Mild steel grades
Full deoxidation alloys are divided into the following groups:
- mild carbon steels of ordinary quality - regulated by GOST 380-2005, designated “sp”;
- high-quality and high-quality - produced in accordance with GOST 1050-88, they do not have a letter index according to this standard;
- All alloy and low-alloy steels are usually made calm and do not have a letter index.
Attention! Steels produced by continuous casting are completely deoxidized during the process.
Structure of a low-deoxidation metal ingot
The main feature of a boiling steel ingot is the absence of a concentrated shrinkage cavity. The structure of the ingot depends on the intensity and boiling period of the melt. In the hardened state it has 5 zones:
- outer dense crust;
- accumulation of honeycomb bubbles having an elongated shape;
- intermediate zone between cellular and secondary bubbles;
- accumulation of deep (secondary) air bubbles;
- the core of the ingot is the zone of deep bubbles.
In high-quality ingots, the outer crust is so dense and thick that when heated and rolling, the accumulation of honeycomb bubbles does not open.
“Clogged” – a type of boiling steel
In terms of the degree of suppression of gas evolution during melt solidification, the material is between boiling and semi-calm steels. The difference between this technology is the closing of the ingot from above after casting by mechanical or chemical means.
- In mechanical capping, the ingot is closed with a heavy cast iron lid.
- Chemical plugging is achieved by adding aluminum or ferrosilicon additives to the top of the mold. This leads to accelerated hardening of the upper part of the ingot, which is cut off and sent to waste.
This technique allows you to reduce the time of gas release and reduce the number of air bubbles inside the ingot.
From the production of long products to the production of nuts
Steel that is completely deoxidized during the production process has lower composition heterogeneity. Semi-quiet type material is cheaper. High-quality rolled products are produced from steel: hexagons, angles, strips, circles, sheets, etc. These are popular types of products used in construction, mechanical engineering, machine tool building, furniture manufacturing, etc.
Semi-quiet steel is used in the production of billets for rolled pipes. Due to its high strength, the material is used to produce load-bearing welded structures that can withstand significant intense loads. Another area of application is the production of fasteners.
When choosing steel, you need to focus on its operating conditions, including temperature conditions and the level of load applied. Buy the material from a large supplier who will offer a wide selection of steel grades and help you make your choice.
Which ordinary quality steel is classified as semi-quiet - Metalworker's Handbook
Carbon steels of ordinary quality have long been a product of mass production, which has made their cost affordable.
According to GOST 380-2005, their composition, in addition to iron and carbon, may include a certain amount of non-metallic inclusions, as well as impurities that worsen the quality characteristics of such steels. Thick plates are produced, as a rule, from structural carbon steel of ordinary quality
Requirements GOST 380-2005
You can familiarize yourself with the GOST requirements for carbon steels of ordinary quality by downloading the document in pdf format from the link below. GOST 380-2005 Carbon steel of ordinary quality. Stamps Download
GOST 380-2005 specifies all the requirements for the characteristics that carbon structural steels of ordinary quality must have. Such steels are used primarily for the production of:
- hardware products;
- products obtained by stamping and forging;
- metal in sheets of various thicknesses;
- long products;
- blanks obtained by casting and rolling;
- broadband rental;
- shaped rolled products;
- metal tapes and wires of various diameters;
- products obtained after metal processing on rolling crimping equipment (slabs, blooms, etc.);
- metal ingots.
Rolled sheets are divided into categories according to standardized characteristics
In accordance with the provisions of the above GOST, the production of carbon steels of ordinary quality occurs in various deoxidation options, according to which they are divided into boiling, semi-calm, and calm. The designations of all grades of such steel alloys begin with the letters “St”, followed by the remaining marking elements.
Immediately after the letters indicating the category of steel, its markings contain numbers by which the grade number can be determined.
You can find out what type of carbon steel of ordinary quality belongs to in terms of degree of deoxidation by the letters “kp”, “ps” and “sp”. In the designation of some brands you can see the letter “G”.
This means that in the composition of this steel, an element such as manganese is present in an amount not exceeding 0.8%.
Areas of application of carbon steels of ordinary quality
Valid elements
The regulatory document (GOST) also regulates the chemical composition of carbon steels of ordinary quality. such an element as silicon in steels with different degrees of deoxidation can vary within the following limits:
- boiling – up to 0.05%;
- semi-quiet (St1ps, St2ps, St3ps, etc.) – 0.05–0.15%;
- calm – 0.15–0.3%.
