Characteristics of steel grade 30
Steel 30 is a structural carbon quality steel that can be welded with restrictions. Welding is carried out without heating and without subsequent heat treatment, methods: manual arc welding, automatic submerged arc welding and gas protection, CTS, ESW.
Not prone to flake sensitivity, no tendency to temper brittleness. Cutting machinability in the hot-rolled state at HB 143 and δB = 470 MPa, K υ solid. spl=1.5 and Kυ b.st=1.26. Forging is carried out at temperatures from 1280 to 750 0C, with air cooling of workpieces with a cross-section of up to 800 mm. Rods, earrings, traverses, levers, shafts, sprockets, spindles, press cylinders, couplings and other low-strength parts, fasteners for pipelines of thermal power plants, nuclear power plants, steam gas hydroturbines are made from steel 30.
Steel 30: chemical composition and physical characteristics
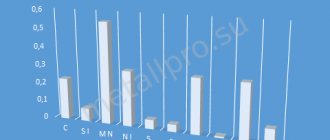
Medium-carbon structural quality alloy grade 30 includes the following chemical elements (percentage):
- Fe – about 97%
- C – 0.27-0.35%
- Mn – 0.5-0.8%
- Si – 0.17-0.37%
- Cr – no more than 0.25%
- Cu – no more than 0.25%
- Ni – no more than 0.25%
- As – no more than 0.08%
- S – no more than 0.04%
- P – no more than 0.035%
With such a set of components, steel belongs to the category of limited weldability, therefore, when using RDS, ESW or ADS, the alloy requires heating, as well as subsequent heat treatment.
The main mechanical and physical characteristics exhibited by grade 30 steel are presented here:
Supply steel 30
Supplied in the form of long products, including shaped steel according to the regulations of GOST 2590-88 Hot-rolled round steel , GOST 2591-88 Hot-rolled square steel , GOST 8239-89 Hot-rolled steel I-beams , GOST 19771-93 Equal-flange bent steel angles, GOST 19772 -93 Bent steel angles, unequal flanges , GOST 8278-83 Bent steel channels, equal flanges , GOST 8281-80 , unequal , GOST 8283-93 steel trough equal flange profiles , GOST 380-94 Carbon steel of ordinary quality , GOST 85 09-93 Steel corners hot-rolled equal flange , GOST 8510-86 rolled steel angles unequal-flanged , GOST 8240-97 Hot-rolled steel channels , GOST 535-88 Rolled bars and shaped carbon steel of ordinary quality , GOST 2879-88 Rolled hot-rolled hexagonal steel, GOST 19903-2015 Hot rolled sheet products , GOST 19904-90 Cold-rolled sheets , GOST 16523-97 Rolled thin sheets of high-quality and ordinary quality carbon steel for general purpose, GOST 503-81 Cold-rolled low-carbon steel strip, GOST 103-76 Hot-rolled steel strip , GOST 82-70 Hot-rolled steel Wide-band universal, GOST 3282-74 Wire Steel low-carbon general purposes , GOST 17305-71 Carbon structural steel wires, GOST 10705-80 steel power steel pipes , GOST 10706-76 Pipes steel eight-dimensional , GOST 3262-75 Pipes steel water and gap-pipes .
