Popular brands
Any professional welder who has been practicing his craft for a long time has long ago developed personal preferences for choosing a machine and compiled his own rating.
It is often subjective because welding machines are somewhat similar to cars. There are many of them, they vary greatly in price, design and characteristics, but it is impossible to say unequivocally that one welding inverter is much worse or better than others. There is also a division into “budget” and “elite” models.
The following brands are in main demand in our country:
- Svarog;
- Resanta;
- Interskol;
- Hitachi;
- Fubag;
- Telwin;
- Blueweld and some others.
Popular equipment is most often purchased and advertised. However, you can always find an alternative if you analyze the ratings and the market, because a lot depends on the place where the buyer lives, his financial capabilities and requests.
Rules for welding work
Welding rules may vary depending on the model of welding inverter you use. For example, some models may have increased protection against dust and moisture, and therefore they do not require careful storage conditions and can be used in field conditions.
Also, some inverters are equipped with indicators that indicate overheating of the device. After this, the device must be turned off and allowed to cool. But if your model does not have such an indication, then you will have to monitor the temperature yourself.
If you have temporarily suspended welding work or finished it, turn off the welding inverter from the network. If there are other people in the work area with you, install a special screen for them to protect them from radiation and sparks.
Use protective clothing made of thick, non-flammable fabric, do not forget about a protective mask (we recommend a chameleon mask), shoes and gloves. Shoes should not conduct current. If you don't have such shoes, you can use a rubber mat. Do not store flammable items in your work clothes.
Check the condition of the cables and the inverter itself before welding. Make sure all cables are connected correctly. Follow safety precautions to avoid harm to health.
Before welding, thoroughly clean the surfaces to be welded. There should be no traces of corrosion, oil, dirt, paint, etc. To clean, use solvent, sandpaper, grinding wheels, etc.
Additional rules
Monitor the airborne dust levels in your work area. All permissible air pollution standards can be found in welding GOST standards. Please note that they do not take into account emissions from the welding machine itself.
If your work location allows, place the welding inverter in the shade. Do not expose it to direct sunlight or precipitation. Yes, there are models with an increased degree of protection, but they are rarely found in the garages of home welders or in small production. So try to store the device correctly. We talk more about storage below in the section “Storing a welding machine”.
Welding work requires adequate ventilation. The ideal option is to install a direct ventilation hood 60 centimeters from the welding site. If these measures are not enough, then you need to use special wind and smoke protection systems.
Separately, we would like to say about connecting the inverter to the network. Do not use voltage higher than standard 220V. If you use, for example, 380V, you risk breaking the welding machine and harming your health. Also make sure that the voltage is more or less stable. Some inverter models are protected from voltage surges and continue to operate stably even during a complete power outage. Naturally, short-term.
When connecting an inverter welding machine to a 220V outlet, you need to protect the outlet itself with a system that automatically stops the supply of electricity in the event of a malfunction in the wiring or in the device itself. Do not use an ungrounded outlet.
If you have not used the welding machine for a long time, check its resistance between each winding. The ideal value is at least 2.5 megaohms.
Budget devices
The main criterion is the price range, although the rating is not based on it. Welding machines of any class are clearly divided into models for domestic use, semi-professional and professional.
The cost of welding machines of the first type varies from 6 to 12 thousand rubles. They can have all the features of expensive devices, such as arc force, anti-stick, and quick start.
But their main difference is the short operating time in PV (continuous on) mode at maximum current. For most state employees it is 30-60%. This means that they cannot cook metal with a thickness of 4 mm or more for a long time. The caliber of the electrodes usually does not exceed 3 mm.
Inexpensive welding machines have an imperfect ventilation system - dust actively settles inside the case, on the electronic boards. In this segment, you should immediately cut off cheap Chinese models - they can break down quite quickly, and such manufacturers usually do not have authorized service centers in Russia. They are in last place in the sales ranking.
The current range of budget inverter devices usually varies from 30 to 160 A, sometimes up to 200 A. The average weight of the device is 5 kg, plus or minus 500 g.
Their lot is minor work around the house and dacha. Welding mode: arc only, MMA. Subjecting an inexpensive device to heavy load is a sure way to damage it.
What to look for when choosing?