Alloys of ordinary quality grade St0 should not contain silicon, like manganese. Such an important element as carbon can be contained in carbon steels of different grades in the following quantities:
- St0 – up to 0.23%;
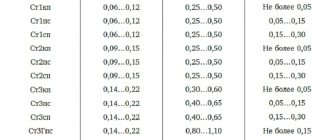
- St1 – 0.06–0.12%;
- St2 – 0.09–0.15%;
- St3 – 0.14–0.22%;
- St4 – 0.18–0.27%;
- St5 – 0.28–0.37%;
- St6 – 0.38–0.49%.
manganese in carbon steels of ordinary quality is regulated by the standard within the following limits:
- St1 and St2 – 0.25–0.5%;
- calm and semi-quiet alloys of grade St3 – 0.4–0.65%;
- boiling steel grade St3 – 0.3–0.6%; St4 – 0.4–0.7%;
- StGsp and St3Gps – 0.8–1.1%;
- semi-quiet, as well as calm alloys St5 and St6 - 0.5–0.8%;
- St5Gps – 0.8–1.2%.
GOST also regulates the content of such an element as nitrogen in carbon steels of ordinary quality. Its quantity may vary within the following limits:
- in steels produced by smelting in converter and open-hearth furnaces - up to 0.01%;
- in alloys that are smelted in electric furnaces - up to 0.012%.
Carbon steel grade St5sp is used for the manufacture of parts operating at temperatures up to 420 degrees: rivets, nuts, bolts, rods. asterisks, etc.
https://www..com/watch?v=Oy3KOx_32Lw
The remaining elements, including harmful impurities, may be contained in carbon steel alloys of ordinary quality in the following quantities:
- phosphorus (except St0) – up to 0.04%;
- sulfur – no more than 0.05%, and in steel grade St0 – 0.06–0.07%;
- chromium, nickel, copper - up to 0.3% (in steel grade St0, the quantitative content of these elements is not standardized).
Other features of the chemical composition
For the St5Gps brand, the carbon content is strictly specified, the amount of which should be in the range of 0.22–0.3%.
In carbon steels of ordinary quality, grades 2, 3 and 4, which are classified as boiling steel and intended for the production of long and shaped steel, the silicon content can be up to 0.07%.
For steel alloys of grade St3, which are classified as calm, semi-quiet and boiling, the minimum carbon content is not standardized. It is important that their mechanical characteristics meet all GOST requirements.
https://www..com/watch?v=gWRIXjiIlGo
If sheet metal with a sheet thickness of up to 10 mm is produced from carbon steels of ordinary quality St3, St4 and St5, corresponding to any degree of deoxidation, then, in accordance with the provisions of the regulatory document, a reduction in the amount of manganese in their chemical composition is allowed by 0.1%.
Advantages of mild steel
Due to the homogeneity and fine-grained structure, deoxidized steels have the following advantages:
- good resistance to dynamic impacts and brittle fracture, due to which they are used in the manufacture of critical structures for which static and dynamic impacts are planned;
- steel, for the deoxidation of which aluminum additives were used, is not subject to aging, which implies a change in the properties of the material without a noticeable change in the microstructure. Plasticity, resistance to brittle fracture, and the threshold of cold brittleness are reduced, and strength is slightly increased;
- uniform distribution of sulfur and phosphorus;
- good weldability.
Application areas of boiling steel
These metal products have certain restrictions on areas of use. It is not allowed for the manufacture of:
- fastening elements for boilers operating under pressure;
- structures and equipment planned for operation at temperatures below -20°C
- devices operated under dynamic, alternating, pulsating loads;
- equipment and structures in contact with aggressive, explosive and fire hazardous environments, compressed and liquefied gases.
Boiling steel ingots are used to produce strips, sheets, thin slabs, wire, rods, strips, and pipes intended for the manufacture of ordinary products.
What types and grades of carbon steel exist?
The technical characteristics of steels directly depend on the quantity and quality of their constituent elements (carbon). The more it is, the harder the alloy and the higher its fragility. Carbon steels of various grades are characterized by a low content of alloying components. Typically, each of them does not exceed 1.5% and has a minor effect on the technical characteristics of the alloy.
