Characteristics of steel grade 13HFA
13HFA - Structural alloy steel with increased corrosion resistance and cold resistance. The pipes differ from conventional oil and gas pipelines in accordance with GOST 8731, GOST 8732, by increased cold resistance, increased resistance to general and pitting corrosion, resistance to sulfide corrosion cracking and the formation of hydrogen cracks. Weldable with restrictions, welding methods: RDS, ADS submerged arc.
It has found its application for the manufacture of pipe blanks and seamless hot-deformed oil and gas pipeline pipes with increased corrosion resistance and cold resistance, intended for use in gas transporting systems, oil and gas pipeline systems, technological field pipelines transporting oil and petroleum products, as well as in systems for maintaining reservoir pressure in the northern climate zone at ambient temperatures from -60°C to +40°C, temperature of transported media from +5°C to +40°C and operating pressure up to 7.4 MPa; seamless hot-deformed pipes of increased corrosion resistance and cold resistance (Article 13HFA), with an outer diameter from 60 to 426 mm, strength class not less than K52, for in-field pipelines transporting oil well products (gas pipelines and pressure oil pipelines at pressures up to 4.6 MPa); for the production of electric-welded expanded straight-seam pipes with increased corrosion resistance and cold resistance, used for gas pipelines, process and field pipelines at operating pressures up to 7.4 MPa, transporting oil and petroleum products, for pipelines for maintaining reservoir pressure in any climatic zones..
Metal composition and characteristics
The characteristics of steel grade 13ХФ GOST 4543-71 should be considered based on its composition and basic properties.
Download GOST 4543-71
Chemical composition
According to its chemical composition, it belongs to the category of carbon alloy steels. In accordance with the established standard, the following composition of elements is allowed. As with any steel, the base is iron. Carbon is allowed as additives - in an amount of 1.25-1.4, silicon up to 0.4. Alloying additives: manganese - no more than 0.45, chromium - up to 0.7, nickel - up to 0.35, vanadium more than 0.25.
Physical properties
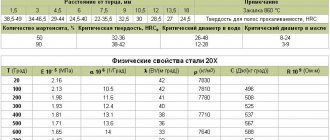
The main physical properties correspond to the established GOST standards and have the following values:
- the linear expansion coefficient changes from 11.9 (TELE x 106 1/deg) at a temperature of 100 °C to 14.9 (TELE x 106 1/deg) when the temperature increases to 700 °C;
- the elastic modulus is about 2.1 MPa at normal temperature, decreasing to a coefficient of 1.89 MPa at 900 °C or more;
- the density of the alloy does not exceed 7680 kg/m3;
- specific heat capacity about 540 J/(kg×deg);
- specific electrical resistance R×109 Ohm.
Structure of 13HFA steel when quenched from 930 °C
The metal has a pronounced ferrite-pearlite structure. Basically, it has a round shape, oriented in the direction of possible deformation, which determines its properties.
Mechanical properties
These properties of 13CFA are determined by the chemical elements included in the alloy. The main numerical characteristics obtained at a temperature of 20 °C have the following values:
- the impact strength value is 196 kJ/m2;
- the permissible limit of short-term strength is in the range from 502 to 686 MPa;
- the realized yield strength is in the range from 353 MPa to 519 MPa;
- the maximum value of relative elongation does not exceed 25%.
All listed properties and characteristics comply with the established GOST requirements for all products made from 13CFA.
Seamless pipe 325x8 mm 13xfa
13HFA has certain advantages, which allows it to be used to solve a whole range of specific problems. These advantages include:
- resistance to prolonged exposure to low and high temperatures (from -60 °C to +40 °C);
- can withstand fairly high external physical loads (which indicates good strength indicators);
- high wear resistance;
- all products have excellent weldability;
- solutions transported inside such pipes can heat up to 40 °C;
- pipes made from this material are able to withstand internal pressure up to 7.4 MPa;
- 13HFA is very resistant to the formation of various types of cracks (sulfide or hydrogen).
