Welding stainless steel, which uses argon as a shielding gas, is one of the most common technologies for obtaining high-quality and reliable connections of parts made from such steel.
The use of argon when welding stainless steel allows you to obtain high-quality welds
Before you begin learning this process, you should become familiar with the characteristics of this alloy, which make it a difficult-to-weld material.
Stainless steel is a metal that successfully resists corrosion processes. It is made this way by alloying additives, the main one of which is chromium (in some brands of stainless steel it can be up to 20%). Titanium, nickel, molybdenum, etc. can also be added to various types of such steel as alloying elements. These additives, in addition to anti-corrosion properties, give stainless steel a number of other necessary physical and mechanical characteristics.
Stainless steel, in addition to exceptional anti-corrosion properties, has an attractive surface appearance. That is why it is often not even covered with paint. This gives rise to additional requirements for the quality of the weld: it must be not only reliable, but also neat.
Only a specialist who has not only the necessary knowledge of the technology, but also sufficient experience in this field can carry out welding work with stainless steel and obtain connections that meet the most stringent requirements. This means that to learn how to weld stainless steel in an argon environment, it is not enough just to watch a video of such a process - you also need to get practical lessons.
general information
This metal alloy has two main advantages - anti-corrosion properties and external aesthetic appearance. Due to the shine, the surface is often left unpainted. And the weld should be virtually invisible. Many welders do not like to work with this steel because the anti-corrosion coating makes the process difficult.
Features of welding stainless steel with argon
You can find an approach and adapt to any alloy if you know special techniques. The basics of welding work remain the same, you also need to prepare the material and equipment, create an electric arc, and make an even seam. But due to impurities in the metal - chromium and nickel - there are difficulties.
Rules to remember:
- reduce the usual current by at least 20%;
- leave a larger gap between the two elements being welded;
- do not use alloyed electrodes; if there are no others, then only short ones will do;
- do not allow heating above 500 degrees;
- Cool parts quickly.
What are the difficulties?
Alloying additives provide the following nuances:
- Low thermal conductivity. For this reason, the workpiece does not warm up completely, and high temperature accumulates at the joint. Burns or excessive deposits may occur.
- Due to linear expansion, final shrinkage is possible, which will lead to deformations and cracks.
- The high electrical resistance of steel when connected to alloyed electrodes leads to overheating.
- Possibility of loss of anti-corrosion properties due to elevated temperatures and the formation of new chemical elements on the surface that are prone to rust.
Pros and cons of this method
Welding stainless steel with argon has many advantages that are provided by its technology:
- When protecting the welded seam with argon, the effect of air on the melt, which negatively affects the hot metal, is eliminated. This makes it possible to obtain a strong, even seam with uniform penetration in depth.
- A metal with low thermal conductivity heats up little. The only exception is a small seam area. In addition to difficulties when performing welding (fear of burn-through), this is also a positive factor, since it makes it possible to connect parts with a complex structure without changing their shape.
- Welding work is carried out quickly due to the high temperature of the arc.
This technology is not without its drawbacks. These include:
The need for fairly complex equipment that requires precise settings, as well as certain skills and knowledge of the intricacies of the process.
Equipment and consumables for argon welding of stainless steel
The welder's kit will consist of:
- liquefied gas cylinder;
- burners;
- inverter;
- oscillator;
- wires, hoses.
This is a basic kit that will last a long time. Only the filler wire will have to be changed (filled), it is more convenient than electrodes, and the inert gas itself. The additive must be of the same composition as the workpiece. Additionally, a gas lens can be installed on the burner. It reduces consumption. And instead of a wire consumable, you can use an electrode method - made of tungsten.
Argon welding using a non-consumable tungsten electrode
This work is carried out when it is necessary to connect elements of insignificant thickness to each other, and thanks to this technology, very high-quality, neat and attractive-looking connections are obtained. Typically, industrial-type welding work involves joining pipes, which will later be intended for transporting liquid or gaseous products. It is worth noting that these pipelines are capable of functioning even under very high pressure.
