General characteristics of steel grade 40HFA
Structural alloyed chrome vanadium grade 40HFA is a hypoeutectoid, low-alloy, medium-carbon steel. It is distinguished by an excellent combination of ductility, strength and ability to resist abrasion , which allows the material to perform well under dynamic loads. In addition, this steel is sensitive to temper brittleness , so it is recommended to cool it after tempering.
|
| Substitute: | 40Х, 65Г, 50ХФА, 30Х3МФ |
| GOST standards: | GOST 8479-70, GOST 1133-71, GOST 8319.0-75, GOST 2590-2006, GOST 2591-2006, GOST 2879-2006, GOST 103-2006, GOST 1051-73, GOST 4543-71, GOST 7417-75, GOST 8559-75, GOST 8560-78, GOST 14955-77 |
| Application: | in improved condition—spline shafts, rods, set screws, traverses, excavator shafts and other parts operating at temperatures up to 400 °C; after hardening and low tempering - worm shafts and other parts with increased wear resistance. |
Read more about the use of 40HFA >>
Mechanical and physical properties of the alloy
Metal of this grade should be classified as difficult-to-weld steel, which must be heated and then cooled during the welding process. There is also a high flake sensitivity of the material, i.e. its tendency to form heterogeneous areas, and the presence of temper brittleness.
Steel 40x - chromium, with a carbon content of 0.40%, as well as grades 65G, 50KhFA and 30Kh3MF, acts as a substitute for the 40xfa alloy. The following types of metals are considered foreign analogues: 4140, 4142 and G41400 - in the USA; 1.7223 and 41CrMo4 - in Germany, SCM440 - in Japan, etc.
The density of 40xfa steel, its hardness under certain temperature conditions and other characteristics are presented in the following tables:
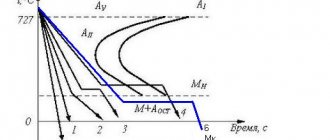
As a mandatory heat treatment in the case of the 40xfa alloy, traditional hardening and tempering is used (in accordance with GOST for steel of this grade). Forging metal should begin at 1250°C and end at 860-800°C.
see stock and prices >>
Chemical composition in % of material 40HFA
| C | Si | Mn | Ni | S | P | Cr | V | Cu |
| 0.37 — 0.44 | 0.17 — 0.37 | 0.5 — 0.8 | up to 0.3 | up to 0.025 | up to 0.025 | 0.8 — 1.1 | 0.1 — 0.18 | up to 0.3 |
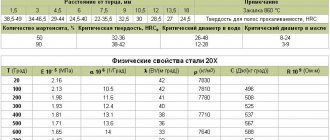
Temperature of critical points of the 40HFA material.
| Ac1 = 760, Ac3(Acm) = 800, Ar3(Arcm) = 725, Ar1 = 680, Mn = 218 |
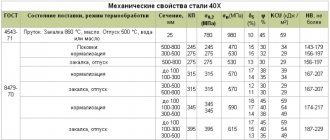
Mechanical properties at T=20oC of 40HFA material.
| Assortment | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Thermal change |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| Forgings | 100 — 300 | 615 | 395 | 15 | 40 | 540 | Quenching and tempering |
| Forgings | 300 — 500 | 615 | 395 | 13 | 35 | 490 | Quenching and tempering |
| The hardness of the material is 40HFA after annealing, | HB 10 -1 = 241 MPa |
Physical properties of the material 40HFA.
| T | E 10- 5 | a 10 6 | l | r | C | R 10 9 |
| hail | MPa | 1/Grad | W/(m deg) | kg/m3 | J/(kg deg) | Ohm m |
| 20 | 2.15 | 37 | 7810 |
| 100 | 2.12 | 12.1 | 37 | 466 |
| 200 | 2.05 | 12.6 | 37 | 508 |
| 300 | 1.99 | 13 | 36 | 529 |
| 400 | 1.82 | 13.3 | 33 | 563 |
| 500 | 1.73 | 13.8 | 31 | 592 |
| 600 | 1.66 | 14.2 | 31 | 621 |
| 700 | 1.44 | 14.6 | 30 | 634 |
| 800 | 1.35 | 11.8 | 28 | 664 |
| T | E 10- 5 | a 10 6 | l | r | C | R 10 9 |
Technological properties of material 40HFA.
