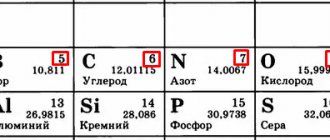
What it is?
Noble metals are distinguished from other elements by their ability to maintain their molecular structure under the influence of an unfavorable environment. They cannot be decomposed, and the melting point of these elements is extremely high. They do not react with oxygen and do not produce oxides. Alloys with precious metals can only be obtained through complex chemical manipulations using the strongest reagents.
The mass share of precious metals in the total production of natural resources is very small, which explains the high price of these elements, as well as their special status.
A complete list of names of precious metals was prescribed in 1998 in the Federal Law “On Precious Metals and Precious Stones”. According to Russian legislation, platinum and five of its group metals, as well as the popular silver and gold, are considered precious.
Signs of nobility and classification of elements
It is very simple to understand which metals are called noble and which are considered basic or, in other words, base. This status is determined by the properties they possess. Substances that are classified as noble metals do not oxidize and are not subject to corrosive effects. These characteristic features strikingly distinguish them from other elements - all other metals cannot boast of such durability, and therefore are considered base.
Without exception, all representatives of the noble category also have the status of precious ones. Belonging to the latter is due to the rarity of these substances. The list of noble metals includes eight elements :
- gold;
- silver;
- platinum;
- iridium;
- osmium;
- palladium;
- rhodium;
- ruthenium.
Substances from the first three are considered the main metals of the noble group. The five others belong to the so-called daughter elements of platinum. Platinum representatives are often divided into two groups :
- light metals;
- heavy metals.
The former include palladium, rhodium and ruthenium. The latter include iridium, osmium and platinum itself.
Some scientists consider another ninth representative to be noble - the chemical element technetium. But most experts do not support this point of view - this metal, which is extremely rare in nature, has a fair amount of radioactivity, so it is not customary to officially call it among the noble ones.
History of appearance
Noble metals are a valuable and non-renewable natural resource. None of the precious metals can be obtained experimentally, so for the scientific community the appearance of these elements on Earth still remains a mystery. At the moment, there are two working versions of their appearance:
- Space. Proponents of this hypothesis believe that we owe the appearance of precious metals in the earth's crust to meteorites that bombarded the Earth at the dawn of its formation. However, this version has a serious drawback - scientists have found that the average meteorite contains only about 0.005% of the total weight of noble metals, which in no way correlates with the volumes mined at different deposits.
- Tectonic. According to this assumption, all precious metals were born under the influence of high temperatures and in the presence of special conditions in the core of the planet, and then were thrown to the surface with lava flows. This version has more supporters than the space version, however, it cannot answer all the questions. In particular, it is not clear why these natural resources stopped forming again and entering the upper layers of the earth's crust along with volcanic lava emissions.
The question of the origin of noble metals and their alloys is one of the most important. If scientists are ever able to answer it, it will change the entire existing system of relationships in the world.
Osmium 187
To produce a unique synthesized black powder with a purple tint, which is a complex isotope, it takes about 280 days. Its creation poses a number of certain difficulties.
Osmium 187 is the densest substance on Earth, the strongest and at the same time fragile metal in the world.
It is of enormous importance for scientific research and is used as a catalyst in chemical reactions. Used for the production of high-precision measuring instruments.
The first and only country providing this valuable element to the world market is Kazakhstan. Cost: $200,000 per 1 g.
Which metals are noble and their properties?
This group of metals received the name “noble” due to their special characteristics. Depending on the variety, their physical and chemical properties may manifest themselves to varying degrees, but they always remain unique.
Rhodium
Rhodium is a member of the platinum group. It is a light metal and has a pale blue color. It is distinguished by a high degree of hardness and, at the same time, fragility.
Valued for its high reflectivity and resistance to chemical attack. Rhodium can only be oxidized with hot sulfuric acid. The melting process begins when heated to almost 2000 °C.
Platinum
Because of its white luster, platinum, discovered in the mines of America, was originally called “silver.” Only in 1751 platinum received the status of a precious metal, and its value instantly surpassed the then known silver and gold. It has high ductility and can be easily forged (which is why it is loved by jewelers). At the same time, platinum is harder than gold, refractory, resistant to chemical influences, and not subject to oxidation.
