Characteristics of metals
Metals are a group of over 90 simple substances from the periodic table. In nature, they are rarely found in pure form, so they are most often mined from ore. This is the name of a type of minerals, which are a combination of several chemical components, such as minerals and the same metals. Metals are characterized by several properties, according to which they are divided into groups:
- hardness - resistance to penetration of another, harder body into the material;
- strength - resistance to destruction under the influence of external load;
- elasticity - a change in the shape of a material under the influence of external forces and its restoration after these forces cease to influence it;
- plasticity - changing the shape of a material under external influence and maintaining it after eliminating this influence;
- wear resistance - maintaining the good appearance and physical properties of the material after severe friction;
- viscosity - the ability of a material to stretch under the influence of external forces;
- fatigue - the ability of a material to withstand repeated loads;
- heat resistance - resistance to oxidative processes when heated to high temperatures.
Scientists have recently created an improved aluminum alloy, 6063, that kills bacteria. It is believed that it will be possible to make door handles for hospitals and other public places from it.
Cast iron and steel
As a rule, ferrous metals undergo several standard phases in production: the extraction of ore and its processing in a blast furnace. After this, cast iron is obtained, from which any types of steel and iron alloys are subsequently obtained. The latter are more often used in heavy industry. In contrast, non-ferrous metals are a softer substance with slightly different properties; they are used in a different area.
The composition of cast iron includes 93% iron and about 3-5% carbon, plus residual elements in small quantities. This material is rarely used for production because it is brittle. It can be found in the manufacture of certain types of pipes, valves or valves. But the majority of the pig iron produced (more than 90%) is processed into steel.
The main types of steel that are made from iron are: carbon and low-carbon (hardened) steel, stainless steel, ferrite-chromium, chrome, martensitic-chromium, chrome-vanadium, alloy, nickel, tungsten, molybdenum and manganese steel.
Black metals
Three main features of ferrous metals: high density, high melting point and dark color. Since ferrous metals in their pure form are difficult to work with, alloying components are added to them - impurities to change the physical and chemical properties of the base material.
To give ferrous metals their shape, they are first heated to high temperatures and then pressed.
Ferrous metals are divided into 5 subgroups:
Iron metals
These include cobalt, nickel and manganese. They are used as additives to iron - most often, strong steel is obtained from alloys, which is used in the manufacture of various parts for large equipment, knives and other products.
Steel is used to make durable and beautiful knives, and not just kitchen knives.
Refractory metals
This subgroup includes niobium, molybdenum, tungsten and rhenium. Their common feature is that the melting point of ox is higher than that of iron - that is, it is more than 1539 degrees Celsius. As a rule, they are used to make parts for equipment and filaments for various light bulbs.
The filaments in light bulbs are usually made of tungsten
Uranium metals
This group includes uranium, californium and other radioactive metals. They are used exclusively in the nuclear energy industry.
In ancient times, uranium was used to make yellow ware
Rare earth metals
This classification includes laptan, praseodymium, neodymium and other metals. They are all silvery-white in color and have almost exactly the same chemical properties. Rare earth materials get their name because they are difficult to find in the earth's crust. They are used in nuclear energy and mechanical engineering. For example, from rare earth metals it is possible to create glasses that do not transmit ultraviolet rays.
The rare earth element scandium is used in mercury gas lamps
Alkaline earth metals
This subgroup includes beryllium, magnesium, calcium, radium and other metals. All of them are colored gray by nature and always remain solid at room temperature. In their pure form, they are practically never used anywhere, with the exception of nuclear reactors.
The alkaline earth element beryllium is used to make X-ray tubes through which the rays escape
This is interesting: Liquid metal robots may appear in the near future
Main types
Compared to black, non-ferrous metal has many more varieties. The addition of various substances to the composition led to the fact that the material began to be classified into seven groups. Non-ferrous metal has refractory, light and heavy, dispersed, rare earth, radioactive, noble, dispersed materials. We will not list all these types, but will focus only on the most popular metals and their properties:
- Copper. Included in the list of elements that make up up to 98% of the earth's crust. It has no magnetic properties and has high electrical conductivity. Used to create wiring, pipes, technical elements.
- Lead. In terms of prevalence, this alloy ranks fourth in manufacturing processes. Suitable for electrically conductive elements, but not used as often as it is considered toxic.
- Brass. It is superior to copper in strength. Used for the production of pipes, sheet metal, foil, wire.