| Weldability: | difficult to weld. |
| Flock Sensitivity: | sensitive. |
| Tendency to temper brittleness: | inclined. |
Remaining steel wheels 40HFA for March 2021.
| Name | steel grade | Size, mm | Quantity, tons | Price > 1 t |
| Circle | 40HFA | 42 | 0,757 | 60000 | get an invoice |
| Circle | 40HFA | 45 | 3,07 | 60000 | get an invoice |
| Circle | 40HFA | 50 | 0,084 | 60000 | get an invoice |
| Circle | 40HFA | 75 | 1,865 | 75000 | get an invoice |
| Circle | 40HFA | 150 | 0,48 | 139000 | get an invoice |
Steel 40HFA
Home->Directory->Steel grade->Structural steel
Steel 45 Steel 40ХС
Structural alloy steel 40HFA
Brand 40HFA – purpose
Structural alloyed chrome vanadium steel 40HFA is used for the manufacture of upgradeable parts operating at temperatures up to 4000C - excavator shafts, traverses, set screws, rods, splined shafts; after hardening and low tempering - products with increased wear resistance - worm shafts, other products.
Steel 40HFA - domestic analogues
| Rolled metal grade | Substitute |
| 40HFA | 30Х3МФ |
| 40X |
| 50HFA |
| 65G |
Material 40HFA - characteristics
| Brand | Classification | Type of delivery | GOST | Foreign analogues |
| 40HFA | Alloy structural steel | Long products | 4543–71 | There is |
| Forgings and forged blanks | 8479–70 |
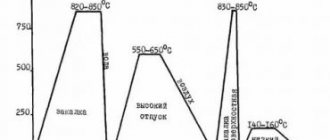
Grade 40HFA – technological features Heat treatment
Forging
| Type of semi-finished product | t, 0С | Cooling |
| Section size | Conditions |
| mm |
| Blank | 1250–800 | up to 200 | In the trough |
| 201–300 | With oven |
Welding
| Weldability | Welding methods | Recommendations |
| difficult to weld | RDS | Heating + heat treatment |
| KTS | Heat treatment |
Flock sensitivity
Sensitive.
cutting
| Initial data | Machinability Ku |
| State | HB, MPa | sB, MPa | hard alloy | high speed steel |
| hardened tempered | ≤241 | 0,75 | 0,65 |
Tendency to temper brittleness
Prone.
Steel 40HFA - chemical composition
Mass fraction of elements no more than, %:
| Vanadium | Silicon | Manganese | Copper | Nickel | Sulfur | Carbon | Phosphorus | Chromium |
| 0,1–0,18 | 0,17–0,37 | 0,5–0,8 | 0,3 | 0,3 | 0,025 | 0,37–0,44 | 0,025 | 0,8–1.1 |
Material 40HFA – mechanical properties
| Assortment | GOST | Dimensions – thickness, diameter | Heat treatment mode | KCU | y | d5 | sT | sв |
| mm | kJ/m2 | % | % | MPa | MPa |
| Bar | 4543–71 | 25 | Hardening | 880 | 50 | 10 | 735 | 880 |
| Vacation |
| Forgings | | 100–300 | Hardening | 540 | 40 | 15 | 395 | 615 |
| Vacation |
| 300–500 | Hardening | 490 | 35 | 13 | 395 | 615 |
| Vacation |
Hardness, MPa
