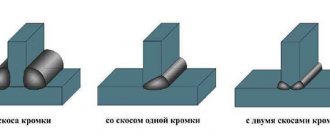
Pipeline supports
Since the pipeline is a critically loaded and very complex structure, its above-ground version cannot be built without a foundation, and underground communications should be protected from external influences and loads on the supports. According to the terminology of the standard, supports are a structural element, and not a transitional structure between pipes and foundations. That is, they are mounted on brackets, racks, other structures, and less often on the support foundations themselves.
Classification of pipeline supports
Initially, supports are divided into categories according to several criteria:
- structural material – reinforced concrete, profile;
- type of rolled metal used - tee, angle, channel, tubular;
- method of supporting pipes and their structures;
- the presence of a body - framed, frameless supports;
- number of provided degrees of freedom – fixed;
- possibility of adjustment - adjustable, non-adjustable, fixed;
- connection method - welded, yoke, with flat bracket;
- purpose - for bends, fittings, with support.
More than 75% of the supports can be used both as fixed steel and as sliding steel, movable steel, depending on the load of the sliding supports.
Types of pipeline supports:
Pipeline sliding supports
Sliding supports for pipelines – Sliding supports for pipelines Sliding supports for pipelines are actively used in the process of installing overhead pipelines. The advantages of such supports include a high level of resistance to vertical loads. The quality of these products makes it possible to talk about their maximum reliability. (sliding T13, T14, T15, dielectric: T16, T17, T18)
Movable pipeline supports
Movable pipeline supports – One of the main tasks of this device is to relieve the load from the pipeline. Movable supports are able to reliably support the pipeline, but at the same time they do not prevent it from moving. The use of movable supports makes it possible to reduce the vertical load from the mass of the pipeline itself. These products help the thermal movement of the pipeline both in the transverse direction and along its axis. (OPX1, OPC2, OPC3, OPP1, OPP2, OPP3, OPB1, OPB2, OPM)
Fixed supports for pipelines
Fixed supports for pipelines – Fixed supports for pipelines are used for the purpose of mounting and fastening pipelines for channelless installation. They can be used in both underground and above-ground systems. Fixed supports for pipelines take on the pressure that inevitably appears in the pipes when temperature changes or pulsations. (T3, T4, T5, T8, T9, T10, T44; T11, T12, OBN, OCN)
Spring block for pipelines
Thanks to its special design, the spring block provides shock absorption, protects pipeline elements from deformation and guarantees a long service life of the pipeline.
Pipeline suspension springs
Thermal power plants and nuclear power plants according to OST 108.764.01-80
Pipe hangers
GOST 16127-70 (PG, PM, PT, PSh)
In their production practice, Sapsan company specialists use all types of metal structures and pipeline supports. We are ready to help you choose the right supports for pipelines that meet the requirements of you and your customers and depending on the tasks.
Standards for the manufacture of pipeline supports
State support standards have been developed for two categories of products under consideration:
- from steel grades OPB (frameless), OPH, OPP (welded);
- GOST 16127 – pendants with the designation PM, PG, PMV, PGV.
Industry standards for supports on assembly units for fastening gas pipeline pipes in Moscow are 2.5 times higher:
- 275.24 – nuclear power plants;
- 125.154 – nuclear power plants, thermal power plants made of high-alloy and special steels;
- 36-94 – mobile highways;
- 36-104 – steel, pumping low-temperature media;
- 36-146 – series KN, VP, TO, KhB, UP, ShP, TP, KH, KP, TX, TP for diameters 57 – 1420 mm.
There are three subordinate specifications to the standards for the production of pipeline supports:
- 1468-012-04698606 – movable piping under pressure 10 MPa, temperature from -70°С to +450°С, diameters 18 – 1620 mm;
- 1468-002-92040088 – suspension, block modules for 32 MPa, DN 15 – 1600 mm;
- 1468-001-00151756 – for diameters 100 – 1400 mm, temperature -70°C, pressure 10 MPa.