- Zinc. Refers to heavy non-ferrous metals. Used to create alloys and as anti-corrosion protection for ferrous metals. In its pure form it is used only in the pharmaceutical and manufacturing industries.
- Aluminum. It is used more often than others for production due to its light weight. It is not modified by external factors, therefore it is widespread in the consumer market.
Ferrous metal does not have many alloys; only 2 varieties are used for industrial purposes:
- Steel. It is a ferrous metal used in many industries. It contains about 99% iron, the rest is carbon. When other substances are added, they increase the strength of the metal, protect against corrosion, and make it resistant to temperature changes. Some steel grades are used for secondary production.
- Cast iron. It contains more carbon (about 5%). It is used in industry and production, but it weighs a lot, so it is not applicable everywhere. After use, cast iron is poured into steel.
Non-ferrous metals
Non-ferrous metals are more expensive than ferrous metals because they are more in demand in the world. They are needed in the manufacture of cars, the construction of houses and in the field of high technology - they are the main materials in the manufacture of smartphones and other electronics. In the construction industry, they are needed for the manufacture of all kinds of fittings, beams, corners, and so on.
Iron and its alloys are classified as ferrous metals, and everything else is non-ferrous metals
Non-ferrous metals are usually divided into three groups:
Heavy metals
The most prominent representatives of this category of non-ferrous metals are copper, brass and bronze. Copper is the most popular among them because it is an excellent conductor of electric current and is widely used in electronics. Various wires, bearings and other metal elements are made from brass. Monuments are often made from bronze because it is not afraid of rain, snow and mechanical damage.
A few years ago, scientists found that copper can prevent the spread of viruses
Light metals
The most popular light metals are aluminum, magnesium and titanium. They are fairly easy to melt and are also lighter than ferrous metals. Due to its resistance to corrosion, high ductility and low weight, aluminum is actively used in the construction of aircraft and cars. Magnesium is widely used in the manufacture of cases for various equipment, from cameras to engines. Titanium is highly durable and lightweight, which is why it is used in the manufacture of space rockets.
In the air, aluminum is instantly covered with a film that protects it from rust.
Noble metals
Noble metals include gold, silver and platinum. Due to the difficulty of mining and their beauty, they are considered the most expensive types of metals. Their value is constantly changing and you can buy them in banks, thereby investing your money in them. Precious metals are also widely used in jewelry. Rings, bracelets and other jewelry are made from them.
You can read about aluminum in the material about the most valuable metals in the world
Why is it necessary to pass ferrous and non-ferrous metals?
Over the past centuries, the amount of metals used to make various products has increased greatly. If waste disposal is not monitored, the volumes of old scrap will cause environmental damage. At the same time, some non-ferrous metals have toxic properties that harm the human body. Storing such products can lead to chronic illnesses among employees.
Also, metal recycling can significantly reduce the costs of enterprises and organizations by melting down old scrap. Selling scrap metal provides economic benefits for all parties, further helping to reduce the risk of environmental disaster. Ours will provide customers with transport and forklifts for quick removal of scrap. High prices and high-quality service at our reception points will provide favorable conditions for our clients.
Types of scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals and alloys, marking, classification and categories of non-ferrous metals
Non-ferrous is a group of different metals and their alloys.
Let's take a closer look at what non-ferrous metal scrap is.
There are two groups of metals:
Iron and its alloys are called black
The rest are non-ferrous or non-ferrous.
Their list is diverse:
- aluminum;
- copper;
- nickel;
- manganese;
- titanium;
- zirconium, etc.
are in demand today both in production and in scientific activities . Their areas of application are varied.
Scrap metal collection points are happy to buy non-ferrous metal scrap at competitive prices, and in order to avoid getting into trouble when handing it over, you need to be familiar with the types and know the standard classification of non-ferrous metals.
Classification of non-ferrous metals according to GOST
The current GOST 1639-2009 clearly indicates what belongs to non-ferrous metal scrap.
The classification of scrap is divided into four main sections that characterize it:
- Name;
- physical parameters;
- chemical composition;
- quality.
GOST metals and their alloys.
The section displays 13 types that are accepted in organizations for receiving recyclable materials.
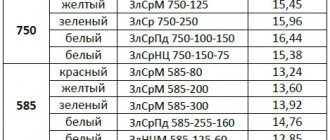
Below is a table in which you can see a list of non-ferrous metals in one list and the number of individual types of scrap:
Pure metal can rarely be found , since most scrap is made up of alloys.