The welded joint will be formed largely due to the metal of the workpieces, so this point should be taken into account and they should be made somewhat larger than implied by the project. If necessary, it is permissible to use filler material, which will have to be supplied manually to the area where the arc will burn. You will also have to move the torch with an electrode made of tungsten by hand. It is worth saying right away that labor productivity if this technology is used will not be too high. The fact is that it is not very convenient to supply the additive manually; besides, at this time you will also have to blow the weld pool with argon and pass the electrode. Only a very professional welder can simultaneously perform such a series of actions with a high-quality result, so it is better to use semi-automatic technology.
Preparation of material
First check the metal. Not everything that has a bright metallic sheen is called stainless steel. You can check it with any magnet. It will not be magnetized to steel with anti-corrosion properties. Then:
- wash off all visible dirt;
- dry;
- carefully walk over the surface with a metal brush (a grinding machine is also suitable), smooth out defects;
- degrease the outer layer with acetone or gasoline.
Pay special attention to the joints.
How to Prepare Small Stainless Steel Parts for TIG Welding
The algorithm remains the same, sometimes it is even easier to completely place the element in a container with a degreasing liquid. The peculiarity is the difficulty of fastening. If possible, secure the small workpiece so that it does not move while welding. After this, select the correct additive with an alloy equal to or slightly less than that of steel. The following models are actively used:
| Welding wire: brand description | Classification | Typical chem. composition of the deposited metal | Mechanical properties |
| OK Autrod 347 Si (OK Autrod 16.11)* Corrosion-resistant chromium-nickel welding machine for stainless steels type 08X18H10, 12X18H9T, 08X18H10T, (304, 308, 347) and the like in shielding gases (Ar). Alloyed with niobium and silicon provides high resistance to intercrystalline corrosion and high quality welds. Widely used in mechanical engineering for the petrochemical and food industries, in the energy sector, etc. Current = (+). | ER 347 Si / AWS A5.9 G 19 9 Nb Si / EN 12072 Wire analog: 06X21H7BT 06X19N9T 01X18N10 01X19N9 | C<0.08 Si 0.8Mn 1.7 Cr 20.0Ni 10.0 Nb 0.6 | Yield strength 440 MPa Tensile strength 640 MPa Elongation 37% KSV +20° C 110 J -60° C 80 J |
| OK Autrod 308LSi (OK Autrod 16.12) Corrosion-resistant chromium-nickel welding machine for joining austenitic stainless steels containing ~18% chromium and ~8% nickel, type 03X17H14M2, 03X18H11, 06X18H11, 08X18H10T, 12X18H10T, 304, etc. in a protective gas environment (Ar). 308LSi weld metal is highly corrosion resistant. The low carbon content reduces the risk of intercrystalline corrosion, and the presence of silicon ensures high quality welds. It is used in the food industry, petrochemical engineering for the manufacture of pipelines, tanks, boilers, etc. Current = (+). | ER 308LSi / AWS A 5.9 G 19 9 L Si / EN 12072 Wire analogue: 06X19H9T 01X18H10 01X19H9 | С<0.03 Si 0.8 Mn 1.7 Cr 20.0Ni 10.0 | Yield strength 370 MPa Tensile strength 620 MPa Elongation 36% KSV+20° C 110 J -60° C 80 J -196° C 60 J |
OK Autrod 318 Si (OK Autrod 16.31) Corrosion-resistant welding for austenitic stainless steels (see austenitic stainless steels) with a chromium content of ~19%, nickel ~12% and Mo ~3% in a shielding gas environment (Ar). The weld metal 318 Si has high corrosion resistance. Alloying:
Used in the food industry, petrochemical engineering. Current = (+). | G 1912 3 Nb Si / EN 12072 Wire analogue: 08X19H10M3Б06X20H111M3TB | C<0.08 Si 0.8 Mn 1.7 Cr 19.0 Ni 12.5 Nb 0.6 Mo 2.7 | Yield strength 460 MPa Tensile strength 615 MPa Elongation 35% KSV +20° C 100 J -60° C 70 J |
How does the work happen?
