Turning and milling works
Pulleys Metal grinding Carousel processing Batch production Axle production Rollers Trunnions Spacers Adapters Large housings Die production Tooling production Fixture production Production of custom parts according to drawings Large flanges Production of variable speed pulleys Production of worm pairs Production of bearing housings Production of gear wheels Production of shafts according to customer drawings a Manufacturing of pulleys Manufacturing of fittings Making cams Making screws Making bushings Making pins
The Metalcentre company offers a wide range of metal services. We prepare design documentation, write control programs in the CAD/CAM system, and carry out any turning and milling work to order in Moscow and throughout Russia. The use of new techniques and functional equipment allows processing to be carried out in the shortest possible time. All operations are carried out in strict accordance with existing norms and standards.
How much does turning and milling work cost?
| Type of service | Price |
| Turning of conical surfaces | Calculate the cost |
| Turning of cylindrical surfaces | Calculate the cost |
| Machining of spherical surfaces | Calculate the cost |
| Processing of shaped surfaces | Calculate the cost |
| Turning of ends and shoulders | Calculate the cost |
| Cutting metal blanks | Calculate the cost |
| Turning of non-ferrous metals | Calculate the cost |
| Turning of ferrous metals | Calculate the cost |
| Rotary turning | Calculate the cost |
| Turning work on CNC machines | Calculate the cost |
| Slotting work | Calculate the cost |
| Gear shaping works | Calculate the cost |
| Planing work | Calculate the cost |
| Gear cutting work | Calculate the cost |
| Rolling corrugations | Calculate the cost |
| Thread cutting | Calculate the cost |
Milling
Milling machines are designed for milling all kinds of parts made of steel, cast iron and non-ferrous metals and alloys with face, end, cylindrical, radius and other cutters. Such machines can process horizontal, vertical and inclined planes, grooves, corners, frames, gears, etc.
Vertical cantilever milling machine VM127M
Technical characteristics of the VM127M machine
| Dimensions of the working surface of the table, mm | 400×1600 | |
| Maximum table movement, mm | longitudinal | 1000 |
| transverse | 320 | |
| vertical | 420 | |
| Maximum movement of the spindle quill, mm | 80 | |
| Spindle head rotation angle, degrees | ±45 | |
Vertical cantilever milling machine 6T13UP
Technical characteristics of the machine 6T13UP
| Accuracy class according to GOST 8-82 | N | |
| Dimensions of the working surface of the table, mm | 400×1600 | |
| Maximum table movement, mm | longitudinal | 1010 |
| transverse | 400 | |
| vertical | 420 | |
Horizontal milling machine 6R82G
Technical characteristics of the machine 6Р82Г
| Accuracy class | N | |
| Dimensions of the working surface of the table, mm | 1250×320 | |
| Maximum table movement, mm | longitudinal | 800 |
| transverse | 250 | |
| vertical | 420 | |
When is turning used?
If you need a batch of metal parts or custom-sized products, we are ready to help. We provide prompt services in Moscow and throughout Russia in the event that the full functioning of your production is stopped due to the breakdown of spare parts. The execution time may be affected by the choice of material - steel, stainless steel, aluminum, bronze, copper, etc. Upon completion of turning work, you receive a finished product made to order, that is, corresponding to the pre-approved dimensions, shape, surface roughness and relative position accuracy.
What does turning and milling work include?
- Turning.
- Cutting off.
- Trimming.
- Treatment of external and internal surfaces.
- Strengthening the fillets of a stepped shaft.
- Making groove and parting cutters.
- Cutting or restoration of external and internal threads;
- Edge processing.
- Drilling and boring works.
- Surface finishing.
- Turning knurling.
- Improving the quality of holes produced by casting, stamping or drilling.
- Processing of internal, external, shaped, cylindrical and conical surfaces.
- Creation of grooves, undercuts and other side elements of steel cutting.
- Cutting ledges vertically and horizontally.
- Processing straight or curved surfaces.
- Creating teeth on wheels and other parts.
- Chamfer milling - spheres, ellipses and much more.
