Typical repair work performed during scheduled repairs 16K20
During the period between repairs, it is necessary to carry out inspections of the machine. The regulations provide for the following procedure for servicing the unit:
— Six inspections — One small repair — One medium repair
The timing of repairs is indicated in the recommended schedule of planned repairs:
Maximum efficiency of using the machine is achieved only with a rational alternation of inspections and scheduled repairs, carried out taking into account specific operating conditions, individual for each case.
Categories of machine repairability:
mechanical part - 12; electrical part - 8.5.
Technical inspection of the machine:
- External inspection without disassembling the machine, both completely and individually, in particular to identify defects.
- Checking the strength and tightness of fixed rigid connections. At the same time, the base with the foundation is inspected; bed with base; spindle head; feed boxes with frame; carriages with apron; pulleys with shafts, etc.).
- Opening the covers of units for inspection and checking the condition of the mechanisms.
- Removing play in the screw pair of the cross slide drive.
- Checking the correct switching of spindle speeds and feeds.
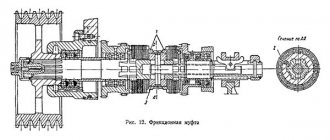
- Adjusting the friction clutch of the main drive and the spindle band brake.
- Checking the condition, cleaning and minor repairs of enclosing casings, shields, etc.
- Checking the condition and minor repairs of the lubrication system.
- Identification of worn parts that require restoration or replacement during the next scheduled repair.
Inspection before major repairs:
Work performed during inspections before other types of repairs and, in addition, identifying parts requiring restoration or replacement, sketching or ordering drawings of worn parts from assemblies undergoing disassembly.
During the inspection, those of the listed works are performed, the need for which is determined by the condition of the machine.
Repair cost
| Type of work | Price |
| Spindle Prevention | 9,000 rub. |
| Troubleshooting clamping devices | 19,000 rub. |
| Burnout (damage) of the stator winding | 30,000 rub. |
| Replacing bearings with rotor balancing | 50,000 rub. |
| Replacing spindle sensors | 10,000 rub. |
| Maintenance | 10,000 rub. |
| Non-standard work | 10,000 rub. |
| Major renovation | 50,000 rub. |
| Modernization of machine tools | 30,000 rub. |
Our main specialization is machine repair
If your machine does not work, our specialist will arrive as soon as possible and fix it. Call and consult by phone: 8
Technologies
Thanks to the use of modern devices, we can more accurately identify faults. And we save your money on repairs
Ideas
If your machine does not break down as usual. We will send it to our technicians and they will solve any problem
Speed.
You need the machine to work as quickly as possible. Our desires coincide.
Read useful information:
Overhaul of machines
Not one unit can work forever. To restore the functionality of turning equipment, they often resort to major repairs. It is difficult to carry out this process on your own, so it is worth contacting a company that specializes in repairing these units.
Further
How to set up a machine correctly
But before you start working, all the machines need to be set up. How this happens and what it means is written below in the article.
Further
Causes of machine gearbox malfunctions, methods for eliminating them, cost
The article talks about common failures of the gearbox of a lathe. Their causes and ways to eliminate them yourself are described. The approximate cost of repairing a machine gearbox in Moscow is also given.
Further
Machine bed repair
The accuracy of its operation depends on the condition of the guide frames of turning equipment. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out timely repairs of equipment and its hotel elements.
Further
Repair of turret lathe
Any equipment fails sooner or later, this also applies to a commodity turret machine. In order for the machine to serve for a long time, and for the products made on it to meet the standards, it is necessary to carry out repairs and maintenance regularly.
Further
When concluding a long-term service agreement, you receive a discount of up to 20%. Don't forget, we have a guarantee on all types of work.
- engineer - mechanic
- CNC programmer
- Service engineer
- Electrician
- Electronics engineer
- Locksmith - repairman
Minor repair of lathe 16K20
For minor repairs to this screw-cutting lathe, only those of the following tasks are performed that are caused by the condition of the machine being repaired. The exception is the last three points - this work must be performed in all cases.
Work carried out:
- Partial disassembly of the spindle head, feed box, apron, as well as other most contaminated components. Opening covers and removing casings for internal inspection and washing of other components.
- Cleaning the mounting surfaces for fixtures on the spindle and tailstock quill without dismantling them.
- Checking the gaps between shafts and bushings, replacing worn bushings, adjusting rolling bearings (except spindle bearings), replacing worn ones.
- Adjusting the main drive friction clutch, adding discs, adjusting the spindle band brake.
- Removing burrs from splines and gear teeth.
- Replacement or restoration of worn fasteners and adjusting parts of tool holders.
- Scraping or cleaning of adjusting wedges, clamping bars, etc.