Two series of assembly units of this type of pipeline supports have been developed:
- 903-10 – 4th outlet for fixed ones, 5th outlet for modifications, 6th outlet for suspensions;
- 903-13 – issue 6-95 suspension, issue 7-95 fixed, issue 8-95.
The album of drawings T-MM-26-05 includes options for the design of movable and dead supports for PS, ONS and OSS. The documentation NTS 65-06 contains working drawings and technical regulations for guides and moving supports of software and scientific organizations.
Hull
The arrangement of pipe support elements in a space often requires a box housing, bent from sheet steel or welded from individual blanks, to withstand high loads. Casing ones can be mounted on a beam, have stiffening ribs, and be equipped with cushions, clamps and support yokes in any combination. The housing provides lifting of the pipe by 100 - 200 mm, convenient fastening and maintenance during pipeline operation. Compared to the assortment of rolled metal, bent corners of technological supports are much cheaper, allowing for lower costs.
Method of mounting supports
During installation, supports should be located as close as possible to concentrated load areas, reinforcement, flanges and fittings. For pipes whose diameter does not exceed 50 mm, the supporting part is located at a distance of at least 50 millimeters from the weld seam.
When the pipeline diameter is over 50 mm, the support is placed at intervals of 200 or more millimeters. It is this installation that ensures a long service life and preserves the functionality of the pipeline for a long time.
You can purchase various pipeline supports (fixed and movable) from North-West ]metal structures[/anchor]. Large selection of parts and high quality guaranteed!
Unframed
The classic version of pipe supports is its open-frame modification. In the minimum configuration of fixed ones, this is a cradle bent from sheet steel to match the outer shape and diameter of the pipelines, usually called a “cushion” for horizontal pipes. In the expanded set of supports, the cradle is supplemented with a round, strip or tape clamp and a support plate for horizontal pipes with holes for its fastening. Due to low material consumption, simplicity of design and a minimum number of parts, a frameless support is considered the most cost-effective option for implementing a horizontal pipeline. Depending on the design of the supports, they are marked T11, HB, OPB.
Tubular
Structurally, tubular brackets consist of a pipe mounted vertically on a plate with mounting holes and welded. To increase the contact area of the support pipe with the pipeline, its upper end is cut to the shape of the junction (saddle-shaped cut with a laser or cutter). The production of such support pipes is regulated by the OST 36-146-88 standard; they are used for pipelines with a diameter of 57 - 630 mm with an ambient temperature within +450°C, and have four pipeline options - A1, B1, A2, B2. Products are marked with TR and their stainless steel, structural and carbon steel pipelines are manufactured.
Complete set of supports for the pipeline
Housing clamp pipeline supports KH, T-welded supports TP, tubular supports for steeply curved bends TO, channel welded supports ShP, coal welded supports UP, frameless clamp supports KhB, supports for vertical pipelines VP, roller guides KN, pipe supports TR are supplied as a set according to the drawings OST 36 -146-88. All stops, if necessary, are supplied together with supports.
You can buy OST 36-146-88 pipeline supports and ask any questions you are interested in, you can contact our managers by making a request by email or calling the office by phone
14454 views
T-bar
There are several constructive technological solutions for supports:
- for welding - a piece of the brand is installed on a single shelf, plates are welded at the ends, their upper part is adjusted to the outer surface (radius cut);
- strip or tape are welded on top of a piece of rolled metal, and holes for fastening are made in its flange.
Welded ones from the brand are designated TP and TX, respectively. Depending on the methods of mutual fastening of the support with the base and the pipeline, absolute immobility of the unit or several degrees of freedom of connection along the entire length can be ensured. Clamp supports The most common, both for movable and fixed connections of pipelines, are clamp supports, of several designs:
- rod;
- strip;
- tape;
- flat;
- drag;
- mounting on the body;
- use with frameless supports;
- installation on supports;
- use as a guiding element.
The clamp fits the pipe tightly around the perimeter and allows the use of gaskets made of dielectric and antifriction materials for fixed pipelines. It is possible to provide one degree of pipeline mobility along the axis of pipeline supports. An inverted U-shaped structure with or without stiffening ribs is considered classic. Sliding supports for pipelines with diameters of 57 – 377 mm are used, and yoke type supports for standard sizes 377 – 1420 mm. Assembly units have different markings, as they are manufactured according to different labor standards.
