What is the act of testing internal sewerage and drainage systems “spill test”, what stages must be passed and what rules must be followed?
The last step in arranging a sewer system in a residential private or apartment building is testing the finished drainage system. This procedure is carried out by forced spilling. This procedure has the primary goal of identifying errors during installation or the presence of defects throughout the pipeline. At the end of the procedure, a test report for internal sewerage and drainage systems must be drawn up, which subsequently serves as proof of acceptance of the object.
When performing a visual inspection, it is necessary to include in the report drawn up all tests of the wastewater system prescribed by the current SNIP. Today, SNIP 3.05.01-85, as well as SP 73.13330.2012, regulates the testing of sewerage for the strait.
When the commission may not sign the act
According to the above regulations, the main feature lies in compliance with the mandatory requirements of the strait. According to this rule, it is implied that up to three-quarters of the total number of drain systems and openings in the house will be involved in the inspection. If the specified number is smaller, the test document cannot be called complete. The commission responsible for signing the act has the legal right to make a negative decision on the acceptance of the building, since the drainage system does not meet the requirements of construction standards.
It is important to remember that launching the sewage system on an ongoing basis can only be done in one case. After a comprehensive check of its performance and only after the moment when a test certificate for the internal sewerage system and drains for spillage is signed.
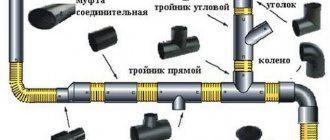
Testing the internal sewer network
When carrying out test work, it is required to be guided by SNiP “Sewerage. External networks and structures.” According to this document, the following is checked:
- compliance with the developed project;
- testing sewerage pipelines for strength and reliability of joints;
- correctness and reliability of installed devices and flushing elements;
- verticality of mounted risers.
Testing of nodes
Compliance with the design is checked visually. Each element of the system must be located exactly in the place where it is indicated on the plan or drawing.
All installed devices must be cleared of debris and thoroughly washed. They should not have visible damage (chips, cracks, etc.) or bending. When installing devices, deflections must not be allowed.
The risers are checked for verticality with a plumb line.
Pipeline testing
Pipeline inspection can be carried out hydraulically or pneumatically.
A hydraulic sewer test involves pumping the system with water, and a pneumatic test with air.
The system can be checked with water if the ambient temperature is not less than 5ºC. In other cases, it is recommended to use the pneumatic method.
If the house has more than one floor, then the system is checked on each of them separately. To temporarily disconnect a floor from the general sewerage system, plugs are used that are inserted into the inspection.
Pipeline testing is carried out according to the following scheme:
- All pipes are checked for the presence of construction debris. If necessary, they are washed;
- Horizontal sections of the pipeline undergo drainage testing. To do this, at least ¾ of all drains are opened. The fenced off section of the sewer system is completely filled with water. If no leaks are detected within 10 minutes of operation, the test is considered passed;
- to check vertical sections of the pipeline, water is supplied under pressure not exceeding 0.08 MPa. The sewerage test for the tightness of pipelines is completed if no leaks or ruptures in the system are detected within 15-20 minutes.
If one or more sections of pipes are found to be leaking, the problem must be corrected and the test must be carried out again.
Proof test stages
Before you start filling out the document, you should go through each stage of verification, which includes mandatory requirements for installation work:
- A comprehensive check of the internal structure of system parts, carried out by performing a forced spill.
- Checking the connection points of the drainage parts along the entire length of the system for compliance with the tightness parameters (the requirement also applies to closed areas).
- Determination of damage to inspection wells.
- Conduct an inspection and issue a test report for a storm sewer installed at a common drainage unit.
An entry corresponding to the first specified paragraph must be included in the sewer spill act without changing the meaning. Accordingly, the official must prescribe the type of sewer system to be audited.
In addition, the inspector is required to indicate the full name of the construction project. Also, the physical address of the building is included in the test report for internal sewerage and drains. All necessary information is taken from the general documentation and the design of the building on which the sewerage inspection is being carried out. The document must contain the date when control tests of internal sewerage and drainage systems were carried out, or information about the time period when the wastewater system was accepted.
Sewerage units and systems to be tested
The entire sewerage system in each building is divided into an internal sewage disposal network and an external sewerage system. Internal sewer wiring includes the following components to be checked:
- plumbing fixtures and their connections with outlet pipes;
- local sections of a horizontal pipeline with pipes flowing into it from plumbing fixtures;
- sewer risers;
- outgoing pipe.
In the external part of the sewer system, sections of the pipeline (between cleaning and auxiliary equipment) are tested for leaks, as well as:
- operability of wells, tightness and slope of the pipeline;
- condition of treatment or storage facilities (reservoirs);
- storm sewer.
Who is on the commission?
As noted earlier, the act for draining internal sewerage must be endorsed by officials. The role of the commission member responsible for drawing up the act can be played by:
- Representative of the customer, whether an individual or a legal entity.
- A representative of the general contractor, since it is this structure that is personally responsible for performing all installation work at the site. If problems are identified during the inspection stage, the contractor will correct the defects.
- Representative of the company developing the project.
