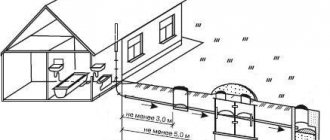
In the absence of a centralized water supply, the water sources are underground interstratal waters. For free access to water, a shaft well is usually installed on the site. If the technology is followed, it gives good water, is durable and easy to use. One of the important conditions for the correct placement of a water source on the site is maintaining the optimal distance from the well to the septic tank, other wells and other structures.
Proper placement of a well on a site is a difficult engineering task that is underestimated by inexperienced owners of country houses. In order for the operation of water supply and sewerage systems to be problem-free, it is necessary to understand even before starting work that there are rules and regulations, non-compliance with which will lead to problems in the future.
Correct location
The necessary conditions that are taken into account when placing wells are often very difficult to fulfill for owners of narrow or small plots. Often, owners with funds try to save meters by constructing a shaft on the site of the house, and then digging a pit for the foundation there. In this case, for a potential source of drinking water, the distance from the house does not matter if the house itself is laid out in accordance with the requirements.
Village house and well
Being located inside a building has many advantages, but there are also tangible obstacles. The undoubted convenience for residents in equipping an indoor toilet and supplying water to the bathroom and kitchen (this will require pipes and a special pump) sometimes does not outweigh other possible circumstances in common sense.
For example, the need for repairs in the event of a breakdown or failure of the shaft. In this case, the water will stop flowing, and repairs will require special equipment. And it will be extremely difficult to use it in the basement of a house.
Layout of structures
In SNT, where the construction of residential buildings is now permitted, in the private sector of urban areas and on individual housing construction sites, the developer resembles a tightrope walker balancing on a rope stretched between abysses and peaks. He has to take into account too many conditions in his choice when it comes to sanitary facilities. The same well should:
- comply with distance standards so as not to cause erosion of the foundation and destruction of a residential building;
- not be located at a significant distance, as this will create inconvenience for residents or force the creation of a local network of an intricate design, fraught with constant blockages;
- do not cause inconvenience to neighbors;
- do not interfere with the passage, driveway, beds or trees, fences, and also do not be close to the road;
- be located at the required distance from potential sources of pollution;
- be located on an elevated site not only in relation to your own septic tank and cesspool, but also to the neighboring one;
- the distance between all buildings and structures required by sanitary standards and building regulations must be maintained.
On the individual housing construction site
Subtleties
SNiP 30-02-97, which after repeated editing became SP 53.13330.2011, and then SNiP 30-02-97 with amendments for 2021, states that a well can be built at a distance of 3 m from the house foundation. But experienced builders, especially if a residential building with a shallow strip foundation is being built, advise increasing it to five meters.
However, in the process of developing the site, you will have to take into account other rules that also have their own specifics. It is also necessary to study special standards before installing a septic tank, local sewage system, bathhouse or toilet, taking into account the presence of nearby pipelines, power lines and other main structures.
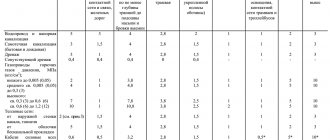
| Structure | Set of rules | SNiP |
| Septic tank | SP 31.13330.2012 | SNiP 2.04.03-85 |
| Toilet | SP 53.13330.2011 | SNiP 30-02-97 |
What you need to know about the distance of the well to the foundation
The problem of the location of a well on a site is especially relevant for owners of small plots. The structure should be as convenient as possible. To do this, it is positioned so that it is possible to easily organize the supply of water to buildings on the site, such as a house or a bathhouse, as well as to a vegetable garden. Usually, the highest place on the site is chosen for the well; it should not be allowed that the cesspools of neighbors are located higher in the terrain.
Find out what a pumping station for a well is here.
In addition, the impact of the mine on the neighboring building should be taken into account. For a well, choose a place closer to the house. This is due to the peculiarities of organizing water supply: supplying water to a house over long distances is an expensive pleasure. Wells can even be built inside a house. Usually, they first build a shaft for the well, and then dig a pit for the foundation. In this case, the type of soil and topographic conditions of the site should be taken into account.
