Steel grade 45: GOST standards
GOST standards for rental of structural carbon quality steel 45:
- GOST 19903-74, 1577-93 – thick sheet
- GOST 16523-97 – thin sheet
- GOST 8733-74, 8731-74, 8734-75, 21729-76, 8732-78 – pipe
- GOST 2284-79 – tape
- GOST 5663-79, 17305-91 – wire
- GOST 7417-75, 8559-75, 8560-78, 1050-88 – calibrated rod
- GOST 14955-77 – ground rod and silver
- GOST 82-70, 1577-93, 103-2006 – strip
- GOST 8479-70, 1133-71 – forged blanks
Main characteristics of steel 45
Any alloy has its own distinctive characteristics, a certain chemical composition, a number of substitutes, and a functional purpose.
Grades 40, 45, 50 are distinguished by their high strength levels, while having low viscosity and ductility. Since the mechanical properties of grade and 45 are identical to grades 40 and 50, these steels are interchangeable.
Chemical composition and properties
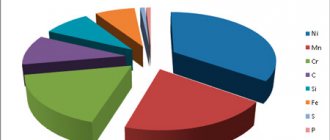
The chemical components of the alloy, in addition to iron and carbon, are a number of other elements, the amount of which is insignificant. The percentage of chemical components of steel 45:
- Iron (Fe) - about 97%.
- Carbon (C) - 0.42-0.5%.
- Manganese (Mn) - 0.5-0.8%.
- Silicon (Si) - 0.17-0.37%.
- Nickel (Ni) - no more than 0.25%.
- Chromium (Cr) - no more than 0.25%.
- Copper (Cu) - no more than 0.25%.
- Arsenic (As) - no more than 0.08%.
- Sulfur (S) - no more than 0.04%.
- Phosphorus (P) - no more than 0.035%.
Its chemical properties directly depend on the chemical composition of steel and its structure. All elements included in the composition are conventionally divided into useful and harmful. The process of adding useful impurities is called doping. If you decipher the 45x marking, it becomes clear that the alloy contains the addition of chromium, 45 g of manganese.
Basic chemical properties of the material:
- oxidation state:
- corrosion resistance;
- heat resistance;
- heat resistance.
Mechanical characteristics
To analyze and control the properties of steel, various methods for determining them are used. For example, the criteria for strength and ductility are determined experimentally, and the samples are stretched until they break. The hardness of alloys is determined by measuring the resistance of the material when a hard element, for example, a diamond tip, is applied to its surface. Viscosity - impact tests of special samples.
Read also: Which metal is aluminum copper or steel
Mechanical properties and characteristics of steel 45 (at t=20C).
Strength is the ability of an alloy to withstand external loads without being damaged internally. It is characterized by the following values: tensile strength, sв [MPa] and yield strength of steel 45, sT [MPa].
- pipe - GOST 8731–87, sв =588 MPa, sT =323 MPa;
- rolled products - GOST 1050–88, sв=600 MPa, sT =355 MPa;
- annealed rolled steel - GOST 1050–88, sв =540 MPa.
Hardness is the ability of an alloy to resist when exposed to solid bodies. It is characterized by the following values: hardness according to N.V. Brinell 10-1 [MPa], according to Rockwell HRC [MPa]. For grade 45 as delivered:
- pipe - GOST 8731–87, HB 10–1 = 207 MPa;
- rolled products - GOST 1050–88, HB 10–1 = 229 MPa;
- annealed rolled steel - GOST 1050–88, HB 10–1 = 207 MPa.
Plasticity is the ability of an alloy to change its shape under the influence of a load and restore it after the end of the impact. Characterized by the value, relative elongation at break, δ5 [%]:
- pipe - GOST 8731–87, δ5 =14%;
- rolled products - GOST 1050–88, δ5 =16%;
- annealed rolled stock - GOST 1050–88 - δ5 =13%.
Impact strength is the ability of a material to resist the dynamic effects of load, KCU [kJ/m2].
Physical properties
The physical characteristics of steel include: density, coefficient of thermal expansion, thermal conductivity, modulus of elasticity, specific heat and electrical conductivity.
Metal alloys have high density, heat capacity and electrical conductivity. Let's consider the physical properties of grade 45 (at t=20C).
Density or specific gravity is the mass of a substance per unit volume, the density of steel is 45 GOST 1050–88 ρ=7826–7595 kg/m3.
