Characteristics of steel grade St3ps
St3ps - Structural carbon steel of ordinary quality, welds well, welding is carried out without heating and without subsequent heat treatment, welding methods: manual arc welding, automatic submerged arc welding and gas protection, KTS, ESW.
According to GOST 27772-88, steel grade St3ps5 in its characteristics and properties is an analogue of steel for building structures S245, steel St3ps is an analogue of steel for building structures S275. For thicknesses greater than 36 millimeters, heating and subsequent heat treatment are recommended; it is not prone to flake sensitivity and there is no tendency to temper brittleness. Machinability by cutting in the hot-rolled state at НВ 124 and σв=410 MPa, Kυ hard alloy. = 1.8 and Kυ b.st. = 1.6, has found its application in load-bearing elements of welded and non-welded structures and parts operating at positive temperatures, and is actively used in general construction solutions. This grade of steel is used to produce parts and components of freight cars, power transmission line supports, excavators and forestry equipment, offshore structures, road bridges, building structures, oil and gas platforms. Forging is carried out at temperatures from 1300 to 750 0C, cooling is carried out in air.
Application of steel St3
When considering different grades of steel, you need to take into account the fact that they are classified according to the degree of deoxidation. This chemical process involves removing oxygen from the composition. Too high an oxygen concentration determines a decrease in physical and mechanical properties.
The classification is carried out as follows:
- Calm is characterized by the fact that the composition includes from 0.16 to 0.3% silicon.
- Semi-calm has an average concentration of the element in question.
- Boiling differs in chemical composition from calm in that it contains at least 0.05% silicon.
Read also: Walk-behind tractor with final drives
St3 material is marked accordingly. Various substances can be used to carry out a chemical process.
It is worth considering that a quiet one is much more expensive than other options. This can be associated with the following points:
- The structure is homogeneous, thereby increasing the degree of protection of the material from environmental influences.
- The composition includes a small amount of oxygen, which determines high performance.
When using mild steel, the following products can be manufactured:
- Rolled sheets and shapes.
- Fittings and parts that can be used to create a pipeline. Various pipes can be used to transport coolant or gas or other media. In order for them to withstand high loads and environmental influences, materials with strength and hardness must be used during production. In addition, attention is paid to cost, since alloys that are too expensive may be less practical to use. Steel 3 is more suitable for the manufacture of such products.
- Primary and secondary elements used in the manufacture of suspended structures and railway elements. In the railway industry, the metals that are most in demand are those that have low cost and high performance. Due to the large size of suspended structures, the price of one square meter is also of great importance.
The semi-quiet variety of steel, which is also widely used, contains about one percent oxygen. Due to this, the characteristics of hardness and ductility are less pronounced. When using steel 3, the following can be produced:
- Pipes. This type of material is widely used today. Pipes are used to create a heating system as load-bearing elements. It is worth considering that pipes can have different diameters and wall thicknesses. The alloy in question has relatively low corrosion resistance, so it is necessary to protect the surface from exposure to high humidity.
- Sheet metal is also used extremely often, especially in the manufacture of cabinet products or cladding of load-bearing structures. The thickness can vary over a wide range. Rolled sheet metal can be used for cold bending or stamping. These two processes are characterized by high productivity. That is why the alloy in question is most widely used.
- Squares and corners are often used to obtain load-bearing structures. They are characterized by high strength, since the edges significantly increase rigidity and can distribute the load. Corners and squares are characterized by a large number of parameters: sheet thickness, angle of planes, length and cross-sectional shape. The scope of application is the manufacture of load-bearing structures and strengthening of existing structures.
- Various hexagons. They are also widely used and can be used in a wide variety of industries.
Steel sheet St3 hot rolled
Boiling alloys have become widespread due to their availability. They are the most affordable in terms of cost, and the resulting structure is characterized by a high degree of workability. In addition, the alloy lends itself well to heat treatment, but its performance is reduced due to the high oxygen concentration.
In conclusion, we note that many analogues of steel 3 have the appropriate performance characteristics. Foreign manufacturers use their own standards for labeling. At the same time, the concentration of harmful impurities is maintained within a certain range. The use of the most modern technologies makes it possible to reduce the amount of phosphorus and sulfur in the composition, making the material more durable and less fragile. In some cases, alloying elements are added.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
St3 steel can easily be called one of the most popular brands of steel alloys. This material can be found almost everywhere, from garden benches to complex welded structures. What causes this?
