Material that does not rust
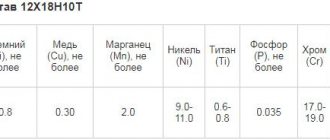
Various alloying additives are added to low-carbon steel: chromium - at least 12%, nickel, etc. Chromium, when interacting with oxygen from the air, forms a very thin oxide film on the surface, which prevents the rusting process and the action of a chemically aggressive environment. The surface anti-corrosion layer is restored if damaged. Stainless steel has its own characteristics:
- Low thermal conductivity prevents heat removal from the welding site. As a result, overheating and burning of the metal occurs, and alloying elements burn out.
- Low melting point reduces energy costs.
- Low electrical conductivity leads to a decrease in voltage on the metal of the workpiece, which causes overheating and the formation of burns, especially on thin parts
- Large thermal expansion deforms parts when heated.
A material with such properties is difficult to weld. There are several methods, one of which is welding using a semi-automatic machine. A beginner can learn how to semi-automatically cook stainless steel on the website mrmetall.ru.
Characteristics
When welding stainless steels, it is important to use a welding wire that contains the same components as the base metal . This is the main condition for obtaining a high-quality seam. Chemical composition is the main indicator.
The wire manufacturing technology provides high physical and mechanical properties . They are not inferior to the same characteristics as the base metal.
When using stainless wire as surfacing, it is important to know the deposition rate. With its help, you can calculate the required amount of consumables and select the optimal current value.
Which gas to choose
To protect the weld pool from the negative influence of air, gas is used. It improves the burning of the wire and its adhesion to the workpiece without reacting with the molten metal.
There are two methods: MIG – welding with protection with inert gases: argon, helium; MAG – with active gases: nitrogen, oxygen, carbon monoxide.
The main gases used are argon (Ar), carbon dioxide (CO2) - carbon dioxide, nitrogen (N2) and their mixtures.
In a carbon dioxide environment, semi-automatic welding of stainless steel is a frequently encountered option, as it is more economically accessible. In this case, the seam turns out to be clumsy due to the strong splashing of metal.
When using argon, you get a reliable seam that has a beautiful shape. The high cost of gas requires its use for products where the appearance of the connection is important. Semi-automatic welding of stainless steel with argon is most used in industry.
Each gas in its pure form has positive and negative qualities. Therefore, for a more efficient process, gas mixtures in various proportions are used. Based on the complexity of the work, the required result and material costs, one or another gas mixture is chosen.
The most commonly used composition is Ar+CO2 in the proportions of 98% to 2%, 95% to 5%, respectively. Without increased requirements for the type of seam, an increase in carbon dioxide up to 32% is allowed. The percentage depends on the thickness of the material, its type and other parameters. Welding stainless steel in such a protective mixture promotes good spreading of the molten metal and improves the structure of the seam.
Sometimes 1-5% oxygen is added to argon - Ar+O2 . This helps to reduce the porosity of the treated surface and small-droplet transfer of metal, and stabilizes the arc.
Types of wire
Welding wire is an indispensable element for successful work operations in various industries and utilities. With its help, several metal segments are connected into a solid structure.
The features of this filler material include ease of use and excellent quality of work performed. Proper selection of wire not only improves the reliability of the weld, but also significantly increases productivity.
Wire for semi-automatic machines is usually supplied in coils, coils and coils. The weight of the first type of packaging sometimes reaches 1.3 tons. The weight of the second type of container can vary from 15 to 120 kilograms. The mass indicators of the third form of packaging range from 5 to 18 kilograms.
Often the wire is placed in boxes or plastic bags. If the product does not have packaging, then before use the wire is dried at a temperature of 200°C.
Powder
This wire is a hollow object made of metal, the free space of which is filled with powder and flux.
These materials help protect the seam from exposure to oxygen and harmful substances formed during the welding process. An important factor here is also ensuring the safety of the respiratory system of the specialist performing technological work.
The use of special additives in welding wire facilitates ignition of the arc and helps reduce metal spattering, which has the most favorable effect on the formation of a high-quality seam. The arc burns in a flux medium, which allows you to protect the area of the welded area from the negative influence of the environment.
For work using flux-cored wire, heavy gas cylinders are not required, which are associated with many hassles: storage, refilling and possible leakage.
Copper-plated
Copper-plated wire is a product designed to work with carbon and low-carbon steels. It is coated with a special copper compound and is used for welding objects in a protective gas environment.
Wire selection
When welding, the wire is both an additive and, together with the molten metal, fills the seam. Two types are used: powder and solid with a very low carbon content and high silicon content, resistant to an oxidizing environment.
The diameter varies from 0.13 to 6-10mm. For household use, wire with a cross-section of 0.6 and 0.8 mm is usually taken; for production, where they work with powerful semi-automatic systems, wire with a cross-section of over 1.0 mm is used.
To weld stainless steel semi-automatically without gas, use flux-cored (self-shielding) wire. It is a thin steel tube filled with flux. When the top layer melts, the flux is released and also protects the welding zone from oxidation. A lot of slag is formed that must be removed.