To weld, you need special equipment, such as a torch.
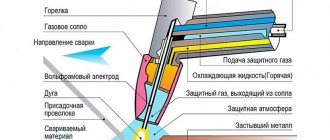
The torch, designed for welding in an argon environment, is equipped with a tungsten non-consumable electrode - the main part on which the device operates.
The electrode is located outside the device body (approximately 2-5 mm).
On the inside, the burner is equipped with a special holder, thanks to which you can use electrodes of different sizes - the holder is able to fix them all.
However, the size of the electrode is selected in accordance with the metal that will be processed, and the energy consumption during operation also depends on it.
Next to the electrode inside there is a nozzle made of ceramic - it is put on so that it surrounds the electrode. With the help of a nozzle, gas will flow into the work area, so this element is also very important.
To work with your own hands, you will definitely need an additive, or, in other words, filler wire - it is made from a material the same as metal blanks.
The diameter of the filler wire must also correspond to the metal you are processing - its exact size can be found in a specialized table.
Welding in an argon environment in manual mode is the most accessible method, easily repeatable with your own hands for beginners.
In this case, the filler wire and torch must be held by the welder.
Before you start welding, you need to degrease the surface of pipes, discs made of steel, brass and other metals with which you are working, and also clean them from oxidation.
Cleaning can be done mechanically or chemically, depending on your preferences and capabilities.
The first stage of welding is the same as in the arc process: a “mass” must be applied to the workpiece.
If you are processing small parts made of steel or other material, then the feed can be carried out simply into the area of the workbench or bath where the work takes place.
With this welding method, there is no wire in the electrical circuit and will be fed separately a little later.
The torch should be fixed in one hand of the master, and the wire in the other. The burner is always equipped with a button that regulates the supply of gas and current.
Gas should be supplied earlier - 20s before the start. When choosing amperage and pressure, you need to focus on the type of material being processed, or your past experience of working with your own hands.
The torch, equipped with an electrode, should be located very close to the material you are working with - at a distance of about 2 mm.
At this distance between the metal and the electrode, an electric arc will appear that can melt the edge of the parts; you just need to direct it in the right direction.
The entire welding process can be followed in a video for beginners - watch it before you start working with your own hands.
This proximity of the location between the electrode and the metal is explained by the fact that in this case a short arc is obtained, and it determines how deeply a part made of steel, stainless steel or other material will be fused.
Read also: Calculation of the bearing capacity of a strip foundation calculator
If the arc is large, then the seam will turn out to be very wide and ugly, this will be especially noticeable on the coating of pipes, disks or decorative objects made of stainless steel, brass, etc.
In addition to the aesthetic factor, a large seam makes the welding of lower quality - the larger it is, the less stable it is, and the greater the stress in it.
The filler wire is fed into the work area through slow, gradual movements: the torch should move along the seam, avoiding crossing the seam across.
The quality of the seam depends on how well the equipment works, as well as on the skills of the craftsman: the smoother and clearer the movements, the better you can make a seam on the surface of pipes, disks made of stainless steel, brass or other metals.
If the wire is fed through the equipment too sharply, the metal will begin to splash, which can be dangerous.
Reproducing the argon welding technology correctly with your own hands is not so easy if you have never done it - smooth and accurate movements are achieved only through practice.
However, it is not worth starting to learn argon welding, because... this is a very complex process.
When working, it is best for the wire to be located in front of the burner.
The torch and wire should be positioned at an angle to the work area, this way it will be easier to make a straight and narrow seam.
To ignite the arc during welding, you will need specialized equipment - an oscillator.
It sends pulses with a high volt content to the electrodes, which are responsible for the ionization processes of the arc gap.