Interpretation of steel grade St3ps
Decoding steel: Letter St. indicate that the steel is of ordinary quality, although most steels are high quality. The numbers from 0 to 6 are the conventional brand number depending on the chemical composition and mechanical properties. Typically, the higher the number, the more carbon and the greater the strength. In our case, the number 3 indicates the carbon content in the alloy is 0.14–0.22%. The letters after the brand number indicate the degree of deoxidation: ps - semi-calm. Steels of the first group, such as St3sp, are supplied with guaranteed mechanical properties and are used mainly without heat treatment.
Production nuances
The characteristics of a metal are determined based on its chemical composition and manufacturing technology. The basis of ST3PS steel is ferrite - a solid solution of carbon, nickel and chromium. The more carbon a material contains, the higher its strength.
Undesirable impurities in the composition are sulfur (0.05%) and phosphorus (0.04%). Sulfur forms sulfur grains, which causes red brittleness in steel. Phosphorus interacts with ferrite, which reduces ductility when working at elevated temperatures and increases cold brittleness in the cold.
For the production of ST3PS steel, open-hearth and converter production methods are used. The basic characteristics of the metal are identical for any method, but the converter method has a lower cost.
Return to content
Supply St3ps
Supplied in the form of long products, including shaped steel according to the regulations of GOST 2590-88 Hot-rolled round steel , GOST 2591-88 Hot-rolled square steel , GOST 8239-89 Hot-rolled steel I-beams , GOST 19771-93 Equal-flange bent steel angles, GOST 19772 -93 Bent steel angles, unequal flanges , GOST 8278-83 Bent steel channels, equal flanges , GOST 8281-80 , unequal , GOST 8283-93 steel trough equal flange profiles , GOST 380-94 Carbon steel of ordinary quality , GOST 85 09-93 Steel corners hot-rolled equal flange , GOST 8510-86 rolled steel angles unequal-flanged , GOST 8240-97 Hot-rolled steel channels , GOST 535-88 Rolled bars and shaped carbon steel of ordinary quality , GOST 2879-88 Rolled hot-rolled hexagonal steel, GOST 19903-2015 Hot rolled sheet products , GOST 19904-90 Cold-rolled sheets , GOST 16523-97 Rolled thin sheets of high-quality and ordinary quality carbon steel for general purpose, GOST 503-81 Cold-rolled low-carbon steel strip, GOST 103-76 Hot-rolled steel strip , GOST 82-70 Hot-rolled steel Wide-band universal, GOST 3282-74 Wire Steel low-carbon general purposes , GOST 17305-71 Carbon structural steel wires, GOST 10705-80 steel power steel pipes , GOST 10706-76 Pipes steel eight-dimensional , GOST 3262-75 Pipes steel water and gap-pipes .
| Metal forming. Forgings | GOST 8479-70; |
| Classification, nomenclature and general norms | GOST 380-2005; |
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 5267.0-90; GOST 5781-82; GOST 8239-89; GOST 8240-97; GOST 8510-86; GOST 8509-93; GOST 10884-94; GOST 30136-95; GOST 9234-74; GOST 4781-85; GOST 10551-75; GOST 25577-83; GOST 5422-73; GOST 535-2005; GOST 19240-73; GOST 19425-74; GOST 2590-2006; GOST 11474-76; GOST 2879-2006; GOST 2591-2006; GOST 30565-98; |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 14637-89; GOST 16523-97; GOST 8568-77; GOST 14918-80; GOST 19903-74; GOST 103-2006; |
| Ribbons | GOST 3560-73; GOST 6009-74; |
| Ribbons | GOST 19851-74; |
| Rails. Overlays. Linings. Crutches | GOST 8142-89; GOST 5812-82; GOST 16277-93; |
| Steel pipes and connecting parts for them | GOST 12132-66; GOST 10705-80; GOST 10706-76; GOST 3262-75; GOST 24950-81; GOST 8696-74; GOST 10707-80; GOST 20295-85; |
Carbon steel grade st3sp - ordinary quality
Substitutes
Steel StZps, Steel S245
Foreign analogues
| Europe EN 10027-1 (EN 10027-2) | S235JR (1.0038) |
| Germany DIN | RSt37-2, USt37-2 |
| USA (AISI, ASTM) | A238/C |
| France (AFNOR) | E 24-2 |
| UK BS | 40B |
| Czech Republic (CSN) | 11375 |
| Poland PN/H | St3SV, St3SJ, St3S4U |
Decoding steel St3sp
- The letters “B” indicate that this steel, supplied according to mechanical properties and with separate requirements for chemical composition,
- The letters "St" stand for "Steel"
- number 3 indicates the conventional brand number depending on the chemical composition,
- the letters "sp" - calm (degree of steel deoxidation),
- If the letter “sp” is followed by a number, then it indicates the category. If there is no number, then steel category 1. Depending on the category, steel has different standardized indicators (see below).
