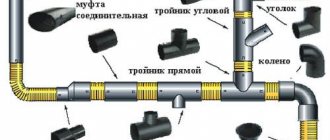
The principle of sewerage pipeline construction. The operating principle and sewage system in a private or apartment building have common and different features.
In an apartment building, all areas for draining water from plumbing fixtures are connected using pipes to a riser located vertically. All apartments located under each other are connected to one riser. Common pipelines from different entrances flow into the house collector, located horizontally. The collector has a slight slope so that the water flows by gravity further into the sewer well. Next, the waste is transported through pipes equipped with technological hatches to the centralized sewer main in the city.
Areas of application
The easiest answer would be: everywhere. Sewage now exists in all cities and towns, in all industries, in agriculture, in mines and oil production complexes, sinter plants and farms, railway stations and airports.
Almost all underground infrastructure of cities falls under the concept of “sewage” - after all, communication lines, the Internet, underground power networks laid in a shell or in boxes are also called sewerage. Houses without sewage systems now remain mainly in small villages and towns, but even there, septic tanks and systems are gradually being built for each house.
Polyethylene is the most popular material for external and internal sewage systems. It is durable and at the same time plastic. With slight movements of the earth, polyethylene communications will retain their integrity when steel or, especially, cast iron pipes break.
In cases of very heavy loads - depths of more than 10 m, aggressive or toxic wastewater and special requirements for the integrity of pipelines - polyethylene pipelines are not used.
Internal sewerage audits
The inspection is a tee, which provides access for cleaning the drainage pipe. Audits are installed in the sewer riser during the installation of the device in places that are prone to blockages.
SNiP regulates the installation of inspections and cleanings in the following places:
- If there are no indentations on the risers, the installation of the revision is carried out on the lower and upper floors of the structure.
- At the beginning of sections of outlet pipes that are connected to 3 or more devices without a cleaning device.
- At the bends of the sewer network.
- On horizontal sections of the pipeline, inspections and cleaning must be installed at least every 8 m.
Cleaning and inspection devices must be installed in places where it will be convenient to use them.
Specifications
Polyethylene sewer pipes are characterized by diameter, length, wall thickness and ring rigidity. In addition, polyethylene pipes are single-layer and double-layer, with a smooth wall and corrugated.
The SDR (Standard Dimension Ratio) coefficient of pipes is the standard ratio of the outer diameter to the wall thickness. Applicable to smooth-walled polyethylene pipes for pressure sewerage. SDR is taken from tabular data; the thickness of the pipeline wall, its annular rigidity, and strength depend on it.
Polyethylene is chemically inert and resistant to organic solvents at room temperature. The density of polyethylene is 0.94–0.96 g/cm³, it is lighter than water.
Production Features
Scientists have created many varieties of polyethylene. In relation to polyethylene pipes for sewerage, three names are usually mentioned: low-pressure polyethylene (LDPE), high-pressure polyethylene (HDPE), and medium-pressure polyethylene (MPD).
The concept of “pressure” in this case describes the features of PE production. PE produced by low and medium pressure methods has approximately the same density and molecular weight. LDPE has lower density and greater ductility. The methods differ in the catalysts and temperatures used.
Water seal for sewerage
A water seal is an artificially created water plug that prevents unpleasant sewer odors from entering the room. All plumbing fixtures are additionally equipped with a water seal device before connecting directly to the pipeline system. And only the toilet is connected directly to the sewer drain lines, since it has a built-in water seal in its design. A water seal for plumbing fixtures is a siphon filled with liquid.
There are different types of water seals:
- Special siphons for bathtubs;
- Double-turn;
- Tubular - used for kitchen sinks;
- Bottle;
- Corrugated;
- Gangways.
Water seals
A special type of siphon is a dry water seal, which combines a conventional water seal and a sewer check valve in one device.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of using polyethylene sewerage systems:
- Durability. When laid without exposure to ultraviolet radiation, you can count on 50 years of operation.
- Durability, resistance to crushing.
- Plasticity, tear resistance.
- Resistance to aggressive wastewater, corrosion, biological pollution, chemical inertness.
- Harmless to humans.
- Frost resistance. Polyethylene pipelines can withstand freezing with liquid inside, and after defrosting they return to their original shape.
- The pipeline does not become overgrown with calcium and magnesium salts from the inside.
- The smooth inner surface facilitates faster evacuation of contents.
