The main difficulties when welding thin metal.
As mentioned earlier, welding a product from thin iron is not as easy as you would like. Metal with a small thickness quickly heats up and burns out. A metal burn is formed. In addition, thin products are greatly deformed if they are overheated.
Another difficulty is the speed of the process. You need to cook quickly or use special methods. The main welding methods and technology for their implementation for thin metal will be discussed below. Experienced welders use certain tricks with which they can easily cope with such a task as welding parts made of thin metal. About these tricks in our article.
Welding metal with a 1mm inverter: existing methods
There are several methods by which metal welding with an inverter is carried out on sheets 1 mm thick:
This method is used when it is necessary to weld sheets of thin metal 1 mm at an angle. In this case, the edges of the sheets are bent at the required angle, fastened with transverse short seams with an interval of 5-10 cm. Then the seam is welded with a continuous movement from top to bottom.
When using this method, the metal product has time to cool down somewhat, which avoids overheating. The intermittent method involves lifting the electric arc from the surface of the sheet for a few seconds, after which the electrode is again lowered to the same place and advanced a few millimeters. The main thing is that the metal sheet does not cool down too much.
- With heat-dissipating pads.
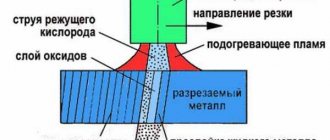
This method is used using heat sink wire or copper plates. Typically this method is used when butt welding thin sheet metal parts. In the first case, a wire of small diameter (2.5-3.0 mm) is laid between the sheets so that on the front side it is flush with the surface of the sheet, and on the back side it protrudes slightly beyond its edges. The welding arc passes through the location of the wire, which takes on the main thermal load. The edges of the parts being welded are heated by peripheral current. As a result, the seam is smooth, the metal does not overheat and does not deform. After welding, the wire is removed without visible traces of its presence.
When using a copper plate under the joint as a heat sink, it absorbs most of the heat, preventing the metal from overheating.
There are the following types of welds:
- Most often, a weld is made when joining sheets with an overlap, because This is a simpler method in which one sheet overlaps the other by 1-3 cm.
- A spot weld is obtained when welding parts with a continuous seam is not required. In this case, spot intermittent welding is carried out at a certain distance of the seams from each other.
- Butt seam. A more complex type in which two sheets are welded to each other end-to-end without overlapping. As a rule, it is obtained using the welding method with heat-dissipating pads.
Read also: How to check the health of a car battery
How to cook thin metal. Welding methods.
Let's look at welding methods suitable for thin metal parts. The most common methods:
- Manual arc (RMA)
- Non-consumable tungsten electrode (RAD) in argon or a mixture of gases.
- Semi-automatic in carbon dioxide.
Manual arc welding (MAW)
Very popular due to inexpensive equipment and ease of use. It is more difficult to weld thin metal than the other two methods. The main advantage when using it is that you do not need a gas cylinder, and many people have the device. For manual arc (MA) this is not a problem
Argon arc welding (RAD, tig or wig).
It is used for products made of thin stainless steel, aluminum and steel. This method provides a very high degree of protection with inert gas. The gas used is argon in its pure form or mixed with other gases in various proportions. For high-quality welding of thin products in argon it is best suited. But the price of gas from filler wire is high, and the equipment is heavy and bulky (gas cylinder). Read more about this method here.
Semi-automatic welding (MP, MIG, MAP)
Often used in car services, just for car body repairs. There thicknesses range from 1.2 to 2 mm. The method is very productive and not difficult to use. For it, just like for the previous method, it is necessary to use a protective gas. CO2 is most often used. Sometimes flux-cored wire is used for semi-automatic machines. Then the process proceeds without gas. Flux-cored wire is an expensive item that can be difficult to find. It is not often used, so we will not dwell on it in detail. Read more about this method here.
Welding thin galvanized steel and its features
To weld galvanized steel, you must first remove the zinc layer from the edge of the metals being joined. This layer is removed manually or by using a machine that performs sanding.
The edge of the metal is also burned out by welding, but this is done very carefully. Zinc tends to emit very toxic fumes when welded, and if they are inhaled, they can cause serious harm to the body. It is recommended to carry out all work in the presence of a hood, or to weld surfaces in the fresh air.
Equipment.