Type of delivery
- Long products, including shaped steel: GOST 2590-88, GOST 2591-88, GOST 535-88, GOST 2879-88, GOST 19771-93, GOST 19772-93, GOST 8278-83, GOST 8281-80, GOST 8282 -83, GOST 8283-93, GOST 380-94, GOST 8509-93, GOST 8510-86, GOST 8239-89.
- Thick sheet GOST 19903-74.
- Thin sheet GOST 19903-74.
- Tape GOST 503-81, GOST 6009-74.
- Strip GOST 103-76, GOST 82-70, GOST 535-88.
- Forgings and forged blanks GOST 8479-70.
- Pipes GOST 8734-75, GOST 10706-76, GOST 10705-80.
Characteristics, application and purpose
St3sp steel belongs to structural carbon steels of ordinary quality for general purpose and is used for the manufacture of the following parts and structures:
- Load-bearing elements of welded and non-welded structures and parts operating at positive temperatures.
- Shaped and sheet products (5th category) - for load-bearing elements of welded structures operating under variable loads: with a thickness of rolled products up to 25 mm in the temperature range from -40 to +425 °C;
- for rolled products with thickness over 25 mm in the range from -20 to +425 °C, subject to delivery with guaranteed weldability.
According to the international standard ISO 630:1995, St3sp steel is designated E 235-C (Fe 360-C)
Steel 3 is a widely used steel in the petroleum, petrochemical and oil and gas industries. Welded and stamped products can be made from steel of this grade:
- frames,
- frames
- heavy oilfield equipment skids
- bases (blocks)
- parts of drilling and production derricks and masts
- brake bands
- pulleys
- Cam couplings for drilling rigs
- keys
- stubs
- mud pump covers
- racks
- brackets
- gear housings
- drilling rig frames, etc.
Temperature of critical points, °C
| Ac1 | Ac3 | Ar3 | Ar1 |
| 735 | 850 | 835 | 680 |
Chemical composition, % (GOST 380-94)
| C | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Ni | Cu | As |
| no more | ||||||||
| 0,14-0,22 | 0,40-0,65 | 0,12-0,30 | 0,04 | 0,05 | 0,30 | 0,30 | 0,30 | 0,08 |
Chemical composition, % (GOST 380-2005)
| steel grade | Mass fraction of chemical elements | ||
| carbon | manganese | silicon | |
| St3sp | 0,14-0,22 | 0,40-0,65 | 0,15-0,30 |
NOTE.
- The mass fraction of chromium, nickel and copper in St3sp steel should be no more than 0.30% each.
- The mass fraction of sulfur in St3sp steel should be no more than 0.050%, phosphorus - no more than 0.040%.
- The mass fraction of nitrogen in steel should be no more than:
- smelted in electric furnaces - 0.012%;
- open hearth and converter - 0.010%.
- The mass fraction of arsenic should be no more than 0.080%.
Standardized indicators of St3sp steel by rolled category (GOST 535-2005)
| Category | Chemical composition | Temporary resistance σв | Yield strength σt | Relative elongation δ5 | Cold bending | Impact strength | ||||
| KCU | KCV | |||||||||
| At temperature, °C | After mechanical aging | At temperature, °C | ||||||||
| + 20 | -20 | + 20 | -20 | |||||||
| 1 | — | + | + | + | + | — | — | — | — | — |
| 2 | + | + | + | + | + | — | — | — | — | — |
| 3 | + | + | + | + | + | + | — | — | — | — |
| 4 | + | + | + | + | + | — | + | — | — | — |
| 5 | + | + | + | + | + | — | + | + | — | — |
| 6 | + | + | + | + | + | — | — | — | + | — |
| 7 | + | + | + | + | + | — | — | — | — | + |
NOTE
- The “+” sign means that the indicator is normalized, the “-” sign means that the indicator is not normalized.
- The chemical composition of steel according to heat analysis or in finished rolled products is in accordance with the order.