| Assortment | GOST | Heat treatment | HB 10-1 |
| Rental | 4543–71 | Annealing | 241 |
Temperature of critical points, 0С
| Critical points | Ac1 | Ac3 | Ar1 | Ar3 | Mn |
| Temperature | 760 | 800 | 680 | 725 | 218 |
Impact strength, J/cm2
| Heat treatment modes | Wednesday | t | KCU at temperatures |
| 0C | -700С | -500С | -400С | -300С | -200С | 00С | +200С |
| Hardening | oil | 850 | 55 | | | | 61 | | 92 |
| Vacation | 600 |
Grade 40HFA – physical properties
| t | r | R 109 | E 10-5 | l | a 106 | C |
| 0C | kg/m3 | Ohm m | MPa | W/(m deg) | 1/Grad | J/ (kg deg) |
| 20 | 7810 | 2.15 | 37 |
| 100 | 2.12 | 37 | 12.1 | 466 |
| 200 | 2.05 | 37 | 12.6 | 508 |
| 300 | 1.99 | 36 | 13 | 529 |
| 400 | 1.82 | 33 | 13.3 | 563 |
| 500 | 1.73 | 31 | 13.8 | 592 |
| 600 | 1.66 | 31 | 14.2 | 621 |
| 700 | 1.44 | 30 | 14.6 | 634 |
| 800 | 1.35 | 28 | 11.8 | 664 |
Steel 40HFA - exact and closest foreign analogues
| England | Belgium | Bulgaria | Germany | European Union | Spain |
| B.S. | NBN | BDS | DIN, WNR | EN | UNE |
| 3111-5/1 |
| 42CrMO4 |
| 708M40 |
41CrMo4
40ChFA
1.7223
41CrMO
40CrMo4
| Italy | USA | France | Czech | Sweden | Japan |
| UNI | — | AFNOR | CSN | SS | JIS |
| 41CrMo4 |
4140
42CD4TS
15240
2244
SCM440
Material 40HFA – area of application
Steel grade 40HFA is used in mechanical engineering for the manufacture of improved parts with increased wear resistance.
Legend
Mechanical properties
| HRСе | HB | KCU | y | d5 | sT | sв |
| MPa | kJ/m2 | % | % | MPa | MPa |
| Rockwell hardness | Brinell hardness | Impact strength | Relative narrowing | Elongation at break | Yield strength | Short-term strength limit |
| Ku | s0.2 | t-1 | s-1 |
| Relative machinability factor | Proof of yield strength with 0.2% tolerance when loaded to plastic strain value | Torsional endurance limit (symmetrical cycle) | Endurance limit under compression-tension (symmetrical cycle) |
| N | number of deformation/stress cycles sustained by an object under load before fatigue failure/crack appears |
Weldability
| No limits | Limited | Difficult to weld |
| Heating | No | up to 100–1200С | 200–3000С |
| Heat treatment | No | There is | annealing |
Physical properties
| R | Ohm m | Resistivity |
| r | kg/m3 | Density |
| C | J/(kg deg) | Specific heat |
| l | W/(m deg) | Coefficient of thermal conductivity |
| a | 1/Grad | Linear expansion coefficient |
| E | MPa | Elastic modulus |
| t | 0C | Temperature |
You can buy rolled metal from structural alloy steel 40HFA in St. Petersburg by calling +. Specialists will place your order and advise you on the assortment, prices, and delivery conditions.