Work examples
Types of milling
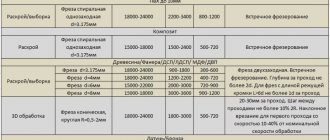
By tool type:
- Tortsevoy. The choice of tool and operating mode depends on the type of processing. The coarse insert pitch is suitable for ferrous fabrication and metalworking of raw materials that produce draining chips. Thanks to this method, the power and cutting force of the machine are reduced. The fine pitch of the inserts is optimal for finishing milling, which does not require high-precision processing and is characterized by a small depth of cut.
- Terminal. Used to create contour ledges and recesses, processing surfaces located at right angles to each other.
- Cylindrical. Used for roughing and semi-finishing of straight planes of parts located parallel to the tool axis.
- Jagged. Allows you to process external gears, racks, external splines, chain sprockets and other parts with similar elements.
- Shaped. Suitable for the production of chamfers and turning of broaching shaped parts. If they are short, then usually milling is not used, but broaching is used.
There are also other types of cutters, which are characterized by versatility and accuracy. These include, for example, double discs, slotted blades and other complex shapes.
By location:
- Vertical. Used for drilling, processing corners, frames. With their help, you can process vertically located planes, as well as horizontal surfaces. The device is characterized by precision due to its extreme rigidity.
- Horizontal. Using the machine, they drill, grind various parts, make blanks according to drawings, remove chips of a given thickness, and create mock-ups.
Modern CNC machines are capable of performing various operations in several planes with automatic tool change. In addition to turning and milling services, we offer drilling, slotting and other types of work with metal products. Thanks to this, we carry out a full cycle of processing workpieces without the involvement of intermediaries.
How turning milling can improve cutting efficiency
Andrey Petrilin is the chief engineer in the field of indexable milling tools at Iscar. Turning milling is the process of cutting using a milling tool while rotating the workpiece around its axis. This method combines elements of milling and turning and has many advantages. But only relatively recently, with the advent of modern multi-tasking machines, has it become possible to fully realize its potential.
For many years, even after the widespread introduction of CNC technology, the production of machining centers remained traditional, while specialized lathes, milling and drilling machines continuously developed in their own individual direction. When the system of tool rotation - milling and drilling - had already been successfully introduced on multi-purpose machines, lathes still continued their development path. The desire to increase productivity by reducing set-up and workpiece transfer from one machine to another has led to the creation of a tool-driven head for CNC lathes. This, in turn, provided the possibility of turning milling. At the same time, modern multi-tasking machines today have additional axes of head movement, advanced control systems and updated software, which allows most operations to be performed in one installation.
Turning milling can be of two types: peripheral, when the axes of the workpiece and the cutter are parallel, and face milling, when these axes intersect. Peripheral milling is similar to helical interpolation milling and can be carried out on the outer and inner surfaces of rotating bodies, while in face milling only the outer part is processed. Although turning milling is very similar to conventional turning (since it involves turning with a rotating cutter), the two processes have a number of significant differences. The cutting speed during turning milling is determined by the peripheral speed of the cutter, and not by the rotation speed of the workpiece, as in turning. The rotation of the workpiece depends on the feed.
So what is the main advantage of the turning milling method and where is it used? First of all, when processing complex body workpieces containing various grooves, recesses, etc. Traditionally, such parts are processed by intermittent turning, which is accompanied by an unwanted impact load and does not provide a high quality surface, causing premature tool wear. All these disadvantages are absent in turning milling due to the use of a cutter designed specifically for intermittent cutting with cyclic load.
When machining materials, long chips can be generated. In conventional turning, chip removal is difficult and selecting a suitable chipbreaker geometry is not an easy task. The cutter used in turning milling produces short chips that are easy to remove.
Take, for example, the machining process of asymmetrical components such as crankshafts and camshafts. As a result of uneven mass distribution in certain areas (such as the crankshaft journal or eccentric cam), unbalanced loads occur during turning, which negatively affects productivity. This negative effect is easily eliminated during turning milling due to the low peripheral speed of the workpiece.