For all of the above methods, the welding machine is currently an inverter. An electronic device with a transformer and a transistor rectifier unit. Sometimes you can find rectifiers, but they are becoming a thing of the past, remaining only in large industries.
For a manual arc, apart from the apparatus, a holder with a set of cables, nothing else is required. All this, as a rule, comes together in one set with the device.
To perform a semi-automatic process, you need a cylinder with protective gas, a reducer, and a set of hoses. In the cold season, a gas heater is also necessary.
In addition to welding cables, mass, the welding torch is also delicate.
For the process in argon, a non-consumable electrode requires, in the same way as in the case of a semi-automatic device, a gas cylinder, a hose, a reducer, equipped with a rotameter to control the amount of gas supplied. A burner is also used, but it has a completely different design than a semi-automatic burner. The burner is equipped with a non-consumable electrode. It is installed in the collet, fixing it with the tip.
Choice of method.
Having first become acquainted with the methods, we need to choose the one that suits us.
We choose welding in argon when:
- It requires welding thin stainless steel.
- It is required to weld aluminum or its alloys.
- If you need to weld steel, provided that the seam must be aesthetically pleasing (decorative elements, furniture, etc.).
We choose semi-automatic when:
- Long seams need to be welded.
- When there is little or no experience.
In other cases, we use a manual arc.
Preparatory work
When performing welding work, you may need the following tools and materials:
- welding machine;
- electrodes;
- metal scissors;
- fasteners;
- sandpaper;
- degreaser.
Before welding metal, you need to properly prepare it for this work. In this case, it is very important to thoroughly clean the site of the future connection from various contaminants: rust, paint, grease, anti-corrosion coating, etc. The presence of these contaminants will result in a low-quality weld. This is because:
- contaminants do not conduct electricity well;
- some substances emit gases when exposed to heat, which leads to splashing of liquid metal in all directions;
- the gases released make the seam porous;
- Heavy smoke may occur during work.
After the metal is cleaned, you can proceed to securing the surfaces to be welded next to each other. For this purpose, various clamps, clamps, clamps, levers, clamping angles, temporary fastenings with self-tapping screws, bolts, etc. are used.
Polarity.
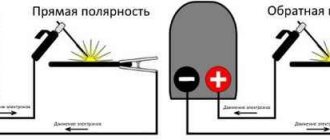
Polarity plays a very important role when welding thin iron parts. This largely determines whether the metal will burn through or not. So what polarity is used to cook thin metal with an inverter? Straight polarity is the polarity in which the terminals are connected to the product and the device in such a way that the plus is connected to the product, and the minus (ground) to the electrode. When direct polarity is used on a surface, the temperature reaches higher values than if reverse polarity is used. Therefore, its use is not advisable. When using reverse polarity – “+” of the device is connected to the holder with the electrode, ground to the product.
About arc welding
According to experienced craftsmen, the success of arc welding depends on the quality of calcination of consumables. The optimal temperature is considered to be 170 degrees. In this thermal regime, uniform melting of the coating occurs. At the same time, it is convenient to manipulate the arc, forming a seam. Welding electrodes for thin metal sheets must have a high-quality coating. In accordance with the technology, an intermittent arc is formed by short-term separation of the electrodes from the weld pools. If the product has a refractory coating, then a kind of “visor” will certainly form at its end, which will interfere with contact and the creation of an arc.
How to weld thin metal with an inverter. RDS - Manual arc welding.
The main difficulty for beginners is igniting the welding arc. If experience and practice are not enough, then a burnout cannot be avoided. You need to train, nothing else.
The polarity used when welding thin metal with an inverter is reverse. Due to this, the parts will heat up and burn out less.
At the very beginning, it is necessary to calcinate the electrodes according to the manufacturer's instructions; they are written on the pack. Without calcination, the process will not be stable and there will be gas pores in the seam.
The first method uses flanging.
Connection type C1 according to GOST 5264.
The blanks are flanged. Its height is from 1 to 4.5 mm. It can be bent either in a vice with a hammer or using special bending devices. Next, we clean the edges from any dirt, as well as moisture. It will be simply gorgeous if you also degrease it. For this, a special degreaser, acetone or solvents like 646, etc. are suitable. All the parts have been prepared.
Now you need to set up the machine for thin metal.
We take electrodes with a diameter from 1.6...2.0 to 2.5 mm. Electrodes can be taken with a basic coating (for example, UONI 13-55), or with rutile (MP-3, Esab OK-46 and others).