Chemical composition of steel 13HFA
| Standard | C | S | P | Mn | Cr | Si | Ni | Cu | N | Al | V | Mo | Zn | Sn | Sb | Pb | Bi | Nb |
| TU 1383-010-48124013-03 | up to 0.15 | up to 0.005 | up to 0.018 | up to 0.7 | 0.5-0.7 | 0.17-0.37 | up to 0.3 | up to 0.25 | up to 0.008 | 0.02-0.05 | 0.04-0.09 | — | up to 0.001 | up to 0.001 | up to 0.001 | up to 0.001 | up to 0.001 | — |
| TU 1317-233-0147016-02 | 0.13-0.17 | up to 0.015 | up to 0.018 | 0.45-0.65 | 0.5-0.7 | 0.17-0.37 | up to 0.3 | up to 0.25 | up to 0.008 | 0.02-0.05 | 0.04-0.09 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| TU 1317-006.1-593377520-2003 | 0.11-0.17 | up to 0.015 | up to 0.015 | 0.4-0.65 | 0.5-0.7 | 0.17-0.37 | up to 0.25 | up to 0.25 | up to 0.008 | 0.02-0.05 | 0.04-0.09 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| TU 1319-369-00186619-2012 | 0.12-0.17 | up to 0.005 | up to 0.015 | 0.47-0.65 | 0.52-0.68 | 0.19-0.38 | up to 0.25 | up to 0.3 | up to 0.01 | 0.02-0.05 | 0.04-0.07 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| TU 1381-116-00186654-2013 | up to 0.13 | up to 0.005 | up to 0.015 | up to 0.7 | 0.5-1 | 0.17-0.4 | up to 0.3 | up to 0.3 | up to 0.01 | 0.02-0.05 | 0.04-0.1 | up to 0.3 | — | — | — | — | — | up to 0.04 |
According to TU 1383-010-48124013-03, the chemical composition is given for steel grade 13KhFA. To ensure fine grain size and nitrogen binding in nitrides and carbonitrides, it is allowed to introduce titanium and niobium in amounts not exceeding 0.030% and 0.040%, respectively. To globularize non-metallic inclusions, steel is deoxidized with silicocalcium or cerium. Total Nb+V+Ni content ≤ 0.15%.
According to TU 1317-006.1-593377520-2003, the chemical composition is given for steel grade 13KhFA. The mass fraction of hydrogen in steel in the pipe metal should not exceed 1.0 ppm (2.0 ppm in the ladle sample). It is allowed to introduce niobium and titanium to obtain a mass fraction of up to 0.030% and 0.010%, respectively. Calcium (silicocalcium) or cerium is introduced into deoxidized steel to globularize sulfide inclusions to obtain a mass fraction of 0.050%.
According to TU 1381-116-00186654-2013, the chemical composition is given for steel grade 13HFA. The mass fraction of calcium in steel should be no more than 0.0050% (50ppm). To globularize inclusions, steel is treated with calcium-containing materials. Alloying of steel with rare earth metals is allowed. The Ca/S ratio is not less than 1, deviation from the regulated Ca/S ratio is allowed, provided that compliance with the requirements of the specifications for corrosion characteristics is ensured. It is allowed to add titanium to obtain a mass fraction in steel of no more than 0.030%. The steel must be subjected to vacuum degassing: the mass fraction of hydrogen in liquid steel after degassing should be no more than 2.5 ppm. The mass fraction of hydrogen is taken according to the document on the quality of rolled sheets. When the hydrogen content is more than 2.5 ppm, the slabs must be subjected to anti-floken treatment (APT) in heated or unheated rings. Mass fraction of Nb+V no more than 0.15%. Permissible deviations in chemical composition: carbon +0.010%, manganese +0.020%, silicon ±0.050%, sulfur +0.0010%, phosphorus +0.0030%, aluminum +0.010%, copper +0.050 %, for nickel +0.050, for chromium ±0.050%, for vanadium +0.020%, for nitrogen +0.0010%. The carbon equivalent value should not exceed 0.43, and the cracking resistance parameter Pcm should not exceed 0.24.
According to TU 1319-369-00186619-2012, the chemical composition is given for steel grade 13KhFA based on a ladle sample. Steel must be subjected to modifying treatment with calcium alloys and (or) rare earth elements (cerium, etc.). In the case of using only calcium as a modifying element, the ratio of the mass fraction of calcium to the mass fraction of sulfur in the steel must be at least 1.0. The total mass fraction of calcium is not more than 0.0060%. The hydrogen content in liquid steel should be no more than 2.5 ppm. It is allowed to introduce titanium, niobium and other carbonitride-forming elements into steel. The total mass fraction of titanium, niobium and vanadium should be no more than 0.15%. The carbon equivalent value should not be more than 0.40% for pipes with a wall thickness of less than 14 mm, and no more than 0.43% for pipes with a wall thickness of 14 mm or more.
Structural alloy steel 13HFA
Decoding steel 13HFA
- According to GOST 4543-2016, the number before the letter designation indicates the average mass fraction of carbon (C) in steel in hundredths of a percent, i.e. The average carbon content in 13HFA steel is 0.13%.
