Types of retaining rings according to GOST
Let's consider such domestic requirements for retaining rings of different sizes according to GOST 13940-13943. Each of them has a specific accuracy category. We have prepared a detailed table with requirements parameters especially for you.
GOST 13940-86
This standard is intended for products whose diameter is from 4 to 200 mm and has a concentric outer ring.
GOST 13941-86
For a concentric internal element, the technical requirements are set from 8 to 320 mm.
GOST 13942-86
Eccentric outer ring requirements from 4 to 200 mm.
GOST 13943-86
Technical standards for eccentric inner product from 8 to 320 mm.
Retaining Rings - Overview
The retaining ring is a flat, open ring made of carbon steel, stainless steel or beryllium copper. Their main purpose is rigid fixation against axial displacement, bearings and other parts on shafts and in holes. In the automotive industry, retaining rings are widely used to secure piston and connecting rod pins. According to their design and principle of operation, locking rings are divided into two types:
- internal – fix the part in the mounting hole;
- external – designed for fixing parts on shafts.
For installation and dismantling, the shanks of all retaining rings have mounting holes or special bevels and grooves; this difference depends not only on the modification of the ring, but also on its diameter. This feature is prescribed by standards and in no way affects the operation, quality and durability of the retaining rings. For installation and dismantling of each type, there is a large number of different locksmith tools, so there are no problems with installing and removing rings of different types.
There are domestic and foreign standards that control the production of these products. On the website you can familiarize yourself with and buy or order retaining rings of all existing standards, types and sizes.
Standards controlled release of retaining rings for fixing parts on the shaft:
GOST 13940 – concentric rings for shafts with a diameter from 4 mm to 200 mm (do not have mounting holes);
GOST 13942 - eccentric rings intended for shafts with a diameter from 4 mm to 200 mm are produced with holes, and for larger diameters without holes;
DIN 471 is an analogue of GOST 13942 and is produced in diameters from 3 mm to 300 mm.
Standards controlled by the production of retaining rings intended for fixing parts in holes:
GOST 13941 – concentric rings for holes with diameters from 8 mm to 320 mm;
GOST 13943 – eccentric rings, used in holes with diameters from 8 mm to 320 mm;
DIN 472 - is an analogue of GOST 13943 and is intended for holes within the range of 8 - 300 mm
There are quite a lot of different imported and domestic equipment on the market, so when selecting retaining rings, it is important to know that even if the diameters are the same, the thickness of some domestic rings differs from their foreign counterparts. And since they are installed in special grooves of increased precision, the slightest discrepancy can affect the operation of the entire assembly. For consultation, contact our managers, or study the reference literature yourself.
In addition to flat ones, there are special circular locking rings, which have a separate position:
DIN 7993 stipulates the production of circular retaining rings of two types: A - for shafts and B - for holes. They are used for installation on shafts and in holes with diameters from 4 mm to 125 mm.
Retaining rings, being small in size and low in price, take on significant static and dynamic loads, and the durability of your components and mechanisms may depend on the quality of these products. You can get more detailed information on each type of ring by following the links in the locking rings section. All supplied rings have official documents indicating testing and compliance with GOST standards, provided by the manufacturers.
You have the opportunity to clarify any questions you may have with our managers at the landline numbers listed on the website. For communication via the Internet there are contacts in Skype, ISQ and E-mail. You can pick up any purchased product yourself from our warehouses in St. Petersburg. We also cooperate with transport companies that will deliver your order to any region of Russia and the CIS.
Types of retaining rings according to DIN
In addition to Russian requirements, there are also foreign standards for retaining rings according to DIN of different sizes, which have nine groups.
DIN 471
Technical standards for eccentric inner product from 8 to 320 mm.
DIN 472
This foreign type is similar to the domestic GOST 13943-86. It includes spring and stainless steel, as well as galvanized steel.
DIN 703
This element is a target, fitted with a threaded hole for screws. In this case, coated and uncoated steel is used.
