Coatings of fasteners according to GOST 9.306
To ensure corrosion resistance of threaded products and give them a marketable appearance, the coatings given in the table are used.
| Type of coverage | Coverage designation | |
| According to GOST 9.306 | digital | |
| Zinc, chromated | Ts.khr | 01 |
| Cadmium, chromated | Kd.hr | 02 |
| Multilayer: copper-nickel | M.N | 03 |
| Multilayer: copper-nickel-chrome | M.N.H.b | 04 |
| Oxidized, oil-impregnated | Chem.Ox.prm | 05 |
| Phosphate, oil impregnated | Chem.Phos.prm | 06 |
| Tin | ABOUT | 07 |
| Copper | M | 08 |
| Zinc | C | 09 |
| Oxidic, filled with chromates | An.Ox.nhr | 10 |
| Oxidic from acidic solutions | Chemical pass | 11 |
| Silver | Wed | 12 |
| Nickel | N | 13 |
High strength bolt technology
One of the important components in fastening technology is the clear recording of the time period after preparation and lubrication of the thread before the direct use of the fastener. This period should not exceed 10 days, which should be indicated in a special journal for installing high-strength bolts after their delivery from the manufacturer. If the preparation was carried out independently, then the data is also recorded by filling out a log. An example of the order of fastening a bolted connection:
- Prepare the entire structure for docking and installation.
- Prepare the necessary fasteners according to standards.
- Carry out installation and installation of the structure.
- Tighten the bolts.
- The joints of all fasteners are sealed.
- Carry out quality control of the assembly of the object.
Preparing High Strength Bolts, Nuts and Washers
Before installation into the structure, high-strength bolts, nuts and washers must be prepared. It includes:
- Technological cleaning of preservative factory lubricants, as well as dust and dirt. It is performed in a heated alkaline solution at a temperature of 80-100°C, which includes water, detergents, soda ash and caustic soda, liquid glass and trisodium phosphate. The ratio is strictly observed according to GOST. The fasteners in a special container are dipped into the solution for 20 minutes, after which they are washed 3-5 times in a washing solution.
- Drying is carried out hot for several minutes, blowing with compressed air.
- Perform running on a lathe or wrenches, checking and lubricating the threads.
- Mandatory lubrication of fastener threads is carried out by immersing it in a solution of special gasoline GOST 2084 and mineral oil GOST 0799 in a ratio of 9 to 1.
- Purified hardware is collected and stored in closed containers. When assembled, each bolt is equipped with a nut and two washers.
- Carry out quality control.
The time period from thread lubrication to installation should be no more than 10 days.
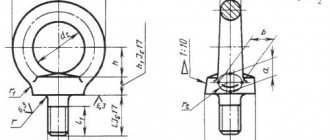
Symbol diagram for bolts, screws, studs and nuts
Examples of symbols for fasteners
Screw - according to GOST 17473-80 accuracy class A, version 2, thread diameter d=12 mm with fine thread pitch, with thread tolerance field 6e, length l=60 mm, accuracy class 5.8, made of mild steel with a zinc coating 9 microns thick , chromated
Screw A2M12×1.25-6e×60.58.S.019 GOST 17473-80
Nut - according to GOST 5916-70 version 2, thread diameter d=12 mm, with a fine thread pitch, with a left-hand thread, with a tolerance range of 6H, strength class 05, made of steel grade 40X, with an ink coating 6 microns thick, chromated
Nut 2M12×1.25-L-6N.05.40Х.016 GOST 5916-70
Notes:
- The symbol does not indicate : version 1, large thread pitch, right-hand thread, lack of coating, as well as parameters clearly defined by product standards; accuracy class B, if the standard for a specific fastener provides for two accuracy classes (A and B).
- If a coating not provided for by this standard is used, its designation is indicated in accordance with GOST 9.306-85.
Related Pages
- Cylindrical threads
- Tapered threads
- Metric thread
- Runs, undercuts, grooves and chamfers according to GOST 10549
- Thread persistent
- Trapezoidal thread
- Mechanical properties of bolts, screws, studs, nuts.