Gold
Like platinum, it has good ductility and malleability, but has lower melting points. Reacts only with aqua regia, invulnerable to alkalis, salts and acids. In nature, specimens of pure gold with a pronounced yellow color and characteristic shine are rarely found. Most often, miners encounter green faded ore.
Osmium
The most refractory of the noble metals. The melting point reaches 2700 °C. In addition, osmium does not dissolve in acids. External characteristics are white and hard. Belongs to the group of heavy metals.
Iridium
Like osmium, it is a heavy metal. The most durable, dense, refractory and insoluble in acids, gray-white in color. The melting point is slightly lower than that of osmium and is 2454 °C.
Ruthenium
In terms of external characteristics, ruthenium can easily be confused with platinum. The noble metal resembles iridium in its melting point and has increased strength and density. It is interesting that only ruthenium and osmium form water-soluble cakes under the influence of alkali, oxidizing agent and high temperatures.
Palladium
Soft, malleable, white with a silver tint. When heated to 860°C, palladium forms oxides, but becomes pure again as the temperature rises further. The melting point is 1554 °C.
Silver
Among the noble metals, silver has the lowest density and a relatively low melting point - 960 ° C. It is best forged and serves as an excellent heat and electrical conductor. It practically does not react with acids, but darkens under the influence of hydrogen sulfide, which is part of the atmosphere.
List of semi-precious metals
In jewelry production and instrument making, metals are actively used that are not essentially precious, but have a certain value. They are conventionally called semi-precious. Among the most popular types are the following:
- titanium;
- tungsten;
- cupronickel
Their price fluctuates in the average price range and does not exceed $2 per gram.
From ore to ingot
Mining precious metals is a labor-intensive process. Gold reserves are decreasing, many are in hard-to-reach places, “under revision.” Companies mining precious metals are constantly improving their mining technology.
There are no easy deposits.
Let's go from a gold-bearing rock to a ring on a woman's finger.
Primary ore mining occurs in already explored deposits. Geologists spend time on expeditions, examine outcrops (rock outcrops), describe the collected samples, and observe whether there are any satellite minerals of noble metals. For silver, these are kerargyrite (silver hornblende), argentite, and proustite.
Before the revolution in the Urals, the “grandfathers-miners” were engaged in searching for gold veins. And they found veins.
The problem with Ural gold mining is water. Groundwater seeps through the walls, drips from the ceiling, and the floor is often flooded with water.
African and Indian gold mines suffer from the heat - it is above 40°C there.
Gold - to the surface
In places determined by geologists, pits are drilled, explosives are dropped into them and the rock is undermined. Then, using special equipment, the ore is delivered to the top and taken to the processing plant.
Extracting gold from ore
You look at the gold ore and pass by. She is not beautiful, she does not (usually) sparkle with gold. Let's start producing gold.
The content of precious metals in the ore dictates the method of processing.
There are several of them:
- Cyanidation.
- Heap leaching.
- Amalgamation.
- Hydrometallurgy.
We received a precious metal, not too pure. Go ahead.
Refining
To remove remaining impurities from gold, it is saturated with sulfur or chlorine. The essence of the process is to make gold liquid, then strain it, separate out impurities and convert it into a solid state.
We recommend: TANTALUM - hard, rare and expensive
Casting
Where does the gold go now - in molds - cast iron molds, gold is poured into them. The metal hardens quickly, so it sparkles in the cradle mold. You've seen gold bars of this shape on TV.
How are they mined?
Placers of precious metals are practically no longer found on the surface of the Earth. For example, gold mines are a kind of underground reservoirs in which ore is first turned into solution, and then filtered and sent for further processing.
The extraction of silver and other precious metals occurs in parallel with the extraction of the main mining ore, such as copper or lead. This is explained by the insignificant content of platinum group precious metals in the earth's crust and the unprofitability of their extraction. Silver is also quite rare in its pure form and makes up only about 20% of the total ore.
How are precious metals processed and purified?
The ore obtained by miners is unsuitable for use without preliminary cleaning and processing. It will be convenient to consider them using the example of gold, which is mined in large quantities.
