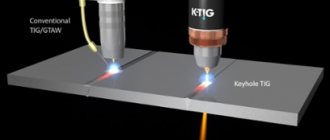
Nowadays, when the speed of the technological process comes first, automatic welding becomes an urgently needed method of joining metals. Modern devices for such welding make it possible not only to automate and speed up the process, but also to ensure the quality of the weld and constant control of its formation.
Automatic welding is mainly performed using the electric arc method, under constant pressure and with the renewal of electrodes.
The essence of the process and options
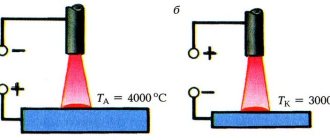
An electric arc generated between a moving electrode and the workpiece surface generates a large amount of heat.
The metal of the part melts and fills the gap between the parts being connected. When the electrode is removed, the melt solidifies, joining the parts into a single whole. In order to protect the working area from contact with oxygen and nitrogen in the air, as well as the water vapor contained in it, it is surrounded by a layer of flux . This is a special powder, the combustion of which releases protective gases. In addition, the flux contains alloying elements and other additives that improve the quality of the weld.
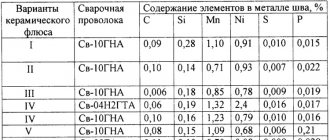
The powder, the composition of which is described in GOST 16130-72, can be included in the composition of the welding flux-cored wire. Sometimes the entire volume of the welding chamber is filled with inert gas, then the need for powder disappears.
The automatic welding machine monitors the distance between the end of the electrode and the workpiece. There are several kinematic varieties of such machines:
- the head is stationary, the welded pipes rotate in the drive rolls;
- the head moves along a specified path on the manipulator;
- the head is mounted on a self-propelled chassis (tractor), which moves along a given path inside the object being welded.
The automatic machine performs welding work such as:
- “in weight”, without protection for the back side of the seam;
- on a copper substrate along the entire seam line, protecting the back of the connection from drips and sagging;
- on a powder bed that creates a cloud of protective gases;
- on a copper plate moved synchronously with the head.
When performing complex types of joints, techniques such as preliminary welding of the root part and welding of the rear part of the seam are used.
Areas of use
In home workshops, due to the high cost of equipment and materials, automatic welding is rarely used. But in production conditions, where payback is ensured by large volumes of work, automatic machines are used for:
- work with non-ferrous and ferrous metals in various combinations;
- connections of workpieces with a thickness of 1.5 to 200 mm;
- assemblies of especially critical products - housings of nuclear and chemical reactors, pressure vessels and others;
- welding of internal seams of pipelines and containers.
Important! Automatic welding allows the operator to be removed from the welding zone, significantly improving working conditions and production safety.
Advantages
Manual and automatic welding use similar welding technologies. The automatic welding method has the following advantages:
- increased productivity, speed is several times higher;
- high stability of seam parameters;
- possibility of deep penetration;
- assembly of vessels and pipes, including large ones;
- a significant reduction in both overall labor intensity and the need for highly qualified welders;
- significant improvement in working conditions and production safety.
Certain advantages come from the use of fluxes, both powdered and supplied from a storage tank through a hose, and those included in the welding wire. These include:
- prevents splashes from the weld pool;
- stabilizes the parameters of the electric arc;
- slows down the cooling of the weld material, improving its properties;
- protects the melt from the effects of oxygen, nitrogen and water vapor contained in the air;
- promotes deoxidation of the weld material and integration of alloying additives into it.
Flux powder is not completely used during welding. Modern tractors clean off and collect the remaining powder along with scale . On older models, this is done manually after the seam has cooled, before applying protective paint coatings.
Varieties
Several types of automatic welding technology are used. On some units, the manipulator moves the head, on others, used for connecting pipes, the head is stationary, and the workpiece rotates. Self-propelled chassis move tractors along a predetermined path inside or outside the parts being connected. In addition to kinematic schemes, methods of creating a protective atmosphere around the welded zone also differ.