Carbon steels are produced in the form of rolled products and shaped castings. They are widely used in all sectors of industry, construction, and everyday life. Metallurgical enterprises transfer slabs and blooms for further processing into sheets, rolled profiles, and pipes of various diameters.
Carbon steel
What are carbon steels?
Carbon steels are an iron alloy with a carbon content of up to 0.6%. The amount of sulfur and phosphorus depends on the quality of the metal. Alloying elements are present in small quantities. Qualitative characteristics depend on the amount of carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, manganese and silicon.
- hardness;
- weldability;
- strength;
- viscosity;
- elasticity.
The more carbon, the higher the hardness, brittleness and worse weldability.
General characteristics
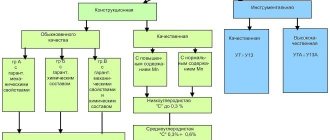
Carbon steel is divided into 3 groups according to the requirements for chemical composition and mechanical properties. Letter designation. The defining factors for the group are:
- A - mechanical properties;
- B - chemical composition;
- B - the chemical composition and basic mechanical properties are strictly maintained.
Group B alloys are chemically tested, and a sample is taken from the ladle during a spill to check mechanical properties - tensile and flexural strength, impact strength. Hardness is controlled by heat treatment.
Composition of chemical elements
The main element is iron. The relationship to the group is determined by the amount of carbon. non-metallic inclusions of phosphorus and sulfur impair mechanical properties. They contribute to red brittleness and cold brittleness, the formation of cracks in hot and cold metal.
Corrosion resistance is ensured by low carbon content and the addition of chromium. The amount of chemical elements in carbon steel, manganese and silicon, depends on the deoxidation method and quality class. Manganese can be present within 1.2% in normal quality alloys, up to 1.8% in high quality alloys. silicon does not exceed 0.3%.
High-quality steels of group B are checked for their properties and chemical composition. The permissible amount of non-metallic inclusions is 0.03–0.0018%.
The amount of carbon determines the hardness of steel, its ability to harden and weld.
The lower the carbon index, the better the metal is welded. St 40X requires heating before welding, St 6 requires heating to 700⁰ and post-welding tempering. Hardenability is the opposite. Up to St4 alloys do not heat up and do not change their hardness. 40x steel can crack when exposed to sudden cooling in water.
Heating steel
Classification by degree of deoxidation
According to the degree of deoxidation, carbon alloys are divided into the following types:
- boiling;
- calm;
- semi-calm.
Boiling alloys of ordinary quality are released from the furnace immediately after adding the deoxidizer. In some cases, deoxidation is carried out in a ladle. As a result, many air bubbles form under the crust.
For tool alloys, the deoxidation reaction begins before the spill and ends completely when poured into the ladle.
Boiling steels are used for the production of ingots, slabs and blooms - large-section rolled products. Subsequently, they are melted down into high-quality metal in electric furnaces or converted into rolled products of a smaller diameter - round, square. During processing, air escapes and the grain is pulled lengthwise, increasing the mechanical properties of the steel. Semi-quiet steels are characterized by increased malleability.
Production methods and quality differences
According to production methods, alloys are divided into three types:
- open hearth;
- convector;
- in electric furnaces.
The production method and quality division are indicated in the metal certificate and can be indicated letter-wise at the end of the marking. For example, VD is electric arc remelting, Sh is slag remelting.
Open hearth furnaces with the lowest quality are used for reworking and rolling of group A. Electric furnaces produce an alloy of high and very high quality.
Application area
Carbon steel is used to make welded building structures, water and gas pipes, parts of machine tools and automobiles, rolled round and other sections for the manufacture of various objects, fences, and gratings.
Marking features
The marking of carbon steels has an alphanumeric meaning and is indicated at the end of the rolled product by a certain color. St at the beginning means normal quality. Then comes a number indicating the amount of carbon and the method of deoxidation.
For a material with increased quality, the designation begins with the word Steel, then carbon in hundredths and the letter designation of alloying elements.
High-quality ones are designated at the end with the letter A. Special, high-carbon, instrumental - U, high-speed - R.
Marked carbon steel
How to decipher steel markings
The grade of carbon steel and its quality group can be determined by the type of marking. Each number and letter has its own meaning and shows quality requirements, the degree of deoxidation, and the presence of alloying elements.