DIN 705
This is a steel adjusting ring for screws, type A (light series), supplied without screws. Manufacturing takes place from several types of steel:
- ordinary;
- coated;
- stainless steel
DIN 983
This standard applies to external locking rings with lugs for shafts with a diameter between 20 and 50 mm. The material used is steel spring.
DIN 984
These requirements apply to an internal retaining ring with lugs for the hole made of a powerful spring.
DIN 7993 external
This international standard is specific to an A-shaped external circlip made from a helix with shaft sizes ranging from 4 to 70 mm.
DIN 7993 internal
The technical standard is the same as in the previous one, only for the internal section, with shape B and a size from 7 to 18 mm.
DIN 6799
This type of standard refers to a quick-release washer that is part of a group of metal rings. In the working position, the element is capable of unbending due to the action of force. In addition, due to some elastic properties, the product can be fixed tightly.
DIN 472 Inner retaining ring
Home»DIN rings» DIN 472 Retaining ring internal sale
DIN 472 Inner retaining ring
for hole, spring-thrust eccentric. Hole diameter from 8 to 300 mm.
Materials:
- Spring steel
- Coated steel: galvanized
- Stainless steel: 1.4034, 1.4122, 1.4310, 1.4568
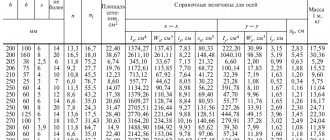
Size chart of internal circlips DIN 472 for bores (normal type) in mm
| d1 | s | d3 | A | b | d5 | d2 | m | n | d4 |
| 8 | 0.8 | 8.7 | 2.4 | 1.1 | 1 | 8.4 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 3 |
| 9 | 0.8 | 9.8 | 2.5 | 1.3 | 1 | 9.4 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 3.3 |
| 10 | 1 | 10.8 | 3.2 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 10.4 | 1.1 | 0.6 | 3.7 |
| 11 | 1 | 11.8 | 3.3 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 11.4 | 1.1 | 0.6 | 4.1 |
| 12 | 1 | 13 | 3.4 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 12.5 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 4.9 |
| 13 | 1 | 14.1 | 3.6 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 13.6 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 5.4 |
| 14 | 1 | 15.1 | 3.7 | 1.9 | 1.7 | 14.6 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 6.2 |
| 15 | 1 | 16.2 | 3.7 | 2 | 1.7 | 15.7 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 7.2 |
| 16 | 1 | 17.3 | 3.8 | 2 | 1.7 | 16.8 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 8 |
| 17 | 1 | 18.3 | 3.9 | 2.1 | 1.7 | 17.8 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 8.8 |
| 18 | 1 | 19.5 | 4.1 | 2.2 | 2 | 19 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 9.4 |
| 19 | 1 | 20.5 | 4.1 | 2.2 | 2 | 20 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 10.4 |
| 20 | 1 | 21.5 | 4.2 | 2.3 | 2 | 21 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 11.2 |
| d1 | s | d3 | A | b | d5 | d2 | m | n | d4 |