In an argon environment
Argon welding is carried out with a non-fusible tungsten electrode in a protective environment of pure argon or its mixture with other inert gases.
The gas mixture is supplied under low pressure to the welding zone through a nozzle built into the head. The method is used both with a fixed head and on tractor systems . Argon welding is especially widespread when joining stainless alloys and some non-ferrous metals.
Cored wire
In this case, a fusible electrode is used. It is a welding wire with a complex cross-section. Under the metal shell there are channels foamed with compressed flux powder. This wire is fed into the welding zone at a constant speed by a special mechanism.
The high cost of manufacturing such wire is compensated by the reduction in the labor intensity of operations for applying powdered flux along the seam line and subsequent cleaning of its residues.
Plasma welding
This technology uses electric arcs, excited between two infusible electrodes in a flow of ionized argon or helium. Due to its elevated temperature, the plasma arc makes it possible to effectively weld workpieces made of high-alloy alloys, including those of great thickness. This method is used to weld the circumferential seams connecting the lids and bottoms of the vessels. If necessary, filler wire is fed into the welding zone by a special mechanism.
Classification of semi-automatic devices
The division of semi-automatic welding devices is carried out according to various criteria.
Device type
This mainly applies to the body of the device. If all the components are in one body, then it will be a single-body type. In two-body models, one block contains a welding torch, a wire feeder, and a control panel. In the second block there is a current source having equipment for regulating the start.
Type of wire
The semi-automatic machine can use two types of wire: aluminum or steel. There are universal devices that can work with any of these types.
Seam protection
This happens in three ways: with a layer of flux, in protective gases, and using flux-cored wire. The most common method is to use shielding gases. The caveat is that cored wire can also be used in a gas environment.
Nature of movement
For mass production, stationary devices are used. In everyday life and for field work, portable semi-automatic devices will be more convenient. Mobile devices move on a chassis with wheels.
Electrical connection
Single-phase semi-automatic devices with low power can be plugged into a regular outlet. Three-phase require special connectors.
Wire feeding
With the push type, the drive pushes the wire into the welding torch. In the pull-type design, the drive is located in the torch handle and pulls the wire from the spool on which it is wound. The hybrid is a pulling-pushing type.
Tools to Ensure
An automatic welding machine is a complete technological complex that carries out most of the technological operations to create a welded joint.
However, it should be understood that they cannot always perform most of the preparatory and final operations, such as:
- mechanical cleaning of the seam area;
- degreasing;
- descaling;
- surface preparation and application of protective coatings.
In most cases, this work is carried out, as before, manually. They require angle grinders, wire brushes, solvent sprayers and rags. Only the most modern tractor models are capable of pre-cleaning the seam area.
An automatic electric arc welding machine involves software control of both welding modes and the supply of the workpiece (or the movement of the tractor along it). Therefore, an important component of modern machines is the processor unit containing control programs . The program is generated in a post-processor based on data from a three-dimensional model of the product loaded from a parametric modeling application.
The creation, testing and debugging of such a program requires the working time of highly qualified specialists, therefore the economic efficiency of automatic welding is achieved in two cases:
- production of a series of products;
- production of unique, but very important structures (aerospace industry, nuclear energy, etc.).
It is more efficient to make a single product or a small series of ordinary parts using semi-automatic welding. In this case, the welder moves the head along the weld line manually, and the modes, wire supply and shielding gas are controlled by mechanisms.
A. Somushenkov, ch. technologist at the Ust-Malonsky Metal Products Plant: “The use of automatic welding machines allowed the enterprise to achieve the specified quality of welds and save on attracting highly qualified welders. It is especially beneficial to use the technology on medium and large batches of parts.”