This method is also suitable for processing heavy parts. Their rotation frequency, which determines the cutting speed during turning, is associated with the limitations of the main drive of the machine. If the drive does not allow heavy parts to rotate at the required speed, the cutting speed is also significantly reduced, which affects the productivity of the machine. Turning milling allows you to effectively cope with these difficulties.
Meanwhile, for productive machining using the turning milling method, it is necessary to correctly position the cutter in relation to the workpiece, select the correct plate geometry and tool path. The location of the cutting tool, in turn, determines the accuracy of the part's shape, the choice of insert geometry and the quality of the surface finish. Typically, the final profile of the part is formed by a wiper insert mounted on the cutter (for example, with Wiper geometry). The issues of using turning milling, selecting tools and determining cutting parameters require in-depth analysis in each specific case.
The turning milling method allows you to solve complex production problems, while significantly increasing work efficiency. The use of this relatively new and promising technology in combination with modern equipment and the right tools is the key to consistently high productivity.
Source of material: translation of the article Turn-milling benefits , SMT Author of the original article: Andrei Petrilin
About the author:
Andrey Petrilin is the chief engineer for indexable insert milling tools ]Iscar[/anchor], located in Tefen, Israel.
There are no related entries.
Stages of cooperation
- To place an order, you must provide design documentation. If you do not have a specialist on staff to prepare technical drawings, you can order this service from us for an additional fee.
- Execution of work. The quality of products is ensured by the latest turning and milling machines. Before being sent to the warehouse, each part is tested to ensure compliance with basic requirements - accuracy and surface roughness.
- Delivery of finished products. We ship products throughout Moscow, the Moscow region, as well as to the regions through transport companies.
Differences between milling and turning metalworking
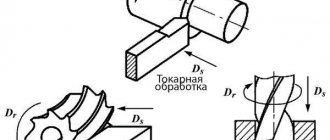
To put it simply, the main difference between turning and milling work is the method of forming the product. On a turning unit, the part itself rotates on a spindle, and a cutter fixed in a holder moves progressively along it (performs a feed movement) and removes the metal layer by layer. And on milling devices, the future part is rigidly fixed on the table, which makes a straight or curved feed movement relative to a rotating cutter fixed in the spindle.
Thus, the workpiece acquires the required shape on a lathe by removing layers of metal, and on a milling machine as a result of deepening the rotating cutter. With turning technology, the workpiece can be processed not only from the outside, but also from the inside. These machines are used to produce bolts, nuts, shafts, cylinders, bushings, studs, etc. Milling technology allows the production of more complex parts, such as worms, gears, gears and the like. It is important to note that both turning and milling work are complex technological processes and require a professional approach - only in this case the order will be completed at the proper level.
Why do they contact us?
- Great experience. For more than 14 years we have been fulfilling orders of various sizes, including for large oil production and mechanical engineering enterprises.
- Acceptable prices. A system of discounts is provided for regular and wholesale customers.
- Developed logistics. We quickly place your order and arrange delivery throughout the capital and regions of Russia.
- Fulfilling urgent orders. The deadlines are specified in the official agreement, for failure to which we bear financial responsibility.
- Modern equipment. The use of CNC machines guarantees the speed of execution of large batches of orders and quality control at all stages of work.
The exact price of turning services and metal milling work is calculated individually. You can agree on all the details with our manager by phone. The cost is fixed in the contract and does not change during the process. Minimum order - from 15 thousand rubles.
Differences between CNC turning and milling machines
CNC turning and milling machines are most profitable and efficient for large enterprises and unprofitable for small industries. The reason is the high cost and volume of work carried out. At large industrial plants, such equipment will provide:
- Maximum performance. To work, you only need to set the necessary part processing program.
- High accuracy. A CNC machine is capable of instantly performing millions of computational processes, processing a workpiece according to a given program.
- Minimum defect. All operations are configured and debugged, which reduces the likelihood of possible defects.
- Economical. The precision of the operations performed eliminates unnecessary operations and idle work. CNC machines can significantly reduce energy costs.