When choosing welding transformers, you should pay attention to the main technical characteristics. These include the following:
- Mains voltage. The indicator must correspond to the value specified by the manufacturer (220 or 380 V).
- Range of regulation. The wider the limits, the more options available to the welder. You can choose electrodes of different diameters. Household varieties are characterized by a regulation range from 50 to 200 A.
- Rated current. Professional devices produce about 1000 A, and household ones - up to 100 A.
- Operating voltage. The output from the arc welding device should be rated at 30-70V.
- Welding duration. The indicator determines how long the unit can operate continuously. Household models perform continuous welding for about 15-20 minutes, and professional ones – for several hours.
- No-load voltage. The indicator should not exceed 70 V.
- Power consumption. The higher this indicator, the more efficiently the equipment operates. However, it is necessary to take into account the capabilities of the household network. Too much load may be unacceptable.
When choosing, you must consider the purpose for which the equipment is purchased. In this case, you will be able to buy a unit with optimal performance at an affordable price.
Forward and reverse polarity
Melting of the metal for welding occurs under the influence of an arc. It, as noted above, is formed between the surface of the product and the electrode, since they are connected to opposite terminals of the device.
There are two main options for welding, differing from each other in the order of connection and called direct and reverse polarity.
In the first case, the rod is connected to the minus, and the part to the plus. In this case, an increased flow of heat occurs into the metal. As a result, a deep and narrow melting zone is formed.
Direct and reverse polarity.
With reverse polarity, the electrode is connected to the positive, and the product to the negative. In this case, the melting zone is wide and shallow.
For example, it is difficult to weld thin metal products due to possible overheating and burning. In this case, the part is connected to the minus. Currents are also selected according to the diameter of the electrode and the thickness of the metal. This data is taken from a special table.
Types of welding power sources
The power source is included in any installation for arc and electroslag welding. It supplies the arc or electroslag process with electrical energy of the required parameters. When arc welding, currents from 1 to 3000 A are used at a voltage of 40-141 V. Welding can be performed on direct and alternating current, both with continuous and pulsed energy supply.
Depending on the type of energy and the nature of its transformation, the following types of power sources are distinguished:
- transformer - reduces the alternating voltage of the network to the required one for welding;
- rectifier – converts the energy of the AC mains current into the energy of direct welding current;
- generator – converts the mechanical energy of rotation of its shaft into direct current electrical energy;
- converter - is a combination of a three-phase asynchronous AC motor and a welding generator and, therefore, converts network energy into DC energy used for welding;
- unit - consists of an internal combustion engine and a direct current generator; it uses the chemical energy of combustion of liquid fuel to produce welding current.
Welding current power sources are classified according to the following characteristics:
- type of current - sources of alternating current (welding transformers) and direct current (converters, units and rectifiers);
- external characteristics - sources with steep, hard, increasing and mixed current-voltage characteristics;
- the number of simultaneously fed posts—single-post and multi-post sources;
- the nature of the drive - sources with electric drive and with independent drive (from an internal combustion engine);
- features of arc combustion - sources for welding with a free-burning arc and a compressed one;
- installation and installation method - stationary and mobile;
- principle of operation and design - welding transformers with normal magnetic dispersion (with a separate reactive coil and on a common core), increased magnetic dispersion (with a movable magnetic shunt and movable windings); welding rectifiers with silicon or selenium valves; converters with independent magnetizing and series demagnetizing windings, split poles; units - generators with internal combustion engines (gasoline carburetor type and diesel);
- purpose - power sources for manual arc welding, automatic and semi-automatic submerged arc welding, gas shielded welding, plasma cutting and welding, electroslag welding and special-purpose current power sources (for three-phase welding, multi-arc).
MODERN SYMBOLS OF WELDING CONVERTERS
DEVICE AND MAIN PARAMETERS OF WELDING TRANSFORMER
In the process of mechanization of welding work, each machine is equipped with the necessary working units. The welding transformer is the leading part of any machine, indispensable for contact welding.