- Low weight facilitates transportation and installation.
- The industry produces fittings of any shape and purpose. From bell-shaped or corrugated polyethylene products, you can easily assemble a sewerage system of any shape.
- Installation is quite simple and does not require highly qualified installers.
- Bell-shaped communications and pipelines on couplings with collet clamps can be disassembled and reassembled if necessary, pressure welded pipelines can also be used after disassembly (the sections will simply have to be increased).
One of the most significant advantages of polyethylene is its price. This is the most inexpensive plastic.
A serious drawback of polyethylene products is their instability to ultraviolet radiation. But for underground sewerage this drawback does not matter. In addition, polyethylene has a high coefficient of thermal expansion - during summer installation it is necessary to provide a small margin in length so that in winter the cold and reduced pipe does not experience stress.
Polyethylene seems to have been created for underground installation - this material has some advantages and no disadvantages at all.
Installation of branch lines
When the installation of sewer risers is completed, you should proceed to the next stage - installation of drain lines that connect plumbing fixtures to the system (bathtub, toilet, sink, cistern). SNiP regulate the installation of outlet lines for internal sewerage made of cast iron or plastic to choose from.
Installation of toilet drain lines
The diameter of the pipes that are used to drain sewage from plumbing fixtures must completely match the diameter of the drain holes to avoid leaks.
When installing branch lines, it is allowed to cut the pipes with a hacksaw perpendicular to the axial section. In this case, it is imperative to treat the resulting hangnails. Fittings and pipe bends must not be cut. If necessary, pipe elements can be treated with soapy water or a specially designed lubricant.
The drainage lines of the internal sewerage must be located at a slope towards the wastewater outlet, for a natural mechanism for draining water.
Kinds
All types of sewerage systems are divided into pressure and non-pressure according to the pressure in the pipelines.
By design - bell-shaped or smooth; smooth or corrugated. The design determines the installation method.
According to the material - from HDPE, LDPE, and other types of plastic.
By purpose - for sewerage in the traditional sense of the word (for transporting wastewater); for power, information networks, communication networks; for storm drainage; for drainage.
Plastic
For sewage systems, pipes made of different types of plastic are used: HDPE, LDPE, polyvinyl chloride, polypropylene. Cross-linked polyethylene is not used - it is too plastic and does not have sufficient ring rigidity. Besides, it's expensive. But my story is about polyethylene pipes, then we will talk only about them.
Gravity
When you hear the word “sewage”, what comes to mind is the traditional gravity flow system of socket elements. This is just a non-pressure sewer system - wastewater, rain or flood waters flow towards a lower level, along a slope. This system is used for small sewers in a private home, as well as when constructing urban infrastructure.
A remarkable advantage of gravity sewer systems is their reliability. Gravity exists everywhere; liquid, under the influence of gravity, tends to find the lowest place, flowing downhill.
If the sewer system is designed correctly and installed with high quality, then it works for many years, requiring virtually no human intervention, except for rare cleaning of pipelines and wells. Constant monitoring is not required.
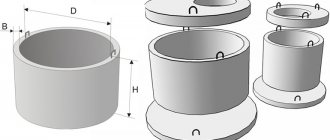
Structurally, such a system consists of polyethylene pipes laid with a slope and wells. The wastewater is collected in a centralized collector and discharged outside the populated area or to treatment facilities. The distance between wells is limited to 50 m, the pipeline should not have more than one turn (so that it can be cleaned from the well).
The slope in external sewerage systems is 1-2 (5) mm per linear meter. You should not exceed the slope, otherwise the sewage system will go deep into the ground, the volume of excavation work will increase, and a pumping station will be needed to transport the wastewater.
Nadornaya
A pressure sewer system is much less common. Pressure sewerage is used only in exceptional cases:
- If the central collector is located above the level of the receiving well or storage tank.
- If there is an obstacle on the pipeline path that cannot be bypassed in any other way except by raising the level (rock, basement, structures, railway track, highway).
- If it is necessary to use a pipe of small diameter and increase the speed of movement of the wastewater.
The design of a pressure sewer includes polyethylene pipelines, a pump or pumping station that pumps contaminated wastewater from a storage well into a gravity collector, storage tank, and municipal treatment facilities. A shredder must be installed in front of the pump to process large waste so that it does not clog the pump.