The usual mains voltage is 220V; with this power, the oscillator is capable of converting and supplying voltage up to 6000V while maintaining a frequency of up to 500 kHz. Thanks to this power, ignition of the electrode occurs quickly and easily.
Equipment that complies with GOST is the only way to properly ignite an electrode, since it is prohibited to ignite it from the surface being welded due to the high ionization potential, which with this ignition method will lead to contamination of the metal of pipes, steel disks, brass and other materials.
Thin metal connection
We recommend placing sheet copper under the parts before the procedure. It will not join the workpiece, but will perform a number of tasks:
- protection against seam deformation on the reverse side;
- absorption of excess heat;
- fixation, hard working surface.
With a cross-section of 1 millimeter, 35 A, 36 A, 37 A current is relevant - in this mode of argon arc welding for stainless steel, you should cook for 3 seconds, feed for cooling - 4 seconds. The procedure can be carried out without filler wire if the parts fit closely.
Welding safety precautions
Remember, violation of safety regulations can lead to serious consequences. You can not only spoil the source material, but also get injured and even mutilated. Never start work without familiarizing yourself with the safety rules and nuances of working with the tool. Therefore, before starting work, take note and review in detail the rules and techniques of work:
- First, it is recommended to insulate all wires that are directly connected to the power supply and the welding arc. Power supplies must have high voltage circuit breakers;
- argon welding of metal products must be carried out in dry clothing, special mittens and galoshes;
- it is important to properly and accurately equip the workplace and remove all unnecessary tools and things;
- It is recommended to carry out welding work in a room with good air ventilation.
Welding work is quite complex and requires some knowledge and training. Remember, watching a training video is not enough. It is important to gain experience and practical skills in working under the guidance of an experienced master who can give practical advice and recommendations.
Pipe connection
Regardless of whether it is a water supply system, sewerage system, or any other overpass, it is necessary to isolate the fragment and clean it inside and out. The process will take place when the internal space is filled with gas. To do this, insert the tube into the connecting valve and make a plug from old rags and tape. Argon filling for welding stainless steel pipes is carried out from both sides. Possible settings – 65 Amps, crater filling – 3 sec., cooling – 4 sec.
Pulse
In common parlance it is called pulse mode. Excellent for thin-walled parts, and if you need to switch to another material, it is simply irreplaceable for aluminum alloys. The advantage is that even with increased current, you cannot get a failure of the weld pool, that is, you will not get a hole in this place. The function also gives excellent results in reducing the porosity of the seam, making it more uniform.
Table of ratios of modes and sheet thickness
| Sheet metal mm. | Seam type | Current | Electrode mm. | Filler mm. | Welding speed mm/min. | Rrgon l./min. | Number of passes | |
| horizontal position | vertical position | |||||||
| 1 (.039i n) | butt | 25-60 | 25-35 | 1.0 | 1.6 | 250-300 | 6 | 1 |
| overhead | 60 | 55 | 1.0 | 1.6 | 250-300 | 6 | 1 | |
| corner external | 40 | 35 | 1.0 | 1.6 | 250-300 | 6 | 1 | |
| corner internal | 55 | 50 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 250-300 | 6 | 1 | |
| 2 (.078i n) | butt | 80-110 | 75-100 | 1.6-2.4 | 1.6-2.4 | 175-225 | 6 | 1 |
| overhead | 110 | 100 | 1.6-2.4 | 1.6 | 175-225 | 6 | 1 | |
| corner external | 80 | 75 | 1.6-2.4 | 1.6 | 175-225 | 6 | 1 | |
| corner internal | 105 | 95 | 1.6-2.4 | 2.4 | 175-225 | 6 | 1 | |