The very first stage of processing for a long time remained cyanidation of gold ore, but over time this method developed into heap leaching. The method involves exposing the ore to cyanide and then filtering the resulting gold sediment - concentrate.
The concentrate undergoes a series of physical and chemical studies, background radiation testing, and only after that it is sent for further purification - refining. In a nutshell, refining is the liquefaction, straining and recovery of the original material, the only difference being that the recovered gold has no impurities. The gold alloys obtained after refining can be sent for casting into ingots.
Precious metal alloys
Alloys of noble metals , as a rule, contain 1-3 precious and the same number of ordinary ones. In modern times, as a rule, only gold bars for banks are made from pure gold.
This product is a reinforcement of ordinary money, a long-term investment. In the old days, pure gold was also used for jewelry, in Ancient Egypt, for example.
However, 100 percent gold, silver, and palladium are so soft that they bend without effort. In order for a piece of jewelry, for example, to be wearable, it needs to be made thick-walled and massive. This is what the Egyptians did using gold.
Noble metals in modern products sometimes take the form of thin threads and plates. Parallel to the fashion for massive jewelry, there is a trend for sophisticated jewelry.
In general, jewelers have to look for hardeners for precious metals. Among the noble ones they can be iridium and rhodium. Thus, when added to palladium, they strengthen it by 2 times. Iridium is taken 4% by weight of the alloy, and rhodium 1%.
Ligature is used to impart special properties to metal
Of the ordinary metals, copper, zinc, and nickel are mixed with precious ones. The first strengthens alloys. If the copper content is about 40%, a red glow appears, as in 585-carat gold. The noble metal content in it is, respectively, 58.5%.
Zinc and nickel themselves are quite soft. The issue here is color. Both metals are capable of making yellow gold into an alloy called white gold without the use of expensive palladium. The latter also brightens the solar cell.
Platinum, due to the prestige and superiority of gold in price, is not usually diluted with ordinary metals. For example, ruthenium is used. It is harder than platinum. Not used separately due to fragility.
Sometimes, impurities of other elements of its group to platinum are “produced” by insufficient purification of noble metals . In nature, platinoids are usually found together. Before use, the ore is disassembled into its components. Fractions of a percent of the same ruthenium may not separate from platinum.
Areas of application
Platinum, gold and silver are familiar to everyone in jewelry. However, the main use of precious metals is in the instrument making industry. They are used in the space, mechanical engineering, automotive, food industry and other areas.
For example, rhodium, due to its distinctive chemical properties, is used as a coating on silver and gold products, which significantly extends their service life and protects them from mechanical damage. Iridium is indispensable in the production of watches and in the manufacture of devices for the chemical industry.
Spheres and areas of use
The unique inimitable qualities of these substances have led to their use in a wide variety of industries and areas. Even the high cost of such materials did not prevent this.
Of course, the first thing precious raw materials are associated with is jewelry. Jewelry and other items made from such metals are in great demand, which is understandable. It is not only beautiful, but also profitable. Jewelry has always been an excellent investment.
No less famous is the use of noble materials as currency . However, in the modern world, coins made of such metals are an object of investment or collecting. In the field of investment, precious metals are invariably popular and in demand. This is especially true for gold.
In addition, these elements are widely used (for the manufacture of complete products, individual parts, and so on):
- in the production of various equipment and electronics, including microtechnology;
- in aviation and astronautics;
- in mechanical engineering (from various units to cars);
- in the production of radio equipment;
- in the chemical industry, including the laboratory sector (from glassware to equipment);
- in medicine;
- in the production of various protective coatings for absolutely any surface (from rockets and equipment to mirrors, pipes, ceramics, metals and wood);
- in the film and photographic industry;
- in the production of watches and watch movements.
Moreover, in medicine, noble metals are used not only for the manufacture of instruments and medical equipment, but also in the production of medicines . And this is not all - it is impossible to list all the areas and areas of application of precious materials.
Substances classified as noble play an extremely significant role. They are found every day in some form and are used in almost every industry. One can only guess what the life of mankind and the world around will become when the natural reserves of these metals run out.
Where can I buy or sell?
The main lots on the market remain platinum and gold. If you represent a company or have an individual entrepreneur, it is more profitable to buy metals from officially registered brokerage companies that work with leading manufacturing plants.
