Structural alloy steel 20Х
Brand 20Х – purpose
Structural alloy chromium steel 20X is used for the manufacture of case-hardened parts with high surface hardness and low core strength, operating under friction for wear - gears, bushings, sleeves, cages, plungers, disks, levers, and other products.
Steel 20Х - domestic analogues
| Rolled metal grade | Substitute |
| 20X | 12ХН2 |
| 15X | |
| 18ХГТ | |
| 20ХН |
Characteristics
| Brand | GOST | Foreign analogues | Classification |
| 20X | 8731–87 | There is | Alloy structural steel |
| 4543–71 | |||
| 10702–78 |
Material 20Х – technological properties
| Flock sensitivity | Weldability | Welding methods | Tendency to temper brittleness |
| insensitive | no limits | KTS, RDS | not inclined |
Brand 20X – chemical composition
Mass fraction of elements no more than, %:
| Silicon | Manganese | Copper | Nickel | Sulfur | Carbon | Phosphorus | Chromium |
| 0,17–0,37 | 0,5–0,8 | 0,3 | 0,3 | 0,035 | 0,17–0,23 | 0,035 | 0,7–1 |
Steel 20Х – mechanical properties
| Assortment | GOST | Dimensions – thickness, diameter | Heat treatment | KCU | y | d5 | sT | sв |
| mm | kJ/m2 | % | % | MPa | MPa | |||
| Pipes | 8731–87 | 16 | 431 | |||||
| Bar | 4543–71 | 15 | Hardening. Vacation | 590 | 40 | 11 | 635 | 780 |
Material – hardness, MPa
| Assortment | GOST | HB 10-1 |
| Rolled after annealing | 4543–71 | 179 |
| hardened. | 229 | |
| The rod is hot rolled. | 10702–78 | 163 |
Brand – temperature of critical points, 0C
| Critical points | Ac1 | Ac3 | Ar1 | Ar3 | Mn |
| Temperature | 750 | 825 | 665 | 755 | 390 |
Steel 20Х – physical properties
| T | R 109 | E 10-5 | l | a 106 | r | C |
| hail | Ohm m | MPa | W/(m deg) | 1/Grad | kg/m3 | J/ (kg deg) |
| 20 | 2.16 | 42 | 7830 | |||
| 100 | 2.13 | 42 | 10.5 | 7810 | 496 | |
| 200 | 1.98 | 41 | 11.6 | 7780 | 508 | |
| 300 | 1.93 | 40 | 12.4 | 525 | ||
| 400 | 1.81 | 38 | 13.1 | 7710 | 537 | |
| 500 | 1.71 | 36 | 13.6 | 567 | ||
| 600 | 1.65 | 33 | 14 | 7640 | 588 | |
| 700 | 1.43 | 32 | 626 | |||
| 800 | 1.33 | 31 | 706 |
Material 20X - exact and closest foreign analogues
| England | Bulgaria | Hungary | Germany | European Union | Poland | USA | Japan |
| B.S. | BDS | MSZ | DIN, WNR | EN | PN | — | JIS |
| 207 |
| 20CrS4 |
| 5120 |
| 5120H |
| G51170 |
| G51200 |
| H51200 |
| SCr420H |
Basic properties
The distribution of the metal in question is due to the fact that it has a relatively low cost and is suitable for the manufacture of a wide variety of parts . The main properties include the following information:
- Normalization is often carried out as a heat treatment. It makes the material more resistant to mechanical stress.
- The specific gravity is 7830 kilograms per cubic meter.
- The surface hardness is relatively low, but often this is quite enough for the manufacture of various non-critical parts.
- It is possible to carry out cutting processing, for which the metal is preheated.
- By adding chromium to the composition, the degree of weldability is significantly increased. An exception is the case when it is necessary to weld parts that have previously undergone a chemical-thermal treatment process.
- No tendency to temper brittleness.
In addition, do not forget that the presence of a small amount of chromium in the composition does not lead to increased corrosion resistance. Therefore, steel is not suitable for the manufacture of parts that will be used in an aggressive environment.
Legend
Mechanical properties
| HB | KCU | y | d5 | sT | sв |
| MPa | kJ/m2 | % | % | MPa | MPa |
| Brinell hardness | Impact strength | Relative narrowing | Elongation at break | Yield strength | Short-term strength limit |
Weldability
| No limits | Welding with restrictions | Difficult to weld | |
| Heating | No | up to 100–1200С | 200–3000С |
| Heat treatment | No | There is | annealing |
20X
- 20X steel products available:
Circle - Sheet
- Band
- Square
- Hexagon
- Forging
to make a request
Steel 20X structural alloy chromium
Substitutes: Steel 18ХГТ, Steel 20ХН, Steel 12ХН2, Steel 15Х
Steel 20X is used: for the production of hot-rolled plates; bushings, gears, cages, sleeves, disks, plungers, levers and other cemented parts, which are subject to the requirement of high surface hardness with low core strength; parts operating under conditions of wear and friction; parts of pipeline fittings made of rolled steel; stamped blanks and forgings (heat treatment required: quenching in water and tempering in air).