| 3 (.012i n) | butt | 120-200 | 110-185 | 2.4-3.2 | 2.4 | 125-175 | 7 | 1 |
| overhead | 130 | 120 | 2.4-3.2 | 2.4 | 125-175 | 7 | 1 | |
| corner external | 110 | 100 | 2.4-3.2 | 2.4 | 125-175 | 7 | 1 | |
| corner internal | 125 | 115 | 2.4-3.2 | 3.2 | 125-175 | 7 | 1 | |
| 4 (.16i n) | butt | 120-200 | 110-185 | 2.4-3.2 | 3.2 | 100-150 | 7 | 1 |
| overhead | 185 | 170 | 2.4-3.2 | 2.4 | 100-150 | 7 | 1 | |
| corner internal | 180 | 165 | 2.4-3.2 | 2.4-3.2 | 100-150 | 7 | 1 | |
| 5 (.2i n) | corner external | 160 | 140 | 3.2-4.0 | 2.4-3.2 | 100-150 | 7 | 1 |
| 6 (.24i n) | butt | 220-275 | 190-230 | 3.2-4.0 | 3.00-4.00 | 150-240 | 7 | 2 |
| overhead | 250-300 | 210-250 | 3.2-4.0 | 3.00-4.00 | 150-240 | 7 | 2 | |
| corner internal | 280-320 | 230-280 | 3.2-4.0 | 3.00-4.00 | 150-240 | 7 | 2 | |
How to cook stainless steel with argon
There are two options - manual equipment using a semi-automatic device and using tungsten conductors. Recommendations for work:
- Both alternating and direct current can be used;
- the tungsten conductor must be infusible;
- gas is blown out of the burner mouth;
- the additive must be placed independently on the surface of the treatment, this ensures the formation of a seam;
- When fed, the wire should make an angle of 15-30 degrees to the workpiece and 90 to the machine;
- movement is smooth, without deviations to the sides;
- blow the connection from the inside to ensure a beautiful joint;
- to ignite the arc, use a graphite plate, and not by touching the workpiece - unsightly marks will remain;
- apply pressure for another 4-10 seconds after the process is completed.
When using a semi-automatic machine:
- the wire must contain nickel;
- Along with the inert composition, it is necessary to release part of the carbon dioxide, it reduces the heating of the edges;
- Various technologies can be used - pulsed, short-arc, jet transfer.
Methods for welding stainless steel
To connect sheet steel or complex structures, several methods are used to help obtain a high-quality seam.
Non-consumable tungsten electrode
Welding with tungsten rods is performed when connecting pipes. The main advantage is the aesthetic appearance of the seams.
Argon-arc technology is also used in the formation of storage tanks for liquid and gaseous substances operated under high pressure. Welding is carried out with both direct and alternating current of direct polarity. To heat the area being treated, a burner with a non-fusible electrode is used, through which gas flows. The seam is formed by melting the additive.
TIG welding has the following features:
- When tungsten particles penetrate into the weld pool, the strength of the connection decreases. To excite an electric arc, a carbon plate is used, which is then transferred to the working surface.
- The supply of argon continues until the rod and seam cool down. This reduces the rate of oxidation of the weld joint and electrode.
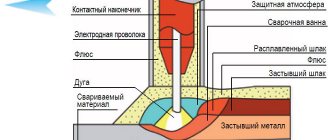
Using a semi-automatic machine
Every novice master should learn to cook using this method. The semi-automatic method is highly productive. The reliability of the resulting seam is not inferior to that of argon arc welding, but its aesthetic qualities are lower. The semi-automatic machine allows you to work with parts of different thicknesses. Increased demands are placed on consumables. The composition must include nickel, otherwise the wire will not meet the standards.
Welding is carried out in the following modes:
- Short arc. The heating temperature of the working area is determined by the length of the discharge. The small distance between the torch and the surface is suitable for joining thin parts.
- Pulse. The wire is fed into the weld pool in small portions, which prevents the melt from spattering and overheating of the parts.
- Jet. Switching the device to this mode helps to brew workpieces more than 1 cm thick.