Expert opinion
Lyudmila Pestereva
Our most experienced gold investor
Ask a Question
It is easier for an individual to cooperate with banks that offer a wide range of services for the purchase of precious metals. For example, buy bullion and put them in your own cell, open a deposit and even make money on your investments.
Which precious metal is the most expensive?
If we are talking about the most popular and popular metals, then the leading place in the price ranking is occupied by palladium, platinum and gold.
However, Californian is rightfully considered the most expensive metal on earth.
It is mined during the operation of powerful nuclear reactors. The price for 1 gram of Californian is 6.5 million dollars. Next on the list of expensive metals is rhodium. It is estimated at 225 thousand dollars per gram.
Ruthenium | Cost of 1 gram – 1.5 US dollars
Ruthenium opens the top ten most expensive metals. The bright silver colored chemical element is distinguished by its refractoriness, hardness and fragility. Ruthenium is one of the rarest elements of the platinum group. It was first discovered by Professor Karl Klaus, who conducted research at Kazan University in 1844. The name of the element comes from the Latin Ruthenia, which means Rus'/Russia. Ruthenium is actively used in jewelry production, electronics and chemical industries.
It is used for the manufacture of electrodes, wires, contacts, etc. The element is also used to produce chlorine and alkalis. The cost of 1 gram of metal is currently estimated at 1.5 US dollars.
Is it profitable to invest in precious metals?
Of course, the rarest metals are valued many times more, but professional investors do not recommend buying them. For successful investments, it is better to choose the most common metals that are in stable demand. Now it is palladium, platinum, gold and silver.
To understand how profitable it is to invest in these metals, it is enough to look at the tables of price changes and profits provided by the Central Bank. Gold | USD | 1 oz
XAUUSD chart courtesy of TradingView
Gold shows the best results in terms of stability.
According to official data over the past 10 years, palladium has proven to be the most profitable investment.
For example, in 2010, one gram of this metal brought investors almost 125 rubles. However, this same metal turned out to be the most unstable. Price crashes happen extremely often.
Palladium | USD | 1 oz
Schedule PL1! provided by TradingView
Investment methods
The list of possibilities here is quite wide, but they all have their pros and cons:
- Buying bullion. The easiest way to invest. However, when selling, you will have to pay 18% VAT, and when selling to a bank, you will also have to pay 13% income tax.
- Buying coins. Collectible coins are not the best type of investment. Reason: high cost and 18% VAT. They are of greater value to numismatists than to professional investors.
- Shares of companies mining precious metals. They can bring large and constant income, but there are also some inconveniences: they can only be bought on the stock exchange, and you cannot do without the services of an experienced broker.
- Securities. Quite a new but interesting way of investing. You can buy securities on the stock exchange. Each security is backed by 3.1 grams of gold reserves held by HSBC in London. The only downside: with a modest investment, you won’t be able to cash out the papers in real gold.
- Bank account. There are two options here: a COX account or a compulsory medical insurance account. In terms of generating income, it is the second option, an impersonal metal account, that is interesting. According to the principle of operation, this is nothing more than a foreign currency deposit. The interest on deposits is small, but if the price of metal rises, you can make good money on the difference in prices. Taxes on gold bars purchased under compulsory medical insurance are paid only if the owner decides to cash out the account after receiving the metal in hand.
Expert opinion
Lyudmila Pestereva
Our most experienced gold investor
Ask a Question
Of all the investment methods described above, the most effective is the compulsory medical insurance contribution. However, for those who keep their finger on the pulse of the cost of precious metals or know a good broker, I advise you to try more interesting options. For example, shares or securities.
Palladium
The silvery-white isotope, a member of the noble platinum metals, was discovered by British chemist William Wollaston in 1803. The main advantages of palladium are ductility, softness, low melting point, resistance to darkening and corrosion.
Palladium is widely used in industry and the medical field. Indispensable in the manufacture of jewelry: thanks to its lightness, you can create real masterpieces of art from it.
The largest deposits were found in Russia (Murmansk, Norilsk, Talnakh), Africa, Canada, Alaska, Colombia, and Australia. Cost: $90 for 1 g.