The current is pre-set on a test workpiece. It is necessary to set the current value so that the metal does not burn through and the arc burns steadily. For products made of thin iron, the welding current values are 30 A - 48 A (in principle, up to 60 A is possible) when using an electrode with a diameter of 2 mm. For each device the value will be individual. That is why we recommend pre-setting the welding current on a test workpiece.
Now the workpieces need to be assembled onto tacks. We assemble the parts without a gap and place tacks along the edges of the product. In order to reduce heating, we move the electrode at an angle forward.
We start cooking on an oven mitt. We move the electrode without oscillating movements, just forward. It is important to stop as little as possible. If it is necessary to interrupt the process, for example to change the electrode, then light the arc and start welding at the welding seam. Having previously cleaned it of slag and then move on to the edges. Otherwise it will be burned.
This method produces a good weld with additional rigidity from the flanging.
Let's consider another way to properly weld thin metal with an electrode.
If you need to weld parts with a wall thickness of 1 mm without flanging, then you need to make a heat sink.
A piece of aluminum or, better yet, copper is suitable for the heat sink. We place the parts on the heat sink.
Now you need to adjust the current. The value is the same 35-45 A. The polarity is reversed. Cook at an angle forward. We install the potholders at a distance of 5-10 mm from the edge. If this is not done, the iron on the edge will heat up very quickly and burn out. The heat will simply have nowhere to go. Electrodes are the same as in the previous method with a diameter of 1.6 - 2.5 mm.
Everything is ready, you can start cooking.
- We start cooking not from the edge, but on an oven mitt.
- We boil a short section of 4-6 mm and break the arc. The length of the welded area is assessed by the color of the metal. As soon as the edges turn red, we break the arc.
- We re-ignite the arc only after the metal has cooled and the redness has subsided. You need to start on the welded area.
- We boil 4 – 6 mm and break the arc. So we repeat this process until the end of the joint. The process is like a lot of welding points.
- After the seam has been welded, it is necessary to finish welding the small area that was left at the beginning.
Ending the process.
In this case, heat removal is very important if there is little experience. Vertical welding with an inverter for beginners or performing it on weight is not easy. In this case, the length of the welding “point” will be very short. Experience is also important in many ways.
When welding thin metal, maintaining a short arc is important. No more than 1/2 the diameter of the electrode. Using this method, you can weld thin metal car muffler or body parts.
Galvanized welding
Galvanized steel is the same thin sheet, only coated with a layer of zinc. If you need to weld it, you will have to completely remove this coating on the edges for welding, until you get clean steel. There are several ways. The first is to remove it mechanically: with an abrasive wheel on a grinder or grinder, sandpaper and a metal brush. There is another way - burn it out by welding. In this case, they pass the electrode twice along the seam. In this case, zinc evaporates (it evaporates at 900°C), and its vapors are very toxic. So this work can be carried out either on the street, or if there is an exhaust hood at the workplace. After each pass, you need to knock off the flux.
It is better to weld galvanization outdoors: evaporating zinc is very harmful
After complete removal of zinc, the actual welding begins. When welding galvanized pipes, to obtain a good seam, two passes with different electrodes will be needed. The first seam is welded with rutile-coated electrodes, for example, MR-3, ANO-4, OZS-4. In this case, the vibrations have a very small amplitude. Make the top seam wider. It is approximately equal to three electrode diameters. Here it is important not to rush and cook well. This passage is used by electrodes with a basic coating (for example, UONI-13/55, UONI-13/45, DSK-50).
Read more about choosing electrodes for inverter welding here.
How to semi-automatically cook thin metal with carbon dioxide.
In order to semi-automatically weld thin metal, we connect the equipment. Each specific device has its own connection features. It is best to take the connection diagram from the manufacturer's instructions. It comes with the device.
How to connect the device:
- We check the integrity of the machine and welding cables.
- We connect the burner and gas equipment to the device.
- Open the cylinder and reducer.
- Turn on the gas heater (if installed).
- Install the welding wire into the feeder.
- We connect the device to the network.
- Turn on the device and press the button on the burner and hold it until the wire comes out of the nozzle.
- We connect the mass to the product.
Welding wire.
