Submerged arc welding technology
The automated welding process involves the presence of bulk flux supplied directly to the product. When the arc is ignited, the electrode wire melts, acting on the metal base. As a result of the reaction of the metal with the substance, which are integrated at the welding site, a gas bath consisting of welding fumes is formed. Submerged arc welding is used in automatic or mechanized production.
The main purpose of the cavity in the welding method under consideration is the formation of a protective shell to avoid the effect of oxygen on the metal.
Also, the design of the electrode wire reacts to flux, subjecting the material to processing, allowing for a high-quality seam to be obtained.
Submerged Arc Welding Diagram
During the arc removal process, the product changes from a molten state to a solid state, forming a hard layer that is easily removed from the surface of the product. Automatic submerged arc welding technology involves a cycle of removing excess material using a special mechanism. The technology has many advantages that allow the method to be used in any enterprise.
- It is possible to combine parts using increased current. Most industries use current from 1000 to 2000 A; for comparison, arc welding does not exceed 650 Amperes. In normal mode, increasing the current has a detrimental effect on quality by spattering the metal. When using the substance, it is possible to increase the power to 4000 A, which allows you to obtain the finished material in combination with the speed of the process.
- The process involves the formation of an arc under a layer of flux operating at great depth. This condition makes it possible not to worry about pre-treatment of welded joints.
- Increased clutch speed allows for more welding work. For comparison, making a seam with identical parameters using arc welding can take 10 times more time.
- The gas bubble formed during the process avoids splashing of hot metal during the process. This condition allows not only to obtain a strong seam, but also to observe safety precautions when working with high temperatures. Due to this, energy and tools are saved.
The welding mode is determined depending on some required characteristics of the seam. Main criteria:
- electrode diameter;
- electric current, its polarity;
- speed performance indicators and voltage;
- composition characteristics.
There are also a number of additional parameters depending on the tools used.
What does the use of flux give?
A chemical substance based on many components is called flux. It is used when necessary to comply with standards, to protect metal products from corrosive conditions during subsequent operation.
The main tasks that the substance can solve:
- stable burning of the welding arc;
- improved properties and shapes of the seam;
- providing a weld pool that protects the metal;
- the use of various fasteners allows you to change the composition of the chemical mixture to obtain the required characteristics.
Read also: Do-it-yourself spot welding for cars
In addition to the above advantages, the main advantage is the ability to create a mechanical joining process. Various chemical compounds are used in automatic lines.
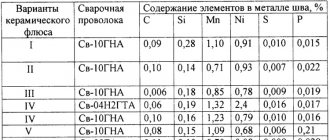
Chemical composition of various brands of flux
Each method has its drawbacks, and the use of flux is no exception:
- work is performed only with the joint in the lower position;
- assembly of parts must comply with the parameters of fitting and edge processing;
- production is carried out only on a rigid support, suspended impact on the material is not possible;
- the cost of auxiliary materials is high, so the method is used in critical structures.
Welding aluminum or other non-ferrous metals is impossible without the use of flux, regardless of the joining method. However, there is a possibility that solid oxide will form and be forced to the surface during the process.
The role of flux in welding
Initially it was used only when fastening elements made of low-carbon alloys, but now the effectiveness of the method has been recognized for virtually any metals, including refractory ones.
The main purpose is to prevent oxidative processes that affect the integrity and quality of the seam. In addition to protecting against oxygen, the substance has the following effects:
- the electric arc burns more steadily;
- the molten component does not splash to the sides;
- you can change the chemical type of the site.
Types of submerged arc welding
Joining non-ferrous metals by welding involves the use of various compositions. The component part is divided into manganese, low silicon, oxygen-free products. Fused compositions have the structure of pumice, alloying properties exist in ceramic products, improving fastening properties. Components of the main varieties:
- Salt compounds are rich in fluorides and chlorides. With their help, manual argon arc welding is performed using active compounds and slag remelting.
- Oxide mixtures have found their purpose in joining fluoride parts, as well as low-alloy materials. This product is distinguished by its silicon content and has up to ten percent fluoride compounds.
- Mixed products are used for high-alloy steels; the structure is made up of all the elements listed in the first two materials.
Choosing the right flux is quite difficult without the appropriate experience; automatic submerged arc welding requires high-quality material.
The type and characteristics of the composition are determined by the technical documentation.
Submerged arc welding modes for steels
Automated welding is carried out in such a way that the operator only performs debugging of the equipment in the appropriate operating mode. Sequence of actions and technology:
- Flux is automatically supplied to the parts to be joined, the layer height is adjusted in relation to the thickness of the metal, and the product is taken from a specially designated hopper.
- The cassette mechanism feeds the electrode wire, without which the process is impossible.
- The operating speed is selected in such a way that a high-quality weld pool is formed, preventing metal spattering.