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION OF THE COMMON UNIT OF THE WELDING MACHINE
The main purpose of the transformer is to convert the voltage in the electrical network into the values most suitable for the welding machine. The transformer regulates the voltage, reducing it to certain levels. He establishes continuous operation of the welding device. Being an indispensable power source, the transformer is capable of delivering maximum power to the welding arc. The perfect design of the welding transformer allows the device to be used for joining materials in the temperature range from -45 to +40°C.
MAIN PARAMETERS AND DEVICE OF THE CONVERTER
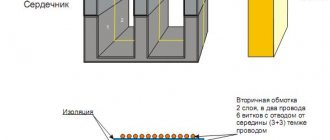
The main parts of the transformer are the following elements:
· core (magnetic circuit);
· output of the primary winding;
· primary winding;
· secondary turn of the winding;
· frame;
· water cooling pipe.
Most converters are produced with secondary and primary windings. They have high mechanical strength and are reliably insulated from moisture, dirt, and dust.
The transformer operates using severe cooling modes. For a welding converter, dimensions are set consisting of such quantities as:
· power (kVA);
· duration of PV switching on (%);
· welding current (A);
· open circuit voltage (V).
The operating time of the converter with normal magnetic leakage is from 65 to 60% (depending on the model). The rated current value ranges from 500 A to 2000 A. The power of the transformer device ranges from 30 kVA to 162 kVA. The amount of heating of the windings is related to the strength of the current for welding and the time it passes. There is a relationship between Tw (welding time) and the duration of switching on the PV. The lower Tw, the greater the welding current.
Figure 2. Diagram of transformers TD-300 and TD-500.
Welding with single-phase and three-phase converters is based on mutual induction.
A three-phase operating mode is established, consisting of the following parameters:
· idling;
· work with load;
· short circuit.
Converters with powerful magnetic fields are capable of performing several functions:
· smooth adjustment of the current value;
· formation of continuous burning of the welding arc.
MODERN SYMBOLS OF WELDING CONVERTERS
· The single-phase transformer belongs to the TD series. It is equipped with a movable winding and a current regulator. When the lead screw is rotated using the handle, the winding moves. Along the entire length of the rods there are primary and secondary windings.
· Transformers TD-300 and TD-500 (Fig. 2) have secondary coils that can move. The TD-502 series converter, operating at a current of 500 A, is equipped with a power capacitor.
· The TDM series of transformers is widely used. They are created from special sheets with a thickness of 0.35 mm. The main task in creating new converters has been completed: new and efficient winding materials have been used.
· The TDM series includes converters operating at currents of 315, 400 and 500 A. Three-phase transformers are less common. Welding is carried out by converting current from 380/220 V to 60 V.
Designation of welding machines
Designation of welding machines
Unified designation structure for electric welding equipment. The designation of electric welding equipment consists of an alphabetic and digital part:
the first letter is the type of product (B - rectifier, T - transformer, G - generator, U - installation),
the second letter is the type of welding (D - arc, P - plasma),
third - welding method (G - in shielding gases, F - submerged arc, U - universal sources), the absence of a third letter indicates manual arc welding with stick electrodes,
the fourth letter is the purpose of the source (M - for multi-station welding, I - pulse welding).
two or one number after the letters - rated welding current in hundreds of amperes,
the next two digits are the product registration number,
the following letters - climatic version (T - for use in countries with tropical climates, U - in areas with temperate climates, HL - cold climates),
the next number is the placement category (1 - in an open area, 2 - trailers, car bodies, 3 - rooms with natural ventilation, 4 - with heating and forced ventilation, 5 - high humidity).
Example, power supplies VDGM-1601T2, we get: rectifier for gas-shielded arc welding, many guards, current 1600 A, product registration number 01, for work in countries with tropical climates, placement category - 2.
Deciphering the functions of a welding machine or inverter
A welding machine (inverter) has long become a popular welder’s tool for welding work.
The variety of models on the market often confuses novice welders with the choice of a machine, while professionals are increasingly paying attention to the presence of modern functions that allow them to perform welding work faster and with better quality.
It is not uncommon to encounter questions related to what this or that function of a welding machine means. This is what the information below is about.
So, decoding (designation) of the functions of a welding machine or inverter :
ANTI STICK - “anti-sticking”. Solves the common problem of electrode sticking during arc ignition. Provides an automatic reduction in the welding current, after which the electrode is easily separated from the welding object, and the welding machine then restores the initial welding parameters.