Semi-automatic welding: principle of operation, variety of types
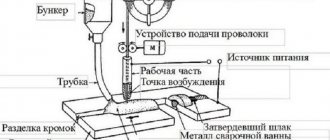
The welding machine consists of the following components:
- burner;
- wire feed hose;
- wire feed mechanism;
- workflow control panel;
- wire in a skein;
- electrical wire;
- semi-automatic control system;
- gas supply hose;
- reducer to reduce gas pressure;
- heater;
- high pressure gas cylinder;
- rectifier.
There is a wide variety of similar equipment on the domestic market. In order to organize its types, let us turn to one of the most common classifications. As welding processes become automated, welding machines can be manual, semi-automatic or automatic.
The first type of such equipment is more suitable for domestic use, and the second and third - for use in large enterprises, since automatic and semi-automatic welding machines are characterized by higher productivity per unit of time, and also make it possible to obtain higher-quality metal joints than when working with a manual welding unit .
But it is worth noting that automatic welding is much more expensive than manual units, since it is characterized by higher user comfort, has greater functionality, and lasts longer.
Semi-automatic machines are the most acceptable option in terms of price, operating comfort and number of functions.
To understand other advantages of semi-automatic welding, you need to understand how semi-automatic welding works:
- inside the device there is a coil of wire that acts as a consumable electrode and an automatic mechanism for feeding such wire;
- a moving wire is passed through a gas nozzle under voltage, which leads to its melting;
- stable arc length is ensured by an automatic welding feed mechanism;
- the operator chooses at his own discretion the direction of the current and the wire feed speed for welding, taking into account the type of metal and the speed of movement of the gas torch.
Dependence of the burner angle on the thickness of the workpiece.
Understanding the operating principle of semi-automatic welding allows you to understand the difference between an automatic welding machine and a semi-automatic welding machine . In the machine, absolutely all processes are automated, that is, they are carried out by the control system. In semi-automatic welding machines, as mentioned above, some of the operations remain with the welder.
Semi-automatic welding is divided into different types, based on the presence of certain characteristics.
Based on the method of protecting the material during welding work, semi-automatic welding machines are distinguished:
- submerged;
- in inert and active gases.
Semi-automatic machines can also be:
- Single-phase. They operate from a network with a voltage of 220V, but if it fluctuates, the electric arc will not be constant. This state of affairs is dangerous for the appearance of defects in welded joints.
- Three-phase. They do not operate from every outlet, but they guarantee high quality work under any load.
To become a highly qualified welder, it is important to understand what is needed for semi-automatic welding : what rules to follow, what consumables to use.
Device design
The main design elements of an automatic welding machine, common to all varieties, are as follows:
- power source: powerful inverter unit, which allows you to receive welding current of the required voltage, strength and polarity;
- welding head, fixed on the machine or on a manipulator, either fixed infusible electrodes or a mechanism for feeding welding (filler) wire, as well as nozzles for supplying shielding gas are attached to it;
- workpiece feed mechanism for stationary machines;
- self-propelled chassis for tractors;
- storage location for gas supplies and wiring;
- control system containing a program for controlling welding modes and movement.
Depending on the technology used and the type of workpieces being welded, automatic machines can be equipped with additional equipment:
- inertial positioning system for orientation inside extended structures;
- CCTV cameras for visual control by the operator of the welding progress;
- systems for preparing the joint area for welding and seam cleaning mechanisms.
Based on the requirements of a specific technology, significant changes can be made to the design of the device, including changing the length and degrees of freedom of the manipulators, equipping the chassis with magnetic fasteners, specific settings of welding modes, and others.
Some of them can be performed at the production site by service departments. Major changes to the design require intervention from the manufacturer.
Automatic welding technology
The main unit of the device is the current-conducting welding head. Submission in progress:
- additives;
- discharge forming an electric arc.
Automatic welding is most often done using filler wire attached to a spool or spool. Due to the roller system, the movement trajectory and speed limit are established. The additive is first straightened and then enters the guide mouthpiece, which is placed above the working area during operation.