Orbital welding is used to install pipelines in the field. This is an automated process for connecting permanent joints. The pipe is boiled by a head mounted on a rotating device. A special clamp secures the device tightly in the working area. Operator skills are required for operation. The welder selects the required mode depending on the size, wall thickness, and chemical composition of the alloy. Monitors parameters during operation.
Features of orbital welding
The arc automatically rotates around the entire circumference, the pipe is evenly welded on all sides. Butt welding of pipes using orbital vehicles is indispensable in hard-to-reach places where it is difficult to weld a stationary workpiece.
The automated welding process is a manual or argon arc electric welding using a refractory tungsten electrode and filler wire. When the arc is ignited, the edges are melted, creating a melt pool. The additive forms a neat roller at the junction. The head extends along the entire circumference (orbit). The workpieces do not rotate during operation and remain motionless.
Methods for welding polymer pipes
The technology for working with polymer pipes is fundamentally different from welding metal products.
When assembling polymer pipelines, the two most popular methods are used:
- Butt joint technology involves heating and subsequent melting of the pipe ends to operating temperature, and compression until a sealed seam is formed. The welding process is carried out using special equipment consisting of a frame, centralizers and a heating element.
Devices for butt joining of polymer pipes are multifunctional and allow you to simultaneously adjust and then center the cut of the connected ends before subsequent heating. Pipes heated to operating temperature are moved using a mechanized jack system.
The use of special machines makes it possible to perform welding work both in stationary and field conditions with a known high quality of the joint.
- Electrofusion joint technology allows you to do without complex equipment, since the heating element is part of the coupling for welding pipes.
A polymer coupling with a fused spiral is placed on the joint of the pipes being connected, after which voltage is applied to the spiral and the plastic is melted, forming a reliable and airtight connection.
Application area
Automatic machines for orbital joining of pipe joints use:
- for linear installation of pipelines;
- flange fastenings;
- connections of rolled pipe sections with bends, tees, and other pipe fittings;
- welding of heat exchanger tube sheets.
Orbital welding of pipes minimizes the percentage of defects, increases the speed of installation of pipelines, assembly of boilers and heat exchangers. The repair of thermal power plants, combined heat and power plants, maintenance of oil pipelines, gas mains, and utilities is simplified.
Areas of application
Due to the fact that it is possible to obtain a reliable high-quality seam, precise connection of pipes of various diameters and sizes, orbital welding has found application in energy production and pharmaceutical enterprises. In addition, it is possible to connect large containers, which is necessary in the chemical industry, since high-quality seams are the key to long service in conditions of contact between metal and a liquid aggressive environment.
Advantages and disadvantages
Butt welding with orbital automatic machines ensures the tightness of pipelines due to high-quality seams. The metal is welded evenly over the entire circumference. Advantages of orbital pipe welding:
- the risk of suture roller defects is reduced;
- arc regulation reduces the area of melt pool splashing;
- the connection of pipeline parts and tube sheets can be made in any spatial position;
- wide range of welded alloys: carbon and alloy steels, non-ferrous metals;
- ability to work with and without additives;
- absence of scale on the seam;
- the process proceeds without the formation of smoke.
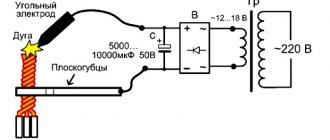
Technology of automatic and semi-automatic welding of pipelines in shielding gases
The gaps for welding between the two edges of the joint should be about 0.5-1.0 mm. Welding of pipes with thin walls, in most cases, occurs without cutting the edges for welding.
The edges of pipes with greater wall thickness are prepared by chamfering them at an angle of 20-30°. High-alloy welding wire Mirki Sv-06X19N9T, with a diameter of 0.8-1.2 mm, is well suited for welding stainless steels.
When welding stainless steels with a non-consumable electrode, it is necessary to use filler wire of the Sv-01Х19Н9, Sv-04Х19Н9 and Sv-07Х19Н10Б grades. In this case, the first layer of the weld is made with a tungsten electrode without the use of filler material. This technique contributes to high-quality welding of the root of the seam. Welding of subsequent layers is carried out with a tungsten electrode using filler material, or they are welded with a consumable electrode.
