GOST 16523-89
| GOST 16523-89: Rolled thin-sheet carbon steel of high quality and ordinary quality for general purposes |
Technical Requirements
For thin sheet hot-rolled and cold-rolled carbon steel of high-quality and ordinary quality for general purpose, manufactured with a width of 500 mm or more, a thickness of up to 3.9 mm inclusive.
Rentals are divided into:
- by production method:
- hot rolled,
- cold rolled;
- sheets,
- rolls;
- cold rolled: especially high finishing - I,
- high finish - II,
- advanced finishing - III (IIIa, IIIb);
- hot rolled: high finish - III,
- regular finishing - IV;
- deep - G,
- normal - N.
- by type of product:
- according to the minimum value of tensile strength (B) for strength groups: K260V, K270V, K300V, K310V, K330V, K350, OK360V, OK370V, K390V, OK400V, K490V;
- according to standardized characteristics into categories: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6;
- by quality of surface finishing into groups:
- by drawing ability (cold-rolled steel up to 2 mm thick, strength groups K260V, K270V, K310V, K330V, K350V):
In terms of product range, rolled products must comply with the requirements of GOST 19903 hot-rolled, GOST 19904 cold-rolled. Rolled products are produced:
- made of carbon steel of ordinary quality of strength groups OK300V, OK360V, OK370V, OK400V;
- made of high-quality carbon steel of strength groups K260V, K270V, K310V, K330V, K350V, K390V, K490V. Steel grades and chemical composition requirements for each strength group are given in Table 1.
Table 1
Steel grades used and chemical composition requirements
| Strength group | Steel grades | Mass fraction of elements and maximum deviations, % |
| K260V | 08kp | According to GOST 1050 For rolled steel grades 08kp and 08ps, the lower limit of the mass fraction of carbon and silicon is not limited |
| K270V | 08ps, 08, 10kp, 10ps, 10 | |
| K310V | 15kp, 15ps | |
| K330V | 15, 20kp | |
| K350V | 20ps, 20 | |
| K390V | 25, 30 | |
| K490V | 35, 40, 45, 50 | |
| OK300V | St1, St2 (for all degrees of deoxidation) | According to GOST 380 The mass fraction of chromium, nickel and copper is formed at the request of the consumer. The lower limit of the carbon mass fraction is not limited. For rolled steel with grade numbers 3, 4, 5 (all degrees of deoxidation), the mass fraction of manganese can be reduced by 0.10%. When deoxidizing semi-quiet steel with aluminum, titanium or other deoxidizing agents that do not contain silicon, as well as several deoxidizing agents (ferrosilicon and aluminum, ferrosilicon and titanium, etc.), the mass fraction of silicon in the steel is allowed less than 0.05%. In this case, the mass fraction of aluminum is allowed up to 0.07%. Deoxidation with titanium, aluminum and other deoxidizing agents that do not contain silicon is indicated in the quality document. |
| OK360V | St3 (all degrees of deoxidation) | |
| OK370V | St3ps, St3sp | |
| OK400V | St4 (all degrees of deoxidation St5ps, St5sp) |
The weldability of rolled steel of strength groups OK300V and OK360V, OK370V categories 4 and 5 is ensured by the manufacturing technology and chemical composition of the steel. Categories of rental depending on the standardized characteristics are given in Table 2.
table 2
| Category | Standardized characteristics | Mode of production | Strength group | |||
| K260V, K270V, K330V, K350V, K310V | K390V | K490V, OK400V | OK370V | |||
| 1 | Bend test | Hot rolled Cold rolled | — | — | — | + |
| 2 | Spherical Well Draw Test | Cold rolled | + | — | — | — |
| 3 | Spherical dimple bending and stretching test | Cold rolled | + | — | — | — |
| 4 | Mechanical properties test | Hot rolled Cold rolled | + | + | + | + |
| 5 | Mechanical and bending testing | Hot rolled Cold rolled | + | + | — | + |
| 6 | Testing of mechanical properties, spherical dimple stretching and bending | Cold rolled Hot rolled (according to customer's request) | + | — | — | — |
The mechanical properties of rolled products and the diameter of the mandrel when tested for 180-degree bending in a cold state must comply with the requirements of Table 3.
