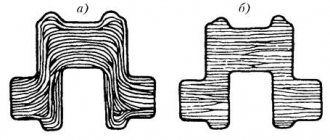
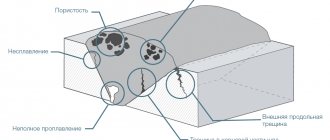
Metal casting is a popular technological process that allows you to produce metal products of the desired shape. Casting is carried out from various alloys that have varying degrees of fluidity in the molten state.
This method of execution allows us to produce high-quality products without the use of bulky equipment and a huge number of workers. In the modern market, this technology is in great demand, and is also among the ten most effective and used in the world.
General information
During the production process, molten material is poured into special molds. After cooling, it takes the desired shape and is subjected to subsequent processing. Such products are used in various sectors of the economy:
- automotive industry;
- aviation industry;
- mechanical engineering;
- dentistry;
- orthopedics;
- jewelry production.
For different types of alloys, a certain casting technology is used to achieve the desired qualities in the finished product and avoid defects. There are different types of components used in foundry production. They have a high fluidity index. This property of the alloy is determined by:
- chemical composition;
- metal alloy structure;
- melting temperature.
The most in demand in industry are metals with a low melting point, since their production is less expensive. The lower the melting point of a material, the easier it is to cast.
Casting of ferrous and non-ferrous metals
Any metal can be melted.
The process of producing products by pouring molten metal into a special mold is called metal casting. Not all metals are the same, both in their melting point and in their physical and chemical properties. Each metal has its own pouring method, methodology and purpose. The main division is the division into non-ferrous, ferrous and precious metals. The latter are least used in industry due to their high cost.
Black metals
Manganese, chromium, iron, cast iron, alloys based on metals belong to this category of metals. Ferrous metals account for more than 90% of consumption among all metal alloys. Steel is ideal for the production of parts in mechanical engineering and housings in machine tool industry. Widely used in the manufacture of household appliances, metal structures in construction, shipbuilding and other industrial sectors.
Non-ferrous metals
Non-ferrous metals, in terms of their physical and chemical properties and specific gravity, are no less significant, but they are assigned a more significant role. They are divided into light and heavy.
Light non-ferrous metals
This group includes magnesium, aluminum, titanium. Due to their rarer presence in earth deposits, their cost is higher than that of ferrous metals. The main advantage is the specific weight, which is significant in such industries as aerospace construction, defense manufacturing, computer technology, telecommunications and the production of household appliances.
Due to the property of titanium interacting with the tissues of the human body, it has found wide application in dentistry and dental prosthetics.
Heavy metals
Heavy metals include nickel, tin, zinc, lead and copper. According to their characteristics, they are optimal for the chemical industry, electronics and electrical engineering. They are used in any industry that requires a strong, elastic metal with special anti-corrosion properties.
Noble metals
The basis of this group is platinum, gold, and silver. But it also includes rarer ones - ruthenium, palladium, osmium, rhodium, iridium.
The main ones, due to their rarity and, accordingly, more significant cost, are used in the manufacture of jewelry, although they are not rarely found in electronics, but in small quantities. Rare, found exclusively in aerospace, high-precision electronics and other areas where it is impossible to do without their participation.
Types of steels
All steels are divided according to their composition, and alloys according to the additives they contain.
They are divided into steels:
- high carbon;
- low carbon;
- medium carbon;
- highly alloyed;
- low alloy.
The most popular in industry is medium carbon steel. Alloying makes it possible to increase the corrosion resistance, strength and ductility of the metal and other significant characteristics.
Metals for pouring
Specialists can cast any prepared alloy in the molten state into the desired shape. The problem is that each type of material has its own special melting point and varying degrees of fluidity. Most often, metals with low melting points are used in industrial casting.
Components suitable for casting are divided into ferrous, non-ferrous and rare earth.
Black iron includes steel, cast iron and ductile iron. All other alloys are classified as non-ferrous and rare-earth.
For each type of alloy, special casting methods are used to produce products from the following materials:
- become;
- cast iron;
- aluminum;
- copper;
- brass;
- gold;
- silver;
- platinum;
- nickel;
- titanium;
- bronze;
- magnesium
Over the entire existence of the foundry, many different technological solutions with different casting conditions have been developed.
When casting ferrous metal products, 5 types of steel with different carbon content are used. Products with increased strength are cast from alloy steel.
This is the most common material used for industrial casting.
Parts casting methods
For the production of machine tool parts and other high-precision engineering products, ordinary malleable cast iron and pearlitic cast iron are used, which have good machinability.
Cast iron, which is used in various areas of production, is divided into four types:
- white;
- grey;
- bleached;
- half-hearted
Its casting is characterized by low cost, the material itself has low strength and is processed using conventional cutting.
Cast iron, which contains nodular graphite, is considered a more durable material for olives.