The pressure system requires frequent human inspection, the chopper and pump require constant attention (however, automation saves the day). But in any case, the equipment requires maintenance and complex repairs. If the chopper malfunctions, the system becomes clogged.
The advantage of the system: the possibility of constructing a long or narrow pipeline, application in conditions of height differences between the well and the collector or treatment facilities.
HDPE
HDPE, or HDPE – low-density polyethylene (high density, HDPE). This is the most inexpensive and widespread type of polyethylene. The phrase “low pressure” refers to the production conditions of PE, and not to the technical characteristics of the material.
Undyed PE is white, thin polyethylene products are transparent. Sewer pipes are painted: external ones are red, drainage pipes are painted green, internal pipes are painted gray or white.
Products made from HDPE have low cost, high plasticity, frost resistance, and do not burst when frozen. The strength of HDPE is sufficient to lay communications to a depth of about 5-6 m. HDPE is usually undesirable to use for internal wiring from a sink - at a temperature of 70-80 ° C it softens and loses strength.
PVD
High-density polyethylene (LDPE), or low-density polyethylene, is less durable than HDPE. It is not used for sewer pipes - it will collapse under soil pressure.
Corrugated
For sewerage pipelines operating in harsh conditions, the industry produces a durable two-layer polyethylene pipe with a corrugated outer layer and a smooth inner layer. Corrugation is a change in the diameter of the outer layer with a certain step. Corrugation gives the structure strength, rigidity, and at the same time flexibility.
There are rigid and flexible corrugated pipes. For underground communications, two-layer rigid corrugations are used - they have higher strength. The inner layer of corrugation is made of HDPE or LDPE. The outer one is made of less plastic HDPE, polyvinyl chloride or polypropylene.
The use of polyethylene corrugated pipes for underground communications has many advantages:
- increased strength;
- high resistance to deformation, rupture, crushing;
- easy installation;
- the ability to bend communications without fittings.
Corrugated pipe is used in situations where the sewerage system experiences heavy loads - when laid at a depth of more than 6 m, in rocky soil. During subsidence, cast iron communications can burst, and plastic corrugated pipes can stretch.
A serious disadvantage of corrugated pipes is their considerable price.
Dimensions, diameters and markings
Socket products in accordance with GOST 22689-2014 have a range of nominal diameters: 32, 40, 50, 63, 75, 80, 90, 100, 110, 125, 160, 200, 250, 315 mm. Wall thickness varies from 3 to 13.6 mm. The effective length of the elements ranges from 0.3 m for small products to 6 m for large diameter products.
Smooth-walled polyethylene pipes for pressure sewerage are produced in accordance with GOST R 54475-2011, Ø from 10 to 2000 mm. Diameters up to 180 mm - in coils and sections, larger sizes - only in sections.
Corrugated pipes in accordance with GOST R 54475-2011 are produced in lengths from 1 to 12 m. The diameters of corrugated two-layer polyethylene sewer pipes reach 2200 mm (starting from 110 mm).
Marking
Markings are applied to the surface of pipes and fittings at a distance of at least 1 m. The code includes the following symbols:
- manufacturer's name;
- international designation of the product brand (PE100, PE80, PE63 or PE 100, PE80, PE63);
- standard dimensional ratio SDR;
- dash;
- nominal diameter and nominal wall thickness;
- purpose - drinking or technical;
- standard.
For example: drinking pipe PE 63 SDR 21 – 32×3 GOST 18599-2001.
On gray and red products the markings are applied to the surface, but not always on black pipes. Marking of socket products:
- product name – TK (sewage pipe);
- nominal diameter (external) in mm;
- name of the material;
- Date of issue.
For example: TK 110-PE – sewer pipe, diameter 110 mm, PE – polyethylene.
Corrugation markings include:
- the word “pipe” or the name of the fitting;
- nominal size DN/OD or DN/ID (inner or outer diameter);
- nominal ring stiffness SN;
- abbreviated name of the material (Latin or Cyrillic);
- standard designations.
For example:
- PE polyethylene pipe with a nominal internal diameter DN/OD 200 mm, nominal hardness SN6;
- pipe OD 200 SN6 RE GOST R 54475;
- 90° tee made of PP polypropylene for pipes with a nominal outer size of DN/ID 300 mm, nominal hardness SN8;
- tee 90° ID 300 SN8 RR GOST R 54475.
