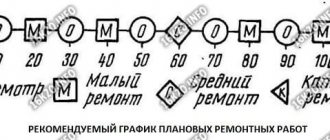
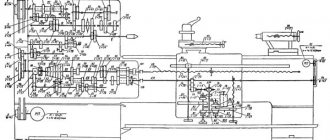
Device for grinding lathe bed
In situations where turning equipment fails, it is not at all necessary to purchase a new expensive unit. After proper repairs, lathes will again be able to efficiently and effectively perform all technological operations for metal processing. Before understanding such a process as repairing a lathe, it is necessary to remember what turning is and how the equipment for its implementation is designed.
It is not always possible to buy new equipment. There is only one way out - repair
Repair of lathes - general principles
During the operation of the lathe, sooner or later you will encounter some kind of malfunction. The likelihood of a breakdown is especially high if you are using a unit with considerable mileage. In this case, you need to be prepared not only for minor malfunctions, but also for the possible need to overhaul the lathe, and this is a very, very expensive undertaking.
Fortunately, the design of most units (especially those produced during the Soviet era) is simple enough for you to cope with the repair of a lathe without the involvement of a third-party specialist.
Below, using the 1K62 model as an example, we will look at the most common breakdowns, the causes of their occurrence and methods of elimination.
If in practice you encounter the problems described, you will most likely be able to carry out repairs on your own, following the recommendations below.
Main breakdowns, causes and methods for their elimination
The initial cause of most malfunctions in the operation of a lathe is improper operation and care of the equipment. The technician should know how to service the unit. This will allow you to save considerable amounts in the future, since major repairs of lathes are expensive, even if you do the repairs yourself.
Experts recommend that before starting to work with the machine for the first time, you study in detail the operating instructions and other documentation that comes with the equipment. If you purchase a used machine without instructions, then it makes sense to find all the documentation related to the 1K62 unit or any other model yourself on the Internet.
Now that you have learned about the intricacies of operating your “assistant,” it’s time to study the most common breakdowns and how to fix them. For ease of understanding, we present tips for repairing a 1K62 lathe in the form of a list:
Features of turning and machine design
When carrying out turning, the problem is solved by reducing the diameter of the workpiece, which performs a rotational movement while being fixed in the spindle of the machine. Removal of the layer of excess metal (due to which the diameter of the workpiece is reduced) is performed by a cutter equipped with a cutting edge.
It can make movements in the longitudinal (feed) and transverse directions. By setting the parameters of these movements (rotation, longitudinal and transverse movement of the cutting tool), you can regulate the thickness of the layer of metal being removed and the shape of the chips and influence the quality of the processing performed.
The main structural components of a lathe group machine include:
Basic elements of a metal lathe
The listed components, which require regular maintenance and sometimes repair, can have various modifications, which determines the purpose and functionality of the machine (multi-tool, turret lathe, etc.).
Installing the lead screw and shaft
The procedure for combining the axes of the lead screw and shaft with the feed box and apron of the lathe is well demonstrated by a video of such a process.
This procedure is performed in the following sequence.
I repair the guides of small calipers, milling attachments - geometry correction, finishing scraping. Dimensions - starting from small watchmaking machines such as Boley, Bergeon, Lorch, etc., T-28, schaublin 70, T-65, etc. up to size schaublin 102, C-1, MN-80, TV-16, TSA-16
The need for repairs and preparation for it
The most common situations in which repair of a turning unit, rather than maintenance, is required are wear of guides, bearings, failure of forks that switch elements of gear connections, etc. Naturally, after a period of prolonged operation, turning equipment needs a major overhaul, to which should be properly and thoroughly prepared.
The level of vibrations and noise emitted by worn-out components of a lathe is determined when the equipment is idling. In addition, the axial and radial runout of the spindle assembly is checked. To diagnose the condition of the rolling bearings, it is necessary to process a test workpiece and compare the obtained geometric parameters with the required values. In many cases, such actions allow you to avoid major equipment repairs and limit yourself to eliminating local faults.
If a major overhaul of a lathe is still necessary, before doing so it is necessary to thoroughly clean the equipment from dirt and dust that has accumulated during its operation. All technical fluids required for the operation of the machine (oil, coolant) must be drained. Then they check whether all structural elements of the equipment are in place.
Lathe repair cost
| Type of work | Price |
| Spindle Prevention | 9,000 rub. |
| Troubleshooting clamping devices | 19,000 rub. |
| Burnout (damage) of the stator winding | 30,000 rub. |
| Replacing bearings with rotor balancing | 50,000 rub. |
| Replacing spindle sensors | 10,000 rub. |
| Maintenance | 10,000 rub. |
| Non-standard work | 10,000 rub. |
| Major renovation | 50,000 rub. |
| Modernization of machine tools | 30,000 rub. |
Our main specialization is machine repair
If your machine does not work, our specialist will arrive as soon as possible and fix it. Call and consult by phone: 8
Technologies
Thanks to the use of modern devices, we can more accurately identify faults. And we save your money on repairs
Ideas
If your machine does not break down as usual. We will send it to our technicians and they will solve any problem
Speed.