| 21 | 1 | 22.5 | 4.2 | 2.4 | 2 | 22 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 12.2 |
| 22 | 1 | 23.5 | 4.2 | 2.5 | 2 | 23 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 13.2 |
| 24 | 1.2 | 25.9 | 4.4 | 2.6 | 2 | 25.2 | 1.3 | 1.8 | 14.8 |
| 25 | 1.2 | 26.9 | 4.5 | 2.7 | 2 | 26.2 | 1.3 | 1.8 | 15.5 |
| 26 | 1.2 | 27.9 | 4.7 | 2.8 | 2 | 27.2 | 1.3 | 1.8 | 16.1 |
| 28 | 1.2 | 30.1 | 4.8 | 2.9 | 2 | 29.4 | 1.3 | 2.1 | 17.9 |
| 30 | 1.2 | 32.1 | 4.8 | 3 | 2 | 31.4 | 1.3 | 2.1 | 19.9 |
| 31 | 1.2 | 33.4 | 5.2 | 3.2 | 2.5 | 32.7 | 1.3 | 2.6 | 20 |
| 32 | 1.2 | 34.4 | 5.4 | 3.2 | 2.5 | 33.7 | 1.3 | 2.6 | 20.6 |
| 34 | 1.5 | 35.5 | 5.4 | 3.3 | 2.5 | 35.7 | 1.6 | 2.6 | 22.6 |
| 35 | 1.5 | 37.8 | 5.4 | 3.4 | 2.5 | 37 | 1.6 | 3 | 23.6 |
| 36 | 1.5 | 38.8 | 5.4 | 3.5 | 2.5 | 38 | 1.6 | 3 | 24.6 |
| 37 | 1.5 | 39.8 | 5.5 | 3.6 | 2.5 | 39 | 1.6 | 3 | 25.4 |
| 38 | 1.5 | 40.8 | 5.5 | 3.7 | 2.5 | 40 | 1.6 | 3 | 26.4 |
| 40 | 1.75 | 43.5 | 5.8 | 3.9 | 2.5 | 42.5 | 1.85 | 3.8 | 27.8 |
| 42 | 1.75 | 45.5 | 5.9 | 4.1 | 2.5 | 44.5 | 1.85 | 3.8 | 29.6 |
| 45 | 1.75 | 48.5 | 6.2 | 4.3 | 2.5 | 47.5 | 1.85 | 3.8 | 32 |
| 47 | 1.75 | 50.5 | 6.4 | 4.4 | 2.5 | 49.5 | 1.85 | 3.8 | 33.5 |
| 48 | 1.75 | 51.5 | 6.4 | 4.5 | 2.5 | 50.5 | 1.85 | 3.8 | 34.5 |
| 50 | 2 | 54.2 | 6.5 | 4.6 | 2.5 | 53 | 2.15 | 4.5 | 36.3 |
| d1 | s | d3 | A | b | d5 | d2 | m | n | d4 |
| 52 | 2 | 56.2 | 6.7 | 4.7 | 2.5 | 55 | 2.15 | 4.5 | 37.9 |
| 55 | 2 | 59.2 | 6.8 | 5 | 2.5 | 58 | 2.15 | 4.5 | 40.7 |
| 56 | 2 | 60.2 | 6.8 | 5.1 | 2.5 | 59 | 2.15 | 4.5 | 41.7 |
| 58 | 2 | 62.2 | 6.9 | 5.2 | 2.5 | 61 | 2.15 | 4.5 | 43.5 |
| 60 | 2 | 64.2 | 7.3 | 5.4 | 2.5 | 63 | 2.15 | 4.5 | 44.7 |
| 62 | 2 | 66.2 | 7.3 | 5.5 | 2.5 | 65 | 2.15 | 4.5 | 46.7 |
| 63 | 2 | 67.2 | 7.3 | 5.6 | 2.5 | 66 | 2.15 | 4.5 | 47.7 |
| 65 | 2.5 | 69.2 | 7.6 | 5.8 | 3 | 68 | 2.65 | 4.5 | 49 |
| 68 | 2.5 | 72.5 | 7.8 | 6.1 | 3 | 71 | 2.65 | 4.5 | 51.6 |
| 70 | 2.5 | 74.5 | 7.8 | 6.2 | 3 | 73 | 2.65 | 4.5 | 53.6 |
| 72 | 2.5 | 76.5 | 7.8 | 6.4 | 3 | 75 | 2.65 | 4.5 | 55.6 |
| 75 | 2.5 | 79.5 | 7.8 | 6.6 | 3 | 78 | 2.65 | 4.5 | 58.6 |
| 78 | 2.5 | 82.5 | 8.5 | 6.8 | 3 | 81 | 2.65 | 4.5 | 60.1 |
| 80 | 2.5 | 82.5 | 8.5 | 7 | 3 | 83.5 | 2.65 | 5.3 | 62.1 |
| 82 | 2.5 | 87.5 | 8.5 | 7 | 3 | 85.5 | 2.65 | 5.3 | 64.1 |
| 85 | 3 | 90.5 | 8.6 | 7.2 | 3.5 | 88.5 | 3.15 | 5.3 | 66.9 |
| 88 | 3 | 93.5 | 8.6 | 7.4 | 3.5 | 91.5 | 3.15 | 5.3 | 69.9 |
| 90 | 3 | 95.5 | 8.6 | 7.6 | 3.5 | 93.5 | 3.15 | 5.3 | 71.9 |
| 92 | 3 | 97.5 | 8.7 | 7.8 | 3.5 | 95.5 | 3.15 | 5.3 | 73.7 |
| 95 | 3 | 100.5 | 8.8 | 8.1 | 3.5 | 98.5 | 3.15 | 5.3 | 76.5 |
| 98 | 3 | 103.5 | 9 | 8.3 | 3.5 | 101.5 | 3.15 | 5.3 | 79 |
| 100 | 3 | 105.5 | 9.2 | 8.4 | 3.5 | 103.5 | 3.15 | 5.3 | 80.6 |
| d1 | s | d3 | A | b | d5 | d2 | m | n | d4 |
| 102 | 4 | 108 | 9.5 | 8.5 | 3.5 | 106 | 4.15 | 6 | 82 |