Plastic products for sewerage are painted - this helps with their installation, storage and transportation. Bright red, blue, red and green communications are also easier to find during excavation work.
Applicable colors for polyethylene pipes:
- Pure black or black-gray are used for technical purposes.
- Products for internal sewerage are painted white, black, gray.
- The drainage is painted bright green.
- External sewer pipes are painted bright orange, red, or orange-brown.
- Black with a blue stripe and bright blue are used for drinking water supply.
- Yellow and black with yellow stripes are used for natural gas.
- Red color is used for protective pipes for laying electrical cables.
How to choose a diameter for connecting plumbing fixtures
The diameters for connecting indoor plumbing facilities are standardized: for a toilet - 110 mm, bathtubs, showers and Jacuzzis - 40-50 mm, bidets - 40 mm, sinks and sinks - 32-40 mm. If a pipeline is laid into a bathroom with several appliances, then all outlets are connected to a 50 mm pipe, while the outlets can have a smaller diameter, just select the appropriate adapters and tees.
A dishwasher or washing machine is connected through a tee to the outlet of a sink or sink of any diameter, or together with the sink to a 50 mm pipe.
The diameter of the drain pipe in a high-rise building is 100 mm; for a riser from kitchen sinks it can be 85 mm. For a riser in a two-story house, 50 mm or a vacuum valve is sufficient. The water consumption even from two vertically positioned toilets is small, so you don’t have to worry about pulling water plugs out of the sinks.
Installation of internal sewerage
Installation of internal sewerage is a responsible and labor-intensive process that must be carried out taking into account SNiP. Correct installation of the drainage system guarantees long-term and reliable operation of the system.
The installation of the sewer network should be carried out according to a pre-planned plan. If you do not have experience in drafting a project, it is better to entrust this task to a professional. After all, any mistake can lead to serious consequences and large financial losses.
Calculation of internal sewerage is carried out according to the formula
V(H/d)1/2 ≥ K, where V is the fluid velocity; H/d – filling; K = 0.5 – for plastic pipes; K=0.6 - for metal pipes.
It is best to start installing internal sewerage with the most labor-intensive process - laying pipes. It is recommended to start laying the pipeline from the plumbing fixtures to the point where the system exits to the outside of the building. In one-story buildings, it is better to install sewerage under the floor. In the case of a two-story house, sewer pipes should pass above the floor of the upper floor.
Requirements for polyethylene pipes according to GOST
GOST standards according to which polyethylene sewer pipes are produced:
- socket pipes and fittings are produced in accordance with GOST 22689-2014;
- smooth – GOST 18599-2001;
- corrugated - GOST R 54475-2011.
All types of pipes must comply with GOST in shape, size, fit within dimensional tolerances, have nominal dimensions from the size range according to GOST, and have strength in accordance with regulatory documents. The most important parameters are the external and internal parameters, dimensions, shape of the socket, wall thickness, ring stiffness.
Tips on how to choose
Almost all sewerage pipes are made from inexpensive and fairly durable HDPE. The choice of a specific type of product and installation method depends primarily on the conditions of laying the sewerage system - depth, pressure; its type - pressure or non-pressure. For pressure pipes, long polyethylene pipes are always chosen and installed like water supply pipelines.
For conventional non-pressure pipes, socket pipes and fittings are used. For very deep sewers, in places with the risk of landslides, land subsidence, in regions with increased seismic hazard, a two-layer corrugation is used.
The diameters for internal wiring are described above. For external systems in private houses, pipelines with a diameter of 110 mm are used; for risers and horizontal sections in a private house, 110 mm is also sufficient; to collect wastewater from several wells, communications with a diameter of 160 mm or more are laid. Large diameter pipelines are used for municipal sewers.
Rules for installing a sewer riser
The location of the sewer riser is most often a toilet or bathroom. According to SNiP, the sewer riser can be of an open or closed type, however, in any case, the distance from the pipe to the wall must be at least 2 cm. The main rules that must be followed when carrying out installation work:
- The diameter of the riser must be the same along its entire length.
- The diameter of the riser must be calculated depending on the amount of wastewater discharged.
- Sewer risers must be positioned strictly vertically.
- Each sewer riser ends with ventilation, which leads to the roof or attic of the house.
- For cleaning, sewer risers are equipped with special inspections.
The permissible SNiP deviation of the riser is only 2 mm per 2 m from the intended vertical.
Installation of a sewer riser