It’s another matter when the house is already ready, but the well is only in the plans. Houses on shallow foundations may suffer from the proximity of well shafts. You should not install wells in close proximity to such buildings. Shallow strip foundations on clay are especially dangerous in this regard. Here it is worth considering the depth of the well. Shallow mines are more troublesome for buildings. Water can wash away the foundation.
You may also be interested in information about decorative covers for wells.
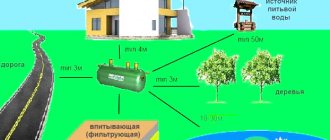
Wells can be located at a distance of at least 3 m from the foundations of buildings. This norm is prescribed in SNiP 30-02-97.
The minimum distance to buildings for keeping animals is 4 m, other buildings – 1 m, trees – 4 m, bushes – 1 m.
What are the requirements for the location of underground communications?
The main regulatory document that guides construction is SNiP 2.07.01-89, indicating the distances when laying communications relative to each other and other objects from the point of view of safety and reliability.
When operating sewer, heating and water supply engineering networks, the negative impact of the transferred environment on the foundation of structures when pipes break must be taken into account. The leaking liquid can wash away the soil foundation and penetrate into the lower and basement rooms, causing significant damage to buildings.
If water-bearing communications are laid near the foundation during the operation of structures, measures should be taken to ensure their safe location relative to the building. When it is not possible to maintain a safe distance from pipelines to a structure for technical reasons, casings are used to protect underground communications. After agreement with the supervisory authorities, it is allowed to lay water pipes in a casing next to the foundations, which provides insulation of the pipes in case of settlement and protects the foundation itself from destruction if the water pipe is damaged.
Typically, on a site with a built house, networks of various types are located; water, sewer, heating, and gas pipes are laid in the ground, and power cables are pulled. For the safe location of different types of highways relative to each other, it is necessary to know the norms of distances between communications in parallel and perpendicular locations.
Also, knowledge of the standards will help save money, because some types of communications can be laid in a single trench without significant negative consequences in the event of a pipe break.
Fig.2 Site plan - example
Distance from underground utilities to foundations
SNiP 2.07.01-89 allows for the laying of underground communications within the boundaries of support foundations and pipeline overpasses, subject to the provision of protective measures in the event of settlement of the foundation base and accidents in the line.
Construction acts SNiP 2.07.01-89 establish the following distance limits to the supporting foundations of houses:
- water supply – 5 m;
- individual and storm (rain) gravity sewerage – 3 m;
- pressure sewer – 5 m;
- drainage pipeline – 3 m, accompanying drainage – 0.4 m;
- gas pipelines of low, medium and high pressure - 2, 4, 7 or 10 m, respectively;
- heating networks - from the tunnel wall 2 m, from the protective shell of pipes for channelless installation - 5 m;
- electrical cable lines and communication cables – 0.6 m;
- switching channels and tunnels – 2 m.
Fig. 4 Construction standards for distances between communications and underground networks
Passage of pipes through the foundations of buildings
The external water supply and sewerage network is introduced into the house through the foundation using steel sleeves of larger diameter; their standard size for HDPE pipes is 75 mm; for PVC sewerage 110 mm, a pipe with a diameter of 160 mm is used.
The rules for laying external water pipelines are regulated by the set of rules SP 31.13330.2012 and includes the following points:
- Communications are introduced into the house through pieces of metal pipes (sleeves) with a minimum diameter of 50 mm.
- To eliminate the consequences of linear expansion due to temperature changes, compensatory bushings are used.
- The distance between the entrance to the foundation of the water and waste pipes should be from 1.5 m, when entering vertically, the gap between the sleeves is from 0.4 m.
- The diameter of the hole in the supporting structures increases the space for inserted sleeves by at least 2 mm.
- To ensure gravity flow, the sewer pipe liner is inserted with a slope of 4 - 7 degrees.
- The depth of the pipelines approaching the house is taken to be more than 0.7 m from the blind area.
