In nature, the purification of melt and waste water is carried out in a natural way, in the reservoir where the water flows from the soil. But this process is long and is not designed for such volumes of pollution as industrial wastewater from nearby enterprises.
Therefore, human help in cleaning up nature is simply necessary. Dirt, grease, dust and small debris require careful filtration before the water in which they are contained reaches the natural body of water. All treatment facilities available to humanity are divided into several categories according to the type of treatment, and we will tell you about each in detail.
Various fields of science have been involved in developing the most effective methods for treating wastewater, and therefore today we have several options for solving the problem. The choice between them depends both on the degree of contamination of the water and on the requirements for the level of its purity when passing through filtering devices.
Main methods (methods) of wastewater treatment
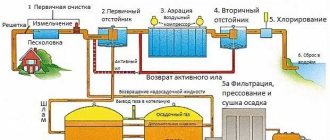
The equipment and technologies with which wastewater will undergo the purification process are selected in accordance with the requirements of many modern standards. They take into account the degree of pollution of wastewater, the concentration of impurities contained in it, their type and other factors. Today, three main types of wastewater treatment are considered: mechanical, biological and physicochemical. A separate type of cleaning is disinfection (disinfection) of water. Most often, wastewater treatment at enterprises is carried out using mechanical, chemical or biological methods, and in some cases combined methods are used.
Mechanical wastewater treatment
This method is also called filtration. Mechanical cleaning is usually divided into several stages. First, the water is passed through mesh filters that trap large particles of debris, then the water is sent to a sand trap - a structure for separating heavy mineral particles (sand, glass, etc.). Next comes the stage of purification from less dense liquids - petroleum products, oils, fats. It is carried out by a grease trap. The final stage on the way of wastewater into the river is its settling in special tanks. However, even after one cleaning cycle, the water is not yet considered “drinkable”, because only 60% of the dirt has been removed from it. Therefore, many treatment plants carry out two or more treatment cycles before discharging water into natural bodies of water.
Biological wastewater treatment
It is more often considered as one of the stages of complex wastewater treatment. The essence of the method is to immerse harmless aerobic and anaerobic organisms in wastewater, the accumulation of which is called activated sludge. During the purification process, the water becomes saturated with nitrogen and phosphorus. After cleaning, the sludge is removed and the water is sent to the next stage of treatment. It is worth noting that biofilm (activated sludge) works well in the fight against foreign organic compounds in contaminated water.
Physico-chemical wastewater treatment
This method is optimal for working with colloidal systems in which dirt and unnecessary minerals are suspended. There are several methods of physical and chemical cleaning:
- Aeration is a process during which a large amount of oxygen is released in wastewater, which promotes the occurrence of oxidative reactions.
- Sorption is a purification process using coal or peat.
- Thermal desalination is a process in which clean water is evaporated from a contaminated liquid.
- Electrochemical treatment is the process of separating sulfates and radioactive substances from water.
- Coagulation is a technology using reagents to separate out sediment of impurities.
- Neutralization is the process of restoring the normal level of activity of hydrogen ions in a solution using various acids, including hydrofluoric acid, whose trivial name is “fluoric acid.”
Purification by adding reagents
The method of purifying liquid waste with reagents is used mainly for purifying water containing a large amount of one type of contaminant, when the normal ratio of the alkaline and acidic components in the water is significantly in one direction.
Most often, this is necessary when the contamination has a pronounced appearance and cleaning by mixing does not give results or is simply irrational due to the increased concentration. The only and most reliable method of neutralization in this case is the method of adding reagents - chemicals that enter into a chemical reaction.
In modern technologies, this method is most often used for acidic wastewater. The simplest and most effective method of neutralizing acid is usually to use local chemicals and materials. The simplicity and effectiveness of the method lies in the fact that waste, for example, from blast furnace production, perfectly neutralizes sulfuric acid pollution, and slag from thermal power plants and power plants is often used to add to tanks with acid discharges.
