Forge welding is one of the oldest methods of permanently joining metals. Humanity used forge or forge welding for almost three thousand years as the only one for the manufacture of various iron products, until they learned to melt it, having also mastered foundry welding. But with the development of technological progress, other effective ways of joining metals to each other appeared, so forging welding has practically ceased to be used in industrial production.
What is forge welding
Forge welding is commonly called the technological process of creating a strong connection between metal parts during thermal heating under the influence of external pressure. That is, parts of iron blanks at the site of future welding are heated to high temperatures, achieving a dough-like surface state. Then they create pressure by hammer blows on the workpiece lying on the anvil, thereby achieving the creation of a strong permanent connection.
Technologically, forge welding includes the following individual operations:
- mandatory preparation of the welded surface,
- thermal heating to a strictly defined temperature,
- joining the ends of workpieces by forging,
- final forging to give the workpiece the required shape.
One of the most important conditions for successful forge welding is temperature. It must be detected by the color tone of the glowing surface. So, for iron, a temperature of 1300⁰ C has a bright yellow surface color, and when it reaches 1400⁰ C, the metal begins to glow with a bright white hue. Immediately upon reaching the required temperature, it is necessary to perform forging welding, since overexposure will lead to burning of the metal and the formation of a larger layer of scale.
Forging
Once you have heated the part, place it on the anvil. It is immediately necessary to make firm blows on the device to clear the part of debris. After this, place the two heated parts side by side and hit them lightly with a special hammer.
To prevent the metal from oxidizing, it is necessary to make frequent and rhythmic blows. The parts must be connected securely. After this, hit the workpiece harder, but do not lose the rhythm.
High impact force will ensure tight joining and obtain a uniform shape of the parts. They will finally unite with each other. To increase density, it is necessary to forge not only the ends of the structure.
Pay attention to all areas. Forging begins in the middle of the structure and smoothly moves towards its edge. This will ensure uniform release of slag.
When forging is completed, you can warm up the finished structure again. After this, many craftsmen perform forging again. Do not overdo it and warm up the parts too often. This can cause the seams to be weak.
Features of forge welding
The ability to join by thermal diffusion under pressure when heated to a plastic state varies greatly among different groups of metals and their alloys.
Forge welding process
Thus, low-carbon steels with a proportion of carbon inclusions of up to 0.6% are welded well; with an increase in carbon content, the welding ability of iron significantly deteriorates.
Poor weldability during forge welding is typical for many alloy steels, non-ferrous metals and their alloys. And also all types of cast iron cannot be thermally joined by forging.
The main obstacle to the possibility of combining iron during heating is the formation of a layer of scale on the heated surface, which consists of fairly refractory oxides FeO and Fe3O4, which are unable to melt at the temperatures at which the surface layer begins to soften. In order for these oxides to interfere with the welding processes as little as possible, the future surface to be welded is coated with various acidic fluxes. Basically, table salt, boric acid and calcined borax are used for this. More often, instead of flux, traditional materials are used in the form of simple broken glass and fine river or quartz sand.
Forge welding is a rather complex technological process and requires certain knowledge and skills to carry out. For example, the possibility of forge welding strongly depends on temperature and, if the required limit of thermal melting of the surface layers is not reached, this will lead to lack of penetration, but if the metal is overheated, burnout or even melting will occur, which will not allow achieving a strong and high-quality connection in both cases details.
Advantages and disadvantages
Modern blacksmiths actively use the forge welding method, but it has positive and negative aspects. Among the advantages are noted:
- the ability to connect almost any metals and alloys, even stainless steel;
- heating below the liquidus point allows maintaining the properties of the metal without changing the composition;
- Proper forging ensures the tightness of the joint, reduces its graininess, and also helps to remove (forge) voids in the seam.
This method also has disadvantages:
- low productivity;
- high probability of defects;
- slow heating.
Forge welding methods
There are several simple, not requiring special preparatory measures, methods for making joints using forge welding, namely:
- end-to-end;
- overlap;
- in girth.
The only mandatory condition for such welding methods is the need to make the ends of the workpieces in the form of a convex shape and with significant thickenings at the ends. This is due to the fact that during forge welding (namely, during thermal heating), a slag film is actively formed on the welded surface and in order for the slag particles to be squeezed out during the forging of the workpieces, a convex surface is required. But the thickened welded ends of the workpieces are, first of all, needed for the process technology itself and allow, after forging the welding area, to bring the cross-sectional shape of the workpiece to the specified dimensions.
More technologically complex methods are:
- split welding, for example, for joining steel strips in the manufacture of steel tires for village carts;
- welding with checkers, which was mainly used to create strong connections of large-sized parts.