- A product with a lower density floats to the surface of the bath, which does not affect the properties of the seam. Unused material is mechanically collected to save money.
The main positive quality is the increased speed through mechanized submerged arc welding. Thanks to this, the method is used by various industries and has proven itself to be a reliable and durable way to connect welded parts.
The seam is made according to several characteristics, and operating modes are selected depending on this. A common type is cold welding, used at low temperatures to join non-ferrous metals.
Each material has a technical specification with permitted welding parameters.
In the absence of instructions, the substance is selected for use using a sample method; it is important to follow some tips:
- A high quality connection can only be achieved with a stable arc. The parameter is adjusted by selecting the speed level of the melting tool and the current strength.
- The speed performance is affected by the degree of wire extension, as well as the alloy composition.
- The current strength directly depends on the depth, and the voltage can be used to adjust the width of the seam.
The mechanism of operation of fluxes during welding
Thus, it is possible to select the required substance as accurately as possible. It is necessary to understand that you should not neglect control, because... The connection may be disrupted during further use.
Characteristics of welding in a protective environment
The parts must be properly prepared for connection:
- clean from dirt, traces of corrosion and old paint;
- process with a grinding wheel or wire brush.
The technology is simplified through the use of machines. The master does not light the arc and does not monitor its combustion. The wire feed speed is controlled by the unit. It is up to the individual to set up the equipment correctly. For each welding mode it is individual, requiring special calculations.
During operation, filler wire is often used. It is loaded into the machine and supplied automatically. It is better to choose a composition similar to the metal being welded.
The flux is first poured into a container, then it covers the metal in an even layer at the junction of the workpieces. Under the influence of the high temperature of the arc, it melts, forming a small cloud of inert gas that protects the seam from oxygen entering it. After cooling, the burnt flux turns into slag, which is removed by the welder.
We recommend reading: How to cook semi-automatically without a gas environment
Equipment for submerged arc welding
At production facilities, an assembly-type stand is used, on which it is possible to fix the elements being processed in a stationary state. The requirement for reliable fastening is especially observed, because During work, the part may shift, resulting in an uneven weld. Often, instead of full-fledged expensive submerged arc welding equipment, mobile heads are used.
Read also: The main parts of an asynchronous motor are
Submerged arc welding machine
A trolley equipped with an electric drive and a mechanical welding head is called a tractor. This device is capable of moving along the seam directions or directly to the parts.
Application area
The automated method makes it possible to put on a conveyor belt the production of various large structures. The most common areas where the method is applied are:
- Shipbuilding uses large-scale assembly; when using flux welding, it is possible to assemble in sections, which reduces the time for production as a whole.
- Requirements for high parameters of abutting surfaces allow the device to be used in the manufacture of various tanks.
- Gas pipes of large diameters.
Technology does not stand still; every year it becomes more advanced. Submerged arc welding allows the production of large, high-quality products by machine. Some manual work takes several days, but mechanized lines produce the finished product in a matter of minutes.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
The most important modes for automatic submerged arc welding are indicators such as the strength of the welding current, the type and polarity of the current, the voltage of the electric arc, the welding speed, the diameter of the electrode wire, and the speed at which the wire is fed into the welding zone.
Less important, but also quite significant modes of automatic welding are the amount of electrode extension, the angle of inclination of the electrode and the edges being welded, the composition of the flux for automatic welding, the type of welded joint, as well as the preparation of the metal for welding.
Types and modes of welding
Various fluxes are used to join metals by welding. Finding the right composition without experience is difficult. Technical documentation and table No. 1 will help with this, which show the operating mode with low-alloy and carbon steels.
| Metal thickness (mm) | Electrode diameter | Number of passes | Current (A) | Voltage (V) | Wire feed (m/h) |
| 30 | 4 | 4 | 650-750 | 28-32 | 87-95 |
| 50 | 4-5 | 8 | 800-850 | 30-32 | 87-95 |
| ˃60 | 5 | 10-15 | 900-950 | 38-40 | 100-110 |
The welding mode for corrosion-resistant steels is presented in Table No. 2.
| Workpiece thickness (mm) | The diameter of the wire | Number of passes | Current (A) | Arc voltage (V) | Electrode feed(m/h) |
| 30 | 4 | 6 | 400-450 | 28-32 | 87-95 |
| 50 | 4 | 10 | 525-600 | 30-32 | 87-95 |
| ˃60 | 5 | 12-18 | 700-750 | 38-40 | 100-110 |
The operator sets up the equipment and fills it with wire and flux.