Specifications
| Chemical composition in% |
| NTD | C | S | P | Mn | Cr | W | V | Ti | Si | Ni | Mo | Cu |
| TU 14-1-3238-81 | 0,17-0,23 | ≤0,030 | ≤0,030 | 0,50-0,80 | 0,70-1,00 | ≤0,20 | ≤0,050 | ≤0,030 | 0,17-0,37 | ≤0,30 | ≤0,15 | ≤0,30 |
| GOST 10702-78 | 0,17-0,23 | ≤0,035 | ≤0,035 | ≤0,60 | 0,70-1,00 | ≤0,20 | ≤0,050 | ≤0,030 | ≤0,20 | ≤0,30 | ≤0,15 | ≤0,30 |
| TU 14-1-4118-86, GOST 4543-71 | 0,17-0,23 | ≤0,035 | ≤0,035 | 0,50-0,80 | 0,70-1,00 | ≤0,20 | ≤0,050 | ≤0,030 | 0,17-0,37 | ≤0,30 | ≤0,15 | ≤0,30 |
According to GOST 4543-71, the content in high-quality steel is regulated: P≤0.025%; S≤0.025%; Сu≤0.30%; in especially high-quality steel: P≤0.025%; S≤0.015%; Сu≤0.25%. In accordance with the order, the content of Si=0.10-0.37%, Mn=0.4-0.8% can be set. According to TU 14-1-3238-81, the chemical composition is given for steel grade 20ХА. For steel grade 20ХА-СШ the content is S≤0.015%.
| Mechanical properties |
| Mechanical properties at 20°C |
| Delivery status | Section (mm) | t test (°C) | holiday temperature (°C) | sТ | s0.2 (MPa) | sB (MPa) | d5 (%) | d4 | d | d10 | y (%) | KCU (kJ/m2) | HB | H.R.C. | HRB | H.V. | HSh |
| Blanks for pipeline fittings. Quenching in water from 880-900 °C (holding time 2.5-4.0 hours, depending on the thickness and weight of the workpiece) + Tempering, air cooling | ||||||||||||||||
| max 80 | 500-560 | ≥345 | ≥590 | ≥16 | ≥45 | ≥588 | 174-217 | |||||||||
| Sections (bars). Quenching in water or oil from 880 °C + Quenching in water or oil from 770-820 °C + Tempering at 180 °C, cooling in air or oil | ||||||||||||||||
| ≤15 | ≥635 | ≥780 | ≥11 | ≥40 | ≥579 | |||||||||||
| Sections (bars). Carburization at 920-950 °C, air cooling + Oil quenching from 800 °C + Tempering at 190 °C, air cooling | ||||||||||||||||
| 40-60 | ≥390 | ≥640 | ≥13 | ≥40 | ≥481 | ≥250 | 55-63 | |||||||||
| Seamless hot-deformed pipes as delivered | ||||||||||||||||
| Sample | ≥431 | ≥16 | ||||||||||||||
| Seamless cold-deformed pipes in the delivered condition, heat-treated (НВ - for wall > 10 mm) | ||||||||||||||||
| Sample | ≥431 | ≥17 | ≤179 | |||||||||||||
| Mechanical properties of the rod |
| Delivery status | Section (mm) | t test (°C) | holiday temperature (°C) | sТ | s0.2 (MPa) | sB (MPa) | d5 (%) | d4 | d | d10 | y (%) | KCU (kJ/m2) | HB | H.R.C. | HRB | H.V. | HSh |
| Hot-rolled and hot-rolled steel with special surface finishing, heat-treated | ||||||||||||||||
| Sample | ≤163 | |||||||||||||||
| Calibrated and calibrated steel with special surface finish | ||||||||||||||||
| Hard-worked (without t/o) | ≥590 | ≥5 | ≥45 | ≤207 | ||||||||||||
| After annealing (vacation) | ≤550 | ≥60 | ≤179 | |||||||||||||
| After spheroidizing annealing | 360-470 | ≥60 | ≤179 | |||||||||||||
| Mechanical properties of forgings |
| Delivery status | Section (mm) | t test (°C) | holiday temperature (°C) | sТ | s0.2 (MPa) | sB (MPa) | d5 (%) | d4 | d | d10 | y (%) | KCU (kJ/m2) | HB | H.R.C. | HRB | H.V. | HSh |
| Forgings. Quenching + Tempering | ||||||||||||||||
| KP 245 | 100-300 | ≥245 | ≥470 | ≥19 | ≥42 | ≥383 | 143-179 | |||||||||