Upon acceptance, belonging to one or another type is assessed by the element that is greater in percentage terms in recyclable materials.
This ratio can be determined using special equipment.
Non-ferrous metal scrap is divided into types according to the following criteria :
- origin;
- chemical composition;
- physical state.
The origin of the scrap may be as follows:
- industrial waste;
- marriage;
- substandard;
- scrap of finished products.
The chemical composition of non-ferrous metal scrap, which is determined in the laboratory, shows which metal or alloy it belongs to.
The most valuable recyclable materials are unalloyed metals with a low content of impurities. Physical parameters are just as important when passing as chemical ones.
According to these characteristics, scrap is divided into the following classes :
- A – directly refers to scrap and lump waste;
- B – includes shavings, tangled wire and small pieces;
- B - powdered waste (mainly found only in rare metals: tungsten, cobalt, molybdenum and titanium);
- G - other recyclables.
Safety
All non-ferrous scrap must be checked for:
- presence of radiation and harmful chemical contamination;
- explosion hazard.
When transporting scrap metal, it must be accompanied by documentation on radiation and explosion safety.
The concentration of harmful substances must not exceed the values specified in GOST 12.1.005.
The Russian Ministry of Natural Resources has identified five classes of chemical, radiation and explosion hazards of non-ferrous metal scrap:
- Hazardous waste with great harm to the ecosystem. These include mercury, polonium and plutonium.
- Highly hazardous waste, the consequences of which take nature thirty years to remove. These are alloys of lead, cobalt and molybdenum.
- Moderate danger , in which it takes ten years to restore the ecology. This is scrap mixed with copper, nickel, iron, zinc, aluminum and silver.
- Low hazardous waste, removal of the consequences takes three years. This includes scrap bronze.
- Low danger , such scrap does not harm the environment. This is the most common class among colored scrap.
Due to the expected harm to humans and nature, all operations with non-ferrous scrap require a license from the points accepting secondary non-ferrous metals. Checking for all types of hazards is carried out according to the following scheme:
Quality
GOST specifies quality parameters that determine the grade of scrap.
characteristics are of great importance here :
- scrap size;
- origin of scrap;
- uniformity;
- amount of blockage;
- chemical composition;
- physical state;
- dimensions and volume.
Quality is determined on a representative sample.
According to GOST, all transported scrap must be marked with the following indication:
- names;
- GOST designations;
- designations of the type of recyclable materials;
- alloy grades.
Marking of non-ferrous metals and alloys must be firmly attached to the cargo during transportation and storage.
To determine the grade of metal, you need to look at the stamp book , a special document with all the markings of the metal or alloy you are interested in.
Kinds
The large number of non-ferrous metals and various characteristics required their classification into separate types.
industrial systematization is in use , reflecting the historically established components of the metallurgical industry and the science of the same name.
The name itself does not fully reflect the essence of non-ferrous metal.
Only gold and copper are colored, while the rest are the usual grey-black shades.
Science usually distinguishes the following types of non-ferrous metals and alloys:
- lungs;
- heavy;
- noble;
- refractory;
- scattered;
- rare earth;
- radioactive.
industry in Russia today is on the rise and includes:
- metal mining;
- ore beneficiation;
- metal smelting
The main non-ferrous metals include:
Aluminum is an excellent electrical conductor. It is flexible, which is both its advantage and disadvantage.
To give it strength add :
- manganese;
- copper;
- magnesium, etc.
Such alloys are used for the production of :
- airplanes;
- sea and river ships;
- space shuttles;
- in construction;
- in the food industry.
Aluminum and its alloys are the cheapest type of non-ferrous metal scrap.
You can find it in a variety of household items, including:
- siding;
- gutters;
- roofing
Copper is a commonly found non-ferrous metal.
It also has good characteristics:
- plastic;
- good electrical conductor;
- good heat conductor.
It is in great demand in alloys and is used in various economic sectors.
Its alloy with zinc and tin is known - brass.
It can be found in:
- cars;
- hours;
- expensive jewelry.
find copper for scrap metal in:
- power cables;
- water pipes;
- household products.
Copper is highly valued at recycling centers.
Popular types at collection points
The most popular non-ferrous metals at collection points:
If you want to find out what is more profitable to rent out, then read this article.
Conclusion
Historically, non-ferrous metals are divided into types:
- lungs;
- heavy;
- noble;
- rare earths, etc.