Steel 30KhGT Steel 35KhN1M2FA Steel 40 Steel 40G Steel 45KhN Grade A20 Grade A30 Steel 08 Steel 08kp Steel 08ps Steel 08Yu Steel 09G2 Steel 09G2S Steel 10 Steel 10G2 Steel 10G2BD Steel 10G2S1 Steel 10kp S hoist 10ps Steel 10Kh14G14N4T Steel 10KhNDP Steel 10KhSND Steel 12GS Steel 12K Steel 12Kh18N10T Steel 12Kh2N4A Steel 12KhN2 Steel 12KhN2A Steel 12KhN3A Steel 14G2 Steel 14G2AF Steel 14Kh2GMR Steel 14KhGS Steel 15 Steel 15G Steel 15G2AFDps Steel 15G2SFD Steel 15K Steel 15kp Steel 15ps Steel 15Х Steel 15ХСНД Steel 15ХФ Steel 16Г2AF Steel 16ГС Steel 16К Steel 17Г1С Steel 17ГС Steel 18Г2AFps Steel 18К Steel 18kp Steel 18Kh2N4VA Steel 18Kh2N4MA Steel 18KhGT Steel 20 Steel 20G Steel 20K Steel 20kp Steel 20ps Steel 20Kh Steel 20Kh2N4A Steel 20KhG2Ts Steel 20KhGNR Steel 20KhGR Steel 20KhGSA Steel 20KhN Steel 20KhN2M Steel 20KhN3A Steel 20KhN4FA Steel 20KhNR Steel 22K Steel 25 Steel 25G2S Steel 25ps Steel 25KhGSA Steel 25KhGT Steel 30 Steel 30X Steel 30G Steel 30KhGS Steel 30KhGSA Steel 30KhGSN2A Steel 30KhN2MA Steel 30KhN2MFA Steel 30KhN3M2FA Steel 31Kh19N9MVBT Steel 33KhS Steel 34KhN1M Steel 34KhN3M steel 3 5 Steel 35G Steel 35G2 Steel 40G2 Steel 40Kh Steel 40Kh2N2MA Steel 40KhS Steel 40KhFA Steel 45 Steel 45G Steel 45G2 Steel 45X steel 60S2A steel 60S2N2A steel 60S2ХА steel 60S2HFA steel 65 steel 65G steel 65S2VA steel 70 steel 70S3A steel A12 Steel A40G Steel VSt3kp Ordinary quality steel VSt2kp Ordinary quality steel VSt2ps Ordinary quality steel VSt2sp Ordinary steel new quality VSt3Gps Ordinary quality steel VSt3ps Ordinary quality steel VSt3sp Ordinary quality steel VSt4kp Ordinary quality steel Vst4ps Ordinary quality steel VSt5ps Ordinary quality steel VSt5sp Ordinary quality steel VSt6sp Ordinary quality steel St0 OsV steel ShKh15 steel ShKh15SG steel ShKh4 steel
Chemical composition of 13HFA
Mass fraction of 13HFA steel elements according to
GOST 4543-2016
| C (Carbon) | Si (Silicon) | Mn (Manganese) | P (Phosphorus) | S (Sulphur) | Cr (Chrome) | Mo (Molybdenum) | Ni (Nickel) | V (Vanadium) | Ti (Titanium) | Al (Aluminum) | Cu (Copper) | N (Nitrogen) | W (Tungsten) | Fe (Iron) |
| 0,11 – 0,17 | 0,17 – 0,37 | 0,4 – 0,65 | 0,5 – 0,7 | 0,04 – 0,09 | 0,02 – 0,06 | rest |
The chemical composition can be changed by agreement with the supplier: the calcium content in the composition should not exceed 0.003. Em = 0.3Cr + 0.5Ni + 0.7Cu.