Welded
Sliding and movable for welding can be fixedly attached only to the base/stands, or sliding to the base and to the pipeline. There are several modifications of welded (sliding) supports:
- guide;
- motionless;
- motionless;
- sliding;
- corner;
- on a support beam with lugs.
Welded supports are made from rolled and bent angles, T-bars, channels, pipes or curved, welded bodies.
Vertical pipeline supports
According to the OST 36-17-85 standard, these vertical type products and piping of technological lines of fixed supports are manufactured. Usually this is a clamp attached to an angle or in a bent body of the supports. The supports of VP pipelines are designated in the documentation; fixed modifications of the supports are mainly used. The main characteristics of stationary ones are construction material, diameter, construction length, temperature and pressure of the working medium for pipelines. Yoke supports A yoke is a type of clamp with fastening elements - studs. There are several options depending on the design of the assembly unit:
- tubular;
- strip;
- case;
- stamped;
- stamped and welded.
The pipe is laid on a cushion or cradle that has holes for studs intended for pipelines. The yoke is installed on top, attracted by the threaded connection of the pipelines. Clamping can be carried out using a special steel mechanism, legs, traverses, clamps or beams. Roller bearings The main structural differences between roller bearings are:
- the presence of two or more support platforms;
- installation between bearing supports;
- the possibility of axial displacement of the pipeline by a given amount;
- lateral displacement of pipes within 50 mm in any direction.
There are one- and two-level supports, with one roller and several blocks, clips for pipelines of energy facilities, steel and spring modifications. Due to the rolling elements, friction and wear of support elements and pipelines are sharply reduced, the service life and maintainability of assembly units are increased.
Movable supports: all types of pipe protection
Movable pipeline supports are used in cases where it is necessary to provide the entire system with the ability to move freely in a certain direction. Such movable supports allow the pipe to move without fixing it strictly in one place. This is important in cases where the pipeline is used to transport liquids and other substances with varying temperatures. Such pipes expand and contract depending on temperature changes, and are therefore in motion. This means that they cannot be fixed motionless, otherwise damage to the entire system will occur. But, at the same time, it is necessary to ensure reliable fixation of the entire structure - that is why movable pipeline supports are used.
Types of supports
Movable supports for pipelines are divided into types depending on their functions:
- Sliding. Such fasteners move along structures along with the pipeline;
- Roller. Allowing the pipeline to move freely;
- Spring - absorb vibration;
- Ball. Such movable supports must accept lateral and axial loads.
Concepts such as sliding and movable support for pipes are often confused. However, in reality they are not the same thing. Sliding is only one of the types of movable supports. However, this type is used very often.
Sliding supports
Such movable supports do not interfere with the movement of pipes. Generally, pipeline sliding supports are easy to install and durable. There are several options for their fastening, including: clamps, welded joints, hangers, etc. The design can be supplemented with special gaskets, which should protect the pipe from abrasion and damage.
Roller supports
Such movable pipe supports consist of several elements. The sliding base and the so-called roller block are the main parts of the support. Roller blocks are divided into single-row and double-row, and are used for laying pipelines in tunnels. Roller movable supports can also be spring-loaded.
Spring supports
Such movable supports are needed to absorb the loads that fall on the pipeline. The movable spring support softens the pressure and protects the structure from damage. It comes in different types and can be single or double. Such a movable support is secured using clamps, support beams, traverses or welded feet. A variety of options will allow you to select fasteners depending on the type of pipes and operating conditions.
Ball joints
This type of movable support must also compensate for the expansion of pipes, which is affected by temperature. Movable ball bearings are suitable for process pipelines of different diameters. Their distinctive feature is a clip with balls. Such movable supports are well suited for large diameter pipes.
Frontal
With respect to the flow of the working medium and the body of the pipes, respectively, the frontal supports for the pipelines are located in a transverse projection. Windshields are classified according to material and design:
- panel - made of reinforced concrete, may have several stiffeners;
- thrust - two stops in the plane on both sides of the pipeline or four stops on all sides.