Table 3
| Strength group | Tensile strength N/mm2 (kgf/mm2) | Relative elongation in %, not less | Bending until the sides are parallel (a is the thickness of the sample, d is the diameter of the mandrel) | ||||
| hot rolled steel | cold rolled steel | ||||||
| up to 2 mm will turn on. | over 2 mm | up to 2 mm will turn on. | over 2 mm | up to 2 mm will turn on. | over 2 mm | ||
| K260V | 260-380 (27-39) | 25 | 28 | 26 | 29 | d=0 (without gasket | d=a |
| K270V | 270-410 (28-42) | 24 | 26 | 25 | 28 | ||
| OK300V | 300-480 (31-49) | 21 | 23 | 24 | 26 | ||
| K310V | 310-440 (32-45) | 23 | 25 | 24 | 27 | ||
| K330V | 330-460 (34-37) | 23 | 24 | 24 | 25 | ||
| K350V | 350-500 (36-51) | 22 | 23 | 23 | 24 | ||
| OK360V | 360-530 (37-54) | 20 | 22 | 22 | 24 | d=a | d=2a |
| OK370V | 370-530 (38-54) | 20 | 22 | 22 | 24 | ||
| K390V | 390-590 (40-60) | 19 | 20 | 20 | 21 | ||
| OK400V | 400-680 (41-69) | 17 | 19 | 19 | 21 | No | No |
| K490V | 490-720 (50-73) | 12 | 13 | 13 | 14 | ||
There should be no tears, cracks or delaminations at the bend. Hot-rolled steel is produced by heat treatment, cold-rolled steel is produced by heat treatment and tempering. Hot-rolled steel from continuous rolling mills may be produced without heat treatment. Hot-rolled steel is produced with both pickled and unetched surfaces. Sheets must be cut on all sides. Sheets obtained from coils rolled on continuous rolling mills may be manufactured with uncut edges, except for cases specified in the order. Rolled products are produced with unedged and trimmed edges. Defects are not allowed on the edges, the depth of which exceeds half the maximum deviation along the width of the rolled product, and which would take it beyond the nominal width size. Rolled products should not have ends and edges turned at an angle of more than 90 degrees. The length of part-width rolls should not exceed the width of the roll. The depth of the hole during the extrusion test must comply with the requirements of Table 4
Table 4
| Rolled thickness | Hole depth, not less, for rental, mm | |||
| deep drawing strength groups | normal drawing of strength groups | |||
| K260V, K270V | K310V, K330V, K350V | K260V, K270VA | K310V, K330V, K350V | |
| 0,35 | 7,5 | 7,2 | ||
| 0,4 | 8,0 | 7,5 | 7,4 | 7,4 |
| 0,5 | 8,4 | 8,0 | 8,0 | 7,6 |
| 0,6 | 8,9 | 8,4 | 8,5 | 7,8 |
| 0,7 | 9,2 | 8,6 | 8,9 | 8,0 |
| 0,8 | 9,5 | 8,8 | 9,3 | 8,2 |
| 0,9 | 9,9 | 9,0 | 9,6 | 8,4 |
| 1,0 | 10,1 | 9,2 | 9,9 | 8,6 |
| 1,1 | 10,4 | 10,2 | ||
| 1,2 | 10,6 | 10,4 | ||
| 1,3 | 10,8 | 10,6 | ||
| 1,4 | 11,0 | 10,8 | ||
| 1,5 | 11,2 | 11,0 | ||
| 1,6 | 11,4 | 11,2 | ||
| 1,7 | 11,6 | 11,4 | ||
| 1,8 | 11,7 | 11,5 | ||
| 1,9 | 11,8 | 11,7 | ||
| 2,0 | 11,9 | 11,8 | ||
The surface of cold-rolled steel must be free of films, through breaks, blistering bubbles, rolled bubbles, adhesion-welding spots, cuts, tears, rolled-in scale, over-etched, under-etched, cold-working stripes, rolled-in metal and foreign particles. Layering is not allowed. The same is true for hot-rolled steel. An unetched surface may retain a non-removable layer of scale, allowing surface defects to be identified. Characteristics of the quality of surface finishing are given in Table 5.