Parameters for the use of electric-welded straight-seam pipes made of St3sp steel (GOST 32569-2013)
| Steel grade, strength class, standard or specifications | StZsp5 GOST 380 | StZsp4-5 GOST 380 | StZsp4 GOST 380 | ||||
| Technical requirements for pipes (standard or specifications) | GOST 10705 group B | GOST 10706 group B | TU 14-3-377-87 | TU 14-3-1399-95 | GOST 10706 group B | ||
| Nominal diameter, mm | 10-500 | 450-1400 | 200-400 | 200, 350, 400, 500 | 400-1400 | ||
| Types of tests and requirements (standard or specifications) | GOST 10705 | GOST 10706 | TU 14-3-377-87 | TU 14-3-1399-95 | GOST 10706 | ||
| Transported medium (see designations in table 5.1) | Group B, C environments | Group B media Group B media, except LPG | Group B media, except steam and hot water | All media except group A(a) and LPG | Group B media, except LPG | ||
| Pipeline design parameters | Maximum pressure, MPa | ≤1,6 | ≤2,5 | ≤1,6 | |||
| Maximum temperature, °C | 300 | 200 | 300 | 200 | |||
| Pipe wall thickness, mm | — | ≤12 | — | ≤10 | — | ||
| Minimum temperature depending on the pipe wall thickness with stress in the wall from internal pressure [σ], °C | more than 0.35[σ] | minus 20 | |||||
| no more than 0.35[σ] | minus 40 | ||||||
NOTE. Groups of media, see table 5.1 GOST 32569-2013
Parameters for the use of electric-welded spiral-welded pipes made of St3sp steel (GOST 32569-2013)
| Steel grade, strength class, standard or specifications | StZspZ, StZsp2 GOST 380 | StZsp5 GOST 380 | ||
| Technical requirements for pipes (standard or specifications) | TU 14-3-943-80 | TU 14-3-954-80 | ||
| Nominal diameter, mm | 200-500 | 500-1400 | ||
| Types of tests and requirements (standard or specifications) | TU 14-3-943-80 | TU 14-3-954-80 taking into account the requirements of clause 2.2.10 GOST 32569-2013 | ||
| Transported medium (see designations in table 5.1) | All media except group A and LPG | All media except group A and LPG | ||
| Pipeline design parameters | Maximum pressure, MPa | ≤1,6 | ≤2,5 | |
| Maximum temperature, °C | 200 | 300 | ||
| Pipe wall thickness, mm | ≤6 | ≤12 | ||
| Minimum temperature depending on the pipe wall thickness with stress in the wall from internal pressure [σ], °C | more than 0.35[σ] | minus 30 | minus 20 | |
| no more than 0.35[σ] | — | minus 20 | ||
NOTE. Groups of media, see table 5.1 GOST 32569-2013
Application of St3sp steel for fasteners (GOST 32569-2013)
| steel grade | Technical requirements | Acceptable operating parameters | Purpose | |
| Wall temperature, °C | Medium pressure, MPa (kgf/cm2), no more | |||
| StZsp4 GOST 380 | STP 26.260.2043 | -20 to +300 | 2,5 (25) | Studs, bolts, nuts |
| 10 (100) | Washers | |||
Conditions for using St3sp steel for bodies, covers, flanges, membranes and valve assembly made from rolled products, forgings (stampings) (GOST 33260-2015)
| Material | ND for supply | Temperature of the working medium (wall), °C | Additional instructions for use |
| St3sp GOST 380 | Forgings GOST 8479 Long products GOST 535, categories 3-5 | -30 to 300 | For welded fittings for pressure PN≤2.5 MPa (25 kgf/cm2) |
| Sheet GOST 14637, categories 3-6 | -20 to 300 | For welded fittings for pressure PN 5 MPa (50 kgf/cm2). For categories 4, 5, sheet thickness for St3sp is no more than 25 mm; for category 3 sheet thickness no more than 40 mm |
Resistance of structural materials against crevice erosion (GOST 33260-2015)
| Durability group | Point | Erosion resistance against steel 12X18H10T | Material |
| Unstable | 6 | 0,005-0,05 | Steel VSt3sp3 and its welded joints. |
NOTE. The coefficient of erosion resistance of a material is the ratio of the rate of erosive wear of the material to the rate of erosive wear of steel 12Х18Н10Т (taken as 1).
Mechanical properties of rolled products under tension, as well as cold bending test conditions (GOST 535-2005)
| steel grade | St3sp | |
| Tensile strength σв, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2), for rolled thickness, mm | up to 10 incl. | 380-490 (39-50) |
| St.10 | 370-480 (38-49) | |
| Yield strength σт, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2), for rolled thickness, mm (not less) | up to 10 incl. | 255(26) |
| St. 10 to 20 incl. | 245(25) | |
| St. 20 to 40 incl. | 235(24) | |
| over 40 to 100 incl. | 225(23) | |
| St. 100 | 205(21) | |
| Relative elongation δ5, %, for rolled thicknesses, mm (not less) | up to 20 incl. | 26 |
| over 20 to 40 incl. | 25 | |
| St.40 | 23 | |
| Bending until the sides are parallel (a - sample thickness, d - mandrel diameter), for rolling thicknesses, mm | up to 20 incl. | d = a |
| St.20 | d = 2a | |
NOTE
- By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, the following is allowed:
- reduction in yield strength by 10 N/mm2 (1 kgf/mm2) for shaped steel with a thickness of over 20 mm;
- reduction in relative elongation by 1% (abs.) for shaped rolled products of all thicknesses.