The coefficient of linear thermal expansion is quantitatively equal to the relative change in the linear dimensions of a substance with an increase (decrease) in temperature in the alloy by 1 degree Celsius, α (1/deg).
Thermal conductivity of a substance is the ability to transfer an amount of heat from a more heated area to a less heated one. It is characterized by the value of the thermal conductivity coefficient, λ [W/(m deg)].
Young's modulus is a physical quantity that indirectly reflects the ability of steel to resist longitudinal deformations (tension or compression). This value indicates the rigidity of the material and is an important physical feature, E 10-5 = 2 MPa;
Read also: Make a part using powder metallurgy
Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat required to heat 1 kilogram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius, Ϲ [J/(kg deg).
Electrical conductivity is the ability of a material to be a conductor of electric current. It is characterized by the value of electrical resistivity, Ṛ [Ohm m].
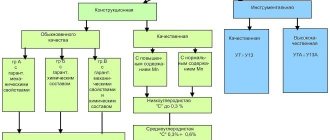
Technological characteristics of using steel 45
The technological characteristics of steel indicate the suitability of the alloy for various processing methods. The material has the following technological characteristics:
- Temperature of the forging process, degrees - 1250 at the beginning, 700 at the end. Cooling of sections up to 400 mm is carried out under normal environmental conditions.
- Weldability - difficult to weld. Types of welding: RDS and KTS, using heating and subsequent heat treatment.
- Conditions for cutting are in the hot-rolled state at HB 170–179 MPa and sB = 640 MPa.
- Not prone to tempering after annealing.
- Has low flake sensitivity.
The formation of a method of heat treatment of the material is determined by the operational requirements regarding parts and mechanisms. In the metalworking industry, the following types of processing are used: normalization, improvement, high-frequency hardening, hardening with low tempering, etc.
Medium-carbon steels have found application in the manufacture of parts characterized by increased material strength with increased exposure to cyclic loads (gear wheels of gearboxes, connecting rod mechanisms). Steel grade 45 is used in the production of:
- gears, pinion shafts, crankshafts and camshafts, bandages, cylinders, cams; spindles;
- seamless pipes and frame pipeline elements require quenching and tempering of steel;
- a number of spare parts and structures in the motorcycle and bicycle industry.
Technological example. Vices, round nose pliers and pliers are made on the basis of steels 45 and 50. When performing thermal hardening, in assembled form, only the jaws of the product should be heated to protect against the formation of hardening cracks. Lead and salt baths are intended for such heating. When processing in a chamber furnace, cooling of the area with a sharp transition (hinge) should occur slowly, with only the surface of the tool jaws lowering and moving in the liquid (before the rest of the part becomes tarnished). Temperature regime of the tempering process is 220-320 degrees in the interval of 30-40 minutes.
Steel 45: characteristics
This high-quality carbon alloy easily withstands temperature tests in the range of 200-600°C. With a specific gravity of 7826 kg/m3, this metal has high hardness - HB 10-1=170MPa.
The density of steel 45 according to GOST 1050-88 is 7826-7595 kg/m3 in the range of 20-800°C.
High-quality carbon steel 45, the Brinell hardness of which is 170 MPa, has an elastic modulus of E 10-5 = 2 MPa (at 20 °C) and a tensile strength of 245 MPa.
The remaining physical and mechanical characteristics of steel 45 are presented below:
a brief description of
Steel has a density of 7850 kg/m3. It stands out among other structural steels due to its mechanical characteristics: the yield strength is 640 MPa. Wear-resistant. Works well under conditions of variable and shock loads: endurance limit 245 MPa, impact strength 66 kJ/m2.
Grade 45 is plastic and amenable to all types of mechanical processing. Elasticity coefficient 2 MPa. The relative elongation is 15%, and the relative narrowing is 40%. The value of the coefficient of linear thermal expansion is in the range of 11.9-15.2 1/deg.
The optimal operating temperature range is 200-400 degrees. After passing this mark, the mechanical characteristics drop significantly.
Grade 45 does not have enhanced anti-corrosion properties. Without applying a protective layer, the surface of the steel becomes covered with rust. Chemically unstable to most acids and alkalis.
Steel 45 belongs to the 3rd group of weldability. The process of welding it is difficult and impossible without preparatory work: heating to 150-200 degrees. Welded seams are unstable in operation and are susceptible to cracking.