In the first case, the ends of the strips are specially prepared by pulling and cutting so that they can be connected to the ceiling before welding, and then, after heating to the required temperature, they are welded on both sides using forging.
In the second case, during the preparation of the future welding site, they are made in the form of angles of 30 or 40 degrees, and additional parts for inserts, which are called checkers, are made of the same angular shape. Next, the entire structure is brought to welding temperature and, using a hammer and anvil, the joint is given strength and the desired shape.
general information
Forge welding (also known as forging welding) is a method of joining metals, the essence of which is to form a weld using forging tools. The metal is brought to a plastic state and struck with a forging hammer. Before the invention of RDS, this welding method was used everywhere. But now forge welding is used only for joining parts made of low-carbon steel.
To get a high-quality seam, you need to thoroughly clean the metal. Contaminants and corrosion should not prevent the weld from forming during forging. But you need to understand that forge welding is labor-intensive and low-productivity work. In addition, the seam is not as strong as desired. For this reason, forging welding is not used in production, but remains the domain of private workshops. However, with the help of such simple technology, you can perform simple repairs in the field with your own hands.
Areas of application
Forge welding is an ancient craft and is still widely used by artists and blacksmiths today.
So, along with hot or artistic forging, they also use artistic welding to create various decorative and design products from metals. This welding method is also used in forges to produce various kinds of composite tools, for example, axes, plows and other agricultural implements.
The industrial use of forge welding is gradually losing its position. This comes with a number of significant disadvantages. Such as:
- slow heating,
- relatively weak strength,
- low productivity,
- heterogeneity of precipitation processes,
- demand for qualified craftsmen.
Although there are still areas of industry where forge welding remains in demand. For example, for the production of steel water pipes with a small diameter of up to 100 mm. To do this, strip steel is heated in thermal furnaces and rolled through coils, and at the end of the process it is pulled through special drawing mandrels at high speed, due to which pressure welding of the longitudinal seam of the pipe occurs.
They use industrial forge welding technology to obtain a multilayer steel structure and to produce bimetallic plates by jointly rolling heated workpieces through rollers or pressing in vacuum thermal chambers.
Treatment
When it comes to the production (welding) of artistic products, then it is impossible to do without finishing work. This allows you to make the design attractive.
If this is important to you, you can finish the finished material. To do this you will need a blacksmith's tool.
This step is not considered mandatory, but can be used in rare cases. Also, parts are occasionally polished and quartzed when repairs are made.
Brushes that contain metal bristles help with this. Polishing paste allows you to make the structure smooth.
Equipment and consumables
In order to independently engage in forge welding and hot artistic forging, you will not need much equipment and tools to organize a small forge.
So, to operate a full-fledged blacksmith’s workshop you will have to purchase:
- portable and stationary forge, i.e. a special device for heating metal to the required temperature (in extreme cases, a simple gasoline autogen will do);
- several types of anvils: large and small, one-horned and two-horned, which must be placed in the workshop with special strength;
- blacksmith pliers of different sizes;
- various types of hammers, ranging in size from a good sledgehammer to a plumber's hammer;
- two containers for cooling: one for water, the other for oil.
Additionally, you may need various scrapers, molds, stands, tools for bending workpieces, and much more.
You should definitely take care of fire safety and personal protective equipment, such as glasses, a leather apron and canvas gloves.
Advantages and disadvantages
Disadvantages of forge welding:
- Provides relatively low connection reliability.
- Low productivity , requires a lot of effort and time.
- Not suitable for production scale.
- Suitable for welding not all types of metal.
- A highly qualified master is required for a high-quality result.
Advantages of forge welding:
- Increases the cost of the product.
- It is the only way to obtain some materials (for example, Damascus steel, mokume, layered steels).
- Creates a colorful appearance of the product.
- Sometimes used for welding large workpieces .
- This type of welding is easy to master .
- Requires a minimum of special equipment.
Composition and physicochemical properties
| Chemical formula | Na2B4O7. |
| Compound | Sodium tetraborate |
| Coloring | Colorless, white, with grey, blue, green and yellow tints |
| Element hardness | 2-25 |
| Crystal shapes | Tall or short prismatic crystals, usually found in a disorganized, chaotic structure |
| Cleavage | 1,1 |
| Tenacity level | Fragility |
| Properties | Soluble in aqueous media, has a metallic taste |
| Melting temperature | 60 °C |
Borax is a compound of soda and boric acid. This substance does not dissolve in alcohols, but forms solutions well with hot water and glycerin.
Molecular structure of sodium tetraborate
Borax reacts with strong acids to form a salt and boric acid. When heated above 400 °C, the substance is completely deprived of water in the crystals. Borax, as a salt of a weak acid, when mixed with water, creates an alkaline reaction with sodium tetraborate. Borax can react with certain metal oxides to form various compounds - borax pearls.
