages that you need to be prepared for when choosing this welding method.
Pros of the TIG method
- local heating eliminates serious deformation of the product;
- a thin tungsten needle allows you to create narrow, neat seams;
- You can weld with or without an additive, affecting the height of the bead;
- the connection is obtained without a slag crust on top;
- in most cases no follow-up is required
- mechanical restoration; can weld stainless steels and non-ferrous metals;
- the seams are sealed and can withstand high pressure;
- there are no metal splashes sticking to the surface.
Disadvantages of the TIG method
- connection speed is inferior to MIG;
- the burner cap interferes with work in hard-to-reach places;
- the ceramic nozzle slightly limits the visibility of the weld pool;
- the quality of the seam depends on the user’s skills (you won’t be able to immediately take it and cook it like a semi-automatic machine);
- it is necessary to constantly feed the additive with the second hand and control its length (when welding, the length of the wire quickly shortens, and long pieces are inconvenient to hold in your hands,
- because they are “walking”);
- tungsten electrodes are more expensive than coated ones;
- additional costs for argon;
- It is impossible to qualitatively weld parts outdoors in strong winds (argon is blown away and the weld pool remains unprotected).