Main types
All bearings can be divided into two main groups - rolling and sliding bearings. The design of the first consists of
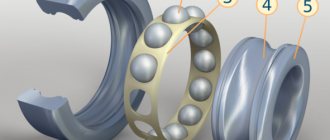
- two rings – external and internal;
- balls;
- separator in which the balls are installed.
- Sliding bearings have the following design:
- outer ring;
- an internal race made of a material with a low coefficient of friction, for example, Teflon (fluoroplastic).
The task that bearings of any type are designed to solve is reducing friction between the rotating and stationary units of the unit. This is necessary to reduce energy losses, heating and wear of parts caused by friction.
Plain bearings
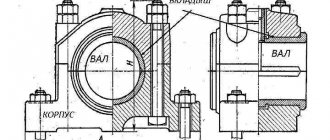
Spherical plain bearings
This unit is usually made in the form of a massive support made of metal. A hole is made in it, into which a sleeve or liner made of a material with a low coefficient of friction is inserted. To increase the efficiency of this unit and reduce friction, liquid or dense lubricant is introduced into it. This results in the shaft being separated from the bushing by a film of oily liquid. The operational parameters of a plain bearing depend on the following parameters:
- The size of the elements included in this node.
- The speed of rotation of the shaft and the size of the loads falling on it.
- Thickness of the lubricant.
To ensure bearing lubrication, you can use any viscous liquid - oil, kerosene, emulsions. Some models of plain bearings use gases for lubrication. In addition to the listed materials, solid lubricants are also used, sometimes called greases.
Some bearing designs include a forced lubrication system.
Rolling bearings
Appearance of a rolling bearing
In bearings of this type, sliding friction is replaced by rolling friction. Thanks to this solution, there is a significant reduction in friction and wear. Rolling bearings come in a variety of designs and sizes. Balls, rollers, and needles can be used as bodies of revolution.
Ball bearings
Ball bearings are the most common type of bearing. It consists of two rings, between which a separator with pre-installed balls of a certain size is installed. The balls move along grooves, which are carefully ground during manufacturing. After all, for the bearing to function properly, it is necessary that the balls do not slip, and at the same time they have a significant support area. The separator into which the balls are installed ensures their exact position and eliminates any contact between them. Manufacturers produce products that are equipped with double-row separators.
Bearings of this class are used with fairly small radial loads and a large number of revolutions of the working shaft.
Roller bearings
In bearings of this class, rollers of various shapes are used as rotating bodies. They can have the shape of cylinders, truncated cones, etc. Manufacturers have mastered the production of a wide range of roller bearings with different sizes of rings and rotating bodies. Tapered roller bearings are used to operate under multidirectional loads (axial and radial) and high shaft speeds. Structurally, a roller bearing is similar to a ball bearing. It also consists of two rings, a cage and rollers. The dimensions of roller bearings are defined in a number of standards that are valid in our country. For example, GOST 8328-75 defines the design, marking and dimensions of bearings with short rollers. And GOST 4657-82 regulates the dimensions and design of needle bearings. That is, for each type of bearing there is its own GOST.
Roller bearings: internal structure
Ball bearings: internal structure
These regulatory documents contain tables of bearing sizes that designers should follow when designing such units.
By the way, to make life easier for designers, bearing reference books have been developed and are successfully used, which outline the principles for calculating bearing units and indicate the dimensions of the products themselves and accompanying parts, for example, the dimensions of plugs.
What are the types and types of bearings?
All assemblies can be classified according to their operating principle. Two main groups are devices that provide rocking and sliding. They are the ones most often used in mechanical engineering. The first can be represented by ball and roller devices.
Magnetic structures deserve special attention. The principle of their operation is different from the others, and they are used less often. In addition, due to their functional features, they must be accompanied by spare units.
Bearings are parts that help to obtain maximum efficiency from a machine, maintaining its performance without special repairs and maintenance.
Sliding supports
This group of parts allows you to slide freely when two contacting surfaces rub against each other. In this case, various lubricants are used - oils, water, chemicals, graphite and some gases. Structurally, such devices can be either integral or collapsible. Manufactured complete with bushing and connecting part.