Top 10 most expensive metals in the world
Only two of the most expensive metals on our planet are produced artificially, the rest are mined from the bowels of our planet. In Russia, nine of them are being mined and synthesized; there is another deposit in the Caucasus and Chita region, but development is not underway - it is not economically profitable.
10th place. Ruthenium
Price for 1 g - 7.91 dollars (525 rubles).
Ruthenium can exist in different valence states, and its appearance differs depending on the extraction method. In 1844, the discoverer of the metal was Karl Karlovich Klaus, a professor at the Imperial Kazan University.
Demand for ruthenium (Ru) is growing rapidly every year
The leading supplier is South Africa, with production also taking place in Canada and Russia. The metal was first found in the Urals. Klaus gave the name to his brainchild - this is one of the medieval Latin names of Rus'.
9th place. Rhenium
Price for 1 g - 9 dollars (597 rubles).
Metal mining is associated with great difficulties. It was opened only in 1925. There is a unique deposit in the Russian Federation, but production is not carried out there. The leaders in rhenium reserves are the USA, Canada, Kazakhstan, Peru and Chile.
Rhenium (Re) - extremely rare in the bowels of the earth
It is used in medicine (research activities, instrument making), aircraft construction and for jewelry making.
8th place. Osmium
Price for 1 g - 19 dollars (1261 rubles).
Osmium is also rarely found in nature; it is mined in Australia (on the island of Tasmania), Russia (Ural Mountains), USA (California, Alaska), South Africa, Kazakhstan.
Osmium (Os) - a metal with a blue tint
Osmium is used to produce containers for storing toxic waste; the substance is used in the manufacture of rockets, implants, and pacemakers.
The density of the metal is incredibly high: a half-liter bottle of osmium is heavier than a bucket of water.
7th place. Platinum
Price for 1 g - 26 dollars (1769 rubles).
It is mined in South Africa, Russia (Sverdlovsk region, Khabarovsk Territory and Kamchatka) and North America. Over the past five years, platinum has fallen in price by 43% due to lower demand for cars, because it is used in the automotive industry.
Platinum (Pt) is also used to make jewelry
Analysts believe that the metal is undervalued and will soon rise in price. The forecast for the price of platinum from experts at the French financial company Société Générale is $31.7 per 1 g over the next six months.
6th place. Iridium
Price for 1 g - 46 dollars (3097 rubles).
Iridium is strong and cannot be cut or machined, but can be processed by heat. Annual production is only a few tons. Iridium is obtained from platinum compounds.
Iridium (Ir) occurs in nature less often than gold and platinum, but is often found in meteorites
Used in the production of medical instruments and spark plugs for cars. This metal is included in alloys to give them wear resistance.
5th place. Palladium
Price for 1 g - 46 dollars (3070 rubles).
The world's largest producer (40%) of palladium is Norilsk Nickel. The second most important source is South Africa (Bushveld complex). Mining takes place in Zimbabwe and North America. About 80% of palladium is used in the automotive industry (production of engines and catalysts).
Jewelers value palladium (Pd) for its good malleability and ductility.
A drop in car sales and an increase in demand for electric vehicles will cause palladium to fall in price by 15% by 2020. This assumption was made by investment analyst Alexandra Ovchinnikova.
4th place. Gold
Price for 1 g - 48 dollars (3201 rubles).
Most gold is mined in China. Experts from global financial data provider Refinitiv report that production amounted to 399.7 tons in 2021. Australia (312.2 tons) is in second place, and Russia (281.5 tons) is in third.
Gold (Au) is a shiny metal with a bright yellow color that is always attractive to people.
Gold is considered rare due to its low content in the earth's crust and the difficulty of mining. The metal became precious due to its aesthetic qualities and chemical inertness.
For 2021, analysts predict a decrease in prices. This will likely be triggered by a drop in investor interest in the asset. The British consulting company Capital Economics suggests that by the end of 2021 the average price will drop to $44.
3rd place. Rhodium
Price for 1 g - 122 dollars (8105 rubles).
Rhodium has a high melting point and is resistant to external influences.