Rice. 9 Scheme of laying the pipe entry into the building
When laying water mains, it is necessary to comply with the norms of distances to the foundation - this will avoid negative consequences in the event of a pipeline break or building subsidence
In domestic housing construction, it is important to adhere to the standards when laying communications, which should be placed in different trenches, then bursting sewer pipes under any circumstances will not lead to contamination of drinking water
The essence of construction requirements
The standards developed for construction are aimed at ensuring the safe operation of utility networks that are laid to buildings.
The requirements of SNiP also include concern for the safety of the structure of buildings, other above-ground structures (supports for communication and electricity lines, fences, roads, etc.), as well as the natural environment and human health. Accidents of water supply and sewerage networks that occur in the immediate vicinity of houses or other communications threaten the flooding of surface soils, undermining the foundations of buildings and fences with the risk of their subsequent subsidence. The proximity of a water line break will result in a situation where water will not be absorbed into the ground quickly enough to prevent it from reaching the foundation structure. Sewage, often containing aggressive substances, once under the base of the building, will quickly destroy the waterproofing. From a sanitary point of view, this is also a very unpleasant situation.
The insufficient distance of the water supply and sewerage from the building is extremely inconvenient from the point of view of repairing communications in the event of a break or disconnection. The excavation work necessary to provide access to the pipelines will have to be carried out in the immediate vicinity of the building, which brings a lot of inconvenience, the risk of damage to supporting structures and underground cables, and the mandatory dismantling of surface structures (blind areas, paving slabs, etc.).
When the required distance of underground communications from foundations, fences, supports for electric cables, roads cannot be maintained due to limited space or landscape features, pipelines are laid in these areas in reliable metal or reinforced concrete cases. The length of protective covers, that is, the distance between their end and the fence or cable support, is also regulated by building codes. In the event of a breakthrough or other similar accident in the area protected by the casing, water will be drained through the casing to a distance that is safe for the ground structure.
Sewage systems of private houses
In the development of suburban areas, autonomous sewage systems are often used, which are distinguished by the presence of a large number of positive qualities. Some systems turn out to be more economically advantageous compared to using a central collector, while others turn out to be the only possible solution to the sewerage problem. For the normal functioning of the external sewerage system and to ensure quality service, the design of the system must be arranged in accordance with the norms and regulations reflected in the relevant documents. Sewage installation diagram the system and its operation largely depend on factors, which include:
- topographic indicators of the selected territory;
- types of soils located on the site;
- availability of water supply sources near the site;
- layout diagram of underground engineering networks that are already present on the territory.
The sewage system can be quite simple: the simplest design consists of a single section of pipeline that transports wastewater to a pit or septic tank located outside the building. You need to know at what distance from the house to install a septic tank. The simplest septic tank can be made from car tires stacked vertically on top of each other: the wastewater will still be filtered, and the solid fractions will be periodically pumped out by a sewer truck. This design is well suited for installation in suburban or small urban areas. For the sewer system to work normally, it is enough to provide a constant slope and periodically pump out.
Distance between rotary wells
In its functionality and design, this type is similar to the previous one. The only difference is that the rotary well is installed in places where the system makes a turn. Congestion most often occurs in places where there are bends or turns, so to make cleaning and repair easier, more attention must be paid to such places.
The distance between them is calculated based on the length of the straight sections between the bends of the pipeline. If the section turns out to be longer than allowed by regulatory documents, then it must be equipped with inspection wells for full control over the operation of the system.
What should be the distance from well to well
To construct a well on the site, there is not enough space with an accessible level of the aquifer. The fact is that there are a number of other requirements for the location of the water supply source, and if they are not met, then the water will easily become unsuitable for food use.
Then we will consider these requirements, by fulfilling which you can avoid troubles associated with poor water quality.
What specific sources of pollution are there?
Sources of pollution include a number of objects:
- Cesspools and pits;
- Burial places for animals and people;
- Warehouses for pesticides and fertilizers;
- Industry enterprises;
- Sewage facilities
- Landfills, etc.