Devices by rolling type
Such units are made in the form of two rings, bodies that provide a rocking effect, and a separator. They are manufactured in accordance with established standards, which allows them to be used in most cars, complex equipment and aircraft.
Ball bearings
Functionally, they are part of a group of node parts that operate on the rolling principle. Ball bodies are located on the surface of the outer rings of the parts. During operation, they create a small friction moment, which means they practically do not limit the rotation speed.
Roller bearings
They are part of the rolling group, but they are based on balls replaced by rollers. This allows them to withstand much greater loads. This performance is highly valued in the design of industrial machines and railway construction.
Magnetic supports
They work on the principle of levitation of attraction, ensuring complete non-contact of two adjacent parts. They can be used in aggressive environments, but are not yet as common as the types already listed. If you do not back up such a design with another, more traditional one, you can lose the entire car overnight.
Lubrication
The service life of bearings is determined by the wear of the rolling elements and tracks located in the rings. To extend the service life of bearings, lubricant is used; it can be liquid, for example, in gearboxes of machine tools, or grease (solid).
Applying grease to the bearing
Grease applied to the bearing
In addition to the wear of bearing parts, the operating temperature in the unit also plays an important role. As a result, uneven thermal deformation may occur. This can lead to increased slippage rates and reduced hardness of the material from which they are made.
Manufacturers produce bearings with closed cages. In such products, even at the production stage, a solid lubricant is added, which is guaranteed to last the entire service life.
Classification by accuracy
Rolling bearings are installed in the units, on which the effective operation of the entire mechanism as a whole depends. At the same time, such products are manufactured in compliance with the standards provided by GOST. In terms of accuracy, rolling bearings can be classified according to:
- sizes;
- rotation parameters.
In the first case, the quality of the product is determined by deviations in the outer and inner diameters, as well as the width of the rings. Rotational accuracy is measured by the degree of runout in the radial and lateral directions. At the moment, in this regard, the following classes of rolling bearings are distinguished:
- 0 - normal with runout of the inner ring (up to 20 µm);
- 6 - increased accuracy with runout (up to 10 microns);
- 5 - high accuracy with runout (up to 5 microns);
- 4 - especially high accuracy (up to 3 microns);
- 2 - ultra-high accuracy (up to 2.5 microns).
The industry also produces coarse, with runout over 20 microns, class 7 and 8 rolling bearings. The price of such products is determined mainly by the class of rotational accuracy. The higher it is, the more expensive the bearing costs.
Types of plain bearings
In total, the dimensions and main characteristics of plain bearings are set out in the relevant GOSTs. There are about six dozen of them in total. For example, GOST 11607-82 normalizes the requirements for split housings of sliding bearings, and GOST 25105-82 sets requirements for liners that are installed in housings of sliding bearings.
Classification of plain bearings
Products of this type can be divided into the following main types:
- Single and multi-surface.
- With displacement of surfaces.
- Radial.
- Axial.
- Radial thrust.
In addition, bearings can be distinguished by design:
- One-piece, they are called bushings.
- Detachable, they consist of two parts of the main body and a cover for it.
- Built-in by design, they form a single whole with the mechanism body.
We must not forget about the number of oil supply points. There are bearings with one and several valves. In addition to the above classes, one more can be named - possibly bearing regulation.
The design of plain bearings is not complicated. The structure may include two rings. One of them (internal) rotates during operation. Instead of rotating bodies, devices of this type use bushings made of antifriction materials. To improve efficient operation, lubricants are pumped into the bearings.
There are two types of plain bearings - hydrostatic and hydrodynamic. In products of the first type, lubricant is supplied from an oil pump. The latter are more convenient in this regard; they themselves can act as a pump. Lubricant will flow into them due to the pressure difference between its components.
Sliding bearings can have spherical, thrust and linear designs. The first bearings are used in those units where low shaft rotation speeds predominate. The main advantage of this design of bearings is the ability to transmit rotation even with significant shaft misalignments.