Table 5
| Finishing group | Mode of production | Characteristics of surface finishing quality | |
| II | cold rolled | Defects are not allowed on both sides of the rolled product, the depth of which exceeds 1/2 of the sum of the maximum deviations in thickness and taking the rolled product beyond the minimum dimensions in thickness, as well as tarnished color at a distance exceeding 50 mm from the edges. On the front side (the best surface quality) scratches and scratches longer than 50 mm are not allowed. | |
| III | cold rolled | Defects are not allowed on both sides of the rolled product, the depth of which exceeds 1/2 the sum of the maximum deviations in thickness, and which do not take the rolled product beyond the minimum thickness dimensions. | |
| IIIa: tarnish colors are not allowed at a distance of more than 200 mm from the edges | IIIb: tarnish colors are allowed over the entire surface of the rolled product | ||
| hot rolled | Defects are not allowed on both sides of the rolled product, the depth of which exceeds 1/2 the sum of the maximum deviations in thickness, and which take the rolled product beyond the minimum thickness dimensions. | ||
| IV | hot rolled | Defects are not allowed on both sides of the rolled product, the depth of which exceeds the sum of the maximum deviations in thickness and that would take the rolled product beyond the minimum dimensions in thickness. | |
Characteristics of the quality of surface finishing are given in Table 6.
Table 6
| Surface condition | Characteristics of the state of surface finishing | Surface quality characteristics |
| glossy | roughness no more than 0.6 microns | Defects are not allowed on the front side of the rental. Individual risks and scratches longer than 20 mm are also not allowed. |
| matte | roughness 0.8-1.6 microns, roughness density no more than 0.20 mm | Defects are not allowed on the reverse side of rolled products, the depth of which does not exceed 1/4 of the sum of the maximum deviations in thickness |
| rough | roughness more than 1.6 microns | Spots of dirt and tarnished colors are not allowed on both sides of the rolled product. |
Category:
Ferrous rolled metal
Next section:
GOST 19281-89.
Previous section:
GOST 14637-89.
See also information about buy beams and pipes in Chelyabinsk in the product catalog on our website.
Chemical composition
Decoding the designation of steel St3ps sounds like a material with a percentage of carbon not exceeding 0.3%, but despite this, St3ps belongs to the section of semi-mild steels. The name corresponds to GOST 380-2005, the main set of rules of which:
- ST – letters with which the name begins.
- The marking number is indicated by numbers at the beginning.
- If the content of manganese elements exceeds 0.8% of the total mass, the letter G must be present in the name.
- The deoxidation of the alloy is indicated by abbreviations - ps, sp, kp.
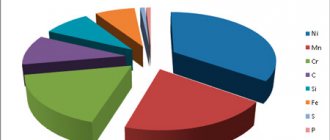
Chemical composition of St3PS steel
And if you are guided by these parameters, it turns out that St3ps is a semi-quiet steel with chemical deoxidation occurring in reaction with a titanium or aluminum alloy, ferrosilicon and ferrosilicon titanium. This is a fairly common type of steel characterized by average characteristics and a low price, standing between a calm and boiling alloy.
The alloy is endowed with so-called ordinary characteristics by inclusions of small particles of other, optional elements.