ARC FORCE - “arc afterburner”. This function makes it possible to increase the current for a short period at the moment of separation of a drop of metal from the electrode. Thanks to this, the process of transferring drops through the arc gap becomes uniform and clear. The welding itself becomes easier to perform, thereby simplifying the creation, for example, of vertical seams.
ARC POWER - “arc power”. Maintains arc combustion and prevents metal from splashing across the working surface.
AC WAVE – “waveform adjustment”. The function allows you to adjust the speed and depth of penetration using a waveform (for example, sine or square).
BALANCE – Allows you to adjust the balance of alternating current polarity, giving the welder the ability to adjust the duration of the balance and, as a result, the shape and width of the weld.
BURN BACK - “annealing of wire”. Automatic arc stretch function. Gives the most correct detachment of the wire from the welding seam, ensuring accurate completion of the welding process and leaving the desired length of the wire end for the next stage.
DOWN SLOPE/ Crater Arc – “crater filling mode”. Smooth decrease in current at the end of welding to obtain a high-quality seam with optimal filling of the “crater”. Especially relevant for stainless steel and aluminum.
FCAW (Flux Cored Arc Welding) - “cored wire welding”. Makes it possible to weld using flux-cored wire without supplying shielding gas. Especially relevant outdoors and at altitude.
FLOW CONTROL
– “flow sensor”. Regulates the fluid flow system. If the device runs out of water, it stops working, thereby preventing overheating/melting of the burner and associated cables.
FOCUS ARC - “focused arc”. When you press the function activation button, the shortest arc with maximum stability is selected, providing deep penetration and less spatter.
HOT START - “hot start”. This is especially true for beginners who have not yet mastered the optimal arc ignition algorithm. This function provides a short-term increase in welding current at the moment the electrode touches the welding object, which ensures an easy and comfortable start to welding.
PFC (Power Factor Correction) - “power factor correction”. The function allows you to increase the voltage level on the inverter module if necessary, thereby increasing the power and performance of the device from the existing network.
PRE GAS and POST GAS – The function carries out the initial and final purging of the working surface with gas. This avoids cracks, voids and oxidation in the weld.
PWS – Adjustment (switching) of polarity directly on the panel of the welding machine (inverter) or using the remote control at any necessary time.
SOFT SWITCH - “soft switching”. Significantly reduces welding current surges, which improves the quality of the seam, the stability of the ignition and the entire welding process.
SWITCHABLE - “switchable”. Allows the welding machine to operate with different mains voltages.
VRD (Voltage Reduction Device) - “voltage reduction device”. Automatically reduces the voltage to a safe level during idle operation of the inverter, i.e. when the device is turned on, but welding is not performed at this moment.
2 and 4 STEP WELDING – “2 and 4-stroke welding mode.” Control over short and long welds respectively. In 2-stroke mode, the welder independently regulates the process by pressing the button on the torch at the right moment. Perfect for welding in hard-to-reach places, spot welding and “sticking” metal. In 4-stroke mode, on the contrary, there is no need to hold the button on the torch for a long time, which greatly facilitates welding long seams.
Types of welding machines
The name electric welding speaks for itself, that is, an electric welding machine is required to connect two metal elements. Manufacturers today offer units operating at 220 or 380 volts. Some models output direct current, others alternating current.
Transformers
Until recently, this was practically the only device with which welding was carried out. It only produces alternating current, and the polarity of the unit constantly changes during the welding process, which is very inconvenient. This is expressed by the fact that the welding electric arc jumps all the time. Therefore, it is difficult to control; a huge number of sparks are produced during welding. Hence the low quality of the weld, so only professionals with extensive experience could work with such welding machines.
They were used for welding only ferrous metals. The design of the transformer is simple - these are two step-down transformers with the ability to adjust the output current. True, the range of settings is small, the adjustment is not the most subtle. But this unit rarely broke down, and its repair was not difficult.
The big disadvantage of welding transformers is their heavy weight. Even the lowest-power device weighs at least 50 kg. What can we say about industrial designs that weighed at least 100 kg. Another negative point is the voltage drop in the supply electrical network, especially when the electrode is ignited. Everyone knows that power surges negatively affect modern household appliances packed with electronics. Therefore, today welding transformers are a rarity in private homes and country houses. And even if someone has them, they are practically not used and are kept by the owners just in case.