Argon-arc welding of stainless steel with foreign metal
Usually there is a need to attach a steel element with anti-corrosion properties to alloys with a small amount of carbon in the composition. To do this, you just need to choose a suitable additive that contains nickel and chromium. Alloying additives are found in the following wire grades: Y310, Y310S, Y309, Y309L, Y309Mo. If you need to attach ordinary ferrous metal, you can use one of the following techniques:
- piece electrodes with winding in MMA mode;
- tungsten conductors, infusible;
- using inert gas.
The first two methods are less effective. When arcing, there is less filling of the seam with oxygen, which means less oxidation. But if you decide to use the first method, then you will need a table with suitable brands of electrodes:
| Brand | Type | Rod material K | Deposition rate, r/a. emergency | Application |
| ozl-8 | e-07 x20n9 | sv-04 x19n9 | 12-14 | chromium-nickel steels, when the weld is not subject to strict requirements against intercrystalline corrosion |
| ozl-3 | e-10x17 n13s4 | sv-15x-18n12s-4tyu | 11,5-12,5 | type 15x18n12s4tyu. Likewise |
| zio-8 | e-10x25 n13g2 | sv-07x-25n13 | 13,3 | structures and pipelines made of two-layer compounds. Likewise |
| uonii-13/nzh | e-12x13 | in-luna_2012 | 10-12 | responsible systems made of chrome 08x13, 12x13 |
| ozl-22 | e-02x21 n10g2 | sv-01x-18n10 | 12-14 | structures made of x8n10 |
| ozl-14a | e-04 x20n9 | sv-01 x19n9 | 10-12 | chromium-nickel, when the weld metal is not subject to strict requirements against intercrystalline corrosion |
| ozl-36 | e-04 x20n9 | sv-01 x19n9 | 13-14 | Likewise |
| ozl-7 | e-08x20 n9g2b | sv-01 x19n9 | 11,5-12 | Likewise |
| tsl-11 | e-08x20 n9g2b | sv-07x19-n10b | 1-12 | chromium-nickel, when stringent requirements are imposed on the weld metal against intercrystalline corrosion |
| tsl-9 | e-10x25-n13g2b | sv-07 x2513 | 10,5-11,5 | chromium-nickel on the alloy layer side of two-layer steels. Likewise |
| ozl-20 | e-02x20-n14g2m2 | sv-01x17-n14m2 | 12,5-14,5 | structures made of 03x16n15m3, 03x17n14m2. Likewise |
| niat-1 | e-08x17 n8m2 | sv-04 x19n9 | 10-11 | welding of structures made of chromium-nickel and chromium-nickel-molybdenum; most suitable for welding thin sheet metal |
| EA-400/10у | e-07x19-n11m3g2 | sv-01x19-n11m3 | 12 | connection of power equipment housings and pipelines operating in contact with an aggressive environment at temperatures up to 350° C |
| ha-400/10t | e-07x19-n11m3g2 | sv-01x19-n11m3 | 14,5 | Likewise |
Semi-automatic welding of stainless steel (MIG)
It is used mainly in enterprises, while manual is used for home use. A semi-automatic installation weighs more, it is more massive, so it cannot be taken with you on the road if the work requires it. There are two design features - there is no need for an electrode, and the wire is fed automatically, so the second hand remains free to move the parts and hold them.
If the sample is thin-sheet, then the short arc method is used. For stronger connections, use the jet technique, and the use of the pulse mode is important for beginners. We provide a table with the parameters of current and wire thickness depending on the material:
| Sheet, mm | Wire, mm | Current strength, and |
| 1 | 0,8 | 65 |
| 1,5 | 0,8 | 115 |
| 2 | 0,8 | 130 |
| 3 | 1 | 215 |
| 3 | 1 | 210 |
| 4 | 1 | 220 |
| 4 | 1,2 | 280 |
| 5 | 1,2 | 300 |
| 5 | 1,2 | 190 |
| 6 | 1,2 | 300 |
| 6 | 1 | 115 |
| 8 | 1,2 | 300 |
| 8 | 1 | 130 |
| 10 | 1,2 | 300 |
Useful tips
Expert recommendations help you understand how to correctly connect parts using the argon arc method:
- The size of the arc should be minimal, so the electrode is installed as close to the surface as possible without touching it. A long discharge is not able to heat the entire thickness of the parts, which is why the width of the seam increases and the strength decreases.