Mass fraction of 13HFA steel elements according to
TU 14-1-5598-2011
| C (Carbon) | Si (Silicon) | Mn (Manganese) | P (Phosphorus) | S (Sulphur) | Cr (Chrome) | Ni (Nickel) | V (Vanadium) | Al (Aluminum) | Cu (Copper) | N (Nitrogen) | Fe (Iron) |
| 0,08 – 0,17 | > 0,17 | 0,5 – 0,7 | 0,04 – 0,09 | 0,02 – 0,05 | rest |
Mass fraction of 13HFA steel elements according to
TU 1303-006.3-593377520-2003
| C (Carbon) | Si (Silicon) | Mn (Manganese) | P (Phosphorus) | S (Sulphur) | Cr (Chrome) | Ni (Nickel) | V (Vanadium) | Nb (Niobium) | Ti (Titanium) | Al (Aluminum) | Cu (Copper) | N (Nitrogen) | Fe (Iron) |
| 0,17 – 0,37 | 0,5 – 0,7 | 0,04 – 0,09 | 0,02 – 0,05 | rest |
Mass fraction of 13HFA steel elements according to
TU 1308-245-0147016-2002
| C (Carbon) | Si (Silicon) | Mn (Manganese) | P (Phosphorus) | S (Sulphur) | Cr (Chrome) | Ni (Nickel) | V (Vanadium) | Al (Aluminum) | Cu (Copper) | N (Nitrogen) | Fe (Iron) |
| 0,13 – 0,17 | 0,17 – 0,37 | 0,45 – 0,65 | 0,5 – 0,7 | 0,4 – 0,9 | 0,02 – 0,05 | rest |
Mass fraction of 13HFA steel elements according to
TU 1317-006.1-593377520-2003
| C (Carbon) | Si (Silicon) | Mn (Manganese) | P (Phosphorus) | S (Sulphur) | Cr (Chrome) | Ni (Nickel) | V (Vanadium) | Nb (Niobium) | Ti (Titanium) | Al (Aluminum) | Cu (Copper) | N (Nitrogen) | Ce (Cerium) | Fe (Iron) | Ca (Calcium) |
| 0,11 – 0,17 | 0,17 – 0,37 | 0,4 – 0,65 | 0,5 – 0,7 | 0,04 – 0,09 | 0,02 – 0,05 | rest |
Mass fraction of 13HFA steel elements according to
TU 1317-233-0147016-2002
| C (Carbon) | Si (Silicon) | Mn (Manganese) | P (Phosphorus) | S (Sulphur) | Cr (Chrome) | Ni (Nickel) | V (Vanadium) | Al (Aluminum) | Cu (Copper) | N (Nitrogen) | Fe (Iron) |
| 0,13 – 0,17 | 0,17 – 0,37 | 0,45 – 0,65 | 0,5 – 0,7 | 0,04 – 0,09 | 0,2 – 0,05 | rest |
Mass fraction of 13HFA steel elements according to
TU 1469-011-593377520-2005
| C (Carbon) | Si (Silicon) | Mn (Manganese) | P (Phosphorus) | S (Sulphur) | Cr (Chrome) | Ni (Nickel) | V (Vanadium) | Nb (Niobium) | Ti (Titanium) | Al (Aluminum) | Cu (Copper) | N (Nitrogen) | Fe (Iron) |
| 0,17 – 0,37 | 0,5 – 0,7 | 0,04 – 0,09 | 0,02 – 0,05 | rest |
Mass fraction of 13HFA steel elements according to
TU 3600-010-88626180-2012
Mechanical properties of 13HFA steel
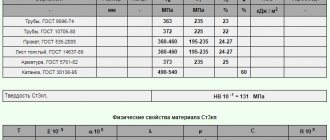
| Type of delivery | Section, mm | sТ|s0.2, MPa | σB, MPa | d5, % | KCU, kJ/m2 | H.R.C. | HRB | HV, MPa |
| Rolled sheets for pipes according to TU 1381-116-00186654-2013 (transverse samples, KCV-40°С is indicated in the KCU column) | ≥375 | 510-610 | ≥23 | ≥882 | — | ≤92 | — |
| Seamless hot-deformed oil and gas pipeline pipes with increased corrosion resistance and cold resistance according to TU 1383-010-48124013-03. As delivered (mechanical properties of pipe metal and KCV-40 °C are indicated) | ≥350 | ≥510 | ≥20 | ≥784 | — | ≤92 | — |
| Seamless hot-deformed, heat-treated pipes in delivery condition according to TU 1319-369-00186619-2012. Column KCU indicates KCV-50°С/KCU-60°С) | 372-491 | ≥510 | ≥23 | ≥981/588 | — | ≤92 | — |
| Seamless oil and gas pipeline heat-treated pipes in the delivered condition according to TU 1317-006.1-593377520-2003 (samples, the strength class is indicated in the delivered condition, the KCV-50 °C value is indicated in the KCU column) | 89-426 | 372-491 | ≥510 | ≥23 | ≥980 | — | ≤92 | — |
| Seamless oil and gas pipeline heat-treated pipes in the delivered condition according to TU 1317-233-0147016-02 (samples, the strength class is indicated in the delivered condition, the KCV-50 °C value is indicated in the KCU column) | — | 338-470 | 502-627 | ≥25 | ≥980 | — | ≤92 | — |
| Pipes according to TU 1381-116-00186654-2013 (transverse samples, KCU-60°C/KCV-20°C is indicated in the KCU column) | ≥350 | 510-630 | ≥20 | ≥392/392 | ≤22 | — | ≤250 |
Technological properties