| Metal forming. Forgings | GOST 8479-70; |
| Welding and cutting of metals. Soldering, riveting | GOST 10543-98; |
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 2591-2006; GOST 2590-2006; GOST 2879-2006; GOST 9234-74; GOST 11474-76; GOST 1133-71; |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 82-70; GOST 14918-80; GOST 19903-74; GOST 16523-97; GOST 103-2006; |
| Ribbons | GOST 3560-73; |
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 8560-78; GOST 8559-75; GOST 1051-73; GOST 7417-75; GOST 14955-77; GOST 10702-78; GOST 1050-88; |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 4405-75; GOST 4041-71; GOST 1577-93; |
| Ribbons | GOST 2284-79; GOST 10234-77; |
| Steel pipes and connecting parts for them | GOST 24950-81; GOST 20295-85; GOST 3262-75; |
| Low carbon steel wire | GOST 5663-79; GOST 1526-81; GOST 792-67; |
| Medium and high carbon steel wire | GOST 9850-72; GOST 3920-70; GOST 7372-79; GOST 17305-91; GOST 26366-84; GOST 9389-75; |
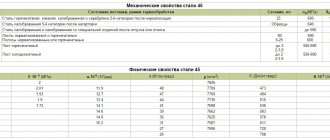
Mechanical properties of rolled steel 30
| GOST | Forging condition | Section, mm | σ0.2 (MPa) | σв(MPa) | δ5 (δ4 ) (%) | ψ % | NV, no more |
| no less | |||||||
| 1050-88 | Hot-rolled, forged, calibrated and silver steel of the 2nd category after normalization | 25 | 290 | 490 | 21 | 50 | — |
| Calibrated steel, category 5: | |||||||
| after cold hardening | |||||||
| after annealing or high tempering | — | — | 560 | 7 | 35 | — | |
| Steel calibrated and calibrated with special finishing: | — | — | 440 | 17 | 45 | — | |
| 10702-78 | after annealing or tempering | ||||||
| after spheroidizing annealing | — | — | Up to 570 | — | 45 | 179 | |
| cold-worked without heat treatment | — | — | Up to 520 | — | 45 | 179 | |
| Annealed or high tempered sheets | — | — | 560 | 7 | 40 | 229 | |
| 1577-93 | Normalized or hot rolled strips | 80 | — | 430 | 24 | — | — |
| 1577-93 | Hot rolled sheet | June 25 | 295 | 490 | 21 | 50 | — |
| 16523-70 (Transverse samples) | Up to 2 | — | 440-590 | -19 | — | — | |
| Cold rolled sheet | 2-3,9 | — | 440-590 440-590 | -20 | — | — | |
| Up to 2 | — | 440-590 | -20 | — | — | ||
| 4041-71(Transverse samples) | Heat-treated sheet of category 1-2 | 2-3,9 | — | 430-590 | -21 | — | — |
| 2284-79 | Cold rolled strip: | Apr.14 | — | 24 | — | 149 | |
| annealed | 400-650 | ||||||
| cold-worked strength class H1 | 0,1-4 | — | 650-850 | (16) | — | — | |
| 10234-77 | Annealed flattened tape | 0,1-4 | — | Up to 600 | — | — | — |
| 0,1-4 | — | 15 | — | — | |||
Steel 30 structural carbon quality
Substitutes
- steel 25
- steel 35
Foreign analogues
| Germany DIN (Euronorm EN) | Japan | USA |
| C30 (1.0528) | S30C | M1031, 1030 |
Decoding
The number 30 means that the average carbon content in steel is 0.30%.
Characteristics and purpose
Steel grade 30 refers to unalloyed special structural high-quality carbon steels and is used in the manufacture of low-strength parts, for example:
- traction
- earrings,
- traverses,
- levers,
- shafts,
- stars,
- spindles,
- press cylinders,
- couplings
Steel grade 30 is also used for the manufacture of:
- slings for swivels,
- hooks and elevators,
- lifting hooks,
- axes,
- traveling blocks and crown blocks,
- clay mixer blades,
- flanges,
- rollers,
- installation rings,
- ground axle boxes of swivels,
- drill drawworks parts
Grade 30 steel is also recommended for the manufacture of certain parts of oil refinery equipment:
- connecting rod bolts,
- valor of steam pump parts,
- piston rods,
- centrifugal pump shafts,
- bolts,
- shut-off elements of valves operating at temperatures up to 300°C in a non-corrosive environment,
- heat exchanger grids with a floating head, designed to work with non-corrosive oil and its products,
- fasteners operating at 375°C
In a normalized state, grade 30 steel is used for the manufacture of parts that experience relatively low stress (swivel bearings, hooks, flanges, mounting rings, etc.), and after hardening and high tempering it is used for the manufacture of parts such as rollers, axles, traverses and forks of drilling drawworks, shafts of centrifugal pumps, etc.