Thrust bearings are used for work where transverse forces predominate. Quite often they are installed in turbines and steam engines.
Thrust bearing diagram
Thrust bearings
Linear bearings act as guides. By the way, their feature can be called their uninterrupted operation even with constant radial forces.
Linear bearing
Long-term, if not centuries-old, practice of using sliding bearings allows us to draw conclusions about the advantages and disadvantages of these designs.
- products of this class provide reliable operation under conditions of high shaft rotation speeds;
- ensuring serious shock and vibration forces;
- quite small in size;
- bearings of this type can be installed in devices operating in water;
- Some models allow you to adjust the gap and thus guarantee the accuracy of the shaft axis.
Meanwhile, sliding bearings also have certain disadvantages.
- during operation it is necessary to constantly monitor the lubricant level;
- with insufficient lubrication and starting, additional friction force occurs;
- lower efficiency compared to other classes of bearings;
- quite expensive materials are used in the production of such products;
- During operation, bearings of this class can generate excessive noise.
Classification by size
In this regard, several groups of similar products are also distinguished. Depending on the ratio of the sizes of the inner and outer rings, the classification of bearings is as follows:
- especially light;
- lungs;
- lungs are wide;
- average;
- medium-wide.
Also, heavy products of this type can be used in units and mechanisms. Below is a table of sizes of single row ball bearings.
Depending on the series, in this case, with the same diameter of the inner ring, the diameter of the outer ring or its width may vary. By width, rolling bearings are classified into:
- especially narrow;
- narrow;
- normal;
- wide;
- especially wide.
The table of ball bearing sizes presented above shows the parameters for light and medium series products.
Plain Bearing Standards
One of the differences between bearings and other types of parts used in industry is that they are all standardized. It was noted above that products of this class are subject to 60 GOST, and this does not count the specifications and other regulatory documentation. GOST not only normalizes the design and dimensions of bearings, but also the order of their designation in drawings, specifications and other working documentation.
In addition, GOST for technical conditions of bearings regulates the parameters of tolerances and fits that manufacturers must comply with.
Main advantages and disadvantages
Sliding bearings are somewhat simpler to manufacture than rolling bearings. They can be used in a variety of nodes. For example, such bearings are often used for electric motors.
The advantages of sliding bearings, among other things, include the following advantages:
- quiet operation;
- Possibility of use in heavily loaded nodes.
In addition, the advantage of bearings of this type is that they eliminate wobble very well.
But products of this variety, of course, also have their drawbacks. The main disadvantage of such bearings is the difficulty of maintenance. In order for such a part to serve for a long time and perform its functions well, it is placed in an oil bath or pumps are used to constantly supply the latter.
Also, the disadvantages of plain bearings are:
- impossibility of use in very hot components (oil may ignite);
- the need to use expensive non-ferrous metals in construction;
- increased triggering factors;
- increased axial dimensions.
Marking
Bearing markings are parameters that show the working diameters of the product (internal and external), design features. All this data is encoded in a set of numbers and alphabetic characters. The coding procedure and detailed decoding are regulated in GOST standards for bearing products. Thus, the coding of single-row ball and roller bearings is given in GOST 3189-89.
The encoded bearing name contains the following data:
- width series;
- execution;
- product type;
- diameter group;
- landing diameter.
By the way, it is important to understand that in our country two bearing designation systems are used - GOST and ISO.
An example of decoding markings on bearings
The marking can be applied to one of the rings. If the bearing is a closed type, then the marking is applied to the seal or protective ring.
Letter "N"
For each type of bearing it means certain features.
| Bearing type | Peculiarities |
| Double row spherical roller radial | in the middle of the outer ring there is an annular groove, and there are also three holes for introducing lubricant |
| Single row ball | presence of holes for lubrication and recesses on the outer rim |
| radial roller with short rollers | They do not have an outer or inner ring |
| persistent | The diameter of the “free” ring meets the requirements of ISO 104:1994, their inner rings differ from each other by a small amount |
Bearing accuracy classes
The accuracy class of a bearing is an indicator that characterizes the maximum deviations of the bearing dimensions from the nominal value.