But besides them, the composition also includes:
| Element | Percentage |
| Iron | 98% |
| Carbon | 0,14-0,22% |
| Manganese | 0,4-0,65% |
| Nickel | No more than 0.3% |
| Chromium | No more than 0.3% |
| Copper | No more than 0.3% |
| Silicon | 0,05-0,15% |
| Arsenic | No more than 0.08% |
| Scandium | No more than 0.05% |
| Phosphorus | No more than 0.04% |
| Nitrogen | No more than 0.008% |
IV. Sampling and sampling, test methods
22. To determine the average chemical composition of the smelting metal, samples are taken as follows. Two samples are taken from under each bucket. Sampling is carried out after half the metal has been poured from the ladle. A second sample is taken in case of repeat testing. The metal for the sample is poured into cast iron conical cups - molds. Recommended cup sizes: cup diameter at the bottom 50 mm, at the top 80 mm, height 120 mm. Cups are not filled approximately 20 mm. Sample weight: at least 2 kg. Filling into cups should be done in an even stream; splashing and splashing of metal is not allowed. Aluminum is added to the sample. After pouring, a tag with the heat number and sample number and with the QC stamp is immersed in each of the cups. The height of the numbers on the tag is 10-12 mm. Samples are released from the cups after the head of the sample has completely darkened. It is recommended to forge the sample on four sides in order to compact the metal. In the case of emergency pouring of the melt, for example, when casting without a stopper when covering the cup with a stopper, samples for chemical analysis are taken from the sprues of two ingots, the middle ones for the casting or the middle siphon.
23. If, for some reason, during steel casting, samples for chemical analysis were not taken or if additional verification of the chemical analysis is required, then samples are taken during the process of cutting the rolled product with scissors or from the finished rolled product, preferably from the middle strip of the average casting ingot. (Typo. Collection of standards “Carbon steel”).
24. Chips for analysis are taken from the sample by gouging the entire cross-sectional surface of the sample or by drilling in the middle part of the sample to a depth of about half its thickness. Selection of chips for analysis is carried out only after complete removal of scale from the surface intended for selection of chips. For control analysis of finished rolled products, chips are selected in one of the following ways: a) by gouging the entire cross-section of the rolled product or a fraction of the cross-section (not less than it); b) by drilling a cross section along the rolling with a uniform distribution of drill bits over the cross section and with the same drilling depth at different points; c) drilling along the center line (along the generatrix) of any face of the profile to a depth of the longitudinal axis.
25. For tensile and bend testing of I-beams, channels and z-beams, flat samples are made, blanks for which are taken along the rolling direction from a vertical stand, closer to the flange, and if this is not possible, from the flange itself. To test angles and tees, flat samples are made, the workpiece for which is taken along the rolling line from one of the flanges, closer to the edge of the flange. Other shaped profiles are tested in their entirety or samples are made from them in accordance with the instructions of the relevant standards or technical specifications. To test strip steel, flat or round samples are made, depending on the thickness of the strips. Blanks for samples are taken along the rolling line, closer to one of the edges of the strip. Round, square and strip steel with dimensions (diameter or width and thickness) within the sample dimensions recommended by GOST 1497-42 are tensile tested without treatment, preserving the outer surfaces of the metal. If the power of the testing machine is insufficient, turning the samples or cutting out part of the profile is allowed. If the standards for individual types and sizes of rolled products do not specify the dimensions of the samples and their location, then their dimensions and the location of the axis of the samples in relation to the axis of the material being tested should be as follows:
Table 4
Dimensions in mm
26. Blanks for making samples from longitudinally rolled sheets (rolled from both ingots and slabs) are cut across the rolling from the middle third of the sheet width from the head of the sheet. From boiling cross-rolled steel sheets (rolled from slabs), blanks for making samples are cut transverse to the rolling direction, anywhere along the width of the sheet. In this case, if the roll is cut into several sheets, then the workpiece is cut between the sheets; if the roll produces one sheet, then the blank is cut from the end of the sheet. From sheets of cross-rolled quiet steel, blanks for making samples are cut transverse to the rolling direction from the end of the sheet, anywhere along the width of the sheet. For sheet thicknesses up to 25 mm inclusive, flat samples are made while preserving the surface layers of the sheet; For larger sheet thicknesses, cylindrical samples are made.
27. To determine impact toughness, samples are taken in such a way that one of the faces of the sample coincides with the surface of the metal, and the axis of the cut is perpendicular to this surface. Impact strength is determined according to GOST 1524-42
.
28. Chemical analysis of steel is carried out according to GOST 2331-43 or another method that provides the necessary accuracy of determination. For arbitration tests, GOST 2331-43 is mandatory.
29. The mechanical properties of steel are determined by tensile testing according to GOST 1497-42.
30. The bend test is carried out according to OST 1683
.