- Cleaning the lead screw, lead shaft, transverse and tool slide drive screws of the caliper.
- Cleaning and washing the seating surfaces of the cutting head.
- Checking the operation and adjustment of levers and handles of controls, locking, locking, safety mechanisms and limiters.
- Replacement of worn crackers, pins, springs and other parts of the specified mechanisms.
- Replacement of worn parts that are unlikely to withstand use until the next scheduled repair.
- Cleaning nicks, burrs, burrs and scratches on the rubbing surfaces of the bed guides, carriages, caliper slides and tailstock.
- Repair of enclosing casings, shields, screens, etc.
- Repair and flushing of the lubrication system and elimination of leaks.
- Regulating the smooth movement of the carriage and caliper slide; tightening the wedges of the clamping bars.
- Checking the condition and cleaning of gear couplings.
- Checking and repairing pneumatic equipment and cooling systems; eliminating leaks.
- Identification of parts requiring replacement or restoration during the next scheduled repair.
- Checking the accuracy of machine installation and selectively other accuracy parameters.
- Testing the machine at idle speed at all speeds and feeds, checking for noise, heating and on the workpiece for accuracy and cleanliness of processing.
Average repair of a lathe 16k20
Work carried out:
- Check for accuracy before disassembly.
- Measuring the wear of rubbing surfaces before repairing base parts.
- Partial disassembly of the machine.
- Washing, wiping parts of disassembled units, washing, cleaning of dirt from undisassembled units.
- Control of the rigidity of the spindle assembly.
- Replacement or restoration of worn bushings and rolling bearings.
- Replacing or adding friction discs and replacing the spindle brake band.
- Replacement of worn gears and couplings.
- Restoration or replacement of worn screw pairs of the caliper slide drive and tailstock quill.
- Replacement of worn fasteners.
- Replacement or restoration and adjustment of adjusting wedges and clamping bars.
- Restoring the accuracy of the lead screw by cutting.
- Checking and cleaning unworn parts left in the machine mechanisms.
- Repair of the coolant supply pump and fittings.
- If the hinge mechanism of the lamp NKS 01 x 100/POO-03 wears out, unscrew the base, turn it counterclockwise 90° and secure it again.
- Repair of the lubrication system pump, equipment and fittings; repair or replacement of oil indicators, gaskets, plugs and other elements of the lubrication system.
- Correction by grinding or scraping guide surfaces in need of repair if their wear exceeds the permissible level.
- Repair or replacement of protectors on the carriage, caliper slide, tailstock.
- Repair or replacement of enclosing panels, casings, screens, etc.
- Assembling repaired components, checking the correct interaction of components and all machine mechanisms.
- Painting external non-working surfaces with putty.
- Running in the machine at idle speed at all speeds and feeds.
- Check for noise and heat.
- Checking the machine for compliance with accuracy standards.
Overhaul of lathe 16K20
Work carried out:
- Checking the machine for accuracy before disassembling.
- Measuring the wear of rubbing surfaces before repairing base parts.
- Complete disassembly of the machine and all its components.
- Washing and wiping all parts.
- Inspection of all details.
- Clarification of the list of defective parts requiring restoration or replacement, previously compiled during inspections and repairs.
- Restoration or replacement of worn parts.
- Cooling system repair.
- Replacing the lubrication system pump and repairing it.
- Grinding or scraping the guide surfaces of the bed, carriage, caliper slide, tailstock.
- Replacement of protectors on the carriage, caliper slide, tailstock.
- Assembling all machine components, checking the correct interaction of components and mechanisms.
- Puttying and painting of all unfinished surfaces in accordance with the finishing requirements of new equipment.
- Running in the machine at idle speed at all speeds and feeds.
- Check for noise and heat.
- Checking the condition of the foundation, correcting it and installing the machine.
Repair cost.
The cost of spindle repair depends on the power manufacturer and the type of fault. Relatively minor repairs (rewinding motor windings, replacing spindle sensors, repairing clamping/unclamping) range from 20 to 60 thousand rubles. Comprehensive repairs can range from 150 to 300 thousand rubles. As a rule, expedient repairs come out to 1/3 of the cost of the spindle. In some situations, it is more profitable to buy a new spindle. When doing your own repairs, you can save money and buy, for example, a set of bearings, but you won’t get much benefit; in addition, you need to have special skills and experience in precise installation and balancing.
Conclusion.
If you have a large enterprise and have highly qualified personnel with experience in repairing spindles, as well as an appropriate workshop and the equipment necessary for repairs, then it makes sense to engage in independent repairs. The benefit here is rather in the downtime of the machine; independent repairs will speed it up. Otherwise, it is better to contact a service center or, under the manufacturer’s warranty, the supplier of the machine (spindle).