- It is allowed to exceed the upper limit of tensile strength by 49.0 N/mm2 (5 kgf/mm2), and by agreement with the consumer - without limiting the upper limit of tensile strength, provided that other standards are met. At the request of the consumer, exceeding the upper limit of temporary resistance is not allowed.
Impact strength of rolled products (GOST 535-2005)
| steel grade | St3sp | ||
| Rolled thickness, mm | St. 5.0 to 10.0 incl. | ||
| KCU, J/cm2 (kgf*m/cm2), not less | Sample type according to GOST 9454 | 2,3 | |
| At temperature, °C | +20 | 108(11) | |
| -20 | 49(5) | ||
| After mechanical aging | 49(5) | ||
| KCV, J/cm2 (kgf*m/cm2), not less | Sample type according to GOST 9454 | 12,13 | |
| At temperature, °C | +20 | 34(3,5) | |
| -20 | — | ||
NOTE
- The “-” sign means that the indicator is not standardized.
- Determination of the impact strength of round rolled products is carried out starting from a diameter of 12 mm, square - starting from the square side of 11 mm.
- It is allowed to reduce the value of impact strength on one sample by 30%, while the average value must not be lower than the standards specified in this table.
- Impact strength KCV is determined for rolled products with a thickness of up to 20 mm inclusive.
Mechanical properties of rolled products
| GOST | Delivery status | Section, mm | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5(δ4),% |
| no less | |||||
| GOST 380-94 | Hot rolled products | Up to 20 | 245 | 370-480 | 26 |
| St. 20 to 40 | 235 | 25 | |||
| St. 40 to 100 | 225 | 23 | |||
| St. 100 | 205 | 23 | |||
| GOST 16523-89 (transverse samples) | Hot rolled sheet | Up to 2.0 incl. | — | 370-480 | (20) |
| St. 2.0 to 3.9 incl. | (22) | ||||
| Cold rolled sheet | Up to 2.0 incl. | — | 370-480 | (22) | |
| St. 2.0 to 3.9 incl. | (24) | ||||
Mechanical properties of forgings
| GOST | Heat treatment | Section, mm | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5,% | ψ, % | KCU, J/cm2 | Hardness HB |
| no less | ||||||||
| GOST 8479-70 | Normalization | Up to 100 | 175 | 353 | 28 | 55 | 64 | 101-143 |
| 100-300 | 175 | 353 | 24 | 50 | 59 | |||
| Up to 100 | 195 | 392 | 26 | 55 | 59 | 111-156 | ||
| 100-300 | 195 | 392 | 23 | 50 | 54 | |||
Impact strength KCU (GOST 380-94)
| Type of rental | Pattern cutting direction | Section, mm | KCU, J/cm2 | ||
| +20 °C | -20 °C | after mechanical aging | |||
| no less | |||||
| Sheet | Transverse | 5-9 | 78 | 39 | 39 |
| 10-25 | 68 | 29 | 29 | ||
| 26-40 | 49 | — | — | ||
| Wide band | Longitudinal | 5-9 | 98 | 49 | 49 |
| 10-25 | 78 | 29 | 29 | ||
| 26-40 | 68 | — | — | ||
| Varietal and shaped | Same | 5-9 | 108 | 49 | 49 |
| 10-25 | 98 | 29 | 29 | ||
| 26-40 | 88 | — | — | ||
Mechanical properties at elevated temperatures
| tsp, °C | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5,% | ψ, % | KCU, J/cm2 |
| Hot rolled billet dimensions 140×120 mm | |||||
| 20 | 220 | 445 | 33 | 59 | 154 |
| 300 | 205 | — | — | — | 199 |
| 500 | 180 | 285 | 34 | 80 | 119 |
| Hot-rolled sheets and shapes up to 30 mm thick | |||||
| 20 | 205-340 | 420-520 | 28-37 | 56-68 | — |
| 200 | 215-285 | — | — | — | — |
| 300 | 05-265 | — | — | — | — |
| 400 | 155-255 | 275-490 | 34-43 | 60-73 | — |
| 500 | 125-175 | 215-390 | 36-43 | 60-73 | — |
| A sample with a diameter of 6 mm and a length of 30 mm is forged and normalized. Deformation speed 16 mm/min, strain rate 0.009 1/s | |||||
| 700 | 73 | 100 | 57 | 96 | — |
| 800 | 51 | 63 | 95 | 95 | — |
| 900 | 38 | 65 | 84 | 100 | — |
| 1000 | 25 | 43 | 79 | 100 | — |
| 1100 | 19 | 31 | 80 | 100 | — |
| 1200 | 14 | 25 | 84 | 100 | — |
Endurance limit
| Sample | σ-1, MPa | n |
| Smooth | 191 | 107 |
| Notched | 93 | 107 |
NOTE. Sheet 40 mm thick in hot-rolled condition.