The change in the mechanical properties of grade 30 steel depending on the tempering temperature is shown in the figure below.
Chemical composition, % (GOST 1050-88)
| C | Si | Mn | Cr | S | R | Cu | Ni | As |
| no more | ||||||||
| 0,27-0,35 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,50-0,80 | 0,25 | 0,04 | 0,035 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,08 |
Chemical composition, % (GOST 1050-2013)
| steel grade | Mass fraction of elements, % | |||||||
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Cu | |
| no more | ||||||||
| 30 | 0,27-0,35 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,50-0,80 | 0,030 | 0,035 | 0,25 | 0,30 | 0,30 |
Temperature of critical points, °C
| Ac1 | Ac3 | Ar3 | Ar1 | Mn3 |
| 730 | 820 | 796 | 680 | 380 |
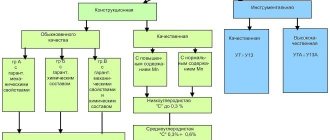
Heat treatment
Steel grade 30 is subjected to normalization at a temperature of 880-900°C.
Quenching is carried out in water at a temperature of 860-880°C and tempering at 550-600°C.
Use of steel 30 for fasteners (GOST 32569-2013)
| steel grade | Technical requirements | Acceptable operating parameters | Purpose | |
| Wall temperature, °C | Medium pressure, MPa (kgf/cm2), no more | |||
| 30 GOST 1050, GOST 10702 | STP 26.260.2043 | -40 to +425 | 10(100) | Studs, bolts |
| 16(160) | Nuts | |||
| -40 to +450 | Washers | |||
Use of steel 30 (GOST 1050) for oxygen fittings (according to GOST 12.2.052)
| Oxygen pressure, MPa (kgf/cm2), no more | In instrumentation shutdown fittings (DN ≤ 6) | ||||||||
| in shut-off valves | in control valves | ||||||||
| when managing | |||||||||
| local | remote | local | remote | ||||||
| frame | shutter parts | frame | shutter parts | frame | shutter parts | frame | shutter parts | frame | valve parts, spindle with locking cone ≥60° |
| 1,6 (16) | 0,6 (6) | 1,6 (16) | |||||||
NOTE. Fittings made of carbon steels and cast irons coated with organosilicate materials are equivalent to fittings made of stainless steels.
Hardness HB (Brinell) (GOST 1050-2013)
| steel grade | Hardness HB, no more, for metal products | |||
| hot rolled and forged | calibrated and with special surface finishing | |||
| without heat treatment | after annealing or high tempering | hard-worked | after annealing or high tempering | |
| 30 | 179 | — | 229 | 79 |
NOTE. The sign “-” means that hardness is not standardized or controlled
Mechanical properties of metal products (GOST 1050-2013)
| Mechanical properties, no less | |||
| Yield strength σ0.2, N/mm2 | Tensile strength σв, N/mm2 | Relative elongation δ5, % | Relative narrowing ψ, % |
| 295 | 490 | 21 | 50 |
Standardized mechanical properties of metal products calibrated in a cold-worked or heat-treated state
| steel grade | Mechanical properties, no less, for metal products | |||||
| hard-worked | annealed or highly tempered | |||||
| Tensile strength σв, N/mm2 | Relative elongation δ5, % | Relative narrowing ψ, % | Tensile strength σв, N/mm2 | Relative elongation δ5, % | Relative narrowing ψ, % | |
| 30 | 560 | 7 | 35 | 440 | 17 | 45 |
Mechanical properties of metal products made from steel 35 depending on size (GOST 105-2013)
| Mechanical properties of metal products size | |||
| Yield strength σ0.2, MPa not less | Tensile strength σв, MPa | Relative elongation δ5, % | Impact work KU, J |
| no less | |||
| up to 16 mm incl. | |||
| 400 | 600-750 | 18 | 30 |
| St. 16 to 40 mm incl. | |||
| 355 | 550-700 | 20 | 30 |
| St. 40 to 100 mm incl. | |||
| 295 | 500-650 | 21 | 30 |
NOTE.