The hardness of “raw” steel is 20-22 Rockwell units. Heat treatment can increase this indicator for steels of this type by 2-2.5 times. For this, the following types are used:
- Normalization is carried out mainly as a preliminary heat treatment. It is carried out before machining to improve the cutting process.
- Hardening increases hardness up to 50 HRC, increases abrasive wear resistance and strength. Quenching is always done in water.
- Low tempering is carried out in order to more evenly distribute internal stresses.
Grade 45 steel: application
Grade 45 steel is widely used in industry, in particular, it is used for the manufacture of shafts (camshafts and crankshafts), gears, dugouts, spindles, cams, cylinders, etc. 45 metal makes it possible to obtain normalized, improved surfaces that are characterized by increased strength. If it is necessary to improve the characteristics of finished products by an order of magnitude, technologists use metal grade 45, alloyed with chromium - 45x (chromium share 0.8-1.1%), or cast steel 45L.
Steel 45 is considered a difficult-to-weld material, but it is not characterized by temper brittleness. This is a fairly significant factor when creating structures of complex shapes and configurations. Welding of this metal is carried out in 2 ways: KTS and RDS.
Chemical composition and decoding
Grade 45 is included in the group of high-quality structural steels. The number “45” means the carbon content of the steel in hundredths of a percent.
The quantity and type of chemical elements in its composition are regulated by GOST 1050-72. The main components are carbon and iron. Carbon imparts greater hardness, the ability to be strengthened by heat treatment, and increases machinability.
In addition to the basic elements, grade 45 steel contains the following components:
- Harmful impurities of phosphorus (up to 0.035%) and sulfur (up to 0.04%) have a negative effect on mechanical properties. Their larger molecules are embedded in the crystal lattice of steel and weaken its strength and wear resistance. In addition, the increased content of phosphorus and sulfur causes red brittleness in steels, i.e. formation of cracks during pressure treatment.
- Beneficial impurities of manganese (0.5-0.8%) and silicon (0.17-0.37%) reduce the internal stress of steel, thereby reducing the likelihood of cracks. Helps increase the effectiveness of hardening from heat treatment. In general, their presence has a positive effect on the ductility of steel.
- Also, 45 steel contains impurities of nickel, chromium, copper and arsenic. The total content of all these elements does not exceed 0.7%. For this reason, their influence on the properties of steel is insignificant.
It is worth noting that the presence of the above-mentioned by-products is associated with imperfect smelting technology and the quality of the chemical composition of the charge.
Analogs
Marking 45 is widespread outside of Russia and has many foreign analogues. Among them are:
- 1044, 1045 U.S.
- 1.0503 Germany.
- S45C Japan.
Application
Grade 45 steel represents the optimal balance of strength, susceptibility to machining and price, which has allowed it to achieve widespread use in production.
It is actively used in the manufacture of power elements of metal structures. Where the use of welding is impractical. A good example would be a hoist line guide beam. The use of steel 45 instead of St3 will allow the use of smaller I-beams, which has a positive effect on the total weight of the metal structure.
In mechanical engineering and machine tools, grade 45 is used as a material for the manufacture of parts such as shafts, spindles, cams, bandages, plungers, calipers, faceplates, etc.
Excellent for the production of bevel and cylindrical gears. In order to increase the service life of the gear, additional hardening of its surface by chemical, thermal or mechanical means is necessary.
In addition, 45 is used for the manufacture of springs and springs operating under conditions of small loads.
The main elements of hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders consist of it. In particular, the sleeve that serves as the direction for the pressure piston, parts of check and exhaust valves, mounting unit, rod, etc.
Application
As already noted, the scope of application of the material is quite wide. When using high-quality steel 45, various workpieces can be produced. Metal is supplied to production lines in the form of long and shaped rolled products.
The uses of steel 45 are as follows:
- Manufacturing of products represented by bodies of rotation. When creating various structures, shafts are often used, which can have several steps and grooves. In this case, the diametrical size can vary over a wide range.
- Spindles and cams, as well as gears. Gears can be called a rather difficult product to manufacture. They are obtained by the process of milling round blanks. The structure may be subject to severe mechanical stress. That is why various heat treatments are often carried out, for example, hardening or tempering. Cams and other similar products are also characterized by the fact that they are subject to severe mechanical stress.