Technological properties
Forging temperature, °C: beginning 1300, end 750. Cooling in air.
Cutting machinability - Kv tv.spl = 1.8 and Kv b.st = 1.6 in the hot-rolled state at HB 124 and σw = 400 MPa.
Flock sensitivity - not sensitive.
Tendency to temper brittleness - not prone.
Welding
Weldability - weldable without restrictions; welding methods: RDS, ADS with flux and gas protection, ESW and KTS. For thicknesses above 36 mm, heating and subsequent heat treatment are recommended.
It is allowed to use steel st3sp for welded connections of pipeline fittings at a temperature of the working medium (wall) from -20 to 300 °C.
Welding materials for electric arc welding
| Base material grade | Electrode type according to GOST, TU (recommended brands of electrodes) | Application temperature, °C | Additional instructions |
| St3sp | E42, E46 GOST 9467 (ANO-4, ANO-5,OZS-6) | Not lower than -15 | — |
| E42A, E46A GOST 9467 (UONI-13/45, UONI-13/45A, 0ZS-2, SM-11) | Not lower than -30 | — | |
| E50A GOST 9467 (UONI-13/55) | below -30 to -40 | After welding, heat treatment - normalization plus tempering (630–660) °C, 2 hours |
Welding materials for gas shielded welding
| Base material grade | Welding wire grade according to GOST 2246, TU, recommended shielding gas or mixture of gases | Application temperature, °C |
| St3sp | Sv-08G2S Carbon dioxide GOST 8050, argon GOST 10157 | -20 to 300 |
Welding materials for submerged arc welding
| Base material grade | Welding wire grade according to GOST 2246, TU, Recommended flux grade according to GOST 9087 | Additional instructions | ||
| Electrodes, type according to GOST 10052 (recommended brands) | Welding wire, GOST 2246 or TU | |||
| Group A | Group B | |||
| 10Х18Н9Л, 12Х18Н9ТЛ GOST 977 08Х18Н10Т, 12Х18Н9Т, 12Х18Н10Т, 12Х18Н9 GOST 5632 08Х18Н10Т-VD TU 14-1-3581 10Х18Н9, 10Х18Н9-VD, 10Х1 8N9-Sh TU 108.11.937 15Х18Н12СЧТУ (EI 654) GOST 5632 10Х17Н13М3Т (EI 432) 10Х17Н13М2Т ( EI 448) GOST 5632 | St3sp GOST 380 | E-10Kh15N25M6AG2 (EA-395/9) E-10Kh25N13G2 (OZL-6, ZIO-8), E-11Kh15N25M6AG2 (NIAT-5, TsT-10) | Sv-07Х23Н13 | The welded joint is of unequal strength |
| E-10Х15Н25М6AG2 (EA-395/9) 582/23, 855/51 | Sv-10X16N25AM6 Sv-06X15N35G7M6B Sv-03X15N35G7M6B | The welded joint is of unequal strength. Welding materials are used for products under the jurisdiction of Rostechnadzor | ||
Welding materials for welding steel st3sp with other steels
| Grades of welded steels | Welding materials | Application temperature, °C |
| St3sp | Sv-08, Sv-08A AN-348A, OSTS-45 ANTS-1 | Not lower than -20 |
Temperature of preliminary and accompanying heating and tempering when welding structures made of steel st3sp
| Grades of welded steels | Thickness of welded edges, mm | Temperature of preliminary and accompanying heating, °C | Interval between the end of welding and the start of tempering, hour | Temperature, °C | |
| welding | surfacing with austenitic class materials | ||||
| St3sp | Up to 36 | Not required | Not required | Not limited | Not required |
| Over 36 to 100 | 630-660 | ||||
| Over 100 | 100 | ||||
Recommended welding modes for correcting weld defects
| Welding materials | Main material | Diameter of electrode, wire, mm | Welding current strength, A | Arc voltage, V |
| USENI 13/45A* USENI 13/55 | St3sp | 3,0 4,0 5,0 | From 100 to 130 From 160 to 210 From 220 to 280 | From 22 to 26 |
| Sv-08G2S | 1,6 | From 100 to 120 | From 12 to 14 | |
| 2,0 | From 140 to 160 |
NOTE. * - along with the electrode brand UONI 13/..., it is possible to use the brand UONII 13/..., depending on the designation of the brand in the specifications of the electrode manufacturer.