Rectifiers
In principle, this is the same welding transformer, in the design of which a rectifying unit is installed. Rectifiers are often called DC welding transformers. The output of the rectifiers is direct current, which simplifies the welding process. The electric welding arc is stable, but experience is still required. Like the transformer, the rectifier is simple in design; in principle, there is nothing to break here.
Among the disadvantages we can highlight:
- Heavy weight;
- Power is lost on the rectifying unit;
- Voltage drop during ignition and during operation;
- The voltage jumps not only for the owner of the unit, but also for the neighbors.
- The price is higher than that of a transformer.
Inverters
As soon as these welding devices appeared in stores, it was impossible to approach them. Their price was too high. But over time, the element base has changed, and accordingly the cost of the equipment has decreased, and with it the weight of the unit. A modern inverter-type home welding machine produces a current of 160-180 amperes, which makes it possible to weld with electrodes up to 4 mm in diameter. The weight of the device is 3 kg, this is the minimum.
The advantages of this type of welding machines include:
- Stable arc that is easy to control.
- Ease of use: the electrode does not stick, the seam is smooth and tight.
- The device does not sag the voltage in the network; it does not jump during operation of the unit.
- Wide range of welding mode settings. Inverters can weld metal products of different thicknesses. The main thing is to correctly set one or another mode on the device.
If you are faced with the question of which welding machine to choose, then you don’t have to think twice and choose an inverter. Of course, with it you will not immediately become a high-quality welder, but you will do many small welding operations at your summer cottage with your own hands.
Semi-automatic welding machines
Since we are talking about welding machines for home and garden use, units of this type are not included in this category. Most often they are used in the field of small businesses, and more specifically, in car repair shops.
Their design is based on one of the welding devices described above, plus a block with which the welding wire is fed automatically. The operating technology of these units is based on welding in a shielding gas zone, which allows the welding of thin parts and products made of non-ferrous metals.
These are ideal welding units with which you can weld thin metal sheets up to 0.8 mm thick. In this case, the seam turns out smooth and beautiful, the sheets do not lead or warp. The only drawback is that this type of welding device cannot weld thick parts. To do this, you will have to purchase a machine with electric arc welding.
The types of welding machines have been reviewed, now you can proceed to the selection to determine the best country or home welding device.
Classification of welding transformers
It is customary to classify welding transformers according to their purpose. They differ in the following indicators:
- Dimensions and weight . They are presented on the market as small models that are equipped with a shoulder strap for carrying; as well as large units that require a hoist or trolley to move.
- Open circuit voltage . It varies over a wide range of values: from 48 to 70V.
- Current strength . On most serial equipment, this parameter ranges from 50 to 400A. There are large industrial designs that generate a current of 1000A.
- Number of phases and current consumption . Single and three-phase welding transformers for power supply lines 220 and 380V.
- Supply of current . Can be continuous or pulsed.
- Electrodes used in the work . Consumables vary in composition and diameter (2-6 mm).
The easiest way to obtain a reliable connection between two metal elements is by using electric welding. It is perfect for performing various types of work in production, at home or anywhere else. Welding machines are easy to use, reliable and efficient. Welded seams tightly connect the workpieces and serve for many decades.
What criteria do you use to choose the right device for yourself?
Criteria for selecting a welding machine:
- By function. What and where are you going to cook? A waterer for turkey poults in the country, a car body in a workshop, or do you have serious industrial projects ahead?
- According to the quality, type and thickness of the weld. Are aesthetics more important to you, such as for decorative grilles or car parts, or strength and reliability in critical facilities such as gas pipelines?
- Depending on the type of metals you are going to work with. Stainless steel? Aluminum? Non-ferrous metals and their alloys? If your set of metals includes aluminum and its alloys, you need to turn towards devices where the abbreviation TIG is present with inert gas cylinders in addition.
- According to the characteristics of the electrical network. If you live and plan to work in a rural area, your network will most likely experience voltage surges. Then you need to look for devices with a wide range of voltage surges - there are such, they are specially produced for Russian regions.