- The mechanical properties of metal products made from grade 30 steel apply to metal products up to 63 mm in size inclusive.
- The values of mechanical properties are given for metal products with a round cross-section. For rectangular sections, the ranges of equivalent diameters are in accordance with Appendix B (GOST 1050-2013).
Mechanical properties of rolled products
| GOST | Delivery status | Section, mm | Yield strength σ0.2, MPa | Tensile strength σв, MPa | Relative elongation δ5, % | Relative narrowing ψ, % | Hardness HB, no more |
| no less | |||||||
| GOST 1050-88 | Hot-rolled, forged, calibrated and silver steel of the 2nd category after normalization | 25 | 290 | 490 | 21 | 50 | — |
| Calibrated steel, category 5: | |||||||
| after cold hardening | — | — | 560 | 7 | 35 | — | |
| after annealing or high tempering | — | — | 440 | 17 | 45 | — | |
| GOST 10702-78 | Steel calibrated and calibrated with special finishing | ||||||
| after annealing or tempering | — | — | Up to 570 | — | 45 | 179 | |
| after spheroidizing annealing | — | — | Up to 520 | — | 45 | 179 | |
| cold-worked without heat treatment | — | — | 560 | 7 | 40 | 229 | |
| GOST 1577-93 | Annealed or high tempered sheet | 80 | 430 | 24 | — | — | |
| GOST 1577-93 | Normalized or hot rolled strip | 6-25 | 233 | 490 | 21 | 50 | — |
| GOST 16523-89 (transverse samples) | Hot rolled sheet | Up to 2 | — | 440-590 | (19) | — | — |
| 2-3,9 | — | 440-590 | (20) | — | — | ||
| Cold rolled sheet | Up to 2 | — | 440-590 | (20) | — | — | |
| 2-3,9 | — | 440-590 | (21) | — | — | ||
| GOST 16523-89 (transverse category samples) | Heat-treated sheet 1 and 2 | 4-14 | — | 430-590 | 24 | — | 149 |
| GOST 2284-79 | Cold rolled strip: | ||||||
| annealed, | 0,1-4 | — | 400-650 | (16) | — | — | |
| cold-worked, strength class H1 | 0,1-4 | — | 650-850 | — | — | — | |
| GOST 10234-77 | Annealed flattened strip | 0,1-4 | — | Up to 600 | 15 | — | — |
Mechanical properties of forgings after normalization (GOST 8479-70)
| Section, mm | KP | Yield strength σ0.2, MPa | Tensile strength σв, MPa | Relative elongation δ5, % | Relative narrowing ψ, % | KCU, J/cm2 | Hardness NV, no more |
| no less | |||||||
| 300-500 | 175 | 175 | 350 | 22 | 45 | 54 | 101-143 |
| 500-800 | 20 | 40 | 49 | ||||
| 100-300 | 195 | 195 | 390 | 23 | 50 | 54 | 111-156 |
| 300-500 | 20 | 45 | 49 | ||||
| 500-800 | 18 | 38 | 44 | ||||
| 100-300 | 215 | 215 | 430 | 20 | 48 | 49 | 123-167 |
| 300-500 | 18 | 40 | 44 | ||||
| 500-800 | 16 | 35 | 39 | ||||
| Up to 100 | 245 | 245 | 470 | 22 | 48 | 49 | 143-179 |
| 100-300 | 19 | 42 | 39 | ||||
| 300-500 | 17 | 35 | 34 | ||||
Mechanical properties depending on tempering temperature
| ttp, °С | Yield strength σ0.2, MPa | Tensile strength σв, MPa | Relative elongation δ5, % | Relative narrowing ψ, % | KCU, J/cm2 | Hardness HB |
| 400 | 420-490 | 560-680 | 16-24 | 53-64 | 90-190 | 153-189 |
| 500 | 390-440 | 540-630 | 18-27 | 61-68 | 120-210 | 150-175 |
| 600 | 350-390 | 490-570 | 21-28 | 66-72 | 150-230 | 138-158 |
NOTE. Rental Quenching at 860 °C in water; samples with a diameter of 60 mm.