In some devices, when choosing a bearing, the consumer is guided by its price, and other parameters are not so critical for him. In some other cases, the consumer chooses a bearing based on the maximum rotation speed at which phenomena such as vibration, etc., will not appear. Such rather stringent conditions are imposed on products operating in transport, machine components, and robotic complexes.
In mechanical engineering, there is a relationship between processing accuracy and its cost. That is, the more accurate the part, the higher its final price.
Separation of bearings by accuracy allows you to select a product that will meet the requirements set by the designer and at the same time with an acceptable price for the consumer.
The accuracy class describes the accuracy of the production of products. To regulate these parameters, there are standards defined in GOST and ISO. They define tolerances for all dimensions - diameters, widths, chamfers, etc.
Comparison between different systems
As follows from the table, the international ISO standard, as well as regional JIS, DIN, ANSI/AFBMA, suggest that the normal accuracy class (Class 6x, ABEC1, RBEC1) is the minimum possible. GOST 520-2002 allows for lower accuracy classes 8 and 7, but their use is not recommended, and in global practice, bearings with such low manufacturing accuracy have fallen out of use. In addition, the Russian standard introduces an accuracy class T, which is not available in ISO.
The table allows you to find the equivalent of bearings from different manufacturing countries. In the case where there is no direct match, the closest class is selected upwards.
For example, on American equipment it is necessary to replace a factory inch tapered roller bearing with Class 2 accuracy with an analogue from a European manufacturer. However, there is no such class in the ISO 578 standard. Then it is necessary to select a Class 3 bearing as the closest in terms of manufacturing accuracy characteristics. Bearings of classes 8, 7, T are replaced in the equipment of Russian manufacturers in a similar way.
Magnetic bearings
Magnetic bearings, which are increasingly used in various machines and mechanisms, operate on the principle of magnetic levitation. As a result of the implementation of this principle in the bearing support there is no contact between the shaft and the bearing housing. There are active and passive executions.
Active products are already in mass production. Passive ones are still under development. In them, permanent magnets of the NdFeB type are used to obtain a constant magnetic field.
The use of magnetic bearings provides the consumer with the following advantages:
- high wear resistance of the bearing unit;
- the use of such products is possible in aggressive environments in a wide range of external temperatures.
Non-contact magnetic bearing
At the same time, the use of such nodes entails some difficulties, in particular:
If the magnetic field disappears, the mechanism will inevitably suffer damage. Therefore, for uninterrupted and trouble-free operation, designers use so-called safety bearings. As a rule, rolling bearings are used as safety bearings. But they are able to withstand several system failures, after which they need to be replaced, so their sizes will be changed.
The creation of a permanent, and most importantly, stable, magnetic field is associated with the creation of large and complex control systems. Such complexes cause difficulties with the repair and maintenance of bearing units.
Excessive heat generation. It is due to the fact that the winding heats up as a result of the passage of electric current through it; in some cases, such heating is unacceptable and therefore it is necessary to install cooling systems, which, of course, leads to a more complex and expensive design.
SKF
This company designates bearing types with the following letters:
- C – toroidal products;
- VK – needle roller bearings with a closed end and a stamped outer ring;
- K - the same as the previous products only without rings;
- N – designation of cylindrical roller bearings;
- NA – needle roller bearings with dimensions corresponding to ISO 15;
- NJ – cylindrical roller bearings with two flanges on the outer ring and one on the inner ring;
- NK – needle roller bearings;
- NN, NNU – double-row roller bearing units;
- NU – single-row cylindrical products, the outer ring of which has no sides, and its inner analogue has two of them;
- NUP - almost the same as the previous product, only its inner ring has a flange and a flange ring;
- T – tapered roller bearings, the parameters of which comply with the ISO 355-1977 standard;
- QJ – ball bearing units with four-stroke contact.