| KP 275 | 100-300 | ≥275 | ≥530 | ≥17 | ≥38 | ≥333 | 156-197 | |||||||||
| KP 275 | <100 | ≥275 | ≥530 | ≥20 | ≥40 | ≥432 | 156-197 | |||||||||
| KP 315 | 100-300 | ≥315 | ≥570 | ≥14 | ≥35 | ≥333 | 167-207 | |||||||||
| KP 345 | 100-300 | ≥345 | ≥590 | ≥17 | ≥40 | ≥530 | 174-217 | |||||||||
| Forgings. Normalization | ||||||||||||||||
| KP 195 | 100-300 | ≥195 | ≥390 | ≥23 | ≥50 | ≥530 | 111-156 | |||||||||
| KP 195 | 300-500 | ≥195 | ≥390 | ≥20 | ≥45 | ≥481 | 111-156 | |||||||||
| KP 195 | <100 | ≥195 | ≥390 | ≥26 | ≥55 | ≥579 | 111-156 | |||||||||
| KP 215 | 100-300 | ≥215 | ≥430 | ≥20 | ≥48 | ≥481 | 123-167 | |||||||||
| KP 215 | <100 | ≥215 | ≥430 | ≥24 | ≥53 | ≥530 | 123-167 | |||||||||
| KP 245 | <100 | ≥245 | ≥470 | ≥22 | ≥48 | ≥481 | 143-179 | |||||||||
| Mechanical properties depending on tempering temperature |
| Delivery status | Section (mm) | t test (°C) | holiday temperature (°C) | sТ | s0.2 (MPa) | sB (MPa) | d5 (%) | d4 | d | d10 | y (%) | KCU (kJ/m2) | HB | H.R.C. | HRB | H.V. | HSh |
| Rod with a diameter of 25 mm. Quenching in oil from 900 °C + Tempering | ||||||||||||||||
| 200 | ≥650 | ≥880 | ≥18 | ≥58 | ||||||||||||
| 300 | ≥690 | ≥880 | ≥16 | ≥65 | ||||||||||||
| 400 | ≥690 | ≥850 | ≥18 | ≥70 | ||||||||||||
| 500 | ≥670 | ≥780 | ≥20 | ≥71 | ||||||||||||
| 600 | ≥610 | ≥730 | ≥20 | ≥70 | ||||||||||||
| Mechanical properties at elevated temperatures |
| Delivery status | Section (mm) | t test (°C) | holiday temperature (°C) | sТ | s0.2 (MPa) | sB (MPa) | d5 (%) | d4 | d | d10 | y (%) | KCU (kJ/m2) | HB | H.R.C. | HRB | H.V. | HSh |
| A sample with a diameter of 6 mm and a length of 30 mm is forged and normalized. Deformation speed 16 mm/min. Strain rate 0.009 1/s | ||||||||||||||||
| 700 | ≥120 | ≥150 | ≥48 | ≥89 | ||||||||||||
| 800 | ≥63 | ≥93 | ≥56 | ≥74 | ||||||||||||
| 900 | ≥51 | ≥84 | ≥64 | ≥88 | ||||||||||||
| 1000 | ≥33 | ≥51 | ≥78 | ≥97 | ||||||||||||
| 1100 | ≥21 | ≥33 | ≥98 | ≥100 | ||||||||||||
| 1200 | ≥14 | ≥25 | ||||||||||||||
| Technological properties |
| Weldability | Weldable without restrictions (except for chemically and thermally treated parts). Welding methods: RDS, KTS. |
| Tendency to temper brittleness | Not inclined. |
| Forging temperature | Start - 1260 °C, end - 760 °C. Workpieces with a cross-section of up to 200 mm are cooled in air, while 201-700 mm are subjected to low-temperature annealing. |
| Flock sensitivity | Insensitive. |
| Critical point temperature |
| Critical point | Temperature °C |
| AC1 | 750 |
| AC3 | 825 |
| AR3 | 755 |
| AR1 | 665 |
| MN | 390 |
| Impact strength |
| Delivery condition temperature | +20 | -20 | -40 | -60 |
| Rod with a diameter of 115 mm. Hardening. Vacation. | 280-286 | 280-289 | 277-287 | 261-274 |
| Endurance limit |
| Heat treatment, steel condition | s-1 (MPa) | t-1 (MPa) | n | sB (MPa) | s0.2 (MPa) |
| Normalization. HB 143-179 | 235 | 1E+7 | 450-590 | 295-395 | |
| Hardening. High holiday. HB 217-235 | 295 | 1E+7 | 690 | 490 | |
| Cementation. Hardening. Low vacation. HRCе 57-63 | 412 | 1E+7 | 930 | 790 |
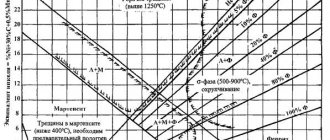
| Hardenability |
Hardening 860 °C.