- General Purpose Hex Head Bolts
- General purpose screws
- Captive screws
- Set screws
- Special purpose bolts and screws
- Self-tapping screws for metal and plastics
- Locking the nut against the bolt with additional elements
- Locking the nuts relative to the body
- Locking the nut relative to the bolt due to additional friction, welding and plastic deformation
- Locking bolts. Preventing screws and nuts from being lost
- Locking screws
- Flange connection parts
- Flange connections for pipes and cylinder heads
- Flange connections for metal structure pipes
- Application examples for set screws
- Terminal connections
- Friction screw clamps
- Ties and stops
- Fastening machines to bases
GOST 2.315-68 ESKD. Simplified and conventional images of fasteners
GOST 2.315-68
INTERSTATE STANDARD
UNIFIED SYSTEM OF DESIGN DOCUMENTATION
SIMPLIFIED AND CONVENTIONAL IMAGES OF FASTENING PARTS
IPC PUBLISHING HOUSE OF STANDARDS
Moscow
Change No. 2 was adopted by the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (Minutes No. 12 of November 21, 1997)
The following voted to approve the change:
| State name | Name of the national standardization body |
| The Republic of Azerbaijan | Azgosstandart |
| Republic of Armenia | Armgosstandard |
| The Republic of Kazakhstan | Gosstandart of the Republic of Kazakhstan |
| Kyrgyz Republic | Kyrgyzstandard |
| The Republic of Moldova | Moldovastandard |
| Russian Federation | Gosstandart of Russia |
| The Republic of Tajikistan | Tajikgosstandart |
| Turkmenistan | Main State Inspectorate of Turkmenistan |
| The Republic of Uzbekistan | Uzgosstandart |
| Ukraine | State Standard of Ukraine |
INTERSTATE STANDARD
| Unified system of design documentation SIMPLIFIED AND CONVENTIONAL IMAGES OF FASTENING PARTS Unified system for design documentation. Simplified and symbolic designations of fasteners. | GOST 2.315-68* In return GOST |
By the Decree of the Committee of Standards, Measures and Measuring Instruments under the Council of Ministers of the USSR of December 1967, the introduction date was established
from 01.01.71
1. This standard establishes simplified and conventional images of fasteners on assembly drawings and general view drawings of all industries and construction. The standard fully complies with ST CMEA 1978-79.
2. In assembly drawings and general view drawings, the image of fasteners (simplified or conditional) is selected depending on the purpose and scale of the drawing.
Fasteners whose rod diameters in the drawing are 2 mm or less are depicted conventionally. The size of the image should give a complete picture of the nature of the connection.
3. Simplified and conventional images of fasteners must correspond to those indicated in the table. 1.
Table 1
| Name | Image | |
| simplified | conditional | |
| 1. Bolts and screws: with hex head | ||
| with square head | ||
| with hammer head | ||
| 2. Bolts: with a semicircular head and mustache | ||
| folding with round head | ||
| folding with fork | ||
| foundation | ||
| 3. Screws: with semicircular head | ||
| with cylindrical head | ||
| with cylindrical head and sphere | ||
| with a semicircular head and a cross-shaped slot | ||
| with cylindrical head, sphere and cross slot | ||
| with cylindrical head and hexagonal socket | ||
| with semi-countersunk head | ||
| with countersunk head | ||
| with countersunk head and cross slot | ||
| with cylindrical head self-tapping | ||
| with countersunk head and cross slot, self-tapping | ||
| 4. Nuts: round | ||
| hexagonal | ||
| hex slotted and crowned | ||
| wing nuts | ||
| 5. Screws: with semicircular head | ||
| with countersunk head | ||
| with semi-countersunk head | ||
| 6. Hairpins | ||
| 7. Washers: simple, locking, etc. | ||
| locking with tongue | ||
| spring | ||
| 8. Pins: cylindrical | ||
| conical | ||
| 9. Nails | ||
| 10. Cotter pins | ||
| 11. Threaded inserts | ||
4. Examples of simplified and conventional images of fasteners in connections are given in table. 2.
table 2
| Image | |
| simplified | conditional |
3, 4. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 2).
5. If the object shown in the assembly drawing has a number of similar connections, then the fasteners included in these connections should be shown conventionally or simplified in one or two places of each connection, and in the rest - with center or axial lines (Figure 1) .
Crap. 1
6. If there are several groups of fasteners in the drawing, different in types and sizes, then instead of applying repeating item numbers, it is recommended to designate identical fasteners with symbols, and apply the item number only once (Fig. 2).
Crap. 2
In construction drawings, it is allowed to outline identical groups of fasteners with a solid thin line with an explanatory inscription on the shelf of the leader line; however, the predominant fasteners are not outlined or specified in the general instructions for the drawing.
7. The slots on the heads of fasteners should be depicted as one continuous line, as shown in Fig. 3: in one view - along the axis of the fastener, in the other - at an angle of 45 ° to the drawing frame.
Crap. 3
If the slot line drawn at an angle of 45° to the drawing frame coincides with the center line or is close to it, then the slot line is drawn at an angle of 45° to the center line (Fig. 4).