The jet of shielding gas (argon, or carbon dioxide, or a mixture of gases) should tightly cover the entire welding zone. If welding takes place in an open area, or in a well-ventilated area, then additional protection (shields, tents, etc.) is required from wind and drafts, and it is also necessary to increase the flow rate of the shielding gas.
Orbital pipe welding equipment
The pipeline welding machine has:
- power source - an inverter delivering from 30 to 400 A, connected to a single-phase network with a voltage of 220 V or three-phase 380 V, with which it is easy to control the strength of the operating current;
- tungsten electrode;
- a connecting head forming a seam;
- pincer fastening system that fixes the head on the pipe;
- gas supply system with adjustable wire nozzle;
- control unit, adjustable:
- head rotation speed;
- bar feed speed;
- inert gas consumption (injection volume);
- angle of inclination of the electrode.
Some models are equipped with a printing device; information about the operating mode can be printed out on paper.
Equipment for orbital welding is used when installing pipes with an outer diameter from 17 to 170 mm. They produce machines for argon-arc and manual arc welding in a protective atmosphere in three main standard sizes (the size of the welded pipes is indicated in mm): 17–50; 33–90; 60–170. By agreement with the customer, some manufacturers make fixing pliers of a different size. The upper limit is increased to 275 mm. Models have been developed for thin rolled pipes, the minimum outer size is 1.6 mm.
Types of orbital heads that hold the torch at a fixed distance from the metal being welded:
- The closed type is designed for connecting small diameter pipes. The joint is located in a chamber filled with protective gas. Such heads are considered the most reliable; they form a sealed seam that does not contain oxides.
- Open type, argon or other inert gas or a special mixture enters the working area under pressure. Such heads are used on thick-walled pipes, where the joint is welded in several cycles. For convenience, the burner tilts at the desired angle up to 45°.
Orbital welding scheme
For tube sheets, heads are designed for repairing heat exchangers; the process is adjusted automatically; the operator only needs to install the clamp.
Kemppi devices - moving from complex to simple
To make orbital technology accessible not only to companies that have welders of 5-6 categories on their staff, Kemppi has developed a special software product - WiseRoot. The use of Kemppi machines with such software allows you to weld highly critical root connections with the formation of a reverse bead that meets the basic requirements - 100% fusion of the edges and reinforcement of the weld on the reverse side.
The root pass in closed metal structures is considered the most difficult pass, since both sides need to be completed equally well. Therefore, only highly qualified specialists were allowed to perform such work. With the new technology, less trained welders can be allowed into this process after appropriate instruction and a little practice. To train personnel, 1 week of active training is sufficient.
stainless steel, front side
stainless steel, reverse side
black steel, front side
black steel, reverse side
Intelligent Kemppi K7 and K8 machines provide precise arc control, high productivity and meet the highest industrial requirements, allowing you to work with such metal structures as:
- tanks;
- bunkers;
- pressure vessels;
- boilers;
- pipelines.
Such equipment, in addition to reducing the requirements for the qualifications of operating personnel, reduces the cost of consumables. This is due to the fact that the cutting angle of the edges is significantly reduced (for some jobs up to 40%), and accordingly, an order of magnitude less filler material is required to fill the seam. This rule applies to working not only with ordinary steel, but also with more “complex” metals, including stainless steel. Read about the importance of edge preparation for stainless steel here.
What gas environment is best to work in?
Orbital technology is based on arc welding in an inert gas environment. As a rule, pure argon is used, although depending on the type of metal and technological requirements (process speed, penetration depth, degree of reinforcement of the back side of the weld, etc.), mixtures of argon with helium or hydrogen can be used. There are also multicomponent compositions, the effect of which, as a rule, outweighs their higher cost. In order to become better acquainted with the types of protective compounds and their use for different types of metal, you can use the information from the articles that are in the section on welding mixtures.