- From the personal experience of the master. If you have recently started welding, it is unlikely that it would be advisable to buy an expensive, sophisticated semi-automatic machine, where you will not need half the functions at all.
A very important point in choosing is the versatility of the device. It depends on the type of work you plan: do you only need a semi-automatic machine with automatic wire feed? Or are you going to work with electrodes too? If yes, let's go choose universal equipment.
Types of construction
Welding transformers are also classified according to the design principle. There are three main groups:
- Equipment with rated magnetic dissipation. It has a choke to regulate the output voltage.
- Equipment with increased magnetic dispersion. It has a complex design. It includes several moving windings, a pulse stabilizer and a capacitor. Other components may also be present.
- Thyristor types of welding transformers. They have a corresponding phase regulator device. Thyristor-type devices are characterized by relatively low weight.
The presented classification is for AC devices. There are DC models. They have larger dimensions and a more complex structure. They contain a rectifier.
Such models are more stable and easier to use. The purpose of the welding transformer, which operates at direct current, in this case is defined as industrial. The equipment allows the master to work with non-ferrous metals and stainless steel. The cost of such devices is quite high. Therefore, welding transformers of this type are used exclusively for professional purposes. AC devices are quite suitable for household needs.
How to choose a welding machine for electric welding
The choice is based on several key parameters.
- Supply voltage. It is clear that this is 220 or 380 volts. This characteristic is important, because all the types of welding equipment presented above, except inverters, respond to the quality of the voltage in the supply network. If the voltage rises sharply, a protective unit is triggered, which turns off the device. At a low voltage value, all welding parameters sharply decrease, which leads to poor quality of the weld. And only inverters can safely operate in the range of 180-250 volts without changing their parameters. As for welding devices operating from a three-phase network, they are practically not used at dachas. Therefore, if we talk about which welding machine is best for the home, then in terms of voltage it is an inverter.
- Open circuit voltage. This is the voltage of the welding machine when it is plugged in, but there is no load on it. Why is it necessary to know this parameter? The thing is that the ease of igniting the electrode depends on it. And the higher this value, the simpler the ignition process, plus the stability of the arc increases. This indicator in modern welding machines varies from 45 to 95 volts. Experienced welders know that open circuit voltage influences the choice of electrode type. If you choose a low-voltage device, it is recommended to purchase rutile-coated electrodes for it. For electrodes with a basic coating, it is better to choose a unit with a high open circuit voltage.
- Output current. This selection criterion will depend on how long the device will operate. That is, periodically or more or less constantly. For most household work, a current of 160-180 amps is suitable. At this current, if you use an inverter, you can cook with electrodes up to 4 mm in diameter. If there is a need to weld thick metal parts, you will have to purchase a device that produces an output current of 190-250 amperes.
- Diameter of electrodes. Basically, this dimensional indicator affects the thickness of the products being welded. The thicker the metal, the larger the electrode diameter required. This relationship is shown in the table below.
| Diameter of welding material, mm | Thickness of welded parts, mm |
| 2,5 | 2 |
| 2,5-3 | 3 |
| 3,2-4 | 4-5 |
| 4-5 | 6-12 |
| 5 | 13 |
And a few general recommendations that determine a good welding machine for home and garden at 220 volts. Much will depend on what tasks you intend to solve on the site. If you plan to weld parts from ferrous metal, then all this can be done using a cheap transformer. If you plan to weld non-ferrous metals, stainless steel or thin steel structures, then it is better to use a semi-automatic machine. The inverter performs well when welding low-alloy or structural steels. Although it should be noted that inverter-type equipment, in addition to non-ferrous metal and stainless steel, welds any steel structures.
At home, the size of the unit matters. Therefore, small and lightweight inverters are the best option for this. Low voltage in the network, which is present in almost all suburban villages, is the reason why the choice is given to inverters. These devices operate at a voltage of 180 volts, some models even at 160 V.
If you are a novice welder, then again it is recommended to opt for inverters. Simplicity of welding is the main criterion for the operation of the device: the electrode does not stick, ignition of the arc is easy, and when the electrode approaches the metal being welded at high power, the inverter immediately turns off. That is, in all respects, this is currently the ideal welding unit for a beginner.