The welding wire must be calcined for 1.5-2 hours at a temperature of 150 to 280 °C. Corrosion must be removed, otherwise the process will not be stable. It is best to remove rust with a solution of HCL-5% acid.
That's all, now you can start setting up. How to set up a semi-automatic machine for welding thin metal? There are special tables for this. They most often come with a semi-automatic machine in the kit. If not, then use the tables below.
After setting, you need to make a test weld on the workpiece. If the process is stable, spattering is minimal and there is no strong crackling, then everything is set up correctly. We can start welding the main part. Semi-automatic carbon dioxide welding copes well with small thicknesses. If we want to weld thin metal without breaking the arc, then we need to use the pulse mode.
The welding process will be as follows:
- We set the gap and install the tacks at a distance of 5-10 mm from the edge of the product.
- It is advisable to cook on a heat sink with a removable lining made of copper, aluminum or stainless steel;
- It is preferable to carry out the process for products with a wall thickness of 0.8-1 mm in a vertical position downhill, i.e. from above to move down. This will ensure minimal heating of the metal.
- Do not make oscillating movements with the burner.
Just as in the case of a manual arc, a heat sink in the form of a lining is required. Semi-automatic welding in a CO2 environment is simple, which is why it is often used for welding thin metal of cars. It is often called campy welding.
By the way, the name camping welding comes from the semi-automatic machine manufacturer Kemppi. By analogy, an angle grinder (angle grinder) is called a “grinder”. This is due to the fact that the first angle grinders began to arrive from Bulgaria to the territory of the USSR. That's how it stuck.
Let's sum it up
Welding thin-walled metal structures has a number of features that are important for an inexperienced welder to understand: you need to know which electrodes should be used, and also understand how to properly weld metal with an inverter.
Electrodes used for welding thin metal must be moved along the weld quite quickly so as not to allow the surface to cool. But at the same time, the movements should not be overly rapid, otherwise failures in penetration, which reduce the strength of the connection, cannot be avoided.
Welding thin metal in argon.
Argon welding of thin stainless steel parts very often occurs using this welding method. Inert gas – argon provides a high degree of protection.
To perform welding, as in previous methods, we prepare the equipment:
- Check the integrity of electrical cables.
- Connect gas equipment to the welding machine.
- Connect the burner and the ground cable to the device.
- Turn on the welding machine.
- Set the mode.
- Purge the gas line.
Setting up a welding inverter for welding in argon.
To configure the device, you must use the parameters recommended by the manufacturer. If there are no such recommendations, then use the tables from our website.
For argon arc welding of thin metal, straight polarity is used.
After setting the welding parameters, we move on to the technology itself. As in the previous methods, we adjust the welding current on a separate workpiece. Taking data from tables as a basis. Gas flow is also adjusted. It is worth considering that if the process is carried out in windy conditions, it is necessary to use a nozzle with a larger diameter, as well as increase gas consumption. At the same time, bring the torch as close as possible to the weld pool.
Preparation for welding:
- The welding wire must be cleaned of rust and calcined for 1.5-2 hours at a temperature of 150 to 280 °C.
- The edges of the product must be cleaned 20-30 mm from the joint to a metallic shine and degreased.
Requirements and technology for welding sheet metal
Welding thin sheet metal has a number of requirements that are recommended to be met to obtain a high-quality result:
- electrodes for welding thin metal should be selected in accordance with the thickness of the work product. If the thickness of the part is no more than 3 mm, a conductor should be used with a diameter of 3-4 millimeters. To do this, you need the thinnest welding electrode;
- in order to avoid deformation of parts, it is necessary to select the appropriate current strength for welding steel sheets of small diameter;
- Welding of thin-sheet steel should be done with electrodes with a special coating, which will melt slowly and make it easy to initiate and hold an arc, without spattering drops of metal.
Particular attention must be paid to the choice of electrode. To weld sheet metal, you need to choose special conductors that provide slow melting and allow you to better hold the arc. Both alternating and direct current can be used for operation. It is best to choose universal electrodes for welding thin metal with an inverter. Experts recommend giving preference to “C”.
Regarding the technology of work, it is better to weld thin products overlapping, this way there is less chance of burning through the metal.
If it is necessary to butt weld sheet metal, then before processing it must be fixed in such a way that they do not move during work. When heated and cooled, metal tends to expand and contract. In this regard, difficulties may arise, especially for a novice welder.