Hardness for hardenability strips HRCе. Distance from the end, mm/HRCе
| 1.5 | 3 | 4.5 | 6 | 7.5 | 9 | 10.5 | 13.5 | 18 |
| 38,5-49 | 34-46,5 | 29-44 | 24,5-40 | 22-35,5 | 32,5 | 30 | 27 | 24,5 |
| Heat treatment | Amount of martensite, % | Crete. dia. in water | Crete. dia. In oil | Crete. hardness, HRCе | Dist. from the cooled end, mm |
| 50 | 26-48 | 8-24 | 32-36 | ||
| 90 | 12-28 | 3-9 | 38-42 |
| Physical properties |
| Test temperature, °C | 0 | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 1000 |
| Modulus of normal elasticity (E, GPa) | 216 | 216 | 213 | 198 | 193 | 181 | 171 | 165 | 143 | 133 | |
| Modulus of elasticity under torsional shear (G, GPa) | 84 | 83 | 76 | 74 | 71 | 67 | 62 | 55 | 50 | ||
| Density (r, kg/m3) | 7830 | 7830 | 7810 | 7780 | 7710 | 7640 | |||||
| Thermal conductivity coefficient (l, W/(m °C)) | 42 | 42 | 42 | 41 | 40 | 38 | 36 | 33 | 32 | 31 | |
| Ud. electrical resistance (R, NΩ m) | |||||||||||
| Linear expansion coefficient (a, 10-6 1/°С) | 10,5 | 11,6 | 12,4 | 13,1 | 13,6 | 13,6 | 14 | ||||
| Specific heat capacity (C, J/(kg °C)) | 496 | 508 | 525 | 537 | 567 | 588 | 626 | 626 | 706 |
| Designations |
Mechanical properties:
|
About the chemical composition and physical properties of steel 20x
As can be determined by the name of this brand, this metal has 0.20% carbon and about 1% chromium. These are not the only chemical elements that provide the alloy with its excellent properties:
- Fe – about 97%
- Cr – 0.7-1.0%
- C – 0.17-0.23%
- Mn – 0.5-0.8%
- Ni – up to 0.3%
- Si – 0.17-0.37%
- S – no more than 0.035%
- P – no more than 0.035%
- Cu – no more than 0.3%
This set of elements makes it possible to obtain steel that is insensitive to the formation of flakes, is not prone to temper brittleness and has a hardness of HB 10-1 = 179 MPa. In addition, 20x steel can be welded with virtually no restrictions: the only exceptions are chemically and thermally treated products.
The physical and mechanical properties of chrome alloy grade 20x are presented in the following tables:
Density of carbon steels
The density of carbon steel at room temperature ranges from 7.83 to 7.87 g/cm3. The table shows the density values of the following carbon steels: steel 08KP, steel 08, steel 20, steel 40, steel U8, steel U12.
The density values in the table are indicated depending on the temperature - in the range from 0 to 1100°C. When steel is heated, it becomes less dense. For example, the density of steel 20 is 7859 kg/m3 at a temperature of 15°C, and when heated to a temperature of 1100°C, the density of this steel decreases to 7496 kg/m3.
Note: The density of carbon steels in the table is expressed in units of kg/m3.
Steel 20x: areas of application and GOST standards
Structural alloy steel of this type is supplied to the workshops of industrial enterprises in the form of rolled products, the manufacturing technology of which is prescribed in GOSTs: forged blanks are produced in accordance with GOST 1133-71 and 8479-70, rolled sheets - GOST 1577-93 and 19903-74, calibrated rods - GOST 8559-75, 1051-73, 8560-78, 7417-75, etc. Finished products made from this alloy are most often cemented parts and elements, including gears, cages, bushings, sleeves, etc. The main requirements for such products relate to the high surface hardness of the metal against the background of low core strength. In other words, 20x steel is excellent for producing wear-resistant parts that experience frictional forces.
Another area of application for 20x steel is the manufacture of measuring instruments. The cemented alloy makes it possible to make a tool of sufficient hardness (minimum Rc = 56-64) while maintaining its complex configuration and long length.