Alloys of non-ferrous metals, primarily copper and aluminum, are widely used for casting. They are highly resistant to corrosion and are inexpensive.
The most expensive technology is considered to be the production of titanium alloy, which requires special conditions for pouring and cooling. This rare earth alloy is used for high-tech industries such as the aerospace industry or medicine.
Precious metal alloys are used in the casting of jewelry, medical products, or electronics parts.
Metal casting
Methods for casting products from metal alloys
Modern foundry production, in addition to the traditional technology of pouring liquid metal into sand molds, also uses other high-tech, productive casting methods:
- vacuum;
- centrifugal;
- under pressure;
- centrifugal;
- shell;
- multiple;
- mercury;
- by lost wax models;
- electroslag.
High-tech types of casting have made it possible to create metal products with certain qualities with high labor productivity and minimal defects.
The following production technologies are most often used on an industrial scale today:
- in metal forms (cocol);
- static casting;
- injection molding;
- into shell forms;
- into lost wax models.
When performing static pouring, stationary molds are used into which liquid metal is poured. Finished products are taken out after they have cooled in a stationary model.
Types of casting, their features
Increased demands on dimensional accuracy and quality of castings have led to the emergence of various casting methods. All of them are mechanized and adapted for mass production of castings. Let's look at the most popular types.
The most common of them is metal casting
into disposable sand molds.
To make a sand casting mold, a model is placed in special boxes (flasks), and the free space is filled with a sealing mixture (sand, clay, or a mixture of them) for molding products. The molding mixture hardens in a drying oven or is compacted by pressing or shaking. Metal is cast into the finished mold and left until it hardens.
Injection molding is used to produce thin-walled castings. The peculiarity of this method is that the mold is filled with metal and its subsequent hardening occurs under pressure of several hundred atmospheres. The castings have precise dimensions, and their surface does not require machining. Custom casting of iron, casting of steel and various alloys in a mold have become widespread. A chill mold is a permanent metal mold into which molten metal is poured and held until it solidifies. Chill casting produces precise-sized shaped castings with a dense metal structure.
Rotation bodies are manufactured by centrifugal casting. In this case, the metal is poured into a rotating mold. Centrifugal forces uniformly fill the mold with metal. There are no slag inclusions or gas cavities in such workpieces. Centrifugal casting machines do not require the use of cores to create internal cavities in the castings. Casting of critical products with high precision requirements will be performed using lost wax models. To do this, a model of the future part and a ceramic shell mold are made from low-melting materials (paraffin or wax). When exposed to heat, the low-melting model is removed and metal is poured.
Titanium production
To produce high-strength alloys from titanium and steel, vacuum casting is used to reduce the gas content in the metal. In this way, a denser structure of a metal alloy is created by melting in a vacuum. The hot metal is then poured into multiple containers in which it cools.
When introducing injection molding technology, special equipment is used to fill molds with liquid metal. It is supplied under high pressure in the range of 7–700 MPa.
This production method is carried out by hot or cold pressing machines.
This technology is used for pouring aluminum, copper, zinc and tin-lead alloys. All these metals have a low melting point, which increases the technological characteristics of products made from them.
Cold and hot injection molding methods make it possible to obtain a product with perfectly accurate dimensions and a smooth surface, which does not require additional processing after completion of the process.
This technology allows you to increase labor productivity. It also reduces the time of the entire technological cycle and simplifies the production of metal products. It also has disadvantages, which include the inability to produce products of complex configurations, since they can become deformed when removed from the mold. This method produces only metal products with a small diameter.
Centrifugal casting uses special molds rotating in a horizontal or vertical plane.
The action of centrifugal forces ensures uniform filling of all cavities in the casting mold. This casting technology is being introduced in the production of pipes, bushings or metal disks. It is also used in the casting of openwork jewelry.
Metal casting methods
The main metal casting methods are as follows:
Traditional method
The metal enters the mold under the influence of gravity. Sand-clay or metal matrices are used. The disadvantage of the method is the high labor intensity of making molds and other operations, difficult working conditions and low environmental friendliness
Low pressure casting
The essence of the method is that a crucible with metal and matrices for castings are located in a sealed chamber. A metal wire made of titanium alloy is lowered from the mold into the molten metal. At this time, low excess pressure of air or inert gas is supplied to the chamber. The metal enters the matrix under pressure, the flow rate is very high and at the same time regulated. The form is filled completely and evenly.
The method makes it possible to obtain high-quality castings, including especially thin-walled ones. The surface quality is also superior to castings produced by the traditional method. Foundry gases are removed through an exhaust pipeline into the cleaning system, from where they enter the atmosphere. The method is characterized by highly automated operations, improved working conditions for personnel and high environmental friendliness. In addition, with such casting, both materials and energy consumption are significantly saved.
High pressure casting
The method is used in both ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy and allows one to obtain the most accurate and uniform castings. Metal under high pressure enters the matrix at a speed of up to 120 m/s and instantly fills it.