- The letter X means that the steel is alloyed with chromium, and the absence of numbers behind the letter indicates that the chromium content in the steel does not exceed 1.5%.
- The letter F means that the steel is alloyed with vanadium, and the absence of numbers behind the letter indicates that the vanadium content in the steel does not exceed 1.5%.
- The letter A indicates that the steel is high quality, i.e. with increased requirements for the chemical composition and macrostructure of metal products made from it compared to high-quality steel.
Characteristics and purpose
Steel 13HFA is a structural alloyed high-quality steel and belongs to the group of chrome vanadium steels.
Chemical composition, % (GOST 4543-2016)
| steel grade | Mass fraction of elements, % | |||||||||
| WITH | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Mo | Al | Ti | V | B | |
| 13HFA | 0,11-0,17 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,40-0,65 | 0,50-0,70 | — | — | 0,020-0,060 | — | 0,04-0,09 | — |
NOTE. The sign “-” means that the mass fraction of this element is not standardized or controlled, unless otherwise specified in 7.1.2.3 GOST 4543-2016.
Brinell hardness (GOST 4543-2016)
The Brinell hardness of metal products in the annealed (HT) or high-tempered (HT) state, as well as hot-rolled and forged metal products, normalized with subsequent high tempering (H+HT), with a diameter or thickness of over 5 mm must comply with the standards specified in the table below.
| steel grade | Hardness NV, no more |
| 13HFA | + |
NOTE. The “+” sign means that hardness control is carried out to accumulate statistical data, and the control results are entered into the quality document.
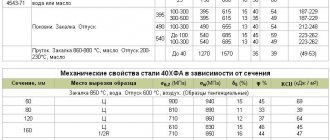
Mechanical properties [1]
| Test name | Unit | results |
| Viscous content, KCV (-50°C) | % | 95-100 |
| Impact strength, KCV (-50°C) | J/cm2 | 295,4-400,1 |
| Impact strength, KCU (-60°C) | J/cm2 | 305,8-431,6 |
| Rockwell hardness | HRB | 84-88.3 |
| Banding | points | 1 |
| Grain size | points | 9 |
| Yield strength, σ0.2 | MPa | 442-482 |
| Temporary tensile strength, σв | MPa | 553-585 |
| Ratio σt/σв | MPa | 442-482 |
| Relative extension | % | 27,4-30,8 |
Bibliography
- The specified parameters are extracted from the quality certificate for seamless oil and gas pipeline ⌀273x24 TU 14-3R-124-2012, class pr.K52, art. 13HFA
Find out more
Steel 40 structural carbon quality…
Spring steel 75
Steel 45 structural carbon quality…
Structural alloyed steel 45KhN2MFA…
Mechanical properties of 13HFA steel
| Type of delivery | Section, mm | sТ|s0.2, MPa | σB, MPa | d5, % | KCU, kJ/m2 | H.R.C. | HRB | HV, MPa |
| Rolled sheets for pipes according to TU 1381-116-00186654-2013 (transverse samples, KCV-40°С is indicated in the KCU column) | ≥375 | 510-610 | ≥23 | ≥882 | — | ≤92 | — | |
| Seamless hot-deformed oil and gas pipeline pipes with increased corrosion resistance and cold resistance according to TU 1383-010-48124013-03. As delivered (mechanical properties of pipe metal and KCV-40 °C are indicated) | ≥350 | ≥510 | ≥20 | ≥784 | — | ≤92 | — | |
| Seamless hot-deformed, heat-treated pipes in delivery condition according to TU 1319-369-00186619-2012. Column KCU indicates KCV-50°С/KCU-60°С) | 372-491 | ≥510 | ≥23 | ≥981/588 | — | ≤92 | — | |
| Seamless oil and gas pipeline heat-treated pipes in the delivered condition according to TU 1317-006.1-593377520-2003 (samples, the strength class is indicated in the delivered condition, the KCV-50 °C value is indicated in the KCU column) | 89-426 | 372-491 | ≥510 | ≥23 | ≥980 | — | ≤92 | — |
| Seamless oil and gas pipeline heat-treated pipes in the delivered condition according to TU 1317-233-0147016-02 (samples, the strength class is indicated in the delivered condition, the KCV-50 °C value is indicated in the KCU column) | — | 338-470 | 502-627 | ≥25 | ≥980 | — | ≤92 | — |
| Pipes according to TU 1381-116-00186654-2013 (transverse samples, KCU-60°C/KCV-20°C is indicated in the KCU column) | ≥350 | 510-630 | ≥20 | ≥392/392 | ≤22 | — | ≤250 |
Welding materials for welding 13xfa steel
Tees made of steel 13HFA with a design in accordance with GOST 17376-2001 are the most economical solutions for the installation of pipelines with chemically aggressive media and low ambient temperatures. The corrosion resistance of 13HFA steel allows the use of such tees at oil and gas production sites. The cold resistance of this material allows use at temperatures from minus 60 to plus 40°C with an ambient temperature from plus 5 to plus 40°C under pressure up to 7.5 MPa.