It follows from this that when choosing a location, you need to focus on the distance from the well to the toilet, and the distance from other objects of pollution in your own and neighboring areas. This is due to the fact that unwanted elements will get into the water, as a result it can cause damage to health.
Choosing a location for drinking and sewerage
When starting to build water supply and sewerage structures for your home, you need to familiarize yourself with the technical conditions and SNiP. Successful implementation of the project depends on the quality of the preparatory work, which includes:
1 ) Drawing up a site plan with exact parameters of buildings and indicating the distance between objects, site fencing and buildings.
2 ) Determining the location for the construction of a drinking source:
- the distance from the drinking well to the sewerage system should not be less than the standard (20 m);
- When choosing a location for a water source, the quality of the aquifer is taken into account, which is studied by preliminary drilling of a well.
3 ) Determining the location for a local treatment facility.
We focus on the standard 5–7 m from the house. This interval was adopted based on possible negative consequences:
- When the structure is located at a greater distance from the building, when it is necessary to maintain a minimum distance to the well, the sewer pipeline may become clogged and the blockage will be difficult to eliminate. If the interval increases, it will be necessary to install an additional viewing chamber;
- location closer than 5 m and possible depressurization of the septic tank - there is a possibility of the foundation of the building being washed away and the smell of sewage entering the room;
- In addition to the standard gap from buildings, the access to the site of a sewage disposal truck for periodic pumping out of accumulated wastewater is taken into account.
4 ) Determination of installation locations for water and sewer chambers in SNT:
- when connecting to a water pipeline, the distance between the inspection well and the sewer system should be at least 5 m. And the inspection water chamber can be 3–5 m away from the house;
- the gap from the drainage chamber to the external water pipeline should be 3–5 m, so that in the event of depressurization of the septic tank or pressure sewer pipe, toxic waste does not enter the inspection shaft of the water main.
Methods for laying underground networks
Collectors, tunnels and channels are used to extend underground utilities in civil engineering; in households, ditches dug in the soil are used to lay pipelines. If digging trenches in an open manner is not possible, trenchless pipe laying is carried out by drilling, piercing or pushing the soil with hydraulic jacks. Abroad (in Germany), an effective method of laying pipes is widely used using special equipment that cuts a trench and simultaneously immerses a polymer pipeline into it.
Based on the method of arrangement of communications in trenches, the following are considered:
Separate method. During installation, each highway is installed in its own channel; the method is expensive when laying a large number of nearby communications.
Collaborative method. According to SNiP 2.07.01-89, in common trenches it is allowed to lay heating mains measuring from 50 to 90 cm, water supply up to 50 cm, more than 10 communication lines or power electrical cables with a voltage of up to 10,000 volts, if there is not enough space for laying lines in individual trenches plot.
It is allowed to lay water pipelines in tunnels with other communications (SNiP 2.04.02-84) except for pipelines carrying combustible and flammable media.
When laying pipeline fittings in the ground, they are placed in technical wells.
If wells or boreholes are used on the site, from which an underground pipeline is laid to transport water to the house, the minimum depth of the water supply system is taken equal to the lowest freezing point of the soil in the given area with the addition of 0.5 m. A layer of soil on top to avoid unwanted heating of water in the pipes in summer leave at least 50 cm.
Rice. 3 Drilling underground utilities with a German pipelayer
Results
- If you decide to install an autonomous sewer system on your site with your own hands, you need to obtain permission for the project from the SES. Firms usually coordinate a septic tank project on their own;
- To develop an installation plan, you should study the following documentation: SNiP 2.04.03-85 (external sewer networks), 2.04.04-84 and 85 (external water supply networks), SanPiNs for the creation of security zones around environmentally hazardous objects;
- When designing an autonomous sewer system, you need to know the type of soil of the site and the height of the groundwater;
- The drainage well should be removed from the house and neighboring property;
- Trees and bushes should not grow near the septic tank. Their wide root system can damage pipes and containers.
Compliance of your autonomous sewage system with sanitary and building standards will ensure reliable operation of the system and protect you from fines.