Parts obtained by this method require virtually no finishing machining. Using this method, you can cast parts of almost any configuration, with thin walls, with ready-made holes and even with ready-made threads.
Injection casting
The injection method differs from conventional injection molding in that the metal enters the matrix in the form of a powder mixed with a binder. The molds are made from high-strength steels.
The high fluidity of the mixture allows you to fill the smallest relief details of forms of the most complex configuration, including internal cavities. The advantage of this method is the high precision of the surface, making additional mechanical processing unnecessary or reducing it to a minimum. Another advantage is the highest physico-chemical homogeneity of the casting.
There are other methods of casting parts that have niche applications.
Process costs
To reduce the unprofitability of the process, conventional casting methods for disposable models have been modernized to create high-strength polymer compositions. To do this, they began to cast into shell containers made of thermosetting powdered polymer. When exposed to temperature, it turns into a solid shell, forming a liquid alloy.
This method is used to cast water and steam heating radiators, assemblies of automobiles, machine tools, aircraft, and other types of high-tech mechanisms. This technology makes it possible to produce large-sized parts and any complex modifications.
Chill casting is considered traditional when a durable mold is used.
The part is pulled out of it after the metal has hardened. In this way, simple steel products of small size are produced. Most often, copper and aluminum alloys with low casting temperatures are cast into the chill mold.
The model for them is made of heat-resistant steel or cast iron, which have a higher melting point than copper or aluminum.
The advantages of this technology include:
- low cost of the production process and the possibility of its inexpensive automation;
- ease of execution;
- safety of casting molds that are used repeatedly;
- accuracy of parameters of manufactured products;
- high-quality metal structure, in which there will be no non-metallic particles;
- smooth surface of the product, which is obtained using this casting method.
Traditional lost wax casting technology has now been improved by the advent of new materials.
If previously the model for pouring the alloy was made of wood or other organic matter, which could be destroyed by high temperatures during burning, today low-melting materials such as paraffin and stearin are used.
Lost wax casting is used when casting artistic products with complex configurations. This is a costly casting technology that is used to create monuments or other artistic products.
The steel container for such pouring is made on the basis of models made of fusible materials, it has precise dimensions, and its surface is carefully polished.
Types of casting molds
For casting metals, different containers are used, which are divided into sand containers, used only once during casting, and multiple containers. Reusable casting containers are made from different materials:
- cast iron;
- heat-resistant steel;
- refractory ceramics;
- graphite
Graphite casting mold
Cast iron chill molds and molds are widely used. When manufacturing products from aluminum, copper and other non-ferrous alloys, metal molds are made of cast iron, copper and brass.
This decision was made a long time ago; it makes it easy to prepare materials for the main process. The process itself does not last long, the models come out of high quality. When implementing this technology, the involvement of a large number of workers is not required.
Metal casting containers can be open or closed. Open ones are molds, and closed ones are chill molds. Closed containers have a cavity that follows the dimensions of the part being melted. Liquid metal is poured into them through a special hole.
Shell casting containers are used for pouring alloys of non-ferrous and precious metals, as well as steel products. For casting non-ferrous metal alloys, they are made from powdered silicon dioxide or gypsum.
When making products from gold, platinum and silver, the mold is made of a low-melting material, which is filled with mercury, paraffin or plastic, which allows you to create a product of complex configuration and small thickness.
Such meticulous work requires high precision and qualifications from all personnel. Each stage of production is carried out in optimal conditions, conducive to the output of only high-quality products.
Types of casting
Casting is not a single process; it is also divided into several methods.
The main ones are:
- static fill. It consists of pouring into a mold until it is filled and the metal workpiece hardens. Is the most common type;
- injection molding. Allows you to provide the produced workpiece with high precision characteristics, surface quality and ensure high productivity, since the process is carried out under pressure and does not allow the formation of microscopic voids;
- centrifugal casting. Used to create pipes and other cylindrical products. The process differs in that pouring into a metal or sand mold occurs while it is rotating. This allows you to produce an ideal round-shaped workpiece;
- vacuum filling. Allows you to eliminate as much as possible the content of gases in the poured metal due to pouring in the absence of air.
Forms for filling
Casting molds are divided into reusable and disposable (sand).
The former are divided into chill molds and molds. Made of metal. Fireproof ceramic and graphite are also used.
The molds are filled from the top. The main metal for production is cast iron. Used for casting rolled and forged steels.
A prefabricated mold of a closed composite type with a small hole for casting - chill molds.
Mechanical processing of graphite allows the production of graphite molds.
If casting using a chill mold is unsatisfactory, a ceramic mold is used together with a graphite one.
Siliceous sand is used to make one-time molds. Such forms are needed when you need to obtain a workpiece of a non-standard size or shape. Suitable for casting any metal.