World reserves of rhodium (Rh) amount to only a few tens of tons
The 45th element of the periodic table is one of the rarest metals on the planet. In 1803, it was discovered by the English scientist William Hyde Wollaston. And in the Urals, rhodium was discovered by the tireless professor K.K. Klaus (discoverer of ruthenium). Until the beginning of the twentieth century, Russia sold the metal for next to nothing, although 95% of the world's reserves of platinum and related rare rhodium, ruthenium, osmium, and palladium were mined in the Urals. The demand for rhodium is increasing every year.
2nd place. Osmium-187
The price for 1 g is 200 thousand dollars (13.28 million rubles).
Producing the osmium isotope under artificial conditions is an incredibly difficult task. The only manufacturer and supplier in the world is Kazakhstan.
The isotope osmium-187 is obtained from such a powder
The isotope is of great importance for the development of science, but is not yet in demand in industry.
Application
The most logical and immediately obvious use for the elements described here is decoration. However, not everything is so simple: only very ductile metals can be used in this process. It is also important that they melt at fairly low degrees (not three thousand, for example). In addition, the metal should not be brittle. Therefore, gold, silver, platinum and palladium are in demand in the jewelry market. Rhodium is also used here, but only for coating products - it is fragile, and such quality is not valued by either jewelers or potential buyers.
Where else can precious metals be used? A lot of places, actually. For example, gold is used in electronics due to its excellent ability to be a conductor. At the Moscow Academy of Precious Metals there is a special scientific center, which, among other things, processes old microcircuits in order to obtain gold. This institution is located near the Medvedkovo or Babushkinskaya metro stations. By the way, this Academy of Precious Metals accepts various metals and scrap.
Silver is actively and very successfully used in medicine, as it has antibacterial properties - they were discovered in ancient Rome. It is no coincidence that in ancient times they loved to drink from silver vessels - this improved the functioning of the digestive system. All this is due to ions that from silver enter the water. Doctors are happy to use this wonderful “healing” property of this noble metal for their medical purposes.
Precious metals are used in all kinds of industries. They are used to make machine parts, laboratory glassware, prosthetics, photographic equipment, and various protective coatings (for example, for mirrors); They are used in rocketry, automotive manufacturing, radio equipment and many other areas of life.
Aurum
Now let's say a little more about each of the list of noble metals, and perhaps we should start with gold - the only such element in the world, which in its pure form has such a bright yellow tint. In addition to the basic qualities characteristic of all metals in this category (softness, fusibility, etc.), aurum also has increased chemical resistance, does not enter into any reactions with acids, alkalis, or salts, and is not susceptible to moisture or same high temperature.
To melt gold, you will need a temperature of over a thousand degrees Celsius! This precious metal becomes solid at 2.5 Mohs, and its density is nineteen point three grams per cubic centimeter.
Interesting and surprising
- It is believed that aurum is such a rare element that it is possible to find more iron in sixty minutes than a given yellow metal has been found in the entire history of its mining. Meanwhile, this is more than one hundred and sixty thousand tons! The most remarkable thing, by the way, is that the vast majority of this amount was discovered in South Africa.
- Gold can be dissolved in a combination of nitric and hydrochloric acids. This “union” is called “royal vodka”.
- The word "silver", just like its British and German synonyms, comes from the ancient Indian word "sarpa", the meaning of which is the moon and the sickle.
- At the end of the twenties of the nineteenth century in Russia, platinum was two times cheaper than silver (now it is about a hundred times more expensive).
- The largest silver nugget weighed almost one and a half thousand kilograms.
- The ancient Egyptians believed that gold was divine particles. The pharaoh had the exclusive right to own them.
- Previously, Olympic medals were made of pure gold (at the beginning of the twentieth century), but now they are only coated with this noble metal - no more than six grams per medal (and in the medals awarded at the 2012 Olympics in London, the gold content does not exceed one percent ).
- Our country is a world leader in the extraction and supply of one of the platinum group metals – palladium.
- Silver in its pure form is found less frequently than gold. Nevertheless, throughout the entire globe there is much less gold than its silver “colleague”.
- In its pure form, gold is very soft. So much so that it can be easily and effortlessly scratched even with fingernails.
Now light has been shed on the question of which metals are noble, and it is clear for what properties and for what reason they are called so.