Double-support frontal supports are used for small axial loads, and four-support for large loads, respectively. The structure is reinforced as necessary with half rings and stiffeners under appropriate loads.
Fixed
In order to eliminate absolutely all degrees of pipeline mobility relative to pipeline supports and foundations, fixed supports are used, taking into account the loads. There are several options for their execution for specific operating conditions under small and large loads:
- "dead";
- for pipes in thermal insulation PPU;
- frontal, side thrust supports of the pipeline;
- drag;
- framed, unframed;
- for vertical boxes;
- persistent reinforced pipeline supports;
- panel reinforced concrete;
- welded
Fixed supports are designated LOP, suitable for diameters 32 – 1420 mm, designed for high operating loads.
Properties of fixed supports
The name itself suggests that they promote a stationary position of the pipeline. The function of fixed supports is to fix the pipes in the form specified in the design plan. Their mission is also to bear loads and resist inevitable pipe damage.
Kinds
| № | Marking | Application |
| 1 | TP | Welded, with a brand |
| 2 | TX | Having a clamp and a tang |
| 3 | TR | Tubular |
| 4 | KP | Welded housing |
| 5 | KH | Housing with clamp |
| 6 | ShP | Welded with channel |
| 7 | UP | Welded from corners |
| 8 | HB | With clamp, without housing |
| 9 | THAT | Made from pipes, designed for highly curved bends |
| 10 | VP | Welded, used for vertical pipelines |
Fixed supports for steel pipelines are classified according to standard grades:
In addition to these, there are about 15 more models; they are not used as often as those described above.
Clamp, welded and T-type fixed supports for steel pipelines are considered the most common and popular. To make a brand, an I-beam is used, which is cut into 2 identical parts. Or they cut out two smooth parts from a sheet of metal and weld them. To make the assembly rigid, intersecting ribs are welded into the T-bar.
The KP units contain a U-like element and internal stiffeners. They are attached with a shelf at the beginning, and the other ends are welded to the pipeline.
Sliding
One degree of freedom, and only in the axial direction, of the pipeline relative to the supporting structure is provided by sliding supports, which are a type of movable modifications. The number of design options is approximately equal to the number of fixed supports:
- welded;
- underlay and in a case for pipes in PPU thermal insulation;
- for power plant pipelines;
- with flat and bracket;
- sliding fixed and guides of several types;
- dielectric and yoke;
- frameless supports.
To reduce wear of pipes and structural elements, supports are used for heating pipelines as anti-friction gaskets, rollers and blocks.
Features of a fixed support
Static metal products are placed in utility lines that experience increased loads. The device compensates for movements of oil, gas, and water pipelines caused by sudden temperature changes, vibration, and an increase in internal pressure. It is used in the construction of heating networks, laying communications in the nuclear and oil and gas industries. Parts to support communications are especially in demand in northern regions, which are characterized by extremely low temperatures.
The fittings are installed next to the stuffing box expansion joints and locking elements. It is also fixed on branches from the main line, on straight sections of the heating main.
The main components of the equipment: load-bearing parts (reinforced concrete slabs, beams), on which special steel devices are firmly fixed.
There are several types of metal structures. The most common:
- frontal (2 and 4 thrust). They are used for large axial loads and effectively reduce local stress in the walls of the system.
- panel Reliably hold the pipe in a vertical plane. They are in demand when laying a pipeline through a wall.
- tow ropes Equipped with welded stiffening ribs that strengthen the metal structure.
- clamp The most common type of support elements is with flat or round clamps. It is easy to assemble, install and maintain. Compatible with process pipelines of different diameters.
Unloading supports
Allows you to compensate for gyro shocks, vibration and mechanical loads arising during the operation of pumping/compressor equipment, an unloading steel support for pipelines from a pipe with several degrees of freedom relative to the foundation for the supports. Unloading supports are manufactured according to SNiP 3.05.05-84 standards and are designated in the GPU documentation. The StroyNefteGaz company sells in Moscow and the regions of the Russian Federation any types of supports for pipelines, valves and fittings for the implementation of your projects. Standard products in the required quantity are always available in warehouses; production for individual orders takes 3–10 days, depending on the complexity of the execution, the range of items and their total quantity. We provide a two-month deferred payment, help with choosing a transport company, and offer delivery by our trucks. Expert advice and qualified technical support for the project as a gift to every customer.