This classification is accepted in technology; today it meets almost all the requirements of the industrial industry.
This makes it easier:
- the task of producing new alloys;
- delivery of secondary raw materials from non-ferrous metal at collection points.
Each operation for the acceptance and delivery of non-ferrous metal must be confirmed by an act that states:
- compound;
- quality;
- volume;
- cost per kilogram and for all scrap.
When handing over scrap, make sure that is honest . Many small points deliberately underestimate the grade of scrap or weigh it using incorrectly working scales.
How to prepare non-ferrous scrap metal for delivery, see this video:
GOST: scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals, classification
Natural resources are being depleted, so scrap and non-ferrous metal waste become a source of raw materials for processing and manufacturing of new items. It is necessary to systematize the process of collecting non-ferrous metal for its further processing.
Recycled raw materials from non-ferrous metals: profitable, economical
As a result of human economic activity, metal waste appears. It is subject to disposal or recycling. Iron is not a non-ferrous metal. All others are divided into 4 groups.
Lungs
They have a specific gravity of less than 5 (for example, lithium - 0.53).
The most in demand are the following:
- titanium;
- magnesium;
- aluminum;
- calcium;
- rubidium.
They act as deoxidizers of molten metals. Aluminum has corrosion resistance and good ductility. Therefore, it is widely used in all branches of mechanical engineering, in the production of tableware and other items.
Various products are produced from secondary cast aluminum alloys.
Heavy
They have high electrical and thermal conductivity and excellent performance characteristics.
These include:
- lead;
- nickel;
- copper;
- cobalt;
- zinc, etc.
With the exception of galvanic coatings, they are used in their pure form. They are semi-finished products: sheets, pipes, wire.
Secondary melting of non-ferrous scrap is more profitable than the labor-intensive process of mining and processing ores.
Does not harm the planet's ecosystem, unlike metal mining.
Noble
High corrosion resistance in most acids and atmospheric conditions is a distinctive feature of such elements.
Their main components may be:
- gold;
- palladium;
- rhodium;
- platinum;
- silver, etc.
The electronics industry supplies waste coated with platinum and silver. Their recycling justifies the cost of recycling. The scrap contains useful components. They surpass natural sources in their value. The current standard specifies what applies to non-ferrous metal scrap.
Rare
The composition is multicomponent. It is better to use raw materials in a comprehensive manner. On this basis, combination is effective, since most elements do not form deposits. They are considered refractory metals.
Some of them:
- vanadium;
- germanium;
- molybdenum;
- tungsten;
- selenium, etc.
Heating elements and parts of electric and radio lamps are made from molybdenum and tungsten. Tantalum is characterized by chemical resistance and great hardness. Suitable for making surgical and dental instruments.
Non-ferrous metal classifications
Non-ferrous metal waste is classified according to physical characteristics; the qualitative characteristic determines the variety; one should be guided by state standards (GOST); According to the chemical composition, a group or brand is distinguished.
It is important to determine the variety.
Therefore it is necessary to identify:
- metal content;
- options;
- clogging;
- cutting condition.
Based on these points, four types of non-ferrous scrap can be distinguished.
The first is distinguished by certain dimensions, weight, high content of the predominant metal, the scrap is not clogged with other components. Scrap does not need special preparation for processing.
The second variety is more contaminated than the first.
The third cannot be sent for remelting; the raw materials must be processed first.
The fourth grade is low quality. The requirements of the previous groups are not met, there is high contamination, the waste is mixed, and needs to be separated.
If you take batteries, pipes, and wire to a landfill, these items will not only rust, but also release hazardous substances.
The general technical conditions contain requirements for the disposal of scrap non-ferrous metals and compliance with the safety regime when working with them. Remaking scrap according to the rules will preserve its useful characteristics.
Recycled materials save money on metal for metalworking industries. Using scrap, you can save minerals without harming the environment.
Meaning of terms
Scrap is called non-ferrous metal scrap, which is melted down and is part of the smelting charges.
Charge is a mixture of materials that is loaded into a smelting furnace to produce metal with a certain chemical composition.
Clogging is determined by the presence of impurities (insulation, paint, packaging, dirt, etc.) in the raw materials.
Galvanic coatings (electrodeposited metal) are applied to the surface of metal products, pipes, and wire. Increases corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
A well-established process for processing non-ferrous metals will save primary resources and improve the environment.