What should be the distance from the septic tank to various objects
- If you are positioning a tank assembled from concrete or polymer-composite rings, you must take into account the distance from the well to the septic tank (house, outbuildings). According to the rules prescribed in SNIP, there must be at least 20 meters from the source to the drainage tank (this is the minimum distance allowed when installing a settling tank). The optimal and desirable distance from the septic tank to the well (septic tank-well) is 50 meters. At the same time, the more meters you retreat from all vital objects (houses, wells, utility buildings), the better it will be for everyone.
- Another point that needs to be taken into account when installing the tank is the level of its location relative to the terrain and other objects on the site. The most correct point for installing a septic tank is the lowest point on the site. In this way, it will be possible to insure against accidental ingress of waste (albeit filtered) water into the receiver with clean liquid.
Distance between storm water inlets
When creating a storm drain on a site, it is important to consider the distance between stormwater inlets. It depends on the slope of the tray and the terrain:
| General slope | Maximum distance (m) |
| Up to 0.004 | 50 |
| Up to 0.006 | 60 |
| Up to 0.01 | 70 |
| Up to 0.03 | 80 |
If the area is wider than 30 m, the distance between storm inlets is no more than 60 m. The length from the storm inlet to the collector inspection is a maximum of 40 m, and the installation of no more than one intermediate device is permissible. The cross-section of the connecting section is determined by the calculated water inflow to the storm drain with a slope of 0.02, but it cannot be less than 20 cm.
Location of treatment wells relative to other structures
The choice of the optimal location depends not only on the nature of the internal buildings, but also on the type of sewerage structure
It is especially important to correctly position objects intended for wastewater treatment, which can be divided into storage (with a sealed bottom) and filtration (without a bottom)
The position of sewerage facilities on the site is regulated by SNiP
The minimum distance from the house to the storage well is 3 m. This is the necessary distance at which the construction of a treatment plant will not have a destructive effect on the foundation of the building. In this case, the maximum distance to the first well should not exceed 12 m. A more distant location can lead to frequent blockages and complicate pipeline maintenance.
When choosing a location for a treatment plant, you should also take into account its volume. If the capacity does not exceed 1 m³, then the object can be placed at the minimum possible distance from the house. As the volume increases, it is advisable to proportionally increase the distance.
Location of storage septic tanks relative to a residential building
As for the roadway and the neighbor's fence, in this case the same requirements are imposed as for a residential building - a distance of at least 3 m. But the location relative to outbuildings has not such strict criteria. The main thing here is to maintain a distance of 1 m.
If the treatment plant does not have a sealed bottom, that is, the wastewater is discharged into the ground after preliminary filtration, then the distance between the sewer well and the building must be increased to 10-12 m. This arrangement will not allow the destruction of the foundation from increased soil moisture.
In the case of domestic wastewater treatment, in addition to protecting the foundations of buildings, sanitary standards must be adhered to. To prevent contamination of the drinking water source, the filtration well is located 50 m from it. The minimum possible distance to the nearest reservoir is 30 m.
Layout of the wastewater discharge point into the ground
Distance between the septic tank and natural reservoirs
This parameter largely depends on the type of natural reservoir. In most cases, a country house is located next to a pond, small lake or river. Then the owner should install the system at a distance of more than 10 meters from such a body of water. If there is a reservoir near the site, then the owner needs to make sure that the distance from it to the septic tank is at least 50 meters.
If these restrictions are violated, the result will be a significant deterioration of the environmental situation in the area. Sewage water entering a natural body of water will cause mass death of the flora and fauna living there. Also, most likely, this will provoke stagnation and swampiness of the area. In some cases, pathogenic microorganisms may begin to multiply in the water, which is a potential threat to the health of swimmers.
For the site owner, this means paying several large fines and possibly lengthy proceedings. It will also be necessary to dismantle the sewer system.
Septic tank and neighboring areas
In most cases, the acquired summer cottage plot is located in a cooperative, which implies the need to discuss construction with representatives of local authorities and neighbors. Like the owner, residents of neighboring plots want to avoid flooding of the garden, erosion of the foundation and the spread of stench throughout their homes. Therefore, it is very important to choose the right location for the structure.