Endurance limit
| Heat treatment | σ-1, MPa |
| Hardening at 830 °C in oil; tempering at 640 °C, σв = 530 MPa | 255 |
| Normalization at 875 °C, cool. in air, σв = 495 MPa | 206 |
NOTE. σ4001/100000 = 108 MPa, σ4251/100000 = 81 MPa, σ4501/100000 = 54 MPa, σ5001/100000 = 22 MPa.
Mechanical properties at elevated temperatures
| tsp, °С, | Yield strength σ0.2, MPa | Tensile strength σв, MPa | Relative elongation δ5, % | Relative narrowing ψ, % | KCU, J/cm2 |
| 20 | 320 | 530 | 25 | 52 | 62 |
| 300 | 205 | 580 | 21 | 51 | 70 |
| 500 | 145 | 350 | 24 | 70 | 43 |
| 600 | 78 | 195 | 35 | 83 | 74 |
| 800 | — | 98 | 49 | 98 | — |
| 900 | — | 77 | 53 | 100 | — |
| 1000 | — | 48 | 56 | 100 | — |
| 1100 | — | 30 | 58 | 100 | — |
| 1200 | — | 21 | 64 | 100 | — |
Impact strength KCU (GOST 105-2013)
| steel grade | Impact strength KCU, J/cm2, not less |
| 30 | 78 |
Impact strength KCU
| Heat treatment | KCU, J/cm2, at temperature, °C | ||
| +20 | -40 | -60 | |
| Quenching at 860 °C in water; tempering at 400 °C | 72 | 45 | 42 |
NOTE. Blank with a diameter of 60 mm.
Technological properties
Forging temperature, °C: start 1280, end 750. Workpieces with a cross-section of up to 800 mm are cooled in air.
Weldability - limited weldability. Welding methods: RDS, ADS under submerged arc and gas shield, ESW. Preheating and subsequent heat treatment are recommended. CTS without restrictions.
Cutting machinability - Kv b.st = 1.7 in the hot-rolled state at HB 143 and σw = 460 MPa.
Flock sensitivity - not sensitive.
Tendency to temper brittleness - not prone.
Hardenability, mm
| Hardness HRCe at a distance from the end, mm (hardening from 900 °C) | ||||
| 1,5 | 3 | 4,6 | 6 | 7,5 |
| 45,5 | 42,5 | 35 | 24 | 20,5 |
Critical diameter d
| Heat treatment | Amount of martensite, % | d, mm, after hardening | |
| in water | In oil | ||
| Hardening | 50 | 18 | 9 |
Type of delivery
- Long products, including shaped steel: GOST 1050-88, GOST 2590-88, GOST 2591-88, GOST 2879-88, GOST 8509-93, GOST 8510-86, GOST 8240-89, GOST 8239-89.
- Calibrated rod GOST 7417-75, GOST 8559-79, GOST 8560-78, GOST 10702-78.
- Polished rod and silver steel GOST 14955-77, GOST 10702-78.
- Thick sheet GOST 1577-93, GOST 19903-74.
- Thin sheet GOST 16523-89.
- Tape GOST 6009-74, GOST 2284-79, GOST 10234-77.
- Strip GOST 103-76, GOST 82-70, GOST 1577-93.
- Wire GOST 5663-79, GOST 17305-91.
- Forgings and forged blanks GOST 1133-71, GOST 8479-70.