- Fasteners have become very widespread. They are used to connect various products or fix them. High demands are placed on fasteners. For example, the surface must withstand significant mechanical stress or load that occurs in the transverse direction.
- Plates and sheet material. Sheet metal has become quite widespread. It is used in the manufacture of various products, as well as cladding of load-bearing structures. It is worth considering that today sheet material is often used for stamping and other pressure processing.
Application of steel 45
Heat treatment can significantly expand the scope of metal application. For example, hardening and surface normalization are carried out. To significantly change the performance qualities, the composition is alloyed with various chemical elements, for example, chromium. Increasing the concentration of chromium causes the metal to become corrosion resistant.
Low temper fragility determines that the metal is used to create products of complex shapes and configurations. An example is gears and sprockets, which are represented by teeth with a complex configuration.
Considering analogues, we note that there are a fairly large number of alloys that are characterized by similar qualities. For example, the USA and Germany apply their own marking standards when creating alloys that are similar to Steel 45. For example, 1044 and 1045, 1.0503 and 1.1191. Analogues are also produced in many other countries. As for metals with similar performance qualities, these include steel 50 and steel 50G, as well as steel 40X, which is alloyed with the use of chromium.
Analog St 45 - steel 1.0503
In conclusion, we note that products made from steel 45 have very attractive performance characteristics and are inexpensive. That is why it is used in the engineering industry as a base metal. The structure is characterized by high machinability. Therefore, the workpieces are subjected to turning and milling.
Pricing
Scrap steel 45 has a cost in the range of 13,000 - 14,000 rubles per ton. This price is lower than that of stainless steel and any non-ferrous metals, but higher than that of cast iron. It is better to find out the exact value of the cost directly at the scrap metal collection points, since it is influenced by many factors:
- The value of quotes on the London Ferrous Metals Exchange. This is what most Russian metal receivers choose as the basis of cost.
- The relationship between consumer demand and supply in your region. The distance from large metal processing plants also plays a role here.
- The percentage of harmful impurities in the composition, especially sulfur.
- The presence of traces of rust on the surface of the scrap.
- Dimensions of scrap pieces.
- Profile type: hexagon, sheet, square, circle, etc.
- Payment by cash or bank transfer. As a rule, scrap metal collection points give preference to purchasing metal non-cash, for which they charge an appropriate markup.
- Delivery weight. Preferred volumes range from 1000 kilograms.
Temperature of critical points of steel 45
As previously noted, to improve the performance properties of the metal, heat treatment is carried out. It involves exerting a certain influence on the structure, after which the crystal lattice is rearranged and the qualities change. When carrying out heat treatment, critical points are often taken into account. Processing of steel St 45 is carried out taking into account the following factors:
- Temperature conditions. It is important to choose the right temperature, since too low will cause incomplete heating of the structure and complete restructuring of the structure will not occur. Too high an indicator causes overheating of the metal, as well as the appearance of scale. A variety of settings can be used to ensure that the required temperature is applied. An example would be blast furnaces or electrical installations. Melting temperatures that are too high determine that it is quite difficult to harden the steel in question at home.
- Rate of temperature increase. The heating rate can also determine which qualities will be transferred to the processed product. Modern equipment allows you to control the heating rate with high precision. For example, HDTVs have an electronic control unit; electrical energy is converted into magnetic energy, which causes heating of the structure.
- The length of time between exposure to different temperatures. When heat treating all metals, the presence of three critical points is taken into account and taken into account. The holding time may depend not only on the chemical composition of the material, but also on the size and shape of the workpiece.
- Features of the cooling process. The quality of the resulting product largely depends on the conditions under which the cooling process took place. For example, it is possible to use oil or water, as well as various powders as a cooling medium.
Quite often, HDTV is used to change the qualities of a metal. It is characterized by high efficiency in application, as well as ease of use. Today there are models that, if desired, can be installed in a home workshop.
Critical points are considered to be temperatures at which restructuring of the structure occurs. There are three main temperature points that are displayed on the plotted diagram.
Attention is also paid to choosing a more suitable cooling medium. For example, it is possible to carry out cooling in water. However, such an environment leads to uneven cooling, which leads to scale and other problems. For higher quality, oil is used. Large workpieces can be cooled in the open air, since it takes a long time to reduce the temperature.