The use of local materials can significantly reduce the cost of the cleaning process, because slag, chalk, limestone, and dolomite rocks perfectly neutralize large amounts of heavily contaminated wastewater.
Waste from blast furnace production and slag from thermal power plants and power plants does not require additional preparation other than grinding; the porous structure and the presence of calcium, silicon and magnesium compounds in the composition allow the use of materials without pre-treatment.
Chalk, limestone and dolomite used as reagents must undergo preparation and grinding. In addition, for cleaning, some technological cycles use the preparation of liquid reagents, for example, using lime and an ammonia water solution. In the future, the ammonia component greatly helps in the process of biological water purification.
Carp check: design and most effective types of treatment facilities
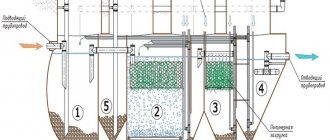
In simple terms, typical treatment facilities are a cascade of tanks located one behind the other. First, there is a rough “catch” of large fragments of garbage that came along with sewage. Then the wastewater is sent for settling, purified with sludge, settled again, freed from surface dirt, again sent for additional treatment to the first “baths,” and so on. As a result, the last “baths” receive clear, odorless water, in which you can even wash your hands if necessary. Particularly advanced treatment plants can even boast that real carp splash freely in the final tanks - living “measures” of the cleanliness of wastewater. But this is only provided that the systems successfully cope with their purpose.
Typical sewage treatment plants installed on the territory of industrial enterprises are also equipped with special “crusher” grids, within which the above-mentioned mechanical filtration of wastewater is carried out. This process is also often called straining. Then other technologies come into play: the feasibility and features of their use are determined depending on the nature of the discharge. The following treatment systems are considered to be the most effective:
Sand traps. These structures, as already mentioned, are used for primary wastewater treatment and, as the name suggests, they “specialize” in removing sand and other small components from water.
Septic tanks. These are special containers whose purpose is to collect wastewater that has undergone mechanical treatment. During settling, suspended particles and impurities contained in wastewater are precipitated. In addition, at this stage, biological wastewater treatment begins.
Clarifiers. A separate, more efficient type of settling tank, with a special design and natural aeration.
Oil traps. Another “telling” name, indicating that this type of treatment is effective for removing petroleum products from wastewater. Oil traps operate due to the difference in density of water and oil products, and are optimal when the content of oil particles exceeds 100 mg/l.
Hydrocyclones. These installations perform cleaning by separating solid particles in a rotating liquid. The type of hydrocyclone is determined based on the size of such particles.
Biofilters. Such systems filter wastewater through a special loading material, which ensures the formation of a thin biological film on the surface of the wastewater, facilitating the effective treatment of domestic and industrial wastewater.
Treatment facilities of chemical enterprises
The variety of methods is due to the composition and concentration of wastewater components. Methods used in the treatment of wastewater from chemical industry enterprises:
- mechanical cleaning;
- flotation;
- physical and chemical cleaning;
- membrane methods;
- biological treatment.
Mechanical cleaning
Water clarification is used to remove suspended substances 5-10 microns in size, solid or liquid fine and coarse particles formed during coagulation and flocculation from wastewater. Clarification can be achieved using sedimentation, filtration, flotation, and sedimentation in a centrifugal field. The degree of clarification depends on the requirements for the quality of purified water.
The clarification method allows you to extract valuable impurities from the solution and then use them in production.
When wastewater flow is low and flows uniformly, batch settling tanks are used. For large wastewater flows, continuous settling tanks are used, which in turn can be vertical, horizontal and radial. To settle in a thin layer of liquid, tubular and plate sedimentation tanks are used.
If there are high requirements for the quality of purified water, filtration is used as the final stage of purification. Filtration occurs on filters with a filter baffle or granular loading.
Flotation
To separate fat-like substances and some suspended matter from wastewater, the flotation method is used, which consists of treating wastewater with dispersed air and forming flotation foam. Using flotation, valuable impurities can be extracted from wastewater.