Density ρп kg/cm3 at test temperature, °С
| Steel | 20 °C |
| 30 | 7850 |
Linear expansion coefficient α*106, K-1
| steel grade | α*106, K-1 at test temperature, °C | ||||||
| 20-100 | 20-200 | 20-300 | 20-400 | 20-500 | 20-600 | 20-700 | |
| 30 | 12,1 | 12,9 | 13,6 | 14,2 | 14,7 | 15,0 | 15,2 |
Thermal conductivity coefficient λ W/(m*K)
| Steel grade | λ W/(m*K), at test temperature, °C | |||||||
| 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | |
| 30 | 52 | 51 | 49 | 46 | 43 | 39 | 36 | 32 |
Young's modulus (normal elasticity) E, GPa
| Steel grade | At test temperature, °C | ||||||
| 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | |
| 30 | 200 | 196 | 191 | 185 | — | — | 164 |
Modulus of elasticity in torsional shear G, GPa
| steel grade | At test temperature, °C | ||||||
| 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | |
| 30 | 78 | 77 | 76 | 73 | 69 | 66 | 59 |
Specific heat capacity c, J/(kg*K)
| steel grade | s, J/(kg*K), at test temperature, °C | ||||
| 20-100 | 20-200 | 20-300 | 20-400 | 20-500 | |
| 30 | 470 | 483 | 546 | 563 | 764 |
Find out more
Steel grade 20: explanation, characteristics, chemical...
Steel 6ХВГ tool stamping…
Steel 5ХНМ tool stamping…
Steel 45X structural alloy…
Mechanical properties of forgings steel 30
| Heat treatment, delivery condition | Section, mm | σ0.2, MPa | σB, MPa | δ5, % | ψ, % | KCU, J/m2 | HB |
| Normalization | |||||||
| KP 175 | 300-500 | 175 | 350 | 22 | 45 | 54 | 101-143 |
| KP 175 | 500-800 | 175 | 350 | 20 | 40 | 49 | 101-143 |
| KP 195 | 100-300 | 195 | 390 | 23 | 50 | 54 | 111-156 |
| KP 195 | 300-500 | 195 | 390 | 20 | 45 | 49 | 111-156 |
| KP 195 | 500-800 | 195 | 390 | 18 | 38 | 44 | 111-156 |
| KP 215 | 100-300 | 215 | 430 | 20 | 48 | 49 | 123-167 |
| KP 215 | 300-500 | 215 | 430 | 18 | 40 | 44 | 123-167 |
| KP 215 | 500-800 | 215 | 430 | 16 | 35 | 39 | 123-167 |
| KP 245 | <100 | 245 | 470 | 22 | 48 | 49 | 143-179 |
| KP 245 | 100-300 | 245 | 470 | 19 | 42 | 39 | 143-179 |
| KP 245 | 300-500 | 245 | 470 | 17 | 35 | 34 | 143-179 |
Steel 30 – impact strength, J/cm2
| Assortment | Dimensions – thickness, diameter, mm | Heat treatment modes | T, 0C | KCU at temperatures | ||
| -600С | -400С | +200С | ||||
| Blanks | 60 | Quenching (water) | 860 | |||
| Vacation | 400 | 42 | 45 | 72 | ||
Mechanical properties of steel 30 at elevated temperatures
| Test temperature, °C | Steel condition, test conditions | σ0.2 (MPa) | σв(MPa) | δ5 (%) | ψ % | KCU (J/cm2) |
| 20 | Delivery status | 320 | 530 | 25 | 52 | 62 |
| 300 | Sample 5 mm in diameter, 25 mm long, deformed. Deformation speed 10 mm/min. Strain rate 0.007 1/s | 205 | 580 | 21 | 51 | 70 |
| 500 | 145 | 350 | 24 | 70 | 43 | |
| 600 | 78 | 195 | 35 | 83 | 74 | |
| 800 | — | 98 | 49 | 98 | — | |
| 900 | — | 77 | 53 | 100 | — | |
| 1000 | — | 48 | 56 | 100 | — | |
| 1100 | — | 30 | 58 | 100 | — | |
| 1200 | — | 21 | 64 | 100 | — |
Mechanical properties of steel 30 at normal temperature
| Type of delivery | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Heat treatment |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| Heat treated sheet, GOST 4041-71 | Apr.14 | 430-590 | 24 | |||||
| Rolled products, GOST 1050-88 | up to 80 | 490 | 295 | 21 | 50 | Normalization | ||