- A representative of the company responsible for work on the land plot, as well as for the condition of the soil in which utilities were laid.
When filling out the document, all personal information about the members of the commission must be entered in legible handwriting. It is important to indicate the full last name, first name, and patronymic and certify the information with the personal signature of each official.
Testing of external sewer network
Testing of external sewerage is also carried out in most cases using a hydraulic method. The check includes:
- testing the pipeline for leaks (carried out as described above. For testing, sections of pipes located between wells or other elements of the system are taken);
- checking the pipeline slope level;
- testing of wells and other equipment;
- checking the performance of storm drains.
A level is used to check the level of pipe laying required for a gravity sewer system.
If a pressure sewer test is being carried out, then water must be supplied to the pipeline system at the pressure specified in the design documents.
The test of pressure sewerage pipelines is considered successful if the pressure value in the flow into the network and at the exit from it is the same.
Well inspection
Leak testing of wells is carried out in various ways, depending on the equipped waterproofing:
- if the well has internal insulation, then the test consists of determining the volume of leakage;
- if the well is equipped with external insulation, then to check it is necessary to determine the level of liquid inflow.
In both cases, to test a well it is necessary to fill it with water to a certain level.
Testing of other devices included in the external sewage system (for example, septic tanks) is carried out in a similar way.
Paper rules
Based on the general requirements of the current regulations, each paragraph of the act must be completed. As soon as the final list of responsible persons is formed and filled out, you can begin to draw up the remaining points of the document.
Act
In order to avoid mistakes and omissions in the act, it is worth remembering all the details in each paragraph:
- First point. This part of the paper contains information about the name of the company that developed and approved the house project. The document compliance code is also written down here, and the serial numbers of the revision of all components of the drainage system based on the working design are listed. In addition, it is necessary to list the working numbers of the drawings used for the drainage system in a specific type of building.
- Second point. This part of the document contains exact values for the number of all simultaneously open visible sanitary points. The time periods during which the checks were carried out are listed. Sanitary points can be all plumbing fixtures that a person uses in everyday activities (toilet, sink, shower, bidet, and so on). It is important to remember that filling out the second paragraph implies hydraulic testing of the sewer system when working at least three quarters of the total number of sanitary points.
- Third point. The violations and inconsistencies identified during the inspection stage are listed. Here it is important to indicate all the comments that the commission had during the testing process with a detailed description of the problem. If there are no deficiencies, “not identified” is written in the column.
- Conclusion. This part of the act contains the final decision of the commission and the recommendatory part to eliminate the identified shortcomings. The last sentence must indicate whether the system is permitted for operation.
You may also like: All about hydrodynamic drain cleaning
Methods for testing sections of internal sewerage
What and how is checked when checking the compliance of the internal network with the project and established standards is described in SNiP “Sewerage. Internal and external networks and structures." According to this fundamental construction document, the following parameters of the sewer system are subject to inspection inside the building and then reflected in the final document (inspection report):
- testing network pipes for strength and their connections for tightness;
- compliance of the location of installed instruments and elements of the outlet pipeline with the design documentation;
- correct installation of plumbing fixtures in relation to the floor surface (the distance from the floor to the upper edge of the receiver of each plumbing fixture is specified in the above-mentioned SNiP);
- the presence of a slope in the horizontal sections of the pipe and the degree of verticality of the risers.
Testing of pipes and connections for leaks in a gravity system, regardless of the material of the pipeline and fittings, is carried out using the spill method. The essence of the technique is that part of the main pipeline (bed) is fenced off in a certain area from the rest of the system. This is done with special plugs through inspection holes. The separated area is checked by filling it with water through the pipes of plumbing fixtures. According to SNiP, the results of a spill deserve attention if the pipeline was filled with the participation of at least ¾ (or 75%) of all devices connected in a given isolated section. Testing of the pipeline using the spill method is considered positive if the connections after filling the system did not give the slightest leak within 10-15 minutes (depending on the volume of the area filled with water).
According to the regulatory documentation, a spill, that is, testing a sewer system by filling it with water, is informative when the air t˚ is above 5˚. If the temperature is lower, a pneumatic leak test of pipes and connections is carried out (compressed air). The integrity of the riser, sometimes of external sections of the pipeline, is also determined by air. We will use the pneumatic testing method to assess the performance of a pressure sewerage system, when wastewater is forced out, under pressure created by pumping equipment.
The location of installed plumbing fixtures and its compliance with project documentation is determined visually. The height of the receiver of each device, the correct connection of the toilet drain, siphons of the washbasin, bathtub, sink, etc. are objectively assessed and reflected in the report. The condition of the plumbing fixtures themselves is also visually assessed. They must be free of visible dirt and mechanical damage.
The correct slope of the pipes inside and outside the building is controlled using a building bubble level. If the slope of the internal sewer network is allowed to be at least 1 cm per linear meter, then on the outside this figure must be increased to 2 cm per meter.
The installation position of the riser (this data is also reflected in the final report) is checked with a plumb line. A deviation from the vertical of 3˚ is allowed. A water tightness test of the riser is also carried out. The pressure should be about 0.8 MPa.