| Name | Meaning |
| Macrostructure and contamination | Contamination of pipe steel according to TU 1319-369-00186619-2012 with non-metallic inclusions should not exceed the average score (not more than): sulfides (C) - 1.5 for pipes produced by PNTZ, 2.5 - for pipes from other manufacturers; oxides (OT, OS) - 2.5; silicates (CX, SP, CH) - 2.5; nitrides - 1.0. |
| Microstructure | In the microstructure of pipes subjected to heat treatment using the “full quenching + tempering” mode there should be no more than two continuous strips of ferrite; Several broken ferrite strips are allowed. The banding of the microstructure of steel pipes subjected to heat treatment according to the “full quenching + quenching from MKI + tempering” mode or according to the “normalization + quenching from MKI + tempering” mode should not exceed 2 points on scale 3 of GOST 5640. |
| Corrosion resistance | In H2S environment: general corrosion rate ≤ 0.5 mm/year; resistance to hydrogen cracking CLR ≤ 3% CTR ≤ 6%; resistance to sulfide stress corrosion cracking ≥ 75% of σ0.2. According to TU 1381-116-00186654-2013: General corrosion rate ≤0.5 mm/year; Resistance to hydrogen cracking CLR≤6%, CTR≤3%; Resistance to stress corrosion cracking σth ≥70% of σT. |
| Corrosion rate | The rate of general corrosion should not exceed 0.5 mm/year. |
Steel 13HFA Moscow and Moscow region
Steel has a wide range of applications in mechanical engineering, manufacturing, construction, shipbuilding, aircraft manufacturing and many other industries. There are many grades of steel, most of them are made to order, there are grades that are constantly in stock due to regular demand. The Resurs company sells 13HFA steel directly from the manufacturer. With constant demand, we are ready to offer mutually beneficial terms for the supply of many grades of steel. Including 13HFA.
The favorable price for the 13HFA brand is determined by the minimum markup and the absence of intermediaries. We take full responsibility for the supplied material and guarantee the quality of delivery. The cost of products is determined by warehouse and logistics costs; we have the ability to supply steel directly from the manufacturer’s plant, this allows our clients to run their business stably.
Description
Steel 13HFA is used : for the manufacture of pipe blanks and seamless hot-deformed oil and gas pipeline pipes with increased corrosion resistance and cold resistance, intended for use in gas transporting systems, oil and gas pipeline systems, technological field pipelines transporting oil and petroleum products, as well as in systems for maintaining reservoir pressure in northern climatic conditions zones at ambient temperatures from -60°С to +40°С, temperatures of transported media from +5°С to +40°С and operating pressure up to 7.4 MPa; seamless hot-deformed pipes of increased corrosion resistance and cold resistance (Article 13HFA), with an outer diameter from 60 to 426 mm, strength class not less than K52, for in-field pipelines transporting oil well products (gas pipelines and pressure oil pipelines at pressures up to 4.6 MPa); for the production of electric-welded expanded straight-seam pipes with increased corrosion resistance and cold resistance, used for gas pipelines, process and field pipelines for operating pressures up to 7.4 MPa, transporting oil and petroleum products, for pipelines for maintaining reservoir pressure in any climatic zones.
Note
Structural alloy steel with increased corrosion resistance and cold resistance. The pipes differ from conventional oil and gas pipelines in accordance with GOST 8731, GOST 8732, by increased cold resistance, increased resistance to general and pitting corrosion, resistance to sulfide corrosion cracking and the formation of hydrogen cracks.