As a food preservative, borax is prohibited for use in most countries, including Russia, due to the inability of the substance to be removed from human organs as a toxic ingredient. As a food additive, the material is called E-285.
Chemical reactions involving borax
What is a good knife
First, let's agree on the functional purpose of the knife that you are going to make with your own hands. Most likely, the best choice will be to focus on making a high-quality hunting knife. With hunting knives, we also need clarity: which one is the most versatile?
Forging a knife from a rope.
He will be the most suitable. After analysis and surveys in hunting sources, a description of the average hunter’s knife appeared, which can be considered the most universal.
For Russian hunting conditions, this would be a knife of medium size with the following dimensions:
- The blade can be from 12 to 14 centimeters long, and no more than 3 cm wide.
- The thickness of the blade is approximately 3 - 4 mm.
- The total length of the knife ranges from 23 to 27 centimeters.
Let's sum it up
Welding using the forging method allows you to join metals quickly. Such cases are known when it comes to the forging production of knife products, as well as stainless steel structures.
Despite the fact that the method is losing its relevance, it is considered special. This can be evidenced by handmade work, which is widely used in the forge.
Modern welding techniques boast practicality and speed of implementation. Forging metalworking (forging) gives products a special status.
Have you been able to work with this method? What were your impressions? Write your opinion in the comments. We wish you success!
Process technology
Do-it-yourself welding of a cast iron exhaust manifold in a garage.
Simplified, forge welding technology looks like this: the metal undergoes pre-treatment, heating, and after that the welding process begins using a hammer and an anvil or other tools, depending on the chosen method. A step-by-step examination of all stages will help you better understand the features.
- Surface cleaning. It is needed to remove traces of oxides and other contaminants from the metal.
- Heating up the metal. In a forge or furnace, you can only use fuel containing a small amount of sulfur - this will ensure high weld strength. The best option is considered to be coal, coal coke. Heating is carried out to white heat: 1350-1370 degrees for low-carbon steels, 1150 degrees for vintage steels, type U7, where the carbon content is higher.
- Heating order. When heating workpieces with a heterogeneous composition, you need to start with the one in which the carbon content is lower. The second part is added later - this way it is possible to obtain parts ready for forging welding at the same time.
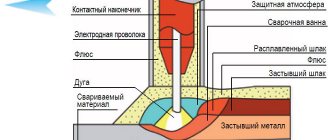
- Application of flux. To avoid the formation of scale, when the temperature reaches from +950 to +1050 degrees, it is coated with flux, which prevents the metal from burning. The most commonly used mixture is 10% sodium tetraborate, also known as borax, with 90% river sand, pre-calcined to remove excess moisture. You can also use a combination of silicate-sand mixtures with soda or ground glass scrap. In its pure form, borax is used when working with metals with lower heating temperatures; river sand can also be used separately, into which the workpiece is immersed.
- Welding. Once the specified temperature is reached, the metal is white-hot, it can be joined by forging, having first been cleared of slag. The parts laid together are easily beaten with light and frequent hammer blows so that all flux residues and contaminants are outside the seam. Next, strong and frequent blows are carried out from the center of the parts to the edges at the junction. This will prevent the formation of undercooked areas and other defects. Areas around the joint area are also forged.
It is important to take into account that before the parts are heated, the temperature in the forge must reach fairly high values. This allows you to burn out all the sulfur from the fuel
When heated, steels with a high carbon content become yellow rather than pure white. When choosing a metal, it is important to know that a magnesium content of up to 0.8% of the total volume has a beneficial effect on the malleability of the metal, but chromium, copper, silicon, tungsten, phosphorus, sulfur worsen it, and carbon volumes should also not exceed 0.4%.
The features and technology of the forge welding process are shown in the following video.
general description
Forge welding is a procedure for fastening metal parts by heating them until plasticity occurs at the points of contact and subjecting them to a shock load. The technology can also be classified as a type of pressure cooking. Such processing of metal products is possible only for steel alloys with low carbon content, as well as other metals with the lowest resistance to deformation.
The forging welding process consists of several main stages:
- The surfaces of the workpieces to be welded are cleaned and processed.
- Next, they are heated to a given temperature - the metal should acquire a dough-like state.
- Then the parts prepared in this way are connected using an impact load.
- Finally, forging is performed to give the product the required shape.
The most important condition for achieving results in forging welding is bringing the workpieces to the specified temperature. So, for steel this figure is about 1300-14000C. Experienced craftsmen always determine the heating level by the color of the glow. If overexposed, the metal surface may burn out and form thick scale. Therefore, as soon as a part acquires a given shade, it is immediately processed.