Watch the video
According to current legislation, the distance to the neighbor’s fence should be at least 3 meters. However, sometimes situations arise when this is not enough and it is necessary to install the structure even further. For example, if the neighbors’ house is located in close proximity to the fence. Then it is advisable to calculate the maximum distance from the septic tank to the house so that it is more than 5 meters.
Thus, when designing a system, it is important to consider the distance not only to your own home and other buildings, but also to objects on neighboring plots. This applies to both the home and drinking water wells, other buildings and gardens. Otherwise, the neighbor has the right to file a lawsuit and demand compensation or relocation of the local sewer system. Therefore, it is better to discuss the location of the septic tank in advance with the owners of neighboring plots.
Septic tank and garden plantings
Quite often during construction, the owner of the site forgets to calculate the distance to the garden plantings.
These include fruit trees, shrubs, greenhouse and garden plants, the fruits of which are then used as food. Current legislation states that the distance to them must be at least 3 meters. Failure to comply with this restriction can lead to two unpleasant consequences:
- in the absence of a high-quality filtration system in the structure (with up to 95% purification), wastewater entering the plants may contain microorganisms harmful to health. Therefore, when consuming fruits of nearby plants, a viral pathogen may enter the human body;
- only a small volume of water has a positive effect on plants. However, if you use the sewer frequently, filtered water will cause your plants to become over-watered. This will cause the plant root system to begin to rot. In this case, shrubs and plants will dry out in the first few years of operation of the autonomous sewer system.
Therefore, it is advisable to take this limitation into account when choosing the location of the septic tank.
How to choose a septic tank location
The easiest way to select a location for installing a structure is to contact a specialized construction company. Professionals will be able to quickly and accurately determine the most suitable location for installation, but this procedure is quite expensive. If desired, the owner of the site will be able to determine an approximate suitable location independently.
The process consists of several stages:
- You need to make a plan. To do this, all the objects located on it (houses and wells, greenhouses and vegetable gardens, roads and fences, natural reservoirs and wells, etc.) must be marked on a copy of the site design. You should also be sure to indicate the dimensions of the buildings.
- Draw circles on each object, the objects are located in the center or on the inner border of the circle. The diameter (or radius) of the circle should be schematically equal to the required distance. The main thing when constructing a diagram is to maintain scale.
- Find a free space on the site plan where there are no circles.
- Consider the location of tanks for storing wastewater and determine the location of the filtration well.
- Find out the plan of the laid communication networks, compare it with the site diagram.
What to do if there is not enough space
In some cases, after the procedure it turns out that there is not enough free space. The small area of the dacha, many objects or their irrational placement leads to the fact that there is no space left for the correct installation of the septic tank while maintaining the required distance to the house, buildings, wells, etc.
Sometimes homeowners decide to install in violation of the rules and regulations contained in SNiP and other regulatory documents. However, this cannot be done; in this case, there are alternative methods.
The best solution in such a situation is to install a storage tank that resembles a cesspool. The storage tank is a type of septic tank and is completely sealed (neither the walls nor the bottom allow liquid to pass through). However, there are several operating features that are important to know about in advance.
Because Such a septic tank does not have a filtration element in its design; the waste tank will need to be emptied regularly. For this purpose, special sewage disposal equipment is used. Therefore, despite the low cost of construction, septic tank maintenance is not cheap.
Why can't you build a septic tank closer
To summarize, the main problems that arise when installing a system in the wrong place are:
- the possibility of wastewater getting into the soil and fruit-bearing plants, which can cause the development of serious diseases and pathologies in humans due to microorganisms found in sewage;
- groundwater pollution, i.e. deterioration of the local environmental situation;
- violation of the system cleaning schedule will cause the wastewater in the tank to overflow, resulting in the entire area being contaminated and an unpleasant odor spreading throughout the house;
- possible flooding and destruction of the foundation of the house, other buildings, as well as roads;
- if the structure malfunctions, the stench will enter the house and the neighbors’ area;
- If the distance from the house to the septic tank is violated, the owner will be fined, and the structure will also need to be dismantled and reinstalled.