There are pressure, impeller flotation and electroflotation. The choice of flotation method depends on the type and concentration of contaminants, wastewater flow rate and the required degree of purification. The efficiency of flotation is increased with the help of reagents (flocculants and coagulants).
Physico-chemical methods
Physicochemical methods include the reagent method of wastewater treatment, in which acids and alkalis are neutralized, ions are converted into poorly soluble compounds, heavy metal ions are removed, and dissolved inorganic impurities are coprecipitated. In some cases, hydrolysis is used.
The neutralization method is used in cases of formation of acidic or alkaline wastewater. It is possible to balance the pH by using reagents or passing through a neutralizing filter, which includes limestone, dolomite, and magnesite.
Membrane methods
Commonly used membrane methods for treating wastewater from the chemical industry are reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration. This is due to the formation of wastewater in production with a high content of dissolved salts and acids.
Reverse osmosis is used to separate low molecular weight compounds, and ultrafiltration is used for high molecular weight suspended particles and colloids.
The advantage of using these methods when treating wastewater from chemical industries should be considered:
- extraction of valuable impurities;
- simultaneous purification from inorganic, organic impurities and microorganisms;
- independence from the concentration of pollutants in wastewater.
Biological treatment
Biological wastewater treatment is used in local installations both as a main method (pharmaceutical enterprises) and as an additional treatment (at most chemical enterprises). The biological treatment method is used for:
- disinfection of wastewater before discharge into water bodies;
- reducing the corrosion rate of equipment and pipelines;
- prevention of salt formation and coating of thermal surfaces by microorganisms when returning contaminated water to the recycling water supply cycle.
Biological treatment is carried out in aeration tanks and biofilters in cases where the concentration of pollutants is low and the polluting components are not toxic to aerobic organisms. Anaerobic treatment in digesters and membrane bioreactors is carried out in the presence of high concentrations of pollutants or the presence of toxic substances.
Among the methods of treating wastewater from chemical enterprises, there are less common, but necessary in some cases methods:
- thermal method;
- a method of forced injection into deep rock layers.
With the thermal method, wastewater, which contains solutions of mineral salts and organic substances, is subjected to various treatment methods. Salt solutions are concentrated and the salts are isolated in solid form. Organic substances are oxidized in the presence of a catalyst or by liquid-phase oxidation. Fire neutralization, the so-called “fire” method, is also used.
When choosing a method, they are guided by economic feasibility and environmental efficiency.
The deep rock injection method is used when treating wastewater or separating pollutants from it is not economically viable, since the costs of treatment exceed the costs of producing the final product. As a rule, these are wastewater containing large amounts of mineral impurities. They are not amenable to biological treatment; when chemical methods are used, they generate a large amount of waste, and when discharged into water bodies they require significant dilution.
The sludge generated during wastewater treatment is subjected to dewatering and subsequent use or disposal. To dewater sediments, filtration, pressing in a centrifugal field or mechanically on belt filter presses, sludge beds, sludge storage facilities and sludge accumulators are used.
Basic methods of wastewater disinfection
In addition to petroleum products and other compounds hazardous to health, almost all wastewater contains organic contaminants that provoke the appearance and growth of pathogenic bacteria. At the same time, the maximum danger can be posed by wastewater, which, along with the current, ends up in places of mass bathing or collecting drinking water. It is no coincidence that a separate method of wastewater treatment is the already mentioned disinfection (disinfection).
It is allowed to carry out disinfection in various ways, which differ from each other in the degree of effectiveness, as well as danger. For example, in the last century, based on long-standing traditions, the main method of wastewater treatment in our country was chlorination. Meanwhile, despite the simplicity and widespread use of chlorine and chlorine-containing agents, this method is characterized by significant drawbacks - for example, low reliability of killing viruses. In addition, excess chlorine has a detrimental effect on aquatic vegetation and living organisms.