- When manual welding, the wire is fed evenly. This prevents oxidation of the work area.
- The quality of the weld is indicated by the shape of the beads that appear when the filler material melts. If they are stretched along the joint, the welding is done correctly. A round shape indicates insufficient heating.
- When completing the work, reduce the current. Abrupt separation of the arc is unacceptable - this reduces the protection of the hot joint.
We recommend reading: How to weld stainless steel to ferrous metal
The gas welding method, with the right approach, is no more complicated than the classical one. Regular practice helps you master it quickly.
TIG
This abbreviation translates from English as “tungsten and inert gas,” the most common being argon. We have already understood that the use of tungsten infusible electrodes is typical for hand-held equipment. Advantages:
- a very beautiful seam is immediately formed that does not require stripping;
- preventing porosity;
- filler wire - from the same composition as the workpiece;
- no oxidation;
- small heating zone, so you don’t have to worry about deformation;
- an easy method, even beginners can use it;
- few harmful substances are released during operation.
Video about this
Argon welding of stainless pipes
We have already mentioned the possibility of repairing water pipes and other spherical parts, now we will explain what the main difference between this method is. There is two-way airflow. And if from the outside this is simply provided by the apparatus, then from the inside it is not easy to do. For this:
- on one side, plug the hole with a plug made of any available material;
- the joint can be taped with electrical tape or tape;
- a small stream is supplied to the connector of the second pipe;
- after filling, the last hole is also closed with cloth or paper;
- welding is performed.
Technology
In general, the process is similar to the classical one - igniting the arc, forming a weld pool, holding the tips at a certain angle in order to form an even seam. But there are a number of nuances:
- move the additive exclusively along the bath; it must not go beyond the blower;
- if there is additional inert gas, then spray the workpieces from the reverse side, then the connection will be more aesthetically pleasing;
- Even when creating an arc, do not touch the electrode to the steel.
Features of the welding process
When planning to weld products made of stainless alloys with argon, you should especially monitor the position of the torch. It must be held so that during the welding process the torch axis has an inclination to the plane of the workpieces being joined by 75...800. And the mouthpiece should be inclined in the opposite direction with respect to the direction of welding.
When carrying out a welding operation, it is necessary to eliminate various vibrations of the electrode. Because this can provoke a violation of the protective “shell” of the weld, creating conditions for unwanted oxidation of the metal in the weld.
When performing a welding operation, it is necessary to place the filler wire with an inclination of 900 to the axis of the torch. In addition, their inclination to the horizontal plane of the semi-finished products being connected should be 15-200.
The greatest efficiency can be achieved if the filler rod is placed directly above the semi-finished products being joined. This will make it possible to minimize the transfer of droplets from the filler metal into the welding zone.
The tungsten electrode must be moved in front of the arc, ensuring its uniform introduction into the space being welded. It is recommended to exclude the transverse movement of the filler rod when creating a permanent connection using the TIG method. This will not allow a stream of shielding gas to flow smoothly from the torch, creating the preconditions for air to enter the welding area.
Upon completion of the welding process, it is recommended to abruptly turn off the argon supply. A delay of 10...15 seconds in stopping the supply of shielding gas will reduce the consumption of tungsten filler rod. As a result of this action, the heated electrode will oxidize less intensively, significantly increasing its service life.
The qualitative and strength parameters of the welded seam will only ensure strict adherence to certain nuances of the TIG welding process.
Only additional work will make it possible to give a welded stainless steel product a finished, marketable appearance. An oxide film is formed on the surface of the connecting seam during the operation. It causes a decrease in the corrosion resistance of the metal. To increase this parameter, it is necessary to process the finished product made of stainless alloys.