Modes of electric arc welding of samples and products
| Electrode brand | Main material | Electrode diameter, mm | Welding current strength, A | Arc voltage, V |
| USENI 13/45A*, USENI 13/55 | St3sp | 3 4 5 | From 110 to 130 From 160 to 210 From 220 to 280 | From 22 to 26 |
NOTE. * - along with the electrode brand UONI 13/..., it is possible to use the brand UONII 13/..., depending on the designation of the brand in the specifications of the electrode manufacturer.
Modes of argon arc welding of samples for incoming inspection of welding materials
| Electrode brand | Main material | Electrode diameter, mm | Welding current strength, A | Arc voltage, V |
| Sv-08G2S | St3sp | 1,6 2,0 3,0 | From 100 to 120 From 150 to 170 From 200 to 240 | From 12 to 14 |
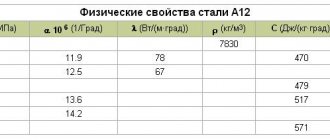
Linear expansion coefficient α*106, K-1
| steel grade | Temperature, K (°C) | |||||||||||
| 323 (50) | 373 (100) | 423 (150) | 473 (200) | 523 (250) | 573 (300) | 623 (350) | 673 (400) | 723 (450) | 773 (500) | 823 (550) | 873 (600) | |
| St3sp5 | 11,5 | 11,9 | 12,2 | 12,5 | 12,8 | 13,1 | 13,4 | 13,6 | 13,8 | 14,0 | 14,2 | 14,4 |
Young's modulus (normal elasticity) E, GPa
| steel grade | Temperature, K (°C) | ||||||||||
| 293 (20) | 323 (50) | 373 (100) | 423 (150) | 473 (200) | 523 (250) | 573 (300) | 623 (350) | 673 (400) | 723 (450) | 773 (500) | |
| St3sp5, | 200 (2,04) | 197 (2,01) | 195 (1,99) | 192 (1,96) | 190 (1,94) | 185 (1,88) | 180 (1,84) | 175 (1,79) | 170 (1,73) | 165 (1,68) | 160 (1,63) |
Thermal conductivity coefficient λ W/(m*K)
| Steel grade | λ W/(m*K), at test temperature, °C | |||||||
| 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | |
| St3sp | — | 55 | 54 | 50 | 45 | 39 | 34 | 30 |
Find out more
Carbon tool steel…
Steel X12F1 tool stamping...
Steel 60S2A spring-spring...
Spring steel 65
Impact strength of steel St3ps
| Type of rental | Pattern cutting direction | Section, mm | +20 °C | -20 °C | After mechanical aging |
| no less | |||||
| Sheet | Transverse | 05-9 | 78 | 39 | 39 |
| 10-25 | 69 | 29 | 29 | ||
| 26-40 | 49 | — | — | ||
| Wide band | Longitudinal | 05-9 | 98 | 49 | 49 |
| 10-25 | 78 | 29 | 29 | ||
| 26-40 | 69 | — | — | ||
| Varietal and shaped | Longitudinal | 05-9 | 108 | 49 | 49 |
| 10-25 | 98 | 29 | 29 | ||
| 26-40 | 88 | — | — | ||
Mechanical properties of steel St3ps
Mechanical properties of steel St3sp according to GOST 380-94 regulations is sold in the form of hot-rolled steel with a cross-section of up to 20 mm, from 20 mm to 40 mm, over 40 mm to 100 mm, and also over 100 mm. Yield strength – 225, 235, 245 MPa. Tensile strength 370-480 MPa. Relative elongation after rupture is 23 – 26%.
Mechanical properties of St3ps steel according to the regulations of GOST 16523-89 and GOST 19903-2006 in the form of hot-rolled sheets. The cross-section is made from 1.5 mm inclusive to mm inclusive. The relative elongation after rupture is 23%, 25%, 26%. Below is the data in tabular form:
| Nominal thickness (mm) | Minimum yield strength, MPa | Tensile strength, (MPa) | Brinell hardness, HB (MPa) |
| ≤ 16 | 235 | 360-510 | 104-154 |
| > 16 ≤ 40 | 225 | 360-510 | 104-154 |
| > 40 ≤ 100 | 215 | 360-510 | 104-154 |
| > 100 ≤ 150 | 195 | 350-500 | 103-152 |
| > 150 ≤ 200 | 185 | 340-490 | 100-149 |
| > 200 ≤ 250 | 175 | 340-490 | 100-149 |
Where and how is it used?