To avoid the unpleasant consequences of incorrect placement, it is recommended to immediately study the relevant regulations and find out about the requirements. Only after this is it advisable to design the sewer system.
Watch the video
Thus, it is definitely recommended to take into account the distance to the house, well and other objects located on the site. You can find a suitable placement yourself, without using the services of professionals. Sometimes the area does not allow the installation of a septic tank without violating the rules. In this case, use alternative design options.
Distance between sewer wells
In addition to storage and filtration structures, there are other types of wells that are used for installation and maintenance of external sewage systems. Among them:
- examination rooms;
- rotary;
- differential.
Since such devices are not designed to accumulate wastewater, they do not pose a danger to the foundations of buildings and natural objects. In this case, these structures must be correctly positioned relative to each other.
Such structures are intended for inspection and maintenance of sewerage systems. They are used in complex external networks with long pipeline lengths. According to SNiP, the distance between sewer inspection wells depends on the size of the pipe. The following standards exist:
- Ø110 mm – 15 m;
- Ø150 mm – 35 m;
- Ø200-450 mm – 50 m;
- Ø500-600 mm – 75 m.
In domestic systems, pipes with a diameter larger than 150 mm are rarely used. Typically, a diameter of 100-110 mm is sufficient for arranging an external sewer system. Accordingly, in this case, an inspection structure needs to be installed every 15 m. Although for straight sections it is possible to increase the interval by several meters.
Location of observation points
Rotating devices perform the same function as viewing devices. The distance between them is not regulated, since they are located in strictly designated places - at a bend in the pipeline, the angle of which exceeds 45°. These points are most susceptible to blockages, so it is necessary to have access to these places for cleaning activities.
The distance between the rotary wells of domestic and storm sewers depends on the design of the network. However, if there is a long straight section between the turns, an additional observation point is installed at this interval.
Large pipeline bends must be equipped with rotating structures
If it is necessary to install a sewer network on a slope, differential structures are used. Such wells are designed to normalize the flow rate of liquid, since too intense movement of drains can lead to blockages.
The distance between such structures depends on the specifics of the terrain and is individual for each area. Some technical nuances should be taken into account:
- the height of the difference should not be more than 3 m;
- to reduce the flow rate, additional damping barriers can be installed;
- if the difference is less than 0.5 m and the pipeline diameter is 600 mm, it is permissible to replace the differential well with an inspection structure with a drain.
Sewage installation diagram on a slope
If you maintain the correct distances between sewer wells and other objects in accordance with SNiP, you will not have problems with either supervisory authorities or neighbors. At the same time, it is better to plan a complex system together with specialists in order to prevent technical errors and inconsistencies that can lead to unpleasant consequences.
Distances between service and control elements
The main elements of sewer system maintenance are three types of collectors:
- examination rooms;
- auditing;
- rotary.
There is no fundamental difference between inspection and inspection wells. Their size depends on the depth of immersion in the ground, the amount of passing drains, and other factors. Rotary units are installed at points of sharp changes in the direction of pipelines. Sometimes they are used to create a difference in the heights of pipeline lines. This allows you to clear the drains of solid particles, but requires frequent cleaning of the well.
The main feature of pipeline laying is the slope, due to which it is necessary to consistently increase the immersion depth of the wells. On long lines this is very noticeable. As the diameter increases, the minimum line slope decreases.
Typically, private systems use pipes with a diameter of 150 mm. This size is quite sufficient for a small network and does not require a large amount of excavation work. The standard distance between sewer wells for 150 mm is 35 m ; it is almost impossible to exceed it in the conditions of a private house site. For comparison, the distance between sewer wells for pipes with a diameter of 100 mm is only 15 m . This must be kept in mind when using small channels. With the channelless method of placing pipelines, all standards are accepted as the same as for water supply.
You may also like:
Distance from water supply to sewerage - device and standards
SNiP - sewerage, external networks and structures
Distance between sewer wells
Distance between sewerage installations for different types of wells
First you need to find out what types of tanks there are:
- Inspection rooms - monitor the operation of sewage drainage areas and facilitate cleaning of the system when blockages form.