Movable supports for fastening pipelines
Movable or sliding structures are used for fastening pipelines from 50 to 1620 mm. They take on vertical loads, which include the weight of the pipeline, the transported environment, atmospheric loads in the form of wind and precipitation.
Sliding steel supports for pipelines allow horizontal movement of the pipeline along its axis, which can occur due to thermal expansion of the steel walls of the pipeline.
The movable structure consists of:
- rigid base in the form of a channel;
- semicircular holder in the form of a clamp;
- clamp fastening;
- paronite gaskets;
- rollers.
Movable structures require a distance between them, taking into account the strength of the working surface of the highway. The distance between the supports can even vary depending on the diameter of the pipe.
Movable or sliding structures are divided into:
- Clamp fastenings with brackets.
- Suspended dielectric supports.
- Movable skating rink structures.
- Sliding ball bearings for lateral movement of the line.
Clamp movable structures are produced for fastening overhead technological lines with various transported substances.
Movable support
Clamp sliding bearings demonstrate the following advantages:
- long service life;
- ease of fastening;
- strength.
Sliding structures keep the pipeline from moving vertically but allow horizontal movement.
Calculation of pipeline fastenings
Calculation of pipeline supports consists of identifying the distance between them based on data on the strength and deflection of the pipeline, as well as the installation method and pipe parameters.
To calculate the values between movable structures, use the table “Design of Heat Networks” by A.A. Nikolaev.
For example, the table shows the following calculation for horizontal placement: with a minimum pipe diameter of 20 mm and a maximum working environment temperature of 60˚C, the distance between the supports will be 60 cm. The larger the pipe diameter, the larger the step between them.
For vertical placement, the calculation of the fastening pitch is carried out according to the same principle. For example, with a pipeline diameter of 40 mm and a temperature of 20 degrees, the pipe support will be placed at a distance of 138 cm, and at a temperature of 70 degrees - 113 cm.
Fixed metal supports are placed depending on the schematic characteristics of thermal communications. As a rule, their calculation involves the location of structures near the main line branch and shut-off valves, as well as on straight sections, based on their characteristics of expansion joints between the supports.
Pipe element blanks with fixed supports
To determine the distance between fixed pipeline structures, a calculation is performed using the formula: L = 0.9 x ∆L / (a(t-tpo)), in which
- ∆L – compensator capacity, calculated in mm (a table is used);
- a is the coefficient of linear expansion of steel walls during temperature fluctuations, calculated in mm/m˚С;
- L – length of the pipeline section for which the calculation is performed, calculated in m;
- t – calculation of the temperature of the working environment during installation, calculated in ˚С;
- t – ambient temperature;
- 9 – error value (10%).
Installation of panel reinforced concrete fixed support for a pipeline (video)
Installation of sliding and fixed supports
Once the calculations of the distance between the supporting structures are completed, installation can begin. The installation of moving elements is carried out before pulling the pipes through the cases. When installing fasteners, you should ensure that the factory integrity of the structure is maintained.
Metal cases should be insulated with seamless waterproofing material. A layer of lubricant is applied to the junction of the support and the case to minimize friction. After installing the structure, the clamps are welded. To ensure secure fastening, they are also tied. After completing all the work, it is better to paint the welding area for additional protection.
The installation of movable support structures occurs simultaneously with the laying of the linear part. To implement it there is no need to use special equipment. To ensure reliable connection, arc welding is used.
To secure fixed supports for gas pipelines or other networks, you must use the following parts:
- steel pipe;
- centralizer;
- thermal tape;
- polyurethane foam;
- hot-rolled sheet of at least 30 mm;
- galvanized or polyethylene sheath.
Installation of the supporting structure is carried out on a concrete base. It occurs in a certain step for the convenience of possible unhindered repair of the highway section.