| 105 | 4 | 112 | 9.5 | 8.7 | 3.5 | 109 | 4.15 | 6 | 85 |
| 108 | 4 | 115 | 9.5 | 8.9 | 3.5 | 112 | 4.15 | 6 | 88 |
| 110 | 4 | 117 | 10.4 | 9 | 3.5 | 114 | 4.15 | 6 | 88.2 |
| 112 | 4 | 119 | 10.5 | 9.1 | 3.5 | 116 | 4.15 | 6 | 90 |
| 115 | 4 | 122 | 10.5 | 9.3 | 3.5 | 119 | 4.15 | 6 | 93 |
| 120 | 4 | 127 | 11 | 9.7 | 3.5 | 124 | 4.15 | 6 | 96.9 |
| 125 | 4 | 132 | 11 | 10 | 4 | 129 | 4.15 | 6 | 101.9 |
| 130 | 4 | 137 | 11 | 10.2 | 4 | 134 | 4.15 | 6 | 106.9 |
| 135 | 4 | 142 | 11.2 | 10.5 | 4 | 139 | 4.15 | 6 | 111.5 |
| 140 | 4 | 147 | 11.2 | 10.7 | 4 | 144 | 4.15 | 6 | 116.5 |
| 145 | 4 | 152 | 11.4 | 10.9 | 4 | 149 | 4.15 | 6 | 121 |
| 150 | 4 | 158 | 12 | 11.2 | 4 | 155 | 4.15 | 7.5 | 124.8 |
| 155 | 4 | 164 | 12 | 11.4 | 4 | 160 | 4.15 | 7.5 | 129.8 |
| 160 | 4 | 169 | 13 | 11.6 | 4 | 165 | 4.15 | 7.5 | 132.7 |
| 165 | 4 | 174.5 | 13 | 11.8 | 4 | 170 | 4.15 | 7.5 | 137.7 |
| 170 | 4 | 179.5 | 13.5 | 12.2 | 4 | 175 | 4.15 | 7.5 | 141.6 |
| 175 | 4 | 184.5 | 13.5 | 12.7 | 4 | 180 | 4.15 | 7.5 | 146.6 |
| 180 | 4 | 189.5 | 14.2 | 13.2 | 4 | 185 | 4.15 | 7.5 | 150.2 |
| 185 | 4 | 194.5 | 14.2 | 13.7 | 4 | 190 | 4.15 | 7.5 | 155.2 |
| d1 | s | d3 | A | b | d5 | d2 | m | n | d4 |
| 190 | 4 | 199.5 | 14.2 | 13.8 | 4 | 195 | 4.15 | 7.5 | 160.2 |
| 195 | 4 | 204.5 | 14.2 | 13.8 | 4 | 200 | 4.15 | 7.5 | 165.2 |
| 200 | 4 | 209.5 | 14.2 | 14 | 4 | 205 | 4.15 | 7.5 | 170.2 |
| 210 | 5 | 222 | 14.2 | 14 | 4 | 216 | 5.15 | 9 | 180.2 |
| 220 | 5 | 232 | 14.2 | 14 | 4 | 226 | 5.15 | 9 | 190.2 |
| 230 | 5 | 242 | 14.2 | 14 | 4 | 236 | 5.15 | 9 | 200.2 |
| 240 | 5 | 252 | 14.2 | 14 | 4 | 246 | 5.15 | 9 | 210.2 |
| 250 | 5 | 262 | 14.2 | 14 | 4 | 256 | 5.15 | 9 | 220.2 |
| 260 | 5 | 275 | 16.2 | 16 | 5 | 268 | 5.15 | 12 | 226 |
| 270 | 5 | 285 | 16.2 | 16 | 5 | 278 | 5.15 | 12 | 236 |
| 280 | 5 | 295 | 16.2 | 16 | 5 | 288 | 5.15 | 12 | 246 |
| 290 | 5 | 305 | 16.2 | 16 | 5 | 298 | 5.15 | 12 | 256 |
| 300 | 5 | 315 | 16.2 | 16 | 5 | 308 | 5.15 | 12 | 266 |
| d1 | s | d3 | A | b | d5 | d2 | m | n | d4 |
Legend: d1 - hole diameter s - ring thickness d3 - outer diameter of the ring a - eye width b - max. ring width d5 - hole diameter m - groove width n - edge height d4 - circle diameter
Analogue DIN 472:
GOST 13943-86 - spring thrust flat internal eccentric rings of accuracy classes A, B and C and grooves for them, intended for securing rolling bearings and other parts against axial displacement in holes with a diameter of 8 to 320 mm.
You can order and buy internal retaining rings DIN 472 in bulk at negotiated prices.
Which snap rings fit on the shaft and which ones fit in the hole?
Before you start working with the selection of elements, you must know where to install the hardware. Let's look at how metal products are used:
- external DIN 471, GOST 13942-86$ is used on the shaft
- the hole includes internal DIN 472, GOST 13943-86.