Without a high-quality shielding gas, it is difficult to achieve a reliable connection. Therefore, it is better to cooperate with reliable suppliers who will not let you down at the most crucial moment. offers different types of mixtures that meet modern production criteria and can be supplied both in standard cylinders and in monoblocks.
Welding technology
To straighten the ends, cutting machines are used to ensure a vertical, straight edge. Thick-walled pipes are prepared for work in the factory: the edges are cut and cut at an angle of 30°. Thin-walled rolled products are melted without additives.
Before orbital welding of pipes, preparatory work is carried out. The ends are cleaned of burrs and dirt. The prepared sections are centered and laid at a specified distance from each other. For orbital welding of small diameter pipes, it is enough to purchase a removable head. It is mounted on universal clamping systems. The joint surface is divided into sectors, for each individual modes are set, taking into account the pressure of the workpiece’s own weight in the lower part. The molten metal should not sag on top. The parameters of the operating current and the feed rate of the filler rod are set by the operator depending on the grade of steel and the shape of the workpiece. The orbiter is attached to the joint area.
Metal welding is performed automatically. After all sectors are sealed, the equipment turns off automatically.
Orbital vehicles are highly specialized. They are purchased for the installation of long-distance pipelines and for the repair of heat exchangers and boilers. This is the most promising method of installing rolled pipes. It is not advisable to use such equipment in everyday life due to the long payback period.
Description of technology
The orbital method usually uses a welding process carried out in an argon environment with a non-consumable tungsten electrode. At the same time, the filler wire is fed. The main principle of this technology, due to which it got its name, is the following.
The welding head of the device with a tungsten non-consumable electrode fixed in it moves along the stationary seam along the exposed guides, while making a 360° rotation, moving in orbit.
The orbital movement of the welding head is fully automated, as well as all other technological operations accompanying it. The length of the welding arc is preset by rigidly fixing the head at the desired height above the pipe surface.
The orbital welding process is controlled by a processor controlled by a special program in which all parameters are specified. The program settings take into account changing welding conditions when the electrode moves along an orbital path.
The weld seam along the perimeter of the pipe being welded is divided into sectors, within which the process parameters have a constant value. Thus, the circular “orbital” seam is divided into horizontal sections (floor and ceiling), vertical (with downward and upward movement), and sections located at a certain angle.
Welding of stainless steel pipes: argon arc, orbital
Stainless steel pipelines, due to the unique properties of the material, are widely used in many industries and utilities. To obtain reliable connections, welding of stainless steel pipes is done using special technologies. This complicates installation, but in some cases it is necessary to comply with regulatory requirements. For example, international regulations indicate that orbital welding of stainless steel pipes must be used if they come into contact with food products.
System components for operation
The equipment has two main elements:
- current source;
- orbital head.
The task of the first is to supply electric current to the point of contact and control the process parameters. The second is the rotation of the burner (electrode), ensuring a continuous cycle of work. The absence of one of the elements makes the process impossible.
Today, an inverter is used as a current source, through which control is carried out:
- current strength;
- head rotation speed;
- gas consumption;
- wire feed speed.
Also, the task of the inverter is to set the seam profile, program the operating mode based on the diameter of the pipes, material and gas used.
There are two types of orbital head (otherwise called simply welding head):
The former are used in closed chambers, pre-filled with inert gas to protect the welded and welded elements. The advantage of heads of this type is the reliability of the process - even a violation of the sealing of the joint of parts does not affect the integrity and quality of the seam, because oxygen will not get there.
Second heads are used when joining thick parts that require filler, and the cycle is repeated many times using it. The working element of the torch is tilted at different angles, and this makes it easier to weld corner areas and small workpieces.
When operating the heads, a tungsten electrode is usually used, and the element itself includes a limiter - an arc length controller.
Orbital welding of stainless pipes using a closed-type welding head ORBIWELD 76S
The client’s task was to automate the process of welding pipes in cramped conditions, which would significantly reduce operating time and, accordingly, increase productivity.