You need the machine to work as quickly as possible. Our desires coincide.
Read useful information:
Repair of turret lathe
Any equipment fails sooner or later, this also applies to a commodity turret machine. In order for the machine to serve for a long time, and for the products made on it to meet the standards, it is necessary to carry out repairs and maintenance regularly.
Further
Machine head repair
The headstock is an important element of the machine. If this part fails, it is very difficult to cope with the repair yourself and you have to contact specialized workshops
How to prevent breakdowns, what is important to know when doing your own repairs and how much the services of qualified craftsmen cost - all this can be found in the article
Further
Repair of the electrical part of the machine
The slightest malfunction of the electrical part of the machine can disrupt the plant’s work schedule
It is important to be able to identify the source of the problem and eliminate it
Further
Turret machine repair
In case of significant breakdowns of the turret machine, a lot of difficulties can arise. In the article you can learn about the types of such equipment, as well as how to carry out repairs yourself and how much the help of specialists will cost.
Further
Guide repair methods
The choice of method for repairing the guides of lathes (it is quite difficult to carry out such repairs yourself, without special equipment) depends on how badly these structural elements are worn, what hardness they have, how well technically equipped the repair team that will carry out this work is. difficult procedure.
Worn lathe bed guides
Bed guides that have undergone significant wear after long-term use can be restored in different ways: planing, milling, scraping (with or without lapping), pulling, grinding, rolling using special rollers. The most common methods used to overhaul a lathe bed include planing, scraping, and sanding.
The amount of wear on the guides can be determined only after all dirt and existing nicks have been removed from their surface. To determine the gaps present on these components of the lathe, apply a metal ruler to them and, using a feeler gauge, identify the most worn areas that require urgent repairs, taking measurements every 30–50 cm.
Checking the bed using a homemade device
Experienced specialists can identify the most worn areas of the bed guides using thin paper, the thickness of which does not exceed 0.02 mm. Such paper is placed on the lathe components in question and pressed against them with a metal ruler. In those places where the guides have not undergone serious wear, the paper does not pull out from under the ruler, but breaks off along its edge.
Scraping, although it is a rather labor-intensive process, is performed quite often, as it allows you to effectively restore the geometric parameters of the lathe components in question.
Determination of the least worn areas of the bed
Repair by scraping
Scraping of guides or scraping followed by lapping remains the most effective way to restore their geometric and technical accuracy. And now this method is often used, demonstrating excellent results in machine bed repair for many decades. First of all, it is necessary to examine the condition of the guides and determine the degree of their wear. The place where the wear is minimal is taken as the base level, and the measurement data is entered into a table, on the basis of which repairs will be made. In a lathe, the base surface is most often taken to be the location of the tailstock, which practically does not wear out during operation of the equipment. The method includes the following steps:
- installation of the machine bed on a rigid base (repair stand), the longitudinal and transverse position of the bed should be adjusted exactly in the horizontal plane using wedges, shoes or using jacks;
- after completion of the preparatory work, rough (preliminary) scraping is performed with a working scraper width of 20-25 mm, while maintaining a length of strokes on the surface of more than 10 mm and achieving 4-6 spots when checking paint in 25x25 mm squares. This achieves the breakdown of large spots into smaller ones;
- semi-finish scraping is performed with a 12-16 mm scraper, stroke length 5-10 mm until 8-15 spots per square are achieved;
- finishing (finishing) scraping is carried out with a scraper 5-10 mm wide and strokes 3-5 mm long to achieve 20-25 spots per square.
[Show slideshow]
Since the guides of the lathe bed are quite long, processing is carried out along the beacons, dividing the total length into sections. The first beacon is always the place of maximum production. At a distance less than the length of the straight edge from the first beacon, a second beacon is scraped, located in the same plane as the first. Then the entire surface between the beacons is scraped, followed by moving to the adjacent area. Periodically, apply a ruler with paint to assess the condition of the guides and the quality of work.
Watch the video of rough scraping
Non-hardened parts of lathe guides are subjected to this treatment; the method guarantees the achievement of high surface accuracy (0.002 mm per 1000 mm length). The tiny holes formed after scraping are able to hold the lubricant well and distribute it evenly. The quality of scraping depends entirely on the professionalism of the worker.
Table of contents
Lathes are used to process cylindrical parts. They include many varieties that differ in size and additional functions. Industrial models such as the 16K20 lathe are very common and widely used in modern industry. In order for the device to function normally, you need to know all the features of its parts.