We recommend reading: What is cold welding and how to use it
Non-ferrous metals are joined by cold welding, in which the arc temperature is lowered. The strength of the operating current depends on the diameter of the wire:
| Electrode diameter (mm) | Current (A) |
| 2 | 200-400 |
| 3 | 300-600 |
| 4 | 400-800 |
| 5 | 700-1000 |
| 6 | 700-1200 |
To carry out work with low-carbon steels, flux AN-348A, ANTs-1 or OSTS-45 is used. The wire selected is Sv-08GA, Sv-08A or Sv-10G2. Metal with an average carbon content is welded at reduced conditions. The work is slow, so the method is rarely used.
Steel parts with an amount of alloying elements of 5% or less are joined using fluxes AN-22, AN-47, AN-22M, AN-67A and wire Sv-08ХМ, Sv-8МХ, Sv-10NMA.
Medium-alloyed metals are subject to increased requirements: resistance to corrosion and impulse loads. The following grades of flux are needed: AN-15, AN-17M, AN-15M, AV-4, OF-6, AN-30. Electrodes Sv-08Kh20N9G7T, Sv-20Kh4GMA, Sv-10KhGSN2MT, Sv-10Kh5M are used with these compositions.
High-alloy steels are widely used in the oil and chemical industries. Welding is carried out with 2-3 mm wire. The brand doesn't play a big role. Flux is used from ANF-5 to ANF-26.
Selecting automatic submerged arc welding modes
When choosing the parameters of automatic submerged arc welding modes, the thickness of the weld edges, the requirements for the geometric shape and size of the weld, which depend on the depth of metal penetration during welding, as well as the width of the weld, are taken into account.
When choosing welding modes, initially select the diameter of the electrode wire based on the thickness to be welded. Next, after choosing the wire diameter, select the welding current value, which depends on the diameter. After this, the feed speed of the electrode wire into the welding zone and the welding speed are determined.
For automatic submerged arc welding, solid electrode wire is used. The wire diameter can be within 1-6mm. The welding current is in the range of 150-2000A. The electric arc voltage is 22-55V. Approximate modes of automatic submerged arc welding can be selected from the table below:
Influence of selected automatic welding modes on penetration depth and weld width
The influence of current and voltage of the welding arc
As the current increases, the thermal power and pressure of the welding arc increase. This helps to increase the penetration depth, but has little effect on the width of the weld.
If you increase the voltage of the electric arc, then the degree of its mobility increases and the proportion of thermal energy that is spent on melting the welding flux increases. In this case, the width of the weld becomes larger, and the effect on the penetration depth is insignificant.
Effect of electrode wire diameter and welding speed
If you increase the diameter of the electrode wire, but do not change the value of the welding current, then the depth of metal penetration will decrease, and the width of the weld will increase due to the increase in the mobility of the welding arc.
Increasing the welding speed will reduce both the penetration depth and the width of the weld, because the metal at a higher welding speed will not have time to melt in the same quantity as it melted at a lower speed.
Influence of the type of welding current and its polarity
The type of welding current and its polarity significantly affect the size and shape of the weld due to the fact that the amount of heat generated at the cathode and anode of the welding arc also changes greatly. If you choose direct current of direct polarity, then the depth of penetration of the metal being welded is reduced by 40-50%, and for alternating current by 15-20%, compared to direct current of reverse polarity.
Based on this, if you need to make a weld of small width with deep penetration of the metal (for example, when welding butt seams, or when welding fillet welds without groove), then it is recommended to choose for this a constant welding current of reverse polarity.
Effect of electrode wire stickout
When the protrusion of the electrode wire increases, its heating rate and melting rate also increase. Because of this, the volume of the weld pool under the electric arc increases due to the electrode metal and this prevents the melting of the base metal. As a result, the penetration depth decreases. A similar feature is sometimes used in automatic surfacing in order to increase surfacing productivity.
In some cases (most often with automatic surfacing), the electrode is set to move across the welded edges with different amplitudes and frequencies. This technological technique allows you to significantly change the shape and size of the weld. During automatic submerged arc welding with transverse movements of the electrode wire, the depth of penetration of the base metal decreases and the width of the weld increases.
This welding method is used to reduce the likelihood of burn-through when welding butt seams with a large gap between the welded edges. The same goal can be achieved if welding is performed with a double electrode, and the electrodes must be positioned transverse to the welding direction. If they are positioned along the welding direction, this, on the contrary, will increase the penetration depth.
General automatic welding technology
The automatic electric arc process has its own characteristics. The main difference is the use of bulk flux. It must be supplied to the product constantly. When welding, the composition melts and forms a shell that protects the metal from oxygen. The seam is of better quality.
We recommend reading: Choosing a welding inverter
The mechanical method involves the use of a higher current, which gives a good penetration depth and allows you to connect thick-walled workpieces at high speed. The flux-cored welding method is economical. Less materials are consumed due to the small splashing of liquid metal.
When manual arc welding (MAW) this parameter is equal to 15%, when working with modern technology - no more than 3%. Electrical energy is consumed almost one and a half times less. Labor costs are also reduced.