Solid wire is used to carry out the process in a gas environment and submerged arc, and it must be identical to the metal being processed, i.e. made of stainless steel. It is better to take wire with a slightly higher content of alloying elements, due to their burnout at high temperatures.
Some brands of welding wire:
- 0.8x20n9g7t – contains chromium, nickel and manganese;
- 0.6x19n9t – high quality, corrosion resistant;
- 0.4x19n11m3 – chrome-nickel with the addition of silicon and molybdenum for resistance to intercrystalline corrosion.
To reduce the formation of splashes from molten metal, a wire of smaller diameter than the electrode is used. The seam is neat, but at the same time its consumption increases.
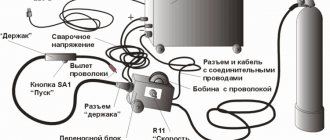
Some devices are equipped with a cable hose, inside which wire, gas, and current pass separately from each other to deliver it to the welding zone - the so-called welding hose.
Types of welding wire for semi-automatic machines
Under normal conditions, just over a dozen types of welding wire are used, out of more than seventy types produced. This is explained by the industrial specifics of using most types of welding machines, and the high cost of some of them. The most popular types are products with a diameter from 0.6 mm to 2 mm, weighing from 1 kg to 5 kg. Products are divided into solid wire and tubular wire with fillers, which have different purposes. According to the chemical composition, it can be aluminum, copper-coated, with titanium impurities and alloying.
The wire for semi-automatic welding of stainless steel is selected with particular care because it should be as close as possible in composition to the material being welded. Current parameters are also important, since overheating when welding stainless steel leads to a loss of the physical properties of this material.
When joining different grades of stainless metal, the following types of stainless welding wire should be selected:
- for chromium-nickel steels 12Х18Н9Т and 08Х18Н10Т, use grades SV-06Х19Н9Т, SV-01Х18Н10 or an analogue OK Autrod 347 Si in an argon environment;
- steel types 03Х17Н14М2 and 08Х18Н10Т are welded using grades SV-01Х18Н10, SV-06Х19Н9Т and OK Autrod 308LSi in inert gas;
- Stainless steel of chromium-nickel-molybdenum composition is welded with wire SV-06Х20Н11М3ТБ, SV-08Х19Н10М3Б and OK Autrod 318 in an argon environment.
These types of wire correspond to grades of stainless steel and provide high levels of strength, elongation, toughness and yield, making the weld strong and elastic after cooling and deslag removal. When working with high-frequency inverter or direct current, the metal in the weld pool does not overheat, which means that the corrosion resistance at the junction of the parts is not impaired.
The parameters and composition of the wire are regulated by GOST 18143-72, which determines the quality assessment criteria and the production method.
Also, flux-cored wire with rutile filler is used to connect stainless materials and dissimilar steels. It is used for welding difficult-to-weld, carbon-manganese and stainless steels in a gas mixture of 80% argon and 20% carbon dioxide. Powder products make it possible to work in any position, and are alloyed with molybdenum, which gives the weld high physical and chemical properties.
For steel grade E 2209, OK Tubrod 14.27 wire is used, for stainless steel 317 and 317L OK Tubrod 14.25 is used, and for grade 309 OK Tubrod 14.22 is suitable. For welding other metals, you can use self-protecting powder products with flux (for example, SV-000009283), which do not require an inert gas atmosphere.
Preparatory work
Before cooking stainless steel with a semi-automatic machine, careful preparation is required:
- Clean work surfaces until shiny;
- degrease parts with acetone or any organic solvent;
- if the metal thickness is more than 4 mm, process the ends so that a small space is formed between them for filling with metal;
- warming up the parts to 100, remove excess moisture;
- heat the metal to 200 to relieve internal stress.
In production, to remove surface contaminants: carbon deposits, traces of grease, rust, parts and wires are etched with a solution of hydrochloric or sulfuric acid. After this, rinse with hot and cold water and dry.
The flow rate of the gas mixture at an operating pressure of 0.2 atmospheres using a reducer is set within the range of 6-12 m3/min. Failure to comply with these indicators reduces the quality of the seam.
Adjustment of current and voltage depends on the power of the device.
The penetration depth, arc length, and weld shape depend on these parameters. As the current increases, the deposited weld becomes wider, and the welding depth decreases.
Some settings for a semi-automatic welding machine:
| Metal thickness, mm | Wire diameter, mm | Gap when butt welding parts, mm | Current strength, A | Welding voltage, V |
| 1 | 0,8 | 0 | 65 | 17 |
| 1,5 | 0,8 | 0 | 115 | 17 |
| 2 | 0,8 | 0,5 | 130 | 17,5 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 210 –215 | 18 |
| 4 | 1 – 1,2 | 1,5 – 2,5 | 220 – 280 | 20 |
| 5 | 1,2 | 2,5 | 190 – 300 | 21 |
| 6 | 1,2 | 2,5 | 300 | 22 |
Each machine is supplied with a table of welding modes. The master selects the semi-automatic operating mode, depending on the welding parameters. After setting up the machine, weld on a test piece. If necessary, adjust the settings.