The lathe bed serves to secure almost all mechanisms and components that are used on this equipment. It is often cast from cast iron to create a massive and durable structure that can last a long time. This is due to the fact that it will be subject to heavy loads. You should also not forget about stability, since massive large models use enormous energy during operation and the base must resist the load well.
Repair by grinding
It is not always possible to use planing or longitudinal milling machines for repairs due to the long length of the lathe bed. In this case, the bed guides are restored using a portable device with a grinding head, which is installed directly on the equipment bed.
Repairs can be made on site, without removing the machine from the foundation. This method ensures high repair accuracy, low surface roughness, and is also indispensable when processing hardened surfaces. This method is many times more productive than scraping, but experts still prefer finishing planing.
[Show slideshow]
How to repair a caliper carriage
A major overhaul of the caliper carriage involves restoring its lower guides connected to the frame guides. In addition, when restoring this unit, it is necessary to ensure that the plane of its movement is perpendicular to the planes on which the apron of the lathe and its feed box are fixed. To determine the degree of deviation of these planes from the norm, a level and probes of various thicknesses are used.
As a result of a major overhaul, the lathe carriage must be aligned parallel to the transverse travel of the support with an accuracy of 0.02 mm over a length of 300 mm. This parameter is checked using a special indicator, which is fixed in the tool holder of the lathe.
Repair of carriage guides
The parameters of the carriage guides are restored using special compensation pads or acrylic plastic, and the cross slides are repaired by grinding. The upper slides of the caliper, if they need repair, are first scraped and aligned, then they are ground.
Communities › Garage Equipment and Tools › Blog › Restoring a TV6 lathe
Hello, I bought myself a TV6 to restore. I've been trying to restore it for 3 months, it seems to me there is no end in sight until completion. I’ll briefly tell you what I managed to do. Let me make a reservation: I’m a newbie when it comes to restoration and scraping. Let me start by saying that I bought it in a rather worn condition for 10 thousand rubles. I took everything apart, cleaned it, cleaned it. Painted it with hammer paint. The hardest part for me was the scraping. I scraped like a collective farm, without special tools. I didn’t find a straight edge, I didn’t buy it for 7t, and I didn’t find a stove either. I went through some friends and found a proprietary milled level (it is the smoothest of all). I couldn’t find the scraper either, a turner I knew told me to scrape it with a file, the Chinese fitted the dial indicators with a stand, and paid 1900 rubles for 2 indicators and a stand (in general, a collective farm set). I shabril for a very long time, more than one week. Everything worked out, I did not expect such a result. There is no gap between the caliper and the bed. When I sharpened the L-shaped clamps under the caliper, I was afraid that the location of the caliper in another would be clamped and the plates would have to be substituted. But everything fit perfectly, the caliper moves smoothly without any snags. Since the old worn-out apron on the machine was lowered and the movement of the caliper occurred in jerks due to the large gap between the longitudinal rack and gear, when the lead screw nut was turned on, the shaft moved higher, and also the longitudinal feed shaft. I got out of this situation by removing one millimeter from the upper parts of the apron (first I scraped it with a grinder, then with a washer). The result is that the jerks disappeared when the caliper moved, it says that when the lead screw nut was closed, the shaft did not move. The small longitudinal one took one day, it was convex. The tool holder was all bent, straightened with a press, scraped with a pneumatic grinder, the minus of this holder was miniature cutters (in the future I will buy a new one with 20mm cutters). I placed a U-shaped plate under the tailstock and raised it by 1mm. I installed 2 bearings in the cross feed, but the nut will have to be changed. I installed seals in both boxes. I replaced one bearing in the headstock. I turned off the thread in the drain hole, made a new plug, drilled the hole to 14 step 1. In the feed box, when installing the oil seal on the longitudinal feed shaft, problems appeared, I don’t know if I did it right, I installed a ball from the bearing between the feed shaft and the box shaft, it’s huge The play at the feed shaft has disappeared. The ball came out about 7mm. I made shaft protection, a tray, and 2 covers for the right frame for electrics. Handles for steering wheels. New tags. The tags were made of aluminum. I used a laser printer to print a mirror photo of the tags on varnished paper. The aluminum was sanded, wiped with acetone, the printed text was placed, covered with a sheet of paper and the sandwich was smoothed with an iron. I waited until it cooled down and removed the paper from it. Where there were any imperfections, I filled them in with spray paint and a toothpick. Then I coated it again with spray varnish. There are just a few small things left, for example, making a shift knob, I want to make it out of epoxy and much more, but the main thing is to at least get it running.
I have a question. I haven’t found a motor for 1500. But I have one for 3000, if I put the frequency control at low speeds will it handle it?
Source