Manufacturing of tees from steel 13HFA
GOST 17380-2001 for technical conditions of seamless pipeline parts does not describe the use of 13HFA steel. However, the strength characteristics of this material make it possible to produce tees from 13HFA steel according to the geometry of GOST 17376-2001.
Semi-finished products for the manufacture of 13HFA tees can be seamless pipes in accordance with TU 1317-006.1-593377520-2003, TU 1308-226-0147016-02, TU 1317-233-0147016-02 and other technical conditions. "Energostandard Company" offers only products from well-known and responsible manufacturers that meet all the required structural, physical and chemical characteristics.
Chemical composition of steel 13HFA
The mechanical characteristics and chemical properties of 13HFA tees are determined by the composition of this material. Structural alloy steel 13HFA is used for the manufacture of hot-deformed pipes for field and main oil and gas pipelines, low-pressure field water pipelines.
The characteristics of 13HFA steel are described in detail in GOST 5640-68.
13HFA steel contains from 0.08% to 0.13% carbon, and on average 0.54% manganese, 0.28% silicon, 0.55% chromium, 0.3% nickel, harmful impurities of sulfur and phosphorus 0. 02 and 0.05% respectively. Steel 13KhFA has a ferrite-pearlite structure with cementite, predominantly round in shape; banding is determined by the general orientation of the structure in the direction of deformation without clearly defined bands.
The closest substitutes for 13KhFA steel are materials 15KhFA, 20KhFA, 09SFA.
Corrosion resistance of tees 13HFA
An advantageous property of 13HFA steel is the manifestation of high-quality properties at a low alloying level. This determines the obtainment of valuable material properties at relatively low costs for alloying elements.
Oilfield facilities are characterized by a high content of hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide and oxygen. GOST 17376-2001 tees made of 13HFA steel can be used in media with mineralization up to 100 mg/l.
Tees 13HFA are significantly superior in corrosion resistance to tees made from steel 09G2S. Manganese, which is part of the 09G2S material, impairs corrosion resistance, since it is more active than iron and forms oxides and sulfides. The parameters of their crystal lattices differ from those of iron oxides and sulfides. As a result, corrosion products loosen and peel off from the metal surface.
Steel 13HFA is chromium-containing. This metal forms an amorphous hydroxide, which coats the surface of the steel, binds the iron carbonate crystals together and protects them from dissolution by the medium. This is evidenced by studies conducted in oil fields of Western Siberia and the Komi Republic.
Steel 13HFA provides tees with a general corrosion rate of no more than 0.35 mm/year and resistance to sulfide cracking under mechanical stress of no less than 0.75∙σ0.2. Resistance to hydrogen cracking along the crack length (CLR) - no more than 1%, along the thickness of the cracks (CTR) - no more than 3%.
Strength of tees 13HFA GOST 17376-01
13HFA tees correspond to strength class K52 and higher, which corresponds to a tensile strength σв = 500 – 627 MPa and a yield strength σт = 334 – 470 MPa.
Steel 13HFA is almost twice as hard (HB=248 MPa) as steel 09G2S. This indicates greater resistance to erosion of 13KhFA tees compared to 09G2S tees.
Installation and operation of tees 13HFA
GOST 17376 tees made of 13HFA steel have good weldability. The low carbon content eliminates hardening and overheating during the welding process, so ductility is not reduced and grain size does not increase. Welding can be carried out without heating.
Steel 13HFA Moscow and Moscow region
Steel has a wide range of applications in mechanical engineering, manufacturing, construction, shipbuilding, aircraft manufacturing and many other industries. There are many grades of steel, most of them are made to order, there are grades that are constantly in stock due to regular demand. The Resurs company sells 13HFA steel directly from the manufacturer. With constant demand, we are ready to offer mutually beneficial terms for the supply of many grades of steel. Including 13HFA.
The favorable price for the 13HFA brand is determined by the minimum markup and the absence of intermediaries. We take full responsibility for the supplied material and guarantee the quality of delivery. The cost of products is determined by warehouse and logistics costs; we have the ability to supply steel directly from the manufacturer’s plant, this allows our clients to run their business stably.