Characteristics of rolling bearings
The main characteristics of rolling bearings include the following:
Angular speed, rolling bearings can show high values of this speed, especially if the cages are made of non-ferrous metal or polymers.
Shaft misalignment. It is acceptable that the skew can reach from 15' to 30'. In addition, rolling bearings are capable of absorbing small axial forces. It should not exceed 70% of the unused radial load capacity.
Rolling bearings show minimal friction losses.
Letter "B"
The main parameters of the bearing units remain the same, but their internal design has been modified. The meaning of this letter depends on which series of bearings it is in.
| Designation | Bearing type | Design features |
| B | tapered roller bearing | a contact angle of 40 degrees is provided |
| BE | single row angular contact ball bearing | in it the internal part is optimized, but the contact angle remains the same |
| BEM | -//- | everything is the same as in the previous version, only there is a machined separator |
| BEJ | -//- | its stamped steel cage is installed in the product along the balls |
| BEP | -//- | it uses a molded cage made of glass-filled polyamide |
| BEY | -//- | The contact angle of the product is 40 degrees, its internal part is optimized, and the brass cage is centered in the bearing along the balls |
Catalog of imported bearings FAG, INA, SKF, NSK, TIMKEN, etc.
The bearing industry occupies a separate place in the global economy, largely due to the importance of the products it produces.
In our country, such products are produced at specialized bearing factories. But recently, imports of bearings from abroad have increased significantly. They are supplied from different countries of the world - the USA, China, Germany, etc.
To get acquainted with the range of supplied products, it is enough to familiarize yourself with the bearing catalogs offered to consumers by foreign manufacturers - FAG, INA, SKF, NSK, TIMKEN and many others. One glance is enough and you can understand the full range of bearings offered.
FAG magnetic bearing
INA brand bearing
NSK bearing
SKF bearings
TIMKEN bearings
But when ordering imported products, you must understand that bearings coming from abroad must meet the requirements of our standards and have documents confirming their quality and safety in operation. Bearings are very often made. We recommend purchasing bearings only from authorized suppliers.
Decoding
Deciphering rolling bearings is important for determining its characteristics. In order for the consumer to have the opportunity to purchase for himself exactly the bearing that he needs, such products are designated by manufacturers in a special way. The labeling of such products always contains several numbers by which its class and series can be determined.
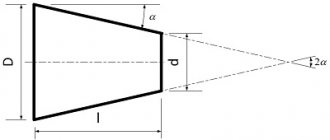
Decoding of rolling bearings is carried out, according to the standards, from right to left. The first and second digits indicate the internal diameter of the product. To determine the actual size, simply multiply this number by 5.
Based on the third number, you can find out the outer diameter of the bearing, that is, its series. The latter are designated as:
- ultra-light - 8 or 9;
- extra light - 1 or 7;
- light - 2 or 5;
- average - 3 or 6;
- heavy - 4.
Using the fourth number from the right in the marking, you can decipher the type of rolling bearing:
- 0 — radial single-row ball;
- 1 - double-row radial ball;
- 2 - radial with cylindrical short rollers;
- 3 - double-row radial roller;
- 4 - needle-shaped;
- 5 - radial with twisted rollers;
- 6 - angular contact ball;
- 7 — angular contact roller conical;
- 8 - thrust ball;
- 9 - thrust roller.
Using the fifth and sixth numbers from the right, you can determine the design features of the bearing that do not have a particular impact on its performance characteristics. Such products can be, for example, non-separable, have a protective washer, a groove on the outer ring, etc.
The seventh number on the right in the marking characterizes the bearing series in width.
Of course, when purchasing, you can easily find out the accuracy class of such a product. Decoding the designations of domestic bearings based on this criterion is also absolutely simple. To the left of the considered series of numbers in the marking of such parts there is another number through a dash. It is by this that accuracy is determined.
Bearings of classes from 0 to 6 can be used in various types of components. In this case, normal products of this type, marked with the number 0, are most often used. In parts operating at high frequencies, very high-quality bearings, designated 4-5, are usually used. Products of class 2 are most often used in hygroscopic devices.