Standards for the composition of industrial wastewater for discharge into sewers and treatment of industrial wastewater
Industrial wastewater contains various aggressive substances that destroy city treatment plants and sewer pipelines. When they enter a body of water, they have a negative effect on both the composition of the water and the living organisms in it. Therefore, before cleaning, you need to check the maximum permissible concentrations of biological and chemical substances and take measures. Requirements for wastewater must be taken into account when designing reconstruction and installation of industrial institutions. Factories should operate using technologies with minimal or no waste, and water after purification should be reused - this will help preserve the resources of our planet and protect the environment from negative external influences.
Basic requirements for wastewater discharged into the central sewer system:
- BOD – no more than the maximum permissible value specified in the design documentation for the treatment plant;
- wastewater should not cause disruptions or interruptions in the operation of sewerage systems or treatment facilities;
- wastewater should not have a temperature of more than 40 degrees and a pH of more than 6.5-9.0;
- the presence of sand, shavings, and abrasive particles in drains is unacceptable (they are the main cause of the formation of sediment in sewer units);
- the drains should not contain impurities that clog grates and pipes;
- absence of aggressive components that cause destruction of pipes and other cleaning elements – 100%;
- There should be no explosive components in wastewater, as well as biodegradable, viral, toxic, bacterial and radioactive impurities.
In situations where the discharged wastewater does not meet the specified parameters, it is pre-treated.
Use of hydrofluoric acid in wastewater treatment process
As we have already mentioned, hydrofluoric (hydrofluoric) acid is often used in the treatment of wastewater from enterprises. This inorganic substance is a monobasic acid, the second name of which is hydrofluoric acid, due to the fact that hydrogen fluoride is formed from fluorspar. Hydrofluoric acid is used in neutralization reactions during wastewater treatment, but quite large volumes of acid are required to support this process, so it is not surprising that it is subsequently found in wastewater. Thus, before discharging wastewater into a reservoir or reusing it, the remaining hydrofluoric acid and its salts are removed. By adding lime milk, fluorides are precipitated in the water, and during this operation calcium fluoride is formed, which must be disposed of.
Classification
Depending on the reagents used, three methods are distinguished:
- oxidation;
- neutralization;
- recovery.
Oxidation is one of the most powerful methods, which is used when others are ineffective. Chlorine, potassium permanganate, and ozone are used as oxidizing agents. All of them are also effective disinfectants. Of these substances, ozone is the most effective; it has unique properties, because it disintegrates quickly in an aqueous environment, and is highly resistant to acidic environments.
The optimal amount of ozone in the purifying ozone-oxygen mixture is no more than 3%. This is enough for high-quality absorption of waste.
There is also a combined type of purification - electrochemical oxidation, which occurs through the anode. One of the most effective and affordable: the anode is cheap, and with its help you can clean a lot of wastewater.
With the help of neutralization, the required hydrogen pH level is achieved; for this, certain types of acids (hydrochloric, sulfuric) or alkalis (sodium hydroxide, soda, lime) are used. Often there is a need for neutralizing loading with the participation of magnesite, chalk or dolomite. This process requires special equipment for treating domestic and industrial wastewater.
If the liquid is saturated with such complex and dangerous compounds as arsenic, mercury, chromium, then a recovery method must be used. It is rarely used in industry and, especially, in everyday life.
Features of environmental control of wastewater treatment
However, it is not so important what methods and methods of wastewater treatment are used within the framework of certain treatment systems, because in any case, treatment facilities of industrial enterprises, as well as municipal treatment facilities, are carefully controlled by special sections of the legislative framework of states. Russia is no exception. According to the current environmental legislation of the Russian Federation, all discharges into water bodies are subject to the strictest regulation. This standardization, in particular, is carried out by agreeing on draft standards for permissible discharges (VAT). For example, the user of natural resources must indicate such key points in the operation of treatment plants, structures and systems, such as their type, productivity and throughput. If the enterprise decides to install new (additional) treatment facilities, then it is necessary to notify local environmental authorities about this so that further actions aimed at wastewater treatment are coordinated and as effective as possible.