- Rotary - help change the direction of movement of wastewater. Provide access to bends where blockages can also form.
- Variable - compensate for large or small slopes of the device, which affect the quality of the tank and contribute to the accumulation of solid fractions in it.
- Nodal - installed in places where the pipes are connected.
For example, according to SNiP, the maximum distance between sewer inspection wells should be:
- if the pipeline diameter is 150 mm, then the distance is 35 m;
- diameter 200-450 mm – 50 m;
- diameter 500-600 mm – 75 m.
The larger the diameter of the pipeline, the further away the inspection structures can be located.
The minimum distance between sewer inspection wells is determined using the size of the pipe that connects the structures. Let's take a closer look at the diameter in the table.
| Diameter, mm | Shortest distance |
| 150 | 35 |
| 200-450 | 50 |
| 500-600 | 75 |
| 700-900 | 100 |
| 1000-1400 | 150 |
| 1500-2000 | 200 |
| over 2000 | 250-300 |
That is, since inspection tanks provide full access to the sewage system, they should have the longest possible length of pipes. The device is located 12 m from the foundation, 15 m between inspection shafts. When installing a straight system, the gap increases to 50 m.
If this is a rotary tank, which is mounted on the bends of the pipeline system, then the following conditions must be met:
- The gap is determined by the total length of the straight sections between the bends of the pipes.
- If the length of this section is greater than specified in the regulatory document, then additional wells must be installed.
The required gap between sewerage devices is most often determined by specialists, since they are the ones who calculate the required slope when laying the pipeline, which affects the installation of rotary systems.
In the case of drop tanks, which are installed on soils where there are slopes, and the slope of the laid pipes must be taken into account, the maximum depth of the drops should be no more than 3 m. Structures are installed in places where the pipes bend, so in principle, it is necessary to calculate the required gap between the shafts in in accordance with the formation of pipeline bends
It is important to consider that if you are building a multi-stage drop structure, then you need to reduce the gaps between the places where the height changes. The drop point should be from 1.5 to 2 m in this case
When installing a junction tank, you need to take into account the equipment of the sewer branches; the sections are determined using the pipeline cross-section.
- The pipe has a diameter of up to 600 mm - then the distance is 1 m.
- 700 mm – 1.25 m;
- 800-1000 mm – 1.5 m;
- 1200 mm – 2 m.
The device, principle of operation, installation of the Tver septic tank can be found on this page
The design, principle of operation, installation of the Topas septic tank can be found on
The device, principle of operation, installation of the Baikal septic tank can be found on this page
If the depth is more than 3 m, then the smallest diameter is 1.5 m.
The distance between the sewer well and the water well must be at least 30 meters so that sewage waste does not affect the purity of the water. Also, the area where the plumbing system will be installed must be at least 50 m from places of contamination, such as a cesspool with an overflow in a private house.
Conclusion
The sewerage system includes inspection, differential and rotary installations, which perform necessary functions, such as providing access to the sewerage structure and the ability to clear possible blockages
In order for the devices to be installed as conveniently as possible and to always have access to them, it is very important to take into account the required gap between the tanks, which complies with all sanitary standards provided for by law
Features of the placement of system elements
An external sewer network is a pipeline system that runs from the outlet from the house to the point of connection to the main line or reservoir. For maintenance and cleaning, inspection or inspection manifolds are installed along the pipeline line. The main task they are designed to solve is to provide access for cleaning and maintenance. The maximum distance between sewer wells is determined by SNiP standards (or current SP). It cannot be increased, as this will eliminate the possibility of cleaning the internal cavity of the pipes from blockages. For each standard size of pipes, a different distance between sewer wells is adopted. It is determined based on operating conditions, the specifics of wastewater movement, and increases with increasing pipe diameter. In practice, the minimum diameter of external pipelines is 100 mm, and the maximum rarely exceeds 200 mm.
It is noteworthy that SNiP does not determine the minimum distance between sewer wells, since it is impractical to install an excessive number of inspection points.