Due to their small dimensions, the ORBIWELD “S” series of orbital welding heads are ideal for use in confined spaces. Control buttons on the head itself allow you to control the welding process without moving the operator.
Specialists have selected the necessary set of equipment, which includes:
- power source ORBIMAT 165 CA, Orbitalum Tools
- trolley ORBICAR S, Orbitalum Tools
- Clamping inserts for pipes with a diameter of 18 mm and 25 mm
- gas reducer
- flash card for saving and viewing welding protocols
The basic prerequisite for productive and high-quality pipe welding with automated orbital joining technology is precise, burr-free, rectangular cutting as well as perfect chamfering of the pipe end. To do this, we used a GFX 3.0 pipe cutter and a portable RPG 2.5 pipe cutter (cordless version).
During the development of the project, DeltaSvar LLC specialists demonstrated equipment, as well as tested welding modes on client samples.
The result of the work done is a fully automated pipe welding process in cramped conditions and a reduction in labor costs.
This project can be implemented in such industries as aerospace, food, dairy and beverage industries, pharmaceutical and chemical industries, and pipeline manufacturing.
Have questions? DeltaSvar will find the right solution for each client. Call us at number or write to us. We are always happy to help with the choice of welding equipment, provide advice on further maintenance, etc.
Technology of argon arc welding of stainless steel pipes
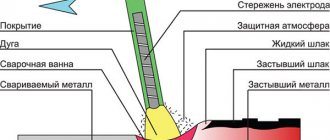
The connection of stainless steel workpieces in this way is carried out using a non-consumable tungsten electrode fixed in the center of the burner nozzle. Through it, argon flows to the joint, creating a protected zone. The weld is created by melting the filler wire, fed manually or automatically.
When applying a seam, do not make transverse movements with the torch, electrode and filler wire. If they leave the protected area, the quality of the connection will decrease. Welding is recommended to be carried out with argon blowing on both sides. Do not touch the surface of the workpiece with the electrode, even to ignite the arc. Experienced welders use graphite or coal plates for this, then transfer the arc to the joint. After completion of the work, the joint area should be in an argon environment for 10 - 15 seconds. This will speed up the cooling of the seam and prevent oxidation of the electrode.
When welding stainless steel pipes, it is necessary to blow the joint with argon both from the outside and from the inside. The problem can be solved simply:
- a plug from any available material is hammered into the end of one of the pipes;
- tape or insulating tape is wound around the joint;
- argon is pumped through the end of another pipe using a burner;
- after filling the entire volume with gas, plug in the second plug;
- remove the adhesive tape or insulating tape and begin welding.
Welding process
The orbital welding technique can provide a high-quality connection only with uniform pipe parameters.
For example, connected elements:
- Must be straightforward.
- Must have the same thickness along the entire length. If this parameter does not correspond, the seam obtained during welding may be uneven.
These properties of the pipes being connected must be carefully controlled using specialized equipment and trained engineers.
Preparation before welding includes:
- Ensuring the required gap between the connected pipes. To solve this problem, cutting machines are used.
- Centering of pipes and welding in several places. After checking the quality of centering, you can proceed to work.
In addition, before the immediate start of welding work, the circumference of the pipes must be divided into sectors. After this, the operator of the device must set individual parameters for each sector so that during the welding process the metal does not sag inside the pipe, but only melts a little.
Features of the metal welding process depend, first of all, on the type of materials being joined and the shape of the product.
To connect stainless steel pipes using orbital welding, the operator must:
- set up the orbital system;
- select and install a head suitable for current conditions;
- secure the device along the line along which you plan to make the weld;
- turn on welding.
If configured correctly, the welding unit will independently perform the following procedures:
- entering the mode by warming up the electrodes;
- creating a weld seam in the first sector of the product being joined;
- connection of stainless pipes in other sectors.
While the orbital welding machine is operating, a qualified operator, wearing a mask and other protective equipment, can only monitor the parameters and observe the quality of the seam. After completing the welding cycle, the machine will turn off automatically and allow you to evaluate the quality of the work performed.