The performance qualities allow the alloy to be used for the manufacture of elements of welded structures operating under load, machine parts and mechanisms. The operating temperature must be above 0 degrees. The fifth category of rolled elements can be used in conditions of negative temperatures -40/-425 C under the action of a variable load.
Complex products require subsequent heat treatment; annealing is most often used. It reduces residual stresses after welding. The scope of application of ST3PS includes the production of At-400S fittings.
The sheets are used to produce parts using cold stamping. The result is pallets for collecting cutting fluids in production, containers of various volumes and purposes, casings, etc.
Mechanical properties of St3ps steel at a temperature of 200C
| ND | Heat treatment mode | Section, mm | σ0.2, N/mm2 | σв, N/mm2 | δ, % | ψ, % | KCU, J/cm2 | Bend | HB |
| no less | |||||||||
| GOST 535-2005 | Hot rolled | To 10 | 245 | 370-480 | 26 | — | — | d=a | |
| St. 10 to 20 | 245 | 26 | — | — | d=a | ||||
| St. 20 to 40 | 235 | 25 | — | — | d=2a | ||||
| St. 40 to 100 | 225 | 23 | — | — | d=2a | ||||
| 3,0-9,9 | — | — | — | — | 1.08E+09 | ||||
| Oct.25 | — | — | — | — | 9.81E+08 | ||||
| 26-40 | — | — | — | — | 881 | ||||
| GOST 8479-70 | Normalization | Up to 100 | 195 | 390 | 26 | 55 | 59 | — | 111-156 |
| St. 100 to 300 | 195 | 390 | 23 | 50 | 54 | — | |||
| GOST 14637-89 | Hot rolled | Up to 20 | 245 | 370-480 | 26 | — | — | d=1.5a | — |
| St. 20 to 40 | 235 | 25 | d=2.5a | ||||||
| St. 40 to 100 | 225 | 23 | d=2.5a | ||||||
| St. 100 to 160 | 205 | 23 | d=2.5a | ||||||
| St. 5 to 9 | — | — | — | — | 34139478 | ||||
| St. 10 to 20 | — | — | — | — | 34129469 | ||||
| St. 21 to 25 | — | — | — | — | 29469 | ||||
| St. 26 to 40 | — | — | — | — | 49 | ||||
| GOST 16523-97 | Heat-treated hot-rolled sheet | Up to 2.0 | — | 360-530 | 20 | — | — | d=a | |
| St. 2.0 | — | 22 | — | — | d=2a | ||||
| Heat treated cold rolled sheet | Up to 2.0 | — | 22 | — | — | d=a | |||
| St. 2.0 | — | 24 | — | — | d=2a | ||||
Foreign analogues of steel grade St3ps
| USA | A284Gr.D, A57036, A573Gr.58, A611Gr.C, GradeC, K01804, K02001, K02301, K02502, K02601, K02702 |
| Germany | 1.0038, 1.0116, Fe360B, Fe360D1, RSt37-2, S235J2G3, S235JRG1, S235JRG2, St37-2, USt37-2 |
| Japan | SS400 |
| France | E24-2NE, E24-3, E24-4, S235J0, S235J2G3, S235J2G4, S235JRG2 |
| England | 1449-2723CR, 1449-3723CR, 3723HR, 40B, 40D, 4360-40B, 4360-40D, 4449-250, 722M24, Fe360BFU, Fe360D1FF, HFS3, HFS4, HFW3, HFW4, S235J2G3, S23 5JR, S235JRG2 |
| European Union | Fe37-3FN, Fe37-3FU, Fe37B1FN, Fe37B1FU, Fe37B3FN, Fe37B3FU, S235J0, S235J2G3, S235JR, S235JRG2, S235JRG3 |
| Italy | Fe360B, Fe360BFN, Fe360C, Fe360CFN, Fe360D, Fe360DFF, Fe37-2, S235J0, S235J2G3, S235J2G4, S235JRG2 |
| Belgium | FE360BFN, FE360BFU, FED1FF |
| Spain | AE235BFN, AE235BFU, AE235D, Fe360BFN, Fe360BFU, Fe360D1FF, S235J2G3, S235JRG2 |
| China | Q235, Q235A, Q235A-B, Q235A-Z, Q235B, Q235B-Z |
| Sweden | 1312, 1313 |
| Bulgaria | BSt3ps, BSt3sp, Ew-08AA, S235J2G3, S235JRG2, WSt3ps, WSt3sp |
| Hungary | Fe235BFN, Fe235D, S235J2G3, S235JRG2 |
| Poland | St3SY, St3W |
| Romania | OL37.2 |
| Czech | 11373, 11375, 11378 |
| Finland | FORM300H |
- Structural steel
- Tool steel