The choice of hardware should be approached with understanding; some dimensions must be removed. Remember, if you are installing it on a shaft, you need to measure the width of the groove and the diameter of the shaft. But for a hole it’s just the opposite.
Types of retaining rings
Retaining rings can be internal - inserted into the hole or external - mounted on the shaft. They are usually rectangular in cross-section, as they are made from sheet or tape. Although there are options made from round or oval wire.
There is also a difference in the anti-corrosion coating. This can be zinc or cadmium plating, or phosphating, as well as chemical oxidation by oiling. The choice of anti-corrosion coating for circlips is determined by the operating environment.
Design features
Metal products are widely used to secure bearings. The rings are inserted into the recesses so that the convex parts act as an offset. Products are made from different types of steel.
Rings may also have an anti-corrosion coating:
- oxidation with oils;
- zinc;
- cadmium;
- phosphating
There are five types of retaining rings.
| Varieties | Characteristic |
| External | used to secure elements to parts |
| Interior | help to hold the element in the body |
| Wire | have an elliptical shape, which provides a more uniform hoop tension, with large oval axes |
| Stamped | made by cutting from sheet materials |
| Chiseled | can be installed in different directions |
In the table below for the categories of retaining rings, it is worth taking into account the dimensions of the products.
Features of installation of retaining rings
Special pliers, also called circlip pullers, are used to install lug rings. Moreover, such forceps can have straight or curved jaws. The second type of jaws is used to install retaining rings in hard-to-reach places . For snap rings without lugs, use any suitable tool. To install a retaining ring on a shaft or inside a hole, it is necessary to make a seating groove of certain dimensions, which is called a “groove”. The groove geometry is clearly defined in the relevant ring standards.
Advantages of Spiral Retaining Rings
Retaining rings do not have “ears,” which make it much more difficult to assemble mating units. The products are made of flat rolled wire, so the surface of the part has no burrs, and its circumference for multi-turn models is 360 degrees.
Retaining rings are easily installed and removed from their internal and external grooves during operational maintenance of equipment using a standard screwdriver or other available tool.
The products have a homogeneous crystalline metal structure, precisely oriented along the rolled strip.
Standard products are made from carbon and stainless steel. For special products, according to customer specifications, special alloys with high temperature and chemical resistance are available.