| Rolled products cold-hardened, GOST 1050-88 | 560 | 7 | 35 | |||||
| Rolled products annealed, GOST 1050-88 | 440 | 17 | 45 | |||||
| Annealed tape, GOST 2284-79 | 390-640 | 16 | ||||||
| Cold-worked tape, GOST 2284-79 | 640-930 |
Physical properties of steel 30
| Temperature | E 10- 5 | a 10 6 | l | r | C | R 10 9 |
| 0C | MPa | 1/Grad | W/(m deg) | kg/m3 | J/(kg deg) | Ohm m |
| 20 | 2 | 52 | 7850 | |||
| 100 | 1.96 | 12.1 | 51 | 470 | ||
| 200 | 1.91 | 12.9 | 49 | 483 | ||
| 300 | 1.85 | 13.6 | 46 | 546 | ||
| 400 | 14.2 | 43 | 563 | |||
| 500 | 14.7 | 39 | 764 | |||
| 600 | 1.64 | 15 | 36 | |||
| 700 | 15.2 | 32 |
Calculated properties: steel density is 7850 kg/m3
Description 30ХГСА
Steel 30xgsa belongs to the class of alloy structural steel. It was created for the needs of aviation, but thanks to its excellent characteristics it quickly became a popular material in mechanical engineering. 30xgsa steel is often called “chromansil”. The alloy received this name due to the alloying elements it contains (chrome, manganese and silicon), the Latin names of which in abbreviation form the word “chromansil”.
The marking of 30xgsa steel includes a number in the first place and showing the percentage of carbon content expressed in hundredths. In this case, it is 3%, that is, it corresponds to the norm for the class of medium-alloy steels (up to 2.5% - low-alloy, from 2.5 to 10% - medium-alloy, from 10% - high-alloy). The letters “X”, “G” and “C” indicate the content of alloying elements in the steel - chromium, manganese and silicon. Since there are no numbers after the letter designations of alloying elements, their percentage is approximately 1%. The letter “A” at the end of the marking indicates that 30xgsa steel belongs to the category of high-quality steels.
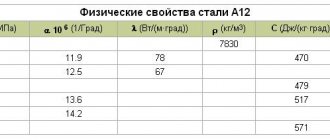
Foreign analogues steel 30
| USA | 1030, G10300, M1031 |
| Germany | 1.0528, C30, C30E, Ck30 |
| Japan | S28C, S30C, S33C, SWRCH30K, SWRCH33K |
| France | C30E, FR32, XC32 |
| England | 080M32 |
| European Union | 1.1178, C30, C30E |
| Italy | C30, C30E, C30R |
| China | 30,ML25Mn,ML30 |
| Bulgaria | 30 |
| Poland | 30, 30A, 30rs |
| Romania | OLC30 |
| Czech | 12031 |
- Structural steel
- Tool steel
Application
Steel 30KhGSA, the use of which is related to the chemical composition and basic qualities, is found in various industries. Most often, alloy steel is used in the following cases:
- In the construction field, fasteners that are used under variable loads have become widespread. Low corrosion resistance determines that fastening materials can only be used to protect the device.
- In the aircraft industry, the alloy is used as a consumable material in the manufacture of shafts, flanges and other parts. It is worth considering that the alloy is not used to create critical elements.
- In the mechanical engineering field it is used to create elements that operate under constant or variable loads.
The cost of the raw materials used largely depends on what kind of scrap was used. There are foreign analogues on sale, for example, 14331 (Czech Republic) and 30ChGSA (Bulgaria). Their chemical composition and basic qualities are largely similar.