Sequence of work progress
Stainless steel welding can be carried out in three main ways:
- Using a short arc - semi-automatic gas welding, especially suitable for working with thin workpieces;
- with jet transfer - cored wire is used;
- The pulse method is the most accurate and efficient, when the wire is fed into the welding zone by pulses in the form of small drops.
Before cooking stainless steel semi-automatically in carbon dioxide, you need to take into account the general provisions:
- Set reverse polarity - turn on the burner in the positive terminal, and the workpiece in the negative terminal;
- the current should be approximately 20% lower than for conventional welding;
- departure, i.e. distance from tip to tip of wire, no more than 12mm;
- To remove water vapor, the gas passes through a dryer located before or after the reducer.
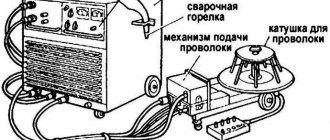
- fill the device with a coil of wire. Using the broaching mechanism, its tension is adjusted.
Kinds
The main technological process where stainless steel wire is used is semi-automatic in an atmosphere of protective gases. To improve process parameters, it can be coated with copper, i.e. be copper-plated (! not to be confused with copper wire). It is used as an additional material in argon arc welding with a non-consumable electrode. Using a gas burner, it is applied to the surface in the form of surfacing.
Useful video
Welding process
Once the equipment is set up and all recommendations are taken into account, you can proceed directly to welding.
To avoid the appearance of deformation and cracks, a gap is left between the parts along the entire length for expansion. The parts are secured in a vice or other way and clamped in several places.
You need to start with minimal consumption of shielding gas. Turn off the wire feed and adjust the gas flow rate to operating mode using the valve on the reducer. Then direct the gas flow to the workpiece and blow through its surface in literally 3-5 seconds.
At the beginning of welding, you need to look at the seam. If pores form, increase the gas supply until they no longer appear. Gas consumption must be adjusted to economical mode. So that the quality of the seam does not suffer.
You need to start cooking 5-6mm away from the edge to prevent cracks from forming. The torch nozzle should be angled slightly back in the direction of the seam and at a height of 10-12mm above the welding joint.
If the angle is tilted forward, the weld width increases and the penetration of the welding arc decreases, which is good for thin sheets.
Welding speed
The speed at which the electric arc moves along the welding site is controlled by the welder. Too high - it can cause a lot of splashes and melting of the metal, while the protective gas does not have time to escape and pores form. Insufficient speed is the reason for changes in the penetration of the welding arc into the parts being welded.
You need to cook with a short arc - this is when the distance between the end of the wire and the surface of the molten metal is 0.5-1.5 mm. Boiled in this way, the seam has the correct outline, a smooth and convex surface.
Another method of welding thin parts is pull-off welding, i.e. short circuits of the arc gap. Press the trigger and release, and gradually fill the joint with a thread seam (rollers).
If the device has a pulse function, then it is better to work on it. Pulses generated by a short circuit in the welding machine are used to melt the metal.
When welding thin (up to 3mm) stainless steel with a semi-automatic machine, guide the torch nozzle along the seam, avoiding transverse movements. Otherwise, there is a possibility of molten metal leaving the protective environment zone. It is better to weld thin parts in a vertical position, moving from top to bottom.
If two workpieces are of different thickness, then keep the nozzle on the thick one. With an instant movement, move the torch to the thin workpiece and return to the thick one again. Otherwise, the thin metal will burn out.
To avoid serious defects during welding, it is worth using ceramic pads, which are self-adhesive tape. They are most suitable for working with thin parts, as well as in awkward spatial positions.
Connection of stainless steel and black steel
Welding of such materials is carried out at direct current. The position of the wire is strictly perpendicular to the working area.
Stainless steel wire must contain manganese and nickel, for example, ESAB OK, Autrod. A special transition wire deposits a buffer layer, which connects the parts.
When welding St40 steel to stainless steel, you can use 08G2S wire. This strengthens the seam between two dissimilar metals after cooling. The most important thing in the process is that the stainless steel does not become too fluid, and the ferrous metal does not remain solid. The seam is made as wide and as deep as possible.
Advantages and disadvantages
The undoubted advantages of semi-automatic welding of stainless steel:
- High performance combined with high-quality connection;
- low smoke emission, which protects health and the environment;
- slight metal spattering due to automatic wire feeding;
- versatility - you can weld workpieces of different thicknesses, as well as dissimilar metals.
One significant drawback is the bulky gas cylinder. These are additional costs for its acquisition and inconvenient movement.
The spread of the method became possible with the development of technology and process automation. Mainly used in industry for large-scale production. Working with a semi-automatic welding machine, although it requires certain knowledge and skills, still remains one of the popular types of metal processing. You can learn more about how to operate a semi-automatic welding machine in our article.