Crap. 4
Fastener materials
According to the fastening standard GOST 1759.4-87 “Bolts, screws and studs. Mechanical properties and test methods" (“Bolts, screws and studs. Mechanical properties and test methods”), the mechanical characteristics of carbon and alloy steels used for the manufacture of bolts, screws and nuts, as well as the steel grade, must correspond to those indicated in Table 1.
Table 1. Mechanical characteristics of corrosion-resistant (stainless), heat-resistant, heat-resistant and heat-resistant steels (at normal temperature) for the production of screws, bolts, studs and nuts.
| Fastener steel grade | tensile strength σв, MPa | yield strength σt, MPa | relative elongation δ5, % | impact strength, aH, J/cm2 | |
| Bolts | Nuts | no less | |||
| 12Х18Н10Т | 12Х18Н9Т, 10Х17Н13М2Т | 520 | 200 | 40 | 40 |
| 20Х13 | — | 700 | 550 | 15 | 60 |
| 14Х17Н2 | 20Х13, 14Х17Н2 | 650 | 12 | 60 | |
| 10Х11Н23Т3МР 13Х11Н2В2МФ | — Х12Н22Т3МР | 900 | 550 | 8 | 30 |
| 25Х1МФ | 25Х2М1Ф 20Х1М1Ф1ТР | 750 | 10 | 30 | |
The use of Bessemer steels for the manufacture of fasteners is prohibited, since such steel fasteners have increased brittleness due to the high content of phosphorus and nitrogen absorbed from the air during purging.
When there are strict requirements for corrosion resistance, strength, dimensions and weight of the connection, fasteners made of titanium and beryllium alloys, high-strength and heat-resistant steels and alloys are used.
↑ To the beginning
Strength
Strength is strictly regulated by GOST, since in some cases this affects human safety and the safety of equipment or buildings. To achieve accurate strength characteristics, high-strength bolts are calculated. The production of high-strength bolts is regulated by GOST 7798-70.
Based on their strength characteristics, bolts are divided into 11 classes. Each category has its own labeling, based on which you can clearly determine which class it belongs to and what load it can withstand. It should be noted that each hardware has a certain margin of safety to the indicators indicated in the marking. Therefore, you should not worry that the safety margin of the bolt will be used for future use.
The strength of bolts depends not only on the type of material used, but also on the manufacturing technology. Based on the strength characteristics of fastening elements, we can distinguish the classification of bolts by strength:
- 3.6 – fasteners made of non-alloy steel, without additional hardening;
- 4.6 – products made of carbon steel (carbon less than 0.55%);
- 5.6 – from steel without tempering (carbon more than 0.15%);
- 6.6 and 6.8 – bolts made of carbon steel without additional additives;
- 8.8 – steel with additional components (chrome, manganese, boron) is used, which after hardening is tempered at a temperature of more than 400 degrees;
- 9.8 - practically no different from class 8.8, having an increased strength index;
- 10.9 - steel with additives is used, which is tempered in the temperature range from 340 to 425 degrees.
- 12.9 – alloy steel with a minimum content of phosphorus and sulfur is used for the manufacture of fasteners.
16.1. Bolts
The bolt consists of two parts: a head and a threaded rod.
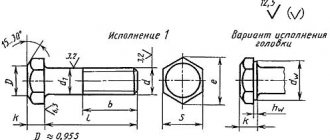
Bolt designation
:
Bolt 2 M 16 × 1.5.
6g × 75. 68. 09 GOST 7798-70-2 – version; M 16 – type and size of thread; 1.5 – fine thread pitch value; 6g – tolerance range; 75 – bolt length ι
; 68 - a symbol of a strength class, indicating that the bolt is made of steel with certain mechanical properties; 09 – zinc coating; GOST 7798-70 is a standard indicating that the bolt has a hex head and is made with normal accuracy.
Figure 16.1
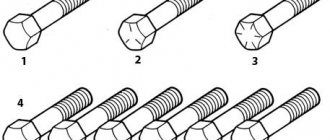
Marking of fasteners
Figure 3. Marking of bolts, studs, and screws.
According to GOST 1759.0-87, the following fasteners must be marked indicating the strength class:
- hexagon socket screws with thread diameter d ≥ 5 mm and
- studs with a diameter of 12 mm and above must be marked indicating the strength class.
Fasteners of strength classes 3.6, 4.6, 4.8, 5.6, 5.8, 6.6, 6.8 and 6.9 are marked as agreed upon by consumers and.
The dimensions of marking signs are established by the manufacturer of fasteners. The factory mark and markings must be applied to the head of the bolt or screw and to the end of the end of the studs (Figure 2). Bolt marking according to application